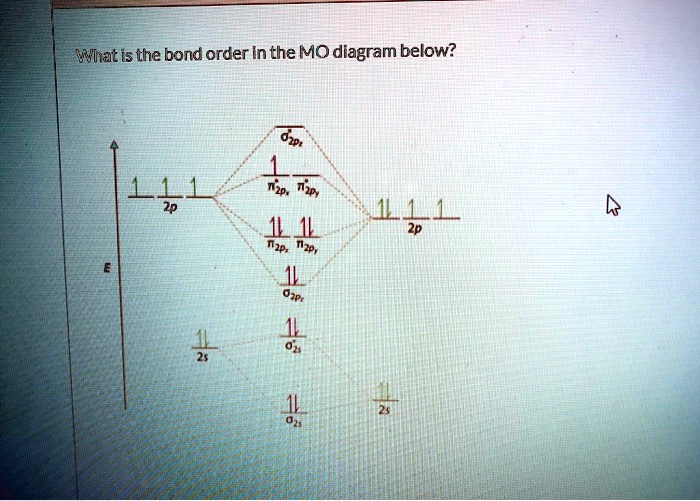
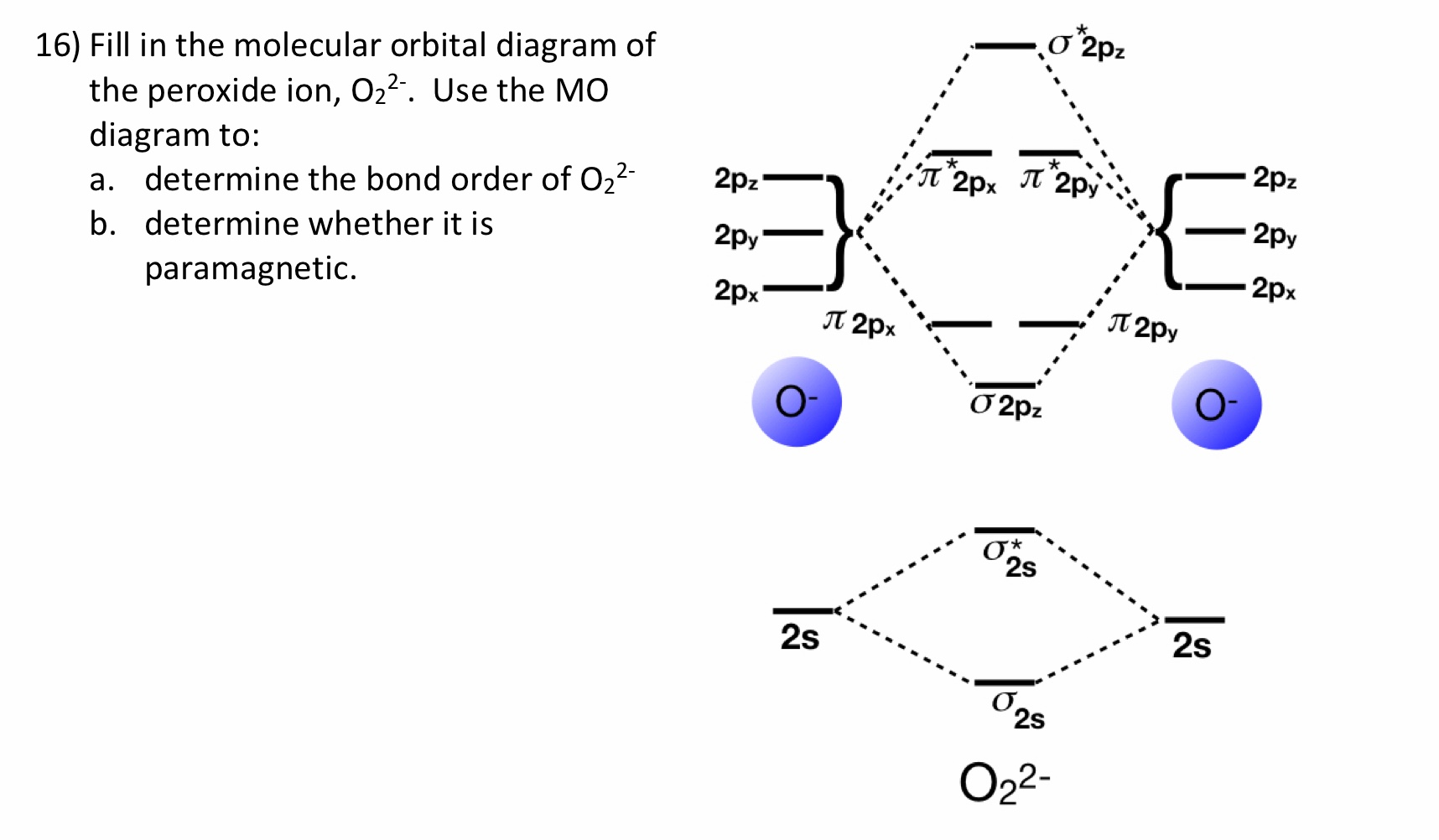
38 use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2.
