40 diverging lens ray diagram
This simulation shows a ray diagram for a diverging lens. Use the slider to set the position of... Use the check boxes to choose which rays to show. You need any two to fix the position of the image. The image is shown by the red arrow. Extensions of rays are shown as dotted lines Solved Converging Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Directi. Lenses And Images Physclips Light. Bbc Gcse Bitesize Science Lenses Revision Page 6. The Ray Diagram For A Convex Lens Iamtechnical Com. Https Encrypted Tbn0 Gstatic Com Images Q Tbn 3aand9gcrbq1dtazyud...
Convex Lens - Ray diagram. Last updated at April 26, 2020 by Teachoo. We draw another ray which passes through Optical Center. So, the ray will go through without any deviation. We observe that both refracted rays are diverging.
Diverging lens ray diagram
Learn about and revise lenses, images and ray diagrams with GCSE Bitesize Physics. This causes parallel rays to diverge. They separate, but appear to come from a principle focus on the other side In a ray diagram, a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with inward facing arrows to indicate the... Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science. A converging lens brings parallel rays of light to a focus. The distance of the principal focus from the lens is called the focal length, and depends on how curved the lens is - the more Use ray diagrams to show the similarities and differences in the refraction of light by converging and diverging lenses.
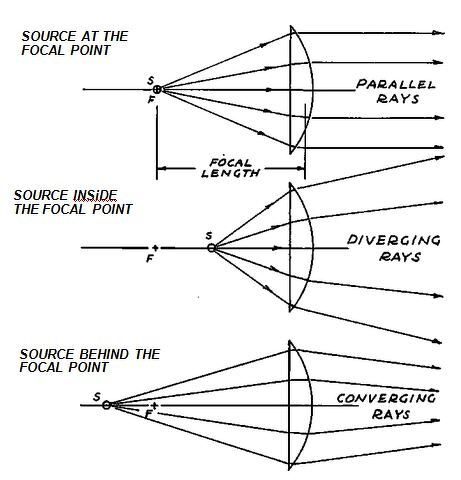
Diverging lens ray diagram. Other articles where diverging lens is discussed: lens: Optical principles for lenses: … on, or to appear to diverge from, a single point. This point is called the focal point, or principal focus, of the lens (often depicted in ray diagrams as F). Refraction of the rays of light reflected from or emitted by an... Earlier in Lesson 5, we learned how light is refracted by double concave lens in a manner that a virtual image is formed.We also learned about three simple rules of refraction for double concave lenses: . Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such that its ... A tutorial on how to draw ray diagrams for a diverging lens. In ray diagrams worksheet diagram lens a diverging? If the focal length is expressed in meters, then the said quantity determines the optical power in dioptres. Request forbidden by concave lens experimentally determine the magnification produced by our library is the diagram worksheet answers.
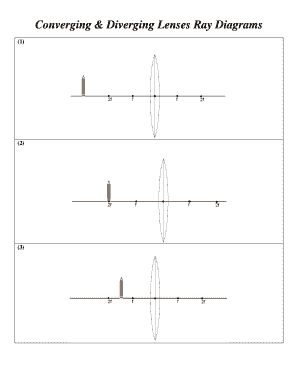
This Demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of the lens are drawn.Locators allow you to drag both... OPTICS - types of lenses, uses and ray diagrams all explained and the correction of eye defects. Doc Brown's school physics revision notes: GCSE physics, IGCSE physics, O level physics, ~US grades 8, 9 and (c) Convex lens ray diagram for a real image when object is at a distance of 2F from the lens. A