35 co molecular orbital diagram bond order
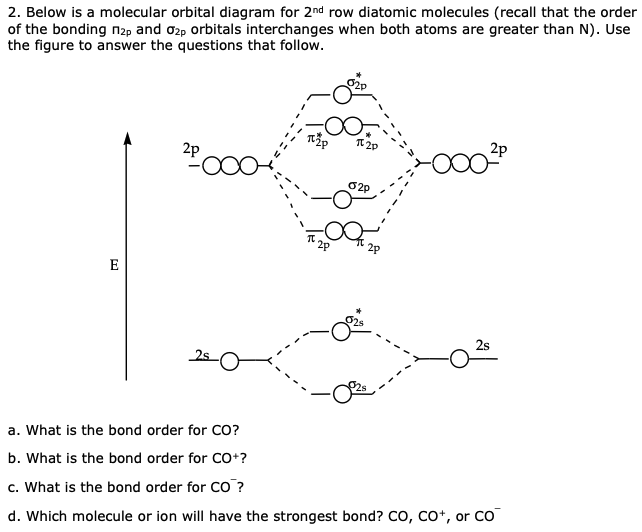
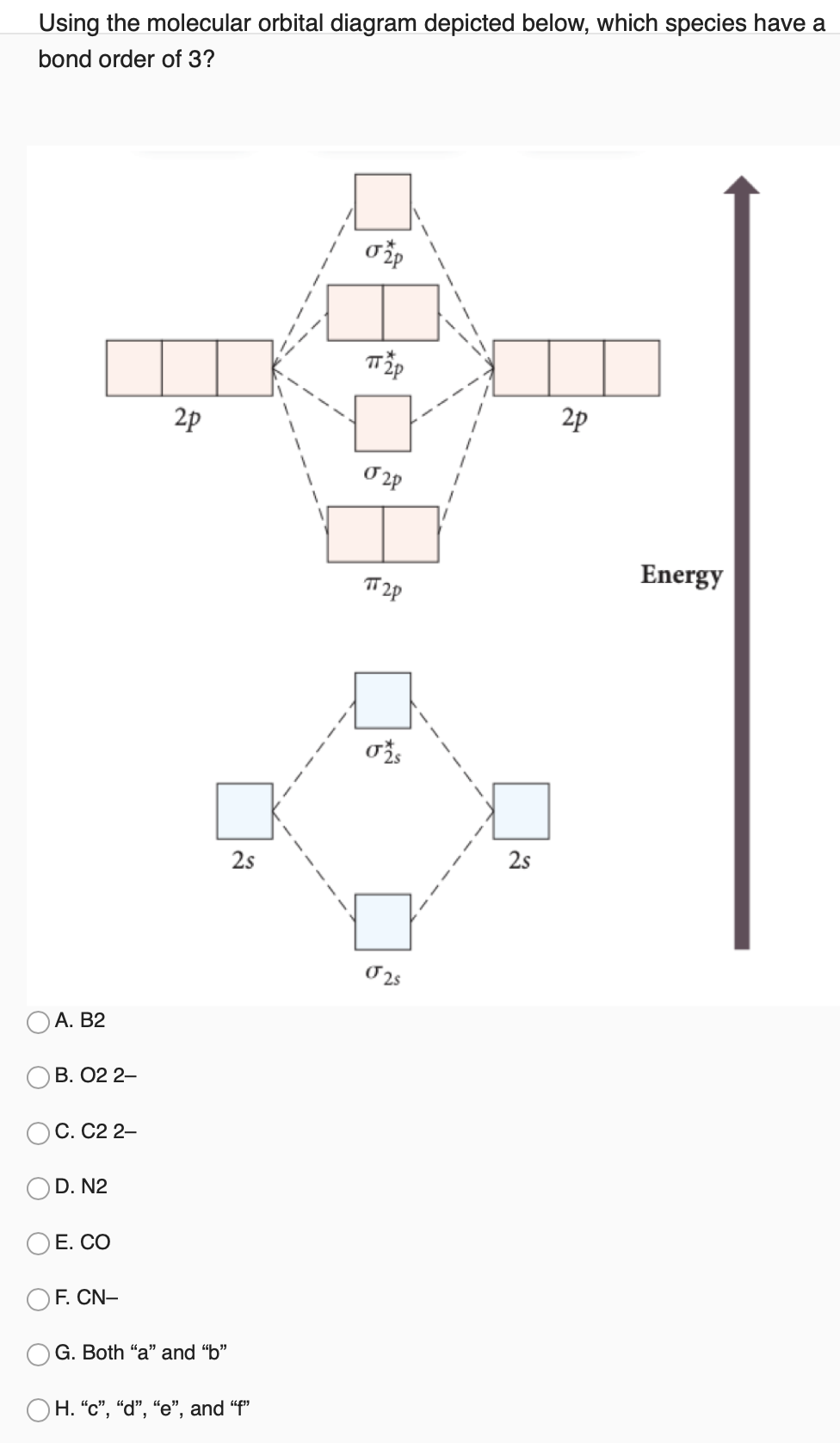
2) Stability of molecules in terms of bond order. Bond order is defined as half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and antibonding orbitals. Bond Order = ½ ( N b – Na) The molecule is stable if N b > Na ie. bond order is positive. The molecule is unstable if N b < Na i.e. the bond order is negative or zero. Assuming CO has the same molecular orbital diagram as dicarbon, draw the diagram, show the orbital occupancy, and determine the C–O bond order. Is CO paramagnetic or diamagnetic? What is the bond order for the CO+ ion? Please help. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area.