January 28, 2017 - Something went wrong. Wait a moment and try again 2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b - Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero.
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagrams are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.

Use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2.
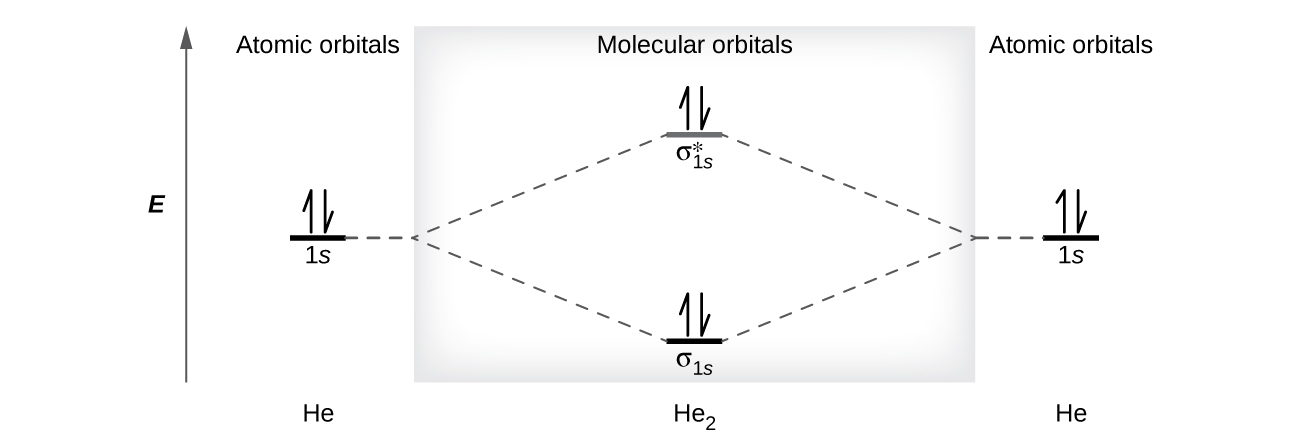
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ... (a) Use the MO diagram from Figure 2.18 from the textbook: The electron configuration for O 2 - is 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 3. This leaves 1 unpaired electron and gives a bond order of 1.5. (b) Use the same MO diagram as in (a), giving an electron configuration for O 2 + of: 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 1. Molecular Orbital Theory -- Homodiatomics use the molecular orbital model to fully describe the bonding in O2+, O2, O2-, and O22-. Determine which of the following statements are true and which ...
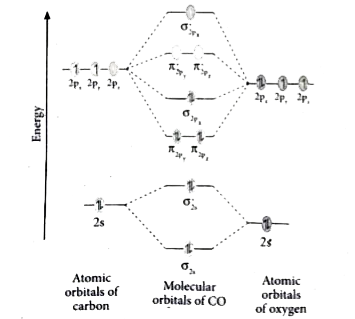
Use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2.. September 1, 2020 - The positions and energies of electrons in molecules can be described in terms of molecular orbitals. A particular spatial distribution of electrons in a molecule that is associated with a particular … Use the drawing of MO energy diagram for CO to predict the bond order. (Use the energy ordering of O2) The two sigma bonds form between a hybrid sp orbital on Be and a p orbital on Br. BO = bonding orbitals ABO = Anti-bonding orbitals O2: Electronic configuration of Oxygen molecule = Bond order in Oxygen molecule (O2)= =½ [(Number of bonding electrons) – (number of anti-bonding electrons)] = ½ [10 – 6] = 2 O2- : Bond order in Oxygen molecule (O2-) =½ [(Number of bonding ... "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram.