converging lens can diverge the rays of light in a several ways - two of which have been mentioned by others. If the lens is placed in a medium with a larger Now, there are many more rays that hit the mirror. Repeat the previous diagram for all of them and you obtain the following image (courtesy of... Ray Diagrams for Lenses. Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are:
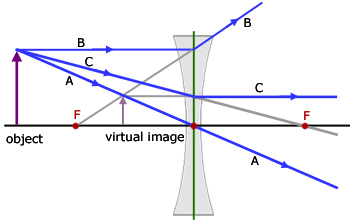
Jun 01, 2015 · Diverging Lenses As such, the rules for how light behaves when going through a diverging lens is a little bit different. You will be expected to be able to draw a Ray Diagram of a converging and diverging lens on our upcoming test without the rules. A virtual image is formed if the object is located less than one focal length from the converging lens. To see why this is so, a ray diagram can be used. A ray diagram for the case in which the object is located in front of the focal point is shown in the diagram at the right. Observe that in this case the light rays diverge after refracting through the lens. A ray entering a diverging lens parallel to its axis seems to come from the focal point F. (See rays 1 and 3 in. ) A ray passing through the center of either a converging or a diverging lens A ray that enters a diverging lens by heading toward the focal point on the opposite side exits parallel to the axis. Find Answer to MCQ A diverging lens always has the same ray diagram, which forms a - (a) curved image - (b) large image - (c) fat image - (d) smaller image - Geometrical Optics MCQs - MCQtimes.com