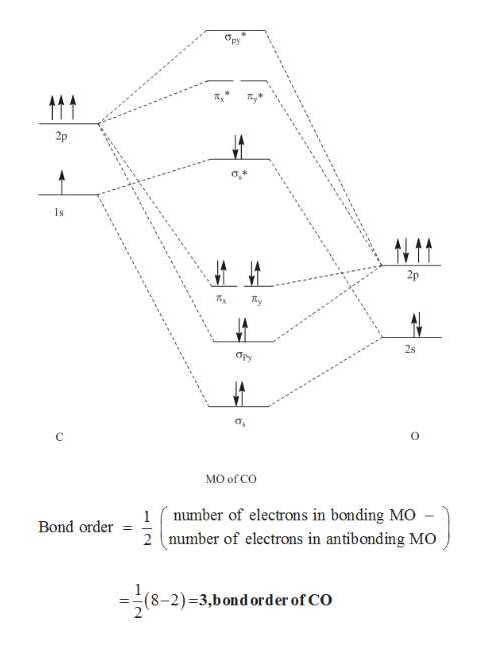
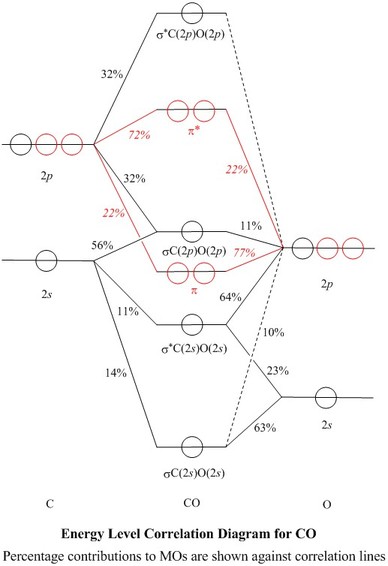
Measured CO bond length is 1.128 Å, & bond length of CO+ is 1.115 Å. The Bond Order in CO+ is 3.5 . The highest occupied molecular orbital (or HOMO) is the σ *2s MO. Bond order is defined as the number of electrons in bonding MOs minus the number of electrons in antibonding MOs .

Co molecular orbital diagram bond order
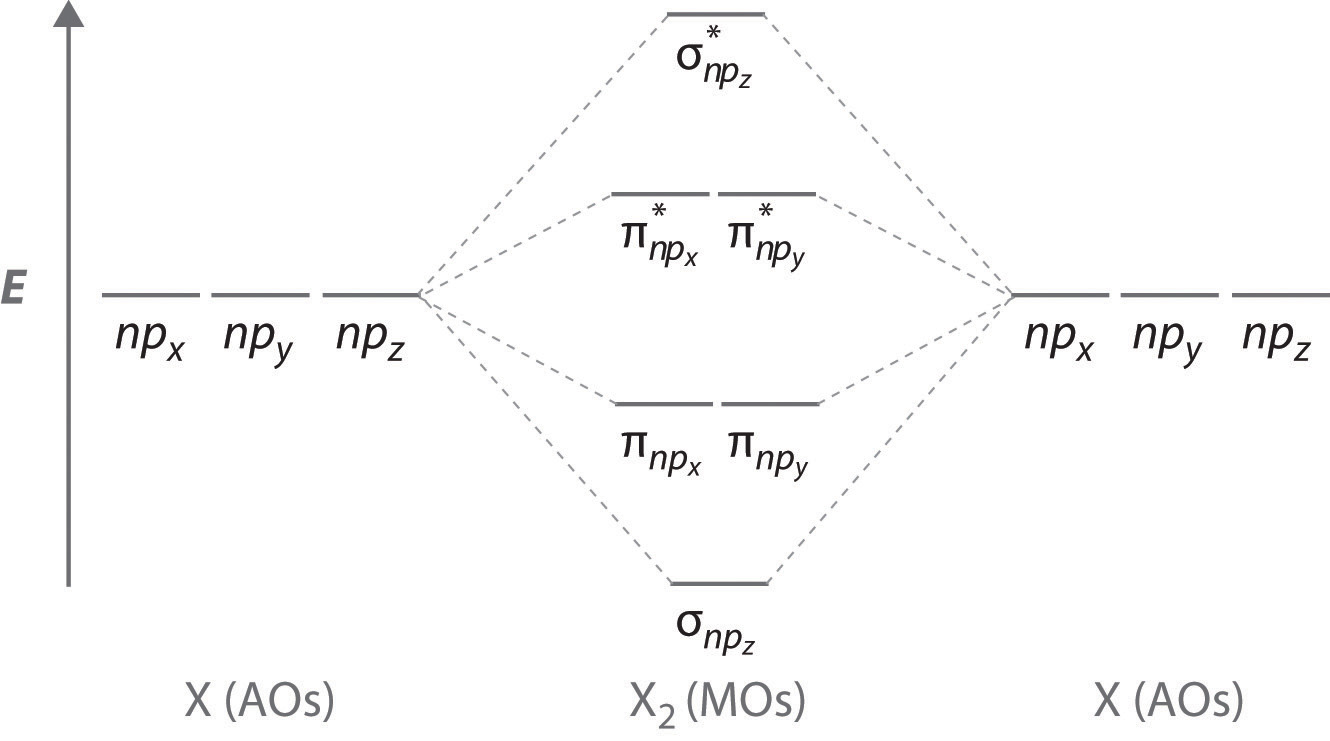
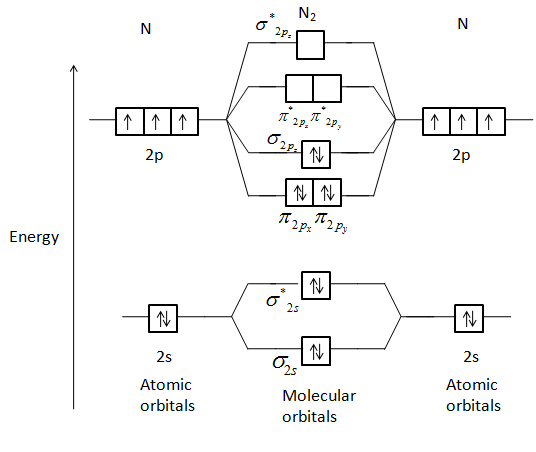
bond orderthe number of overlapping electron pairs between a pair of atoms. antibondingan atomic or molecular orbital whose energy increases as its constituent atoms converge, generating a repulsive force that hinders bonding. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond ... 4) or carbon dioxide (CO 2), a MO diagram may show one of the identical bonds to the central atom. For other polyatomic molecules, an MO diagram may show ... 8 Aug 2020 — Bonding in some heteronuclear di - atomic molecules : Molecular orbital diagram of Carbon monoxide molecule (CO)2 answers · Top answer: Solution: Bonding in some heteronuclear di - atomic molecules : Molecular orbital diagram of ...