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ Draw molecular orbital diagram of O2 or N2 with magnetic behavior and bond order.1 answer · Top answer: As it can be seen from the MOT of O2 , The electrons in the highest occupied molecular orbital are unpaired therefore it is paramagnetic in nature. Also, ... Without 2s-2p mixing With 2s-2p mixing CK :O r 25 20 2s AO MO AO AO MO AO A MO energy levels for O Fa. and Ne B MO energy levels for Ba Cz and Ng 0.5 This problem has been solved! See the answer See the answer See the answer done loading For almost every covalent molecule ... and come close to predicting bond angles. However, one of the most important molecules we know, the oxygen molecule O2, presents a problem with respect to its Lewis structure. We would write the following Lewis structure for O2... On the basis of this principle discuss the conditions for obtaining the maximum yield of SO3 in the following reaction. 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌2SO3(g); ∆𝐻= - 42k.cal.(ii) Calculate the pH value of 0.01M CH3 COOH if it is 5% dissociated.
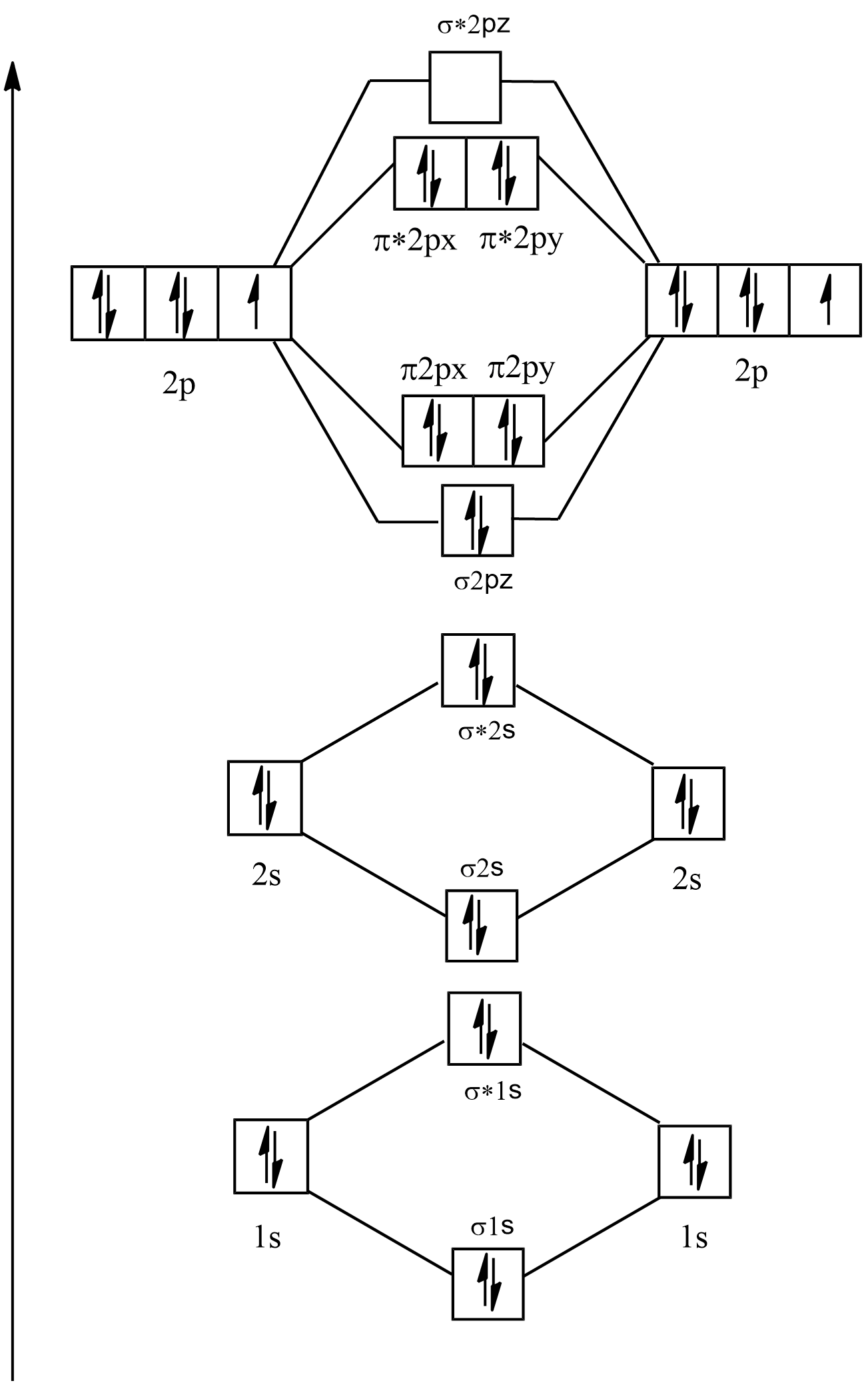
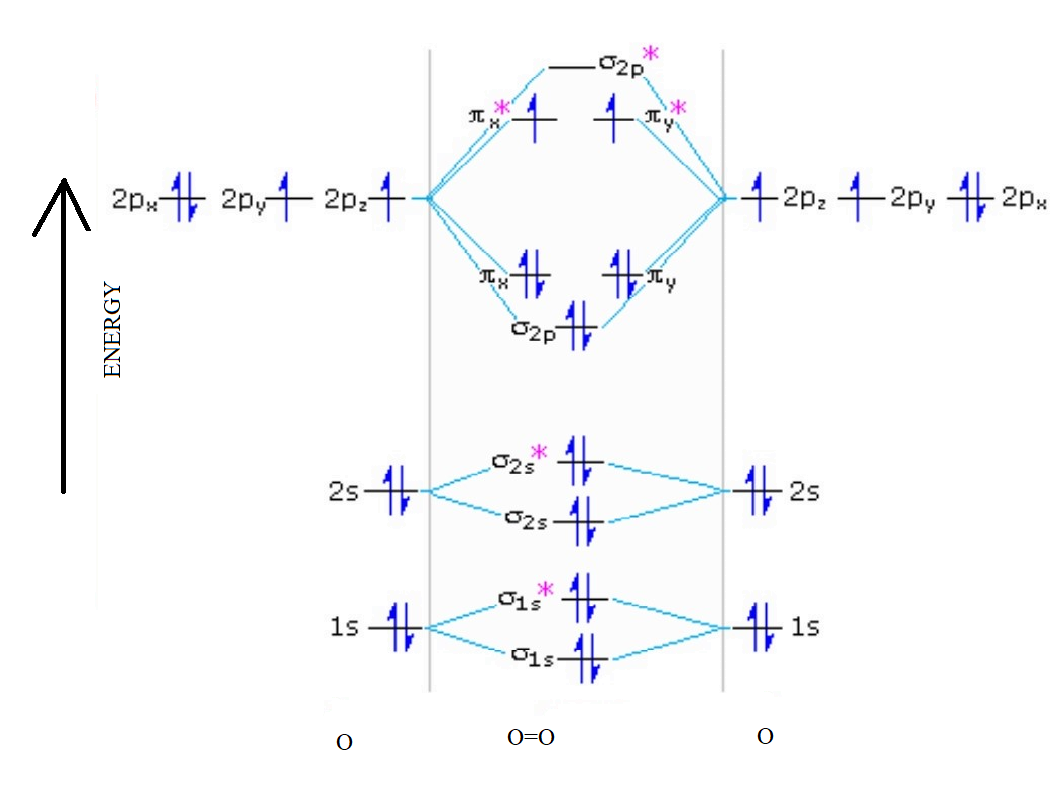
The bond order varies from one molecule to another. Oxygen is a diatomic molecule. Let us first know what is meant by bond order. Bond order. The bond order may be defined as half the difference between the number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals (Nonbonding) and the number of electrons in the antibonding molecular orbital. Formula ... Electron Configurations and Bond Orders Just as with atoms, we can write a molecular electron configuration for O2 σ2σ*2σ2π4π*2 We can also calculate the O–O bond order: BO 1 2 # bonding e # anti-bonding e 1 2 8 4 2 LCAO MO theory also predicts (correctly) that O2has two unpaired electrons. October 27, 2015 - Since each oxygen has 6 valence electrons you have a total of 12 electrons to distribute throughout the molecular orbital diagram, while following the aufbau and Pauli's exclusion principle as well as Hund's rule. Molecular orbitals with stars represent antibonding orbitals. So for O2 the bond ... Exercise 3.3.4. 3. Construct a qualitative molecular orbital diagram for chlorine, Cl 2. Compare the bond order to that seen in the Lewis structure (remember that an electron in an antibonding orbital cancels the stabilization due to bonding of an electron in a bonding orbital). Answer.