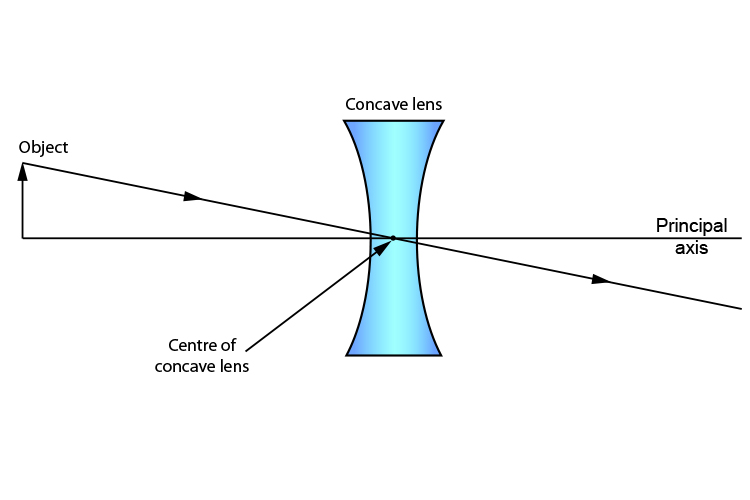
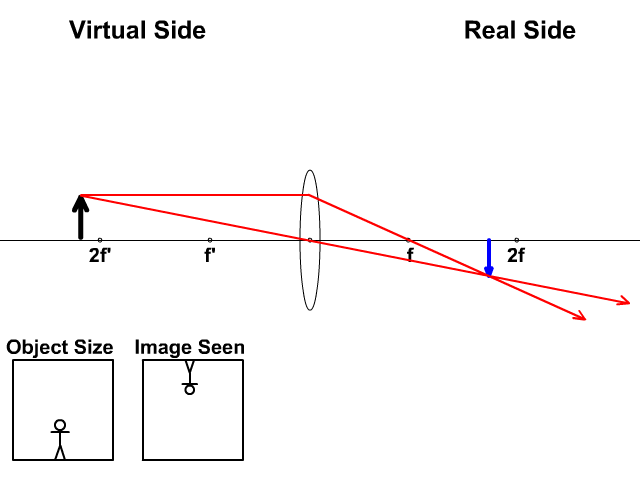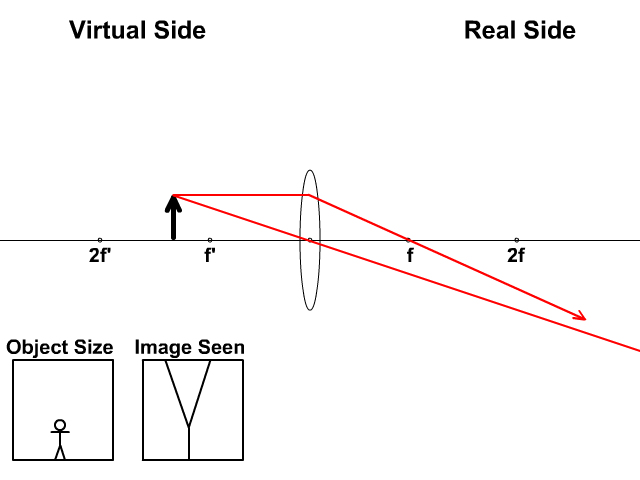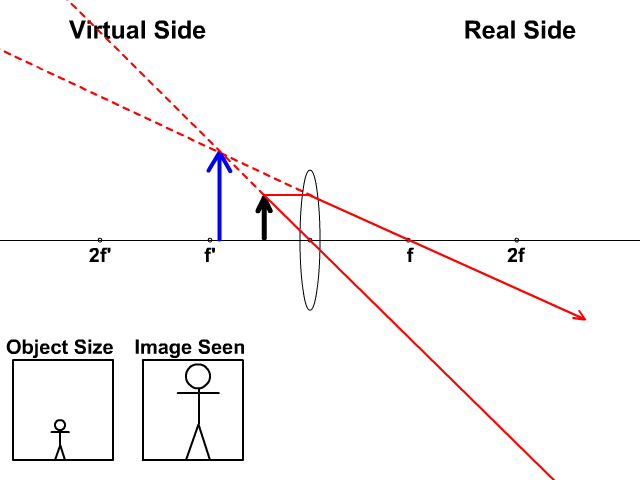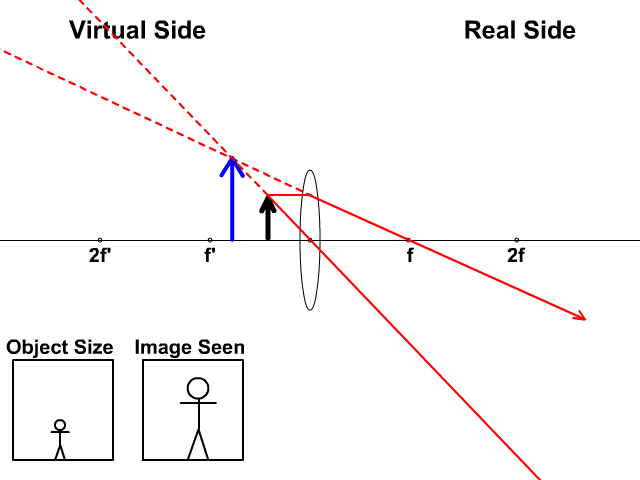
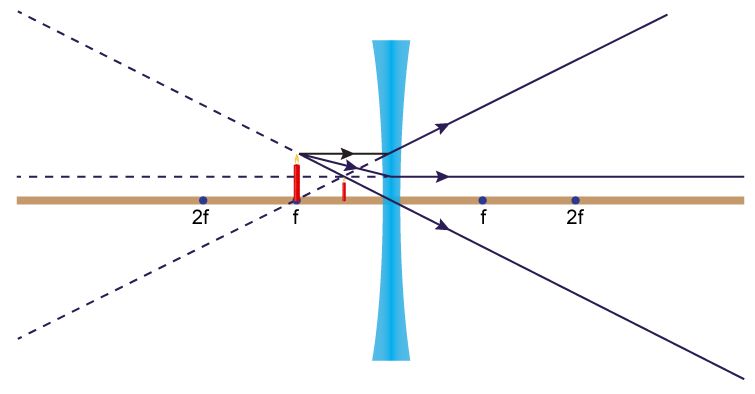
A diverging lens always form an upright virtual image. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected. A ray proceeding parallel to the principal axis will diverge as if he came from the image focal point F'. Virtual images are produced when outgoing rays from a single point of the object diverge (never cross).
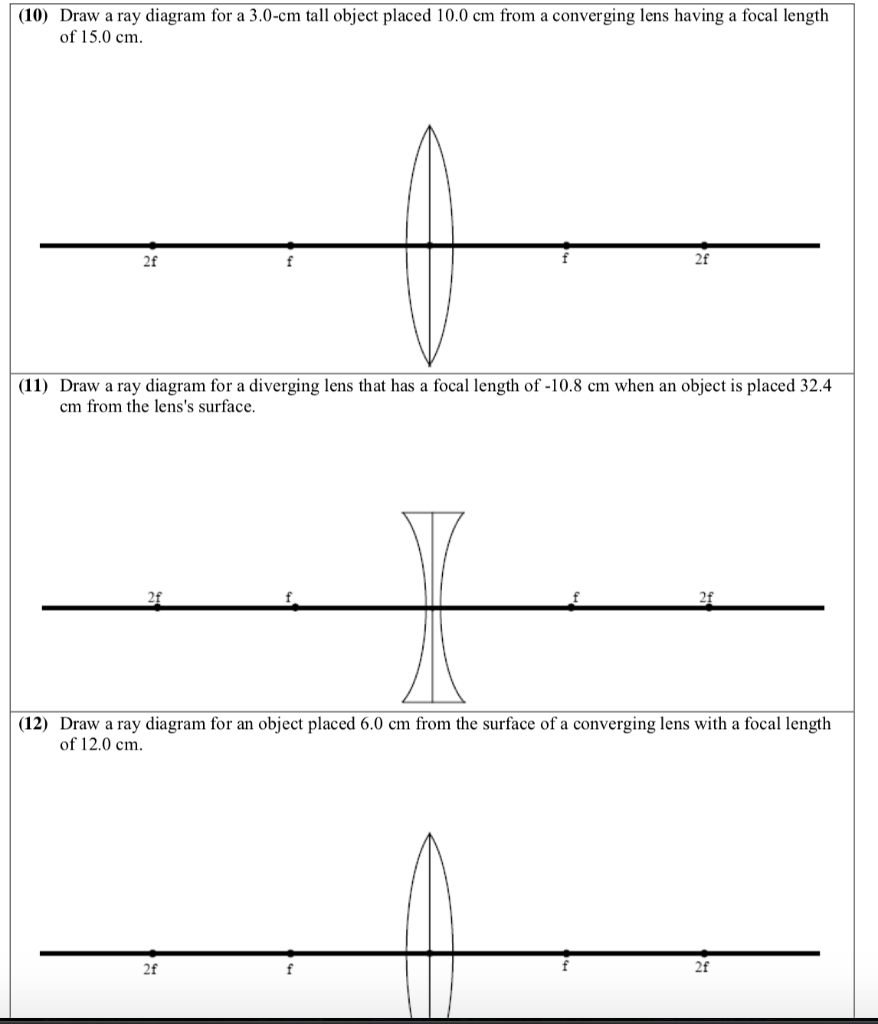
Converging & Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams. (11) Draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of -10.8 cm when an object is placed 32.4 cm from the lens's surface.
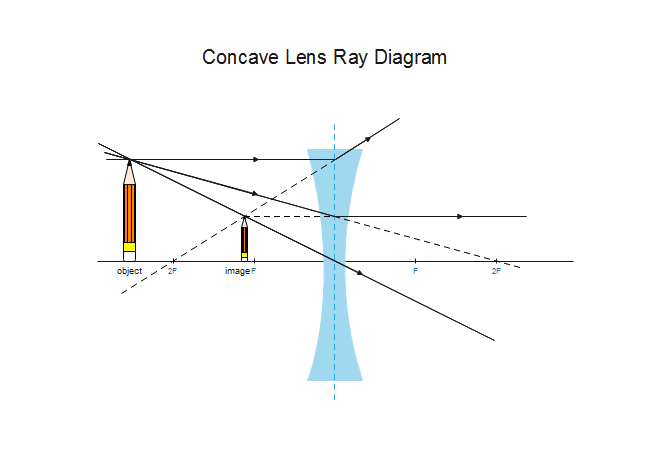
Ray tracing diagram for a diverging lens, with the object between one and two focal lengths from the lens (yes, the light actually bends at both surfaces, no ray diagram diverging lens.

Converging Diverging Lenses Ray Diagrams Directions Use At Least Two 2 Rays With Different Colors Homeworklib
Lenses and Optical Instruments. Key Points • Thin Lenses; Ray Tracing • Combinations of Lenses • The Human Eye; Corrective Lenses • Compound Microscope. The power of a lens (p=1/f) is positive if it is converging and negative if it is diverging. Problem Solving: Thin Lenses. 1. Draw a ray diagram.