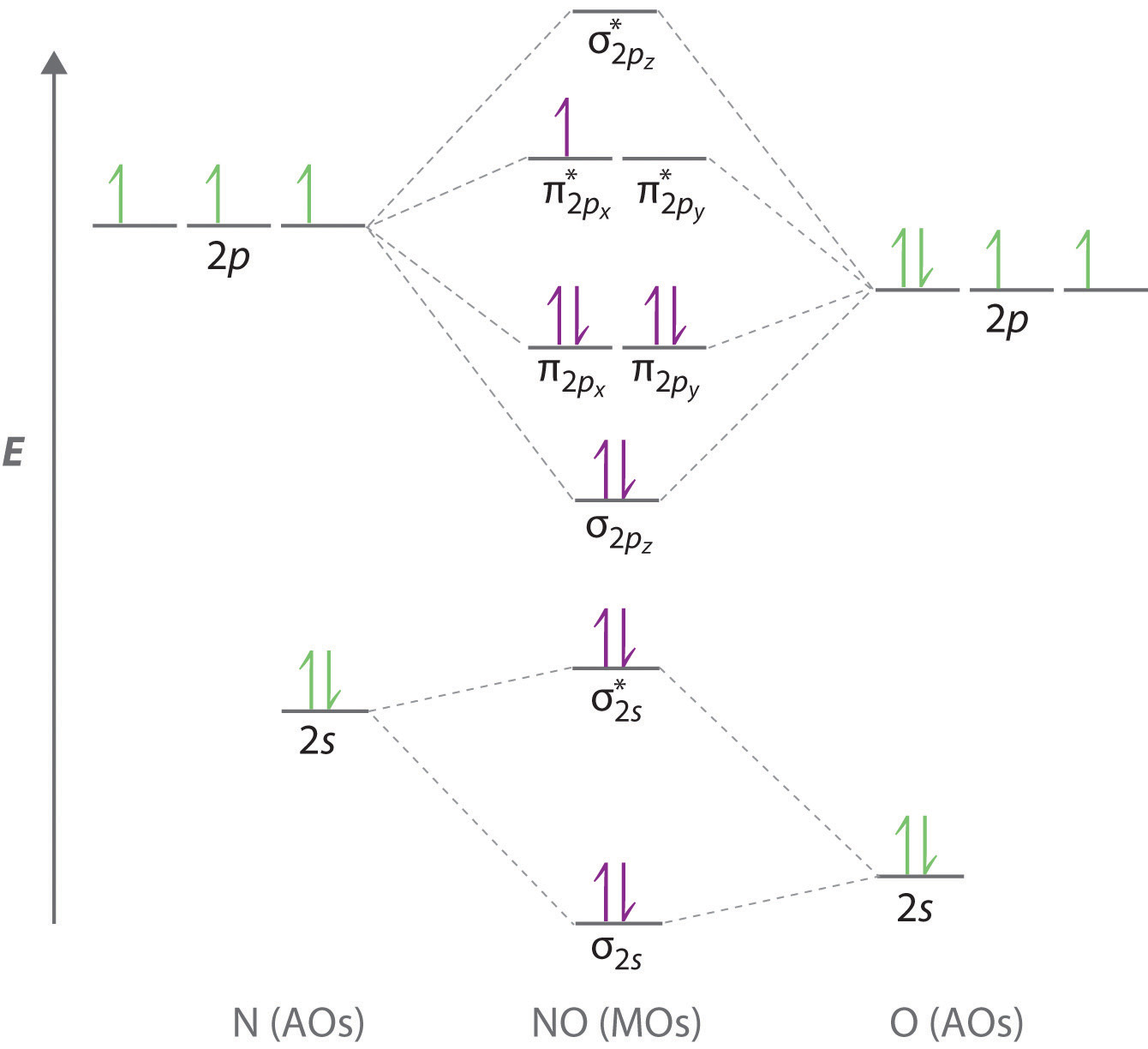
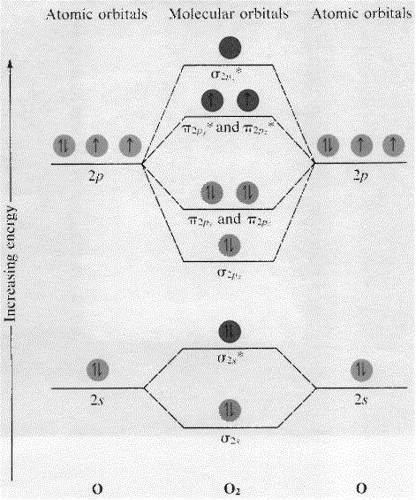
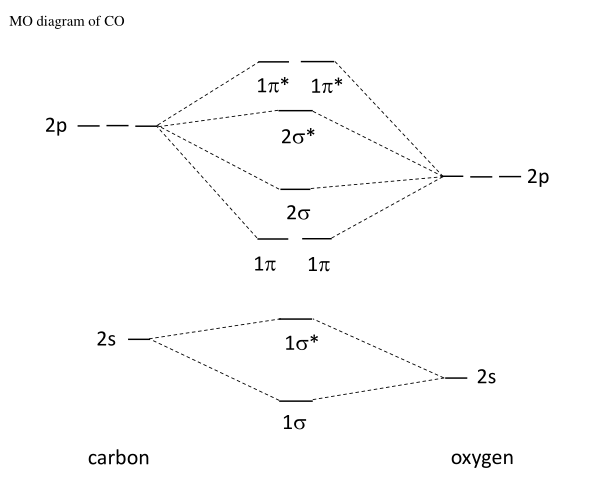
Co molecular orbital diagram bond order. "O"_2 is well-known to be paramagnetic, and it is one of the successes of molecular orbital theory. You can see that "CO" is not (as it has zero unpaired electrons), but "NO" is (it has one unpaired electron). Well, the MO diagram for "O"_2 is: The bond order is already calculated in the diagram. Higher is the bond order greater is the stability of molecule. i) If Nb > Na, then molecule ... Molecular Orbital diagram of Carbon monoxide molecule (CO):. Calculate a molecule's bond order given its molecular orbital diagram. ... In carbon monoxide (CO), the oxygen 2s orbital is much lower in energy than the ... The bond order of CO molecule on the basis of molecular orbital theory is: (1) Zero (2) 2 (3) 3 (4) 1 ... The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds ...1 answer · Top answer: Answer: (3) The bond order shows the number of chemical bonds present between a pair of atoms. The Bond Order Formula can be defined as half of the difference ...
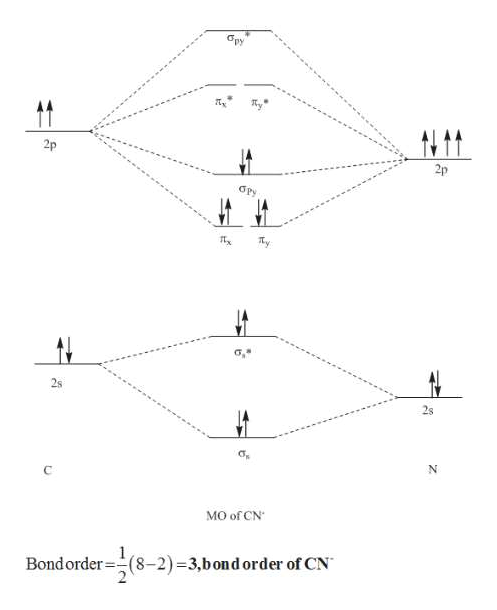
7. Draw the molecular orbital diagrams for NO, NO, and NO. For each molecule, determine the bond order, if the molecule is stable, and if the molecule is stable if it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Rank the molecules in increasing order of bond strength. Question: 7. Draw the molecular orbital diagrams for NO, NO, and NO. Answer (1 of 10): The bond order of CO is 3. as Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N the bond order is 3, in acetylene H−C≡C−H the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C−H bond order is 1. Bond order give... MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine So, from the above calculation the bond order of carbon monoxide molecules is 3. Now, we will find the bond order of Nitric oxide by the same molecular orbital ...1 answer · Top answer: Hint: We should know that bond order is the number of bonded electron pairs between two atoms. We can find the bond order of the above atoms by the ...
Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding the difference between two major theories: Valence Bond Theory and Molecular… Bond order=1/2 (bonding−anti-bonding) According to molecular orbital diagram, the bond order of CO+ is 3.5. The highest occupied molecular orbital is sigma*2s MO. In the case oc CO, the 2s atomic orbital on oxygen is much lower than the energy than the 2s atomic orbital of carbon. This discrepancy of energy allows the pi2px & pi2py BMO to ... 17 Dec 2020 · 1 answer1. Electronic configuration of C atom: · Electronic configuration of O atom: · 2. Electronic configuration of CO molecule is: · 3. Bond order =. 8 Aug 2020 — Bonding in some heteronuclear di - atomic molecules : Molecular orbital diagram of Carbon monoxide molecule (CO)2 answers · Top answer: Solution: Bonding in some heteronuclear di - atomic molecules : Molecular orbital diagram of ...

Use Molecular Orbital Theory To Determine Whether He2 2 Or He2 Is More Stable Draw The Molecular Orbital Diagram For Each And Explain Study Com
4) or carbon dioxide (CO 2), a MO diagram may show one of the identical bonds to the central atom. For other polyatomic molecules, an MO diagram may show ...
bond orderthe number of overlapping electron pairs between a pair of atoms. antibondingan atomic or molecular orbital whose energy increases as its constituent atoms converge, generating a repulsive force that hinders bonding. Bond order is the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms; in diatomic nitrogen (N≡N) for example, the bond ...

Mot Diagram Of Co With Its Bond Order Chemistry Chemical Bonding And Molecular Structure 13064899 Meritnation Com

Draw The Molecular Orbitals For Co In Order Of Energy And Fill Them With The Appropriate Number Of Electrons Label The Orbitals The Best You Can As Sigma Or Pi And As

How To Rationalise With Mo Theory That Co Is A Two Electron Donor Through Carbon Chemistry Stack Exchange












0 Response to "35 co molecular orbital diagram bond order"
Post a Comment