November 27, 2017 - Before we can draw a molecular orbital diagram for B₂, we must find the in-phase and out-of-phase overlap combinations for boron's atomic orbitals. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons.
Molecular Orbital Theory The goal of molecular orbital theory is to describe molecules in a similar way to how we describe atoms, that is, in terms of orbitals, orbital diagrams, and electron configurations. For example, to give you a glimpse at where we are headed, the following are orbital ...
For almost every covalent molecule ... and come close to predicting bond angles. However, one of the most important molecules we know, the oxygen molecule O2, presents a problem with respect to its Lewis structure. We would write the following Lewis structure for O2...
Bond order is a simple calculation, based on the number of bonding versus antibonding electrons ... The following figure illustrates our sigma and sigma-star molecular orbitals pictorially and ... There would be four electrons to fill into our molecular orbital diagram and that would force us to fill in the bonding sigma MO and the anti-bonding ...
September 17, 2017 - The MO diagram for "NO" is as follows (Miessler et al., Answer Key): (The original was this; I added the orbital depictions and symmetry labels. For further discussion on the orbital energy ordering being "N"_2-like, see here and comments.) Quick overview of what the labels correspond to what ...
Answer (1 of 6): O2 2- bond order = 1 O2 - bond order = 1.5 O2 bond order = 2 O2+ bond order = 2.5 O2 2+ bond order =3 I hope it'll work out :)
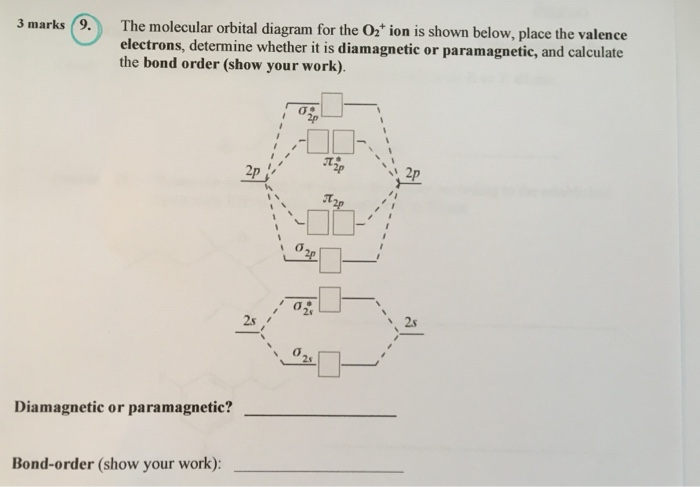
Problem 7.92: Use the MO diagram in Figure 7.18b to describe the bonding in O 2 +, O 2, and O 2-. Which of the three should be stable? What is the bond order of each? Which contain unpaired electrons? First, here is the image: This diagram actually applies to this problem and to the next.
August 11, 2020 - The molecular orbital configuration dictates the bond order of the bond. This in turns dictates the strength of the bond and the bond length with stronger bonds exhibiting small bond lengths. The …
Explanation: In a molecule, there are total 16 electrons. The molecular orbital configuration of molecule is as follows.. The formula for bond order is as follows. Bond order = There are 10 bonding and 6 non-bonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration.