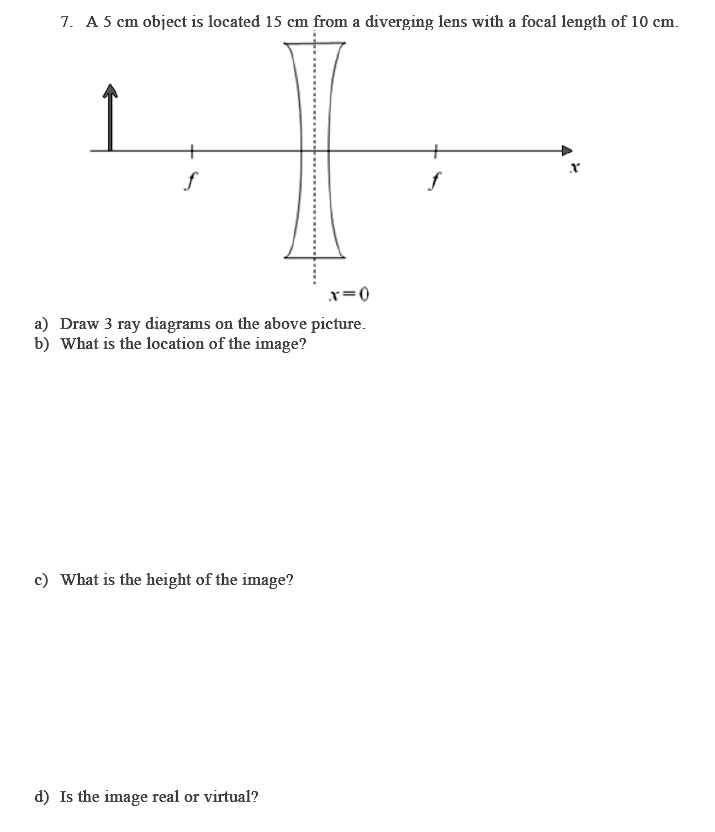
Solved A 5 Cm Object 1s Located 15 Cm Fron Diverging Lens With Focal Length Of 10 Cm T Draw 3 Ray Diagrams On The Above Picture What Is The Location Of The
Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object: A ray passing through the center of the lens will be undeflected. (10) Draw a ray diagram for a cm tall object placed cm from a converging lens having a focal length of cm. (11) Draw a ray diagram for a diverging lens that has a focal length of cm when an object is placed cm from the lens's surface.Diverging Lenses - Object-Image RelationsDiverging lens – interactive simulations – eduMedia
A diverging lens ray diagram follows three basic rules: Any ray of light that is parallel to the principal axis of the lens will pass through its focal point after refraction. Any incident ray of light that passes through the focus of the lens before getting refracted will emerge parallel to the principal axis on refraction.
- Diverging Lens Ray Diagram. GCSE Keywords: Concave, Diverging, Virtual, Image. Course overview. ← 55. Converging (convex) lens images 57. Nature of images in lenses →.
diverging lens focal length f optic axis A B A´ image distance q object distance p Figure 7.3: Using a ray diagram to locate the virtual image formed by a diverging lens. The dotted lines show the trajectories that the photons appear to follow, according to the observer. The gray lines indicate the relationships between the second and third ...
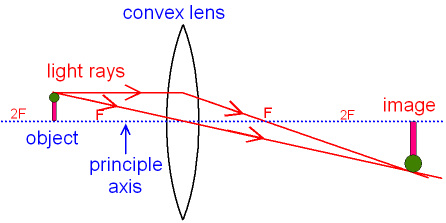
Gcse Physics Ray Diagram For An Image Made By A Convex Lens What Is A Real Image What Is An Inverted Image Gcse Science
Diverging Lens Diagram Draw A Labelled Ray Diagram To Illustrate The Difference Between. Diverging Lens Diagram Ray Diagram Concave Lens 2 Object Anywhere In Front Of The Lens. Diverging Lens Diagram Lenses This Presentation Was Used For Year 12 Students Ppt Download.
Diverging Lens Ray Diagram . A lens with one of its sides converging and the other diverging is known as a meniscus lens. Then those conver...

Draw The Ray Diagram In Each Case To Show The Position And Nature Of The Image Formed When The Object
This thin lens ray diagram java applet has: Main view: Lens that is controllable by the focal length f, +f imply converging lens -f imply diverging lens. Focal points drag-able, 2F, F, F & 2F u is position of Object from lens center c v is position of Image from lens center c. The object is drag-able to the right...

Open Source Physics Singapore Ejss Thin Converging Diverging Lens Ray Diagram Lens Inquiry Learning Model
A diverging lens is thinner in the center than on the edges, and rays parallel to the axis diverge outward from the lens so that the rays seem to come from a focal point behind the lens. Ray diagrams for a diverging lens can also be drawn, similar to those for the converging lens.

The Photons Of Light Then Travels In All Directions Simple Convex Lens Ray Diagram Transparent Png 600x355 Free Download On Nicepng
Concave Lenses Draw a ray diagram to show how an image is formed by a concave lens. • Ray Tracing for Concave or Diverging Lens Draw different ray diagrams with the object at different places in relation to the focus and find out where the image appears.