In this section, we will compare MO diagrams for diatomic molecules X-X, from Li 2 to Ne 2. We will predict their bond order and see how the energies of the different orbitals change. We will also compare our predictions to experimental evidence. First, though, we need to talk about a new effect, s-p mixing.
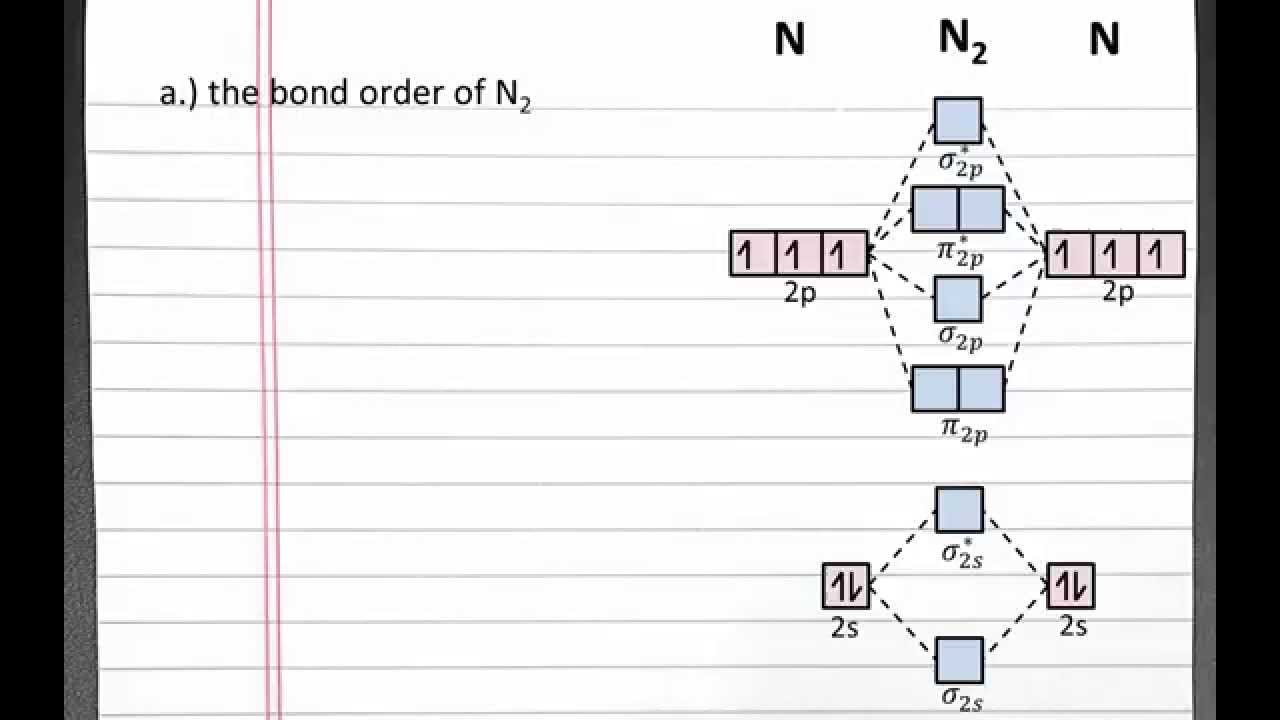
Transcribed image text: Use the MO diagram provided below to answer the following questions: • What is the bond order for N? [Select] • Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic?__ (Select] netic? _ [ Select] • What is the bond order for N? (Select] • Is N2 paramagnetic or diamagnetic?__ (Select] • What is the bond order for Not?
Use the drawing of the MO energy diagram to predict the bond order of Li2+. Express the bond order as an integer or fraction. Part B. Use the drawing of the MO energy diagram to predict the bond order of Li2?. Express the bond order as an integer or fraction. Part C. Which molecules are predicted to exist in the gas phase? Check all that apply
Problem Details. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown below to determine which of the following diatomic species has the highest bond order. a. F 22⁻ b. F 22⁺ c. O 22⁺ d. F 2 e. Ne 22⁺. Learn this topic by watching MO Theory: Bond Order Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems MO Theory: Bond Order Practice Problems.
Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Use MO diagrams and the bond orders you obtain from them to answer: (a) Is O2- stable? (b) Is O2- paramagnetic? (c) What is the outer (valence) electron configuration of O2-?.
Use MO diagrams to place C2^- ,C2, C2^+ in order of the following proper... ... 4. Draw an MO diagram for the valence electrons in the O2^+. What is the bond order? How many o and π bonds are there? What is the HOMO and LUMO? What is the magnetism of the species?
First Year Chemistry in the School of Chemistry at the University of Sydney
The bond order tells us the average number of bonds between the bonded atoms. In a diatomic molecule such as `O_2`, the bond order simply tells the number of bonds between the two atoms. The bond order can be interpreted from MO diagrams using the following formula: `"Bond Order" = 1/2 [("Bonding "e^-)-("Antibonding " e^-)]`
0:21 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Oxygen Molecule 3:30 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Florine Molecule 5:25 Molecular Orbital Diagram of Neon Molecule So as we...
August 15, 2020 - In O2 and F2, there is a crossover of the sigma and the pi ortbials: the relative energies of the sigma orbitals drop below that of the pi orbitals'. Information from the MO diagram justify O2's stability and show that it's bonding order is 2. The LUMO (lowest unoccupied molecular orbital) ...
O 2 2-. is 1. So, the correct order of bond order is O 2 2- O 2 − O 2 O 2 +. So, the correct answer is “Option B”. Note: You should notice that bond order is indirectly proportional to the length of the bond. The higher the bond order, the shorter and stronger will be the bond. The addition of each electron in the antibonding molecular ...
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...
It is sigma2s(2)sigma2s*(2)sigma2p(2)pi2p(4)pi2p*(4) Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion. Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com
Remember: When two oxygen atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. They are flipped compare...
To find the bond order of O2+ we can use the concept of Molecular Orbital Theory. In this method we have to count the number of molecules in the Bonding ...6 answers · 56 votes: O2 2- bond order = 1 O2 - bond order = 1.5 O2 bond order = 2 O2+ bond order = 2.5 O2 ...
February 14, 2019 - The relative energy levels of atomic and molecular orbitals are typically shown in a molecular orbital diagram (Figure 8.34). For a diatomic molecule, t...
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory helps us to explain and understand certain Part B - Molecular Orbital Energy Diagrams & Bond Order . + and Be2.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic ...
Diatomic molecules consist of a bond between only two atoms. They can be broken into two categories: homonuclear and heteronuclear. A homonuclear diatomic molecule is one composed of two atoms of the same element. Examples are H2, O2, and N2. A heteronuclear diatomic molecule is composed of ...
On the basis of this principle discuss the conditions for obtaining the maximum yield of SO3 in the following reaction. 2SO2(g)+ O2(g)⇌2SO3(g); ∆𝐻= - 42k.cal.(ii) Calculate the pH value of 0.01M CH3 COOH if it is 5% dissociated.
greater bond polarity in BeH2. 5.16 BeF2 uses s and p orbitals on all three atoms, and is isoelectronic with CO2. The energy level diagram for CO2 in Figure ...29 pages
Welcome to Sarthaks eConnect: A unique platform where students can interact with teachers/experts/students to get solutions to their queries. Students (upto class 10+2) preparing for All Government Exams, CBSE Board Exam, ICSE Board Exam, State Board Exam, JEE (Mains+Advance) and NEET can ask questions from any subject and get quick answers by subject teachers/ experts/mentors/students.
Bond order of B2 molecule. So the bond order of B2 is equal to 1, which you can get by drawing the molecular orbital diagram and performing the equation Bond Order = .5 * (# of bonding electrons - # of antibonding electrons). However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B2, you get a triple bond.
The bond order in sulfur dioxide, for example, is 1.5 the average of an S-O single bond in one Lewis structure and an S=O double bond in the other. In molecular orbital theory, we calculate bond orders by assuming that two electrons in a bonding molecular orbital contribute one net bond and that two electrons in an antibonding molecular orbital ...
This ion has been observed in the gas phase. D) O2^2+ E) F2^2-2) Use molecular orbital diagrams to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Molecular orbital diagram of o2. 3 Bond energy and bond order both increase with decreasing bond length. O2 molecular orbital diagram oxygen ...
Molecular Orbital Theory -- Homodiatomics use the molecular orbital model to fully describe the bonding in O2+, O2, O2-, and O22-. Determine which of the following statements are true and which ...
(a) Use the MO diagram from Figure 2.18 from the textbook: The electron configuration for O 2 - is 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 3. This leaves 1 unpaired electron and gives a bond order of 1.5. (b) Use the same MO diagram as in (a), giving an electron configuration for O 2 + of: 1σ g 2 1σ u 2 2σ g 2 2π u 4 2π g 1.
A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single electron orbitals, and σ∗. 1s is higher in energy. Draw this out using an energy level diagram: 2 He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+. 2,. H−.A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical ...









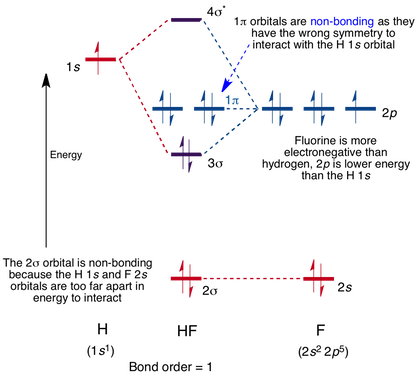






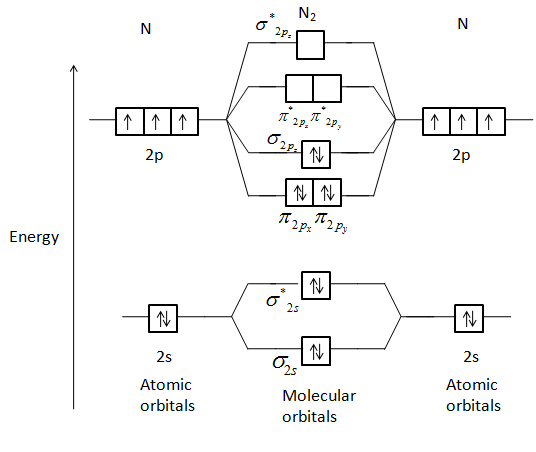

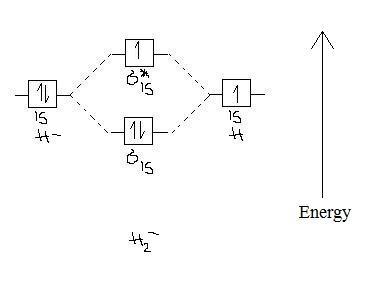


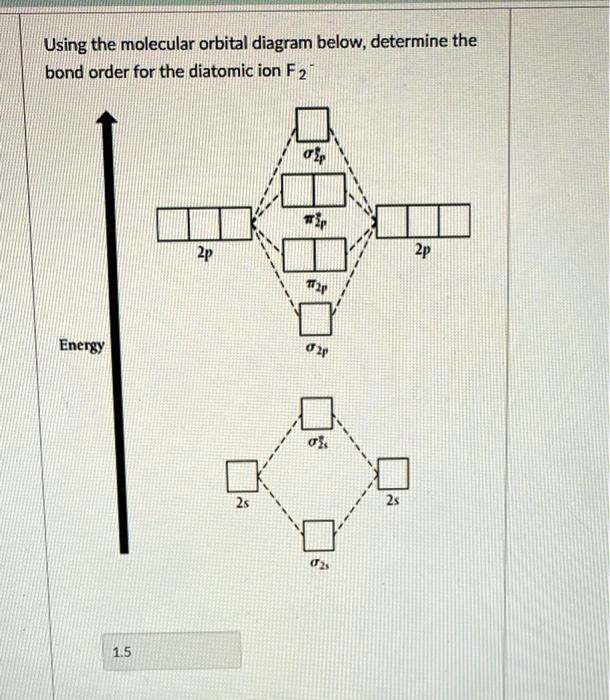
0 Response to "38 use the following mo diagram to find the bond order for o2."
Post a Comment