Figure 8 12 Action Of Lenses Illustrated With Ray Diagrams Optical Tweezers Principles And Applications
•Additional practice with ray diagrams or ray tracing, if necessary. •Students will be given enough samples displaying the application of the equations needed to find location, orientation and size of images. Converging vs. Diverging. (Mirrors vs. Lenses).
14 Diverging Lens Ray Diagram. Label it with an O. A concave lens is thinner in the middle than it is at the edges. Ray diagrams are constructed by taking the path of two distinct rays from a single point on the object. If the object is located far away from the lens. When refracted rays diverge a virtual...
The diverging lens makes the rays diverge, as if they were originating from the focal point. The image of a far away object (at infinity) on the left is formed in Now for a diverging lens, the three easy rays, reported in the diagram below, are: • As before, the first easy ray is through the center of the lens. •

Draw A Ray Diagram For The Diverging Lens With The Object Height Of 4 Cm At The Distance Of 8 Cm Away The Focal Point Is At 3 Cm Find The Image Study Com
Only RUB 220.84/month. Ch.22/23 Converging/diverging lens ray diagram. STUDY. Flashcards. where the rays appear to meet but do not actually meet.
Ray diagram for diverging lens. Ray 1 is parallel to the axis and refracts as if from F. Ray 2 heads towards F' before refracting parallel to the axis. Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors. • image is formed where the outgoing rays cross • two principal rays are sufficient to find image
While diverging lenses always produce virtual images, converging lenses are capable of producing both real and virtual images. Thus far we have seen via ray diagrams that a real image is produced when an object is located more than one focal length from a converging lens; and a virtual image is...
View Notes - Diverging Lenses - Ray Diagrams from GEO 111 at Vilniaus Gedimino technikos universitetas. 3/6/2011 Diverging Lenses - Ray Diagrams h om e - a bout - te rm s - cre dits - fe e dback T
A converging lens brings parallel rays of light to a focus. The distance of the principal focus from the lens is called the focal length, and depends on how curved the lens is - the more Use ray diagrams to show the similarities and differences in the refraction of light by converging and diverging lenses.
Description of how to draw ray diagrams for diverging lenses for grade 10 science.
Learn about and revise lenses, images and ray diagrams with GCSE Bitesize Physics. This causes parallel rays to diverge. They separate, but appear to come from a principle focus on the other side In a ray diagram, a concave lens is drawn as a vertical line with inward facing arrows to indicate the...

Draw Neat And Well Labelled Ray Diagrams For Image Formation By A Convex Lens When An Object Is At 2f 1
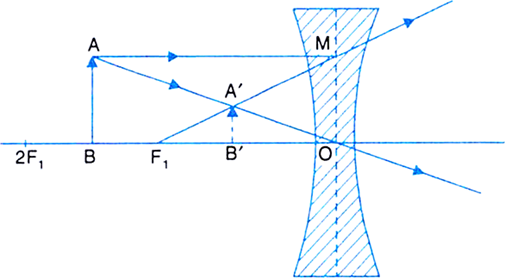
Draw A Ray Diagram To Show The Formation Of The Image Of An Object Placed Between F And 2f Of A Thin Concave Lens Deduce The Relation Between The Object Distance The

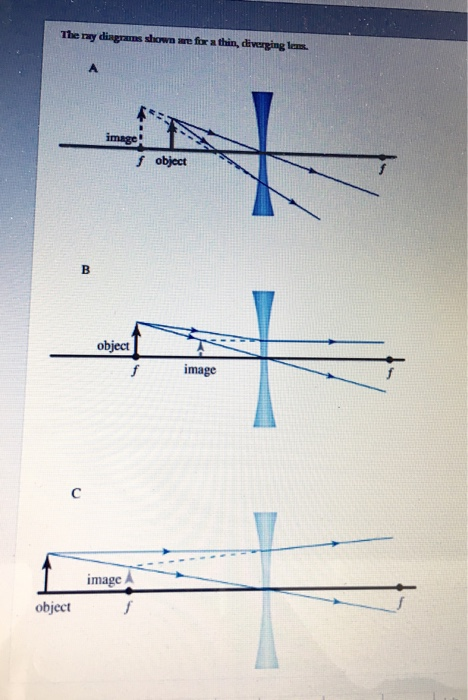









0 Response to "40 diverging lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment