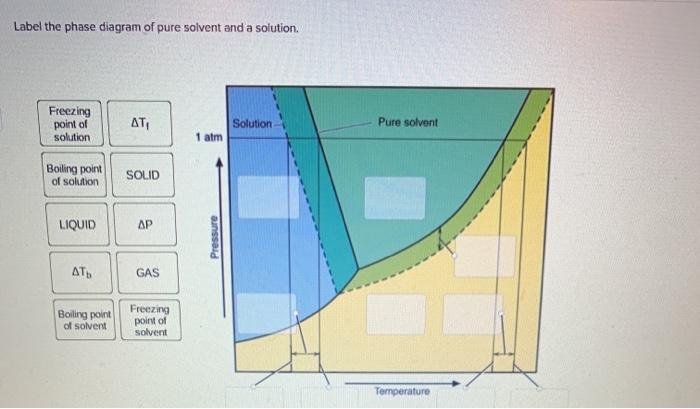
37 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution
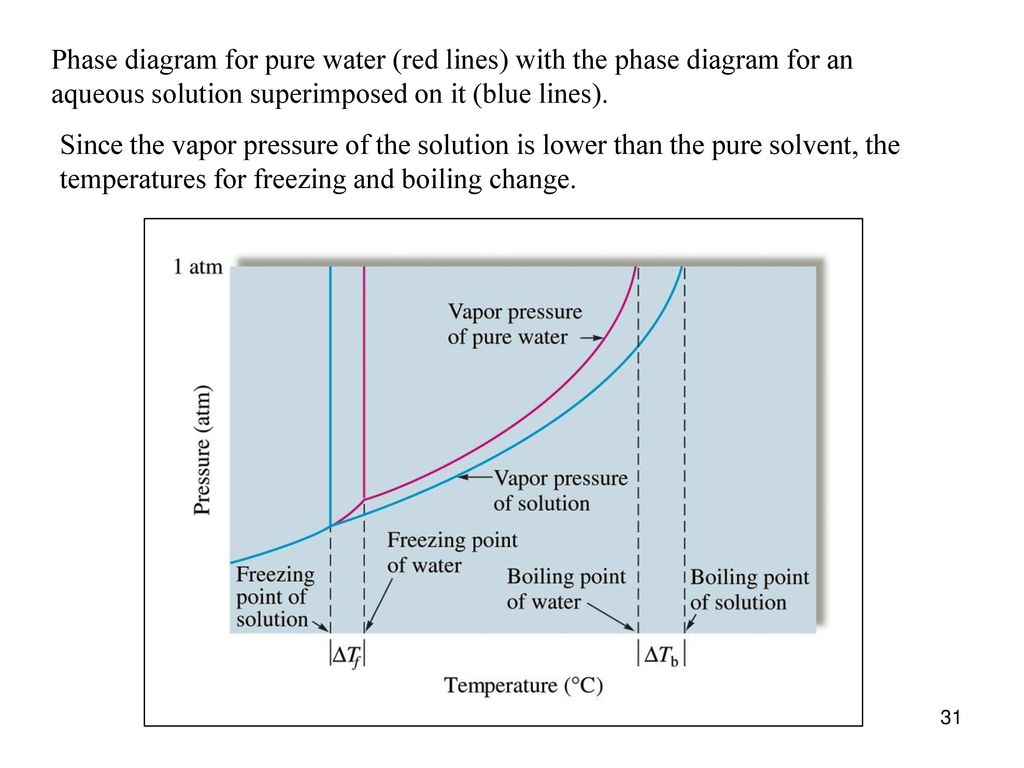
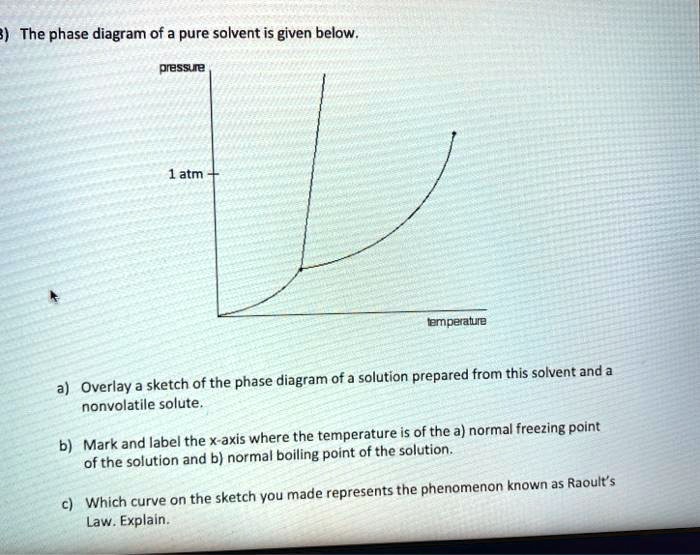
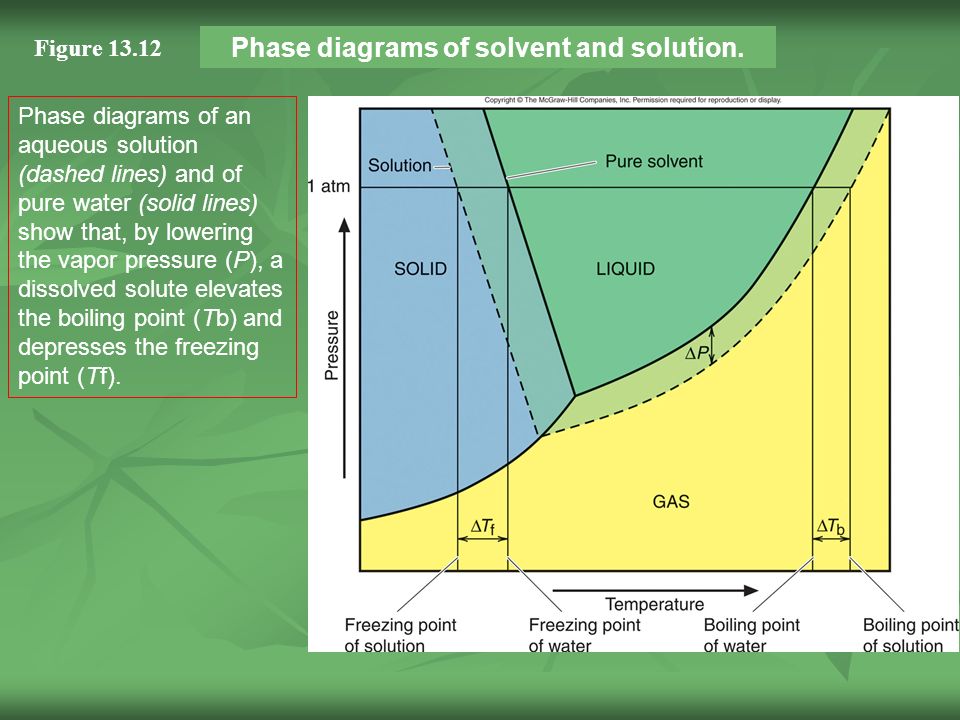
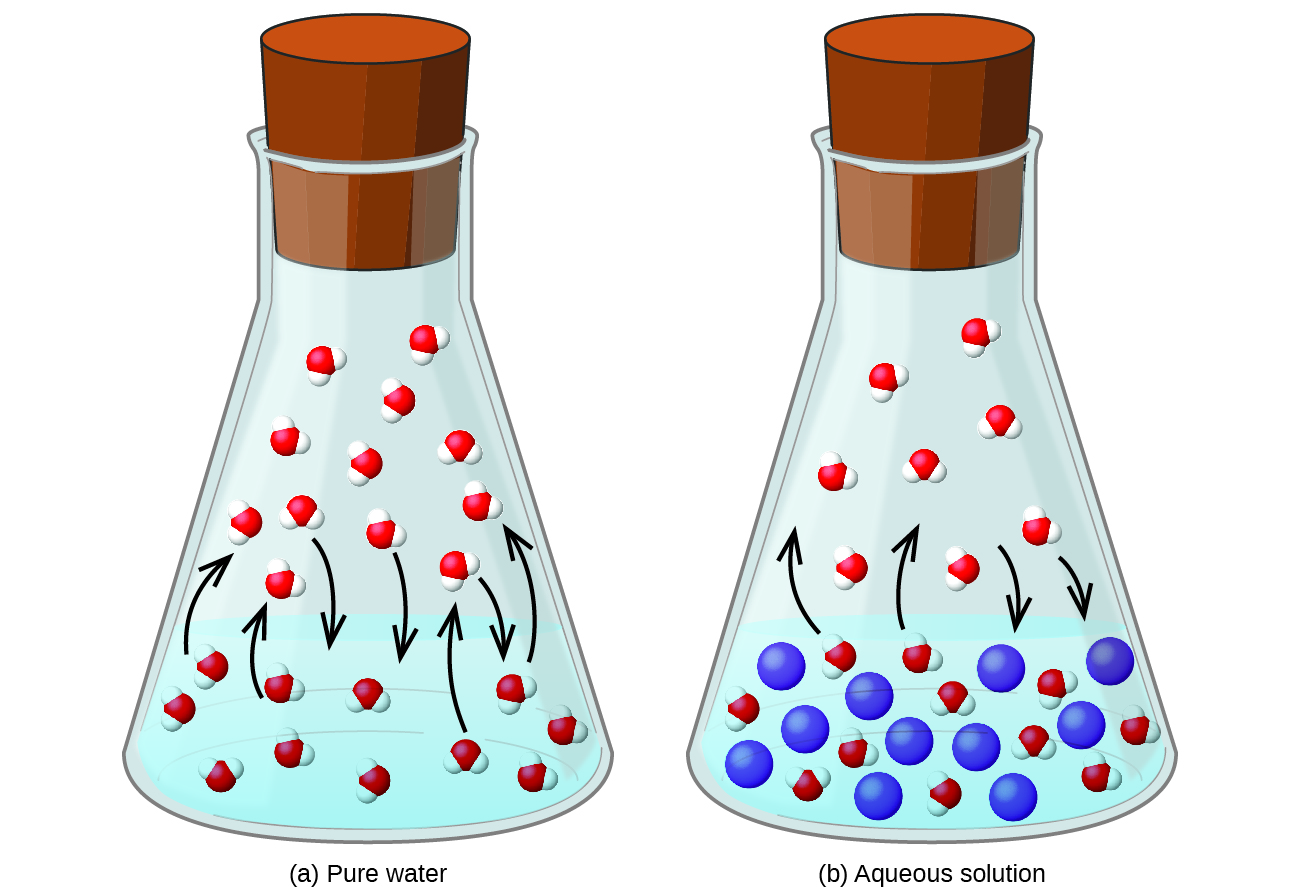
Similar to liquids, these fluids ... solutes. They exhibit essentially no surface tension and very low viscosities, however, so they can more effectively penetrate very small openings in a solid mixture and remove soluble components. These properties make supercritical fluids extremely useful solvents for a wide ... The effect of Raoult's Law is that the saturated vapor pressure of a solution is going to be lower than that of the pure solvent at any particular temperature. That has important effects on the phase diagram of the solvent. The next diagram shows the phase diagram for pure water in the region ...
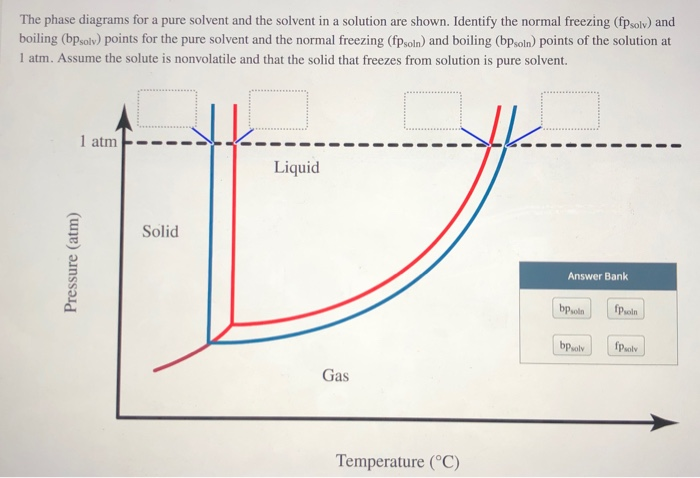
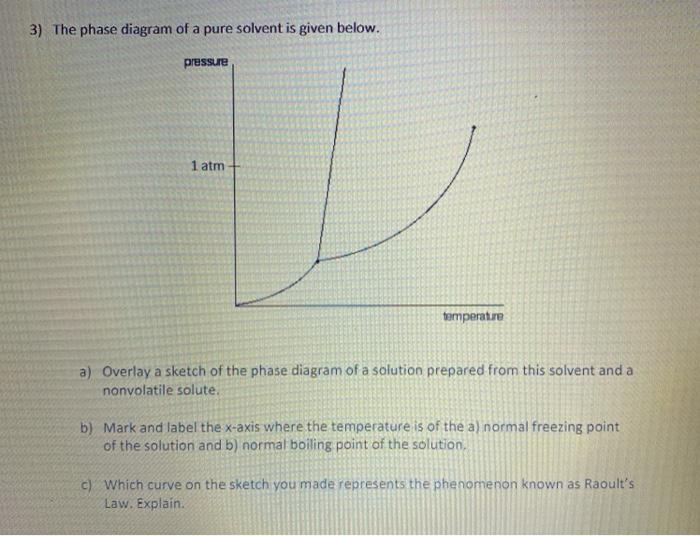
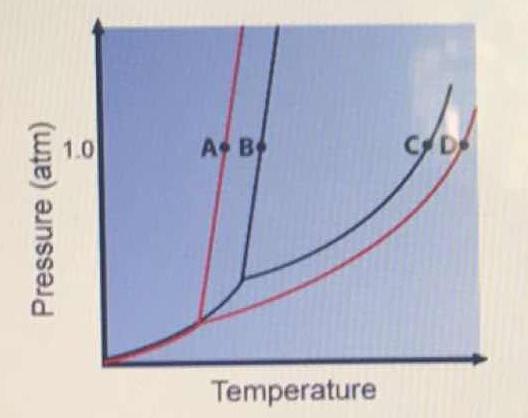
Transcribed image text: The phase diagrams for a pure solvent and the solvent in a solution are shown. Identify the normal freezing (fp_solv) and boiling (bp_solv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fp_soln) and boiling (bp_soln) points of the solution at 1 atm. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution
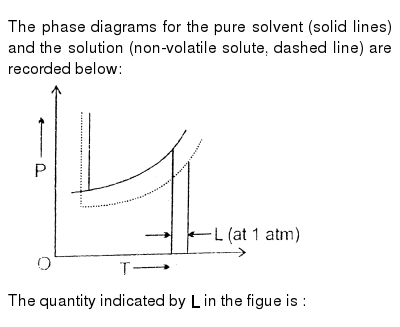
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below. The quantity indicated by L in t As suggested by the Gibbs Phase Rule, the most important variables describing a mixture are pressure, temperature and composition. In the case of single component systems, composition is not … January 31, 2018 - Export articles to Mendeley · Get article recommendations from ACS based on references in your Mendeley library
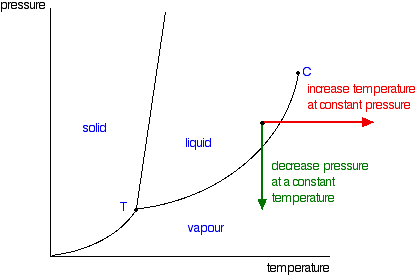
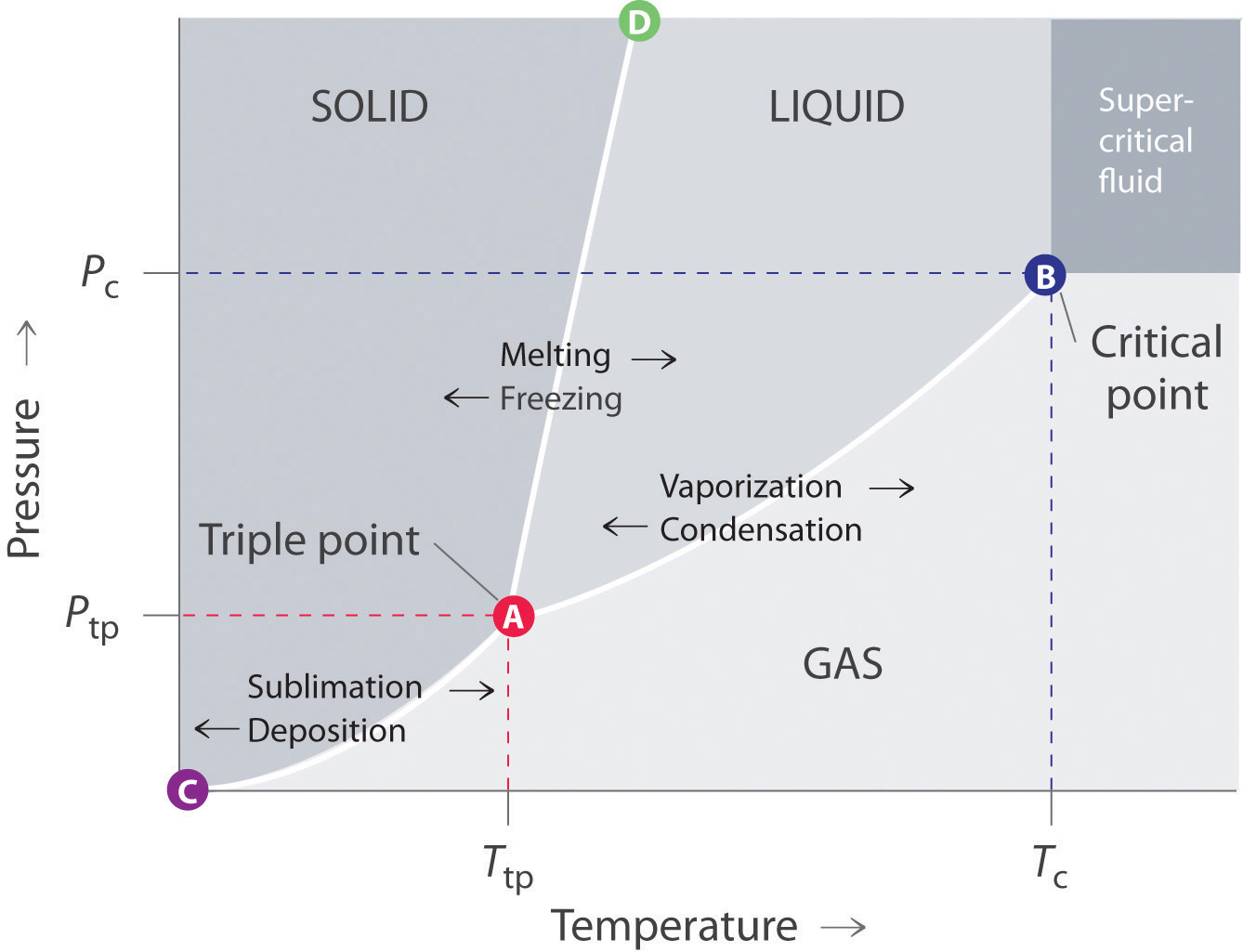
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Elemental carbon has one gas phase, one liquid phase, and two different solid phases, as shown in the phase diagram: (a) On the phase diagram, label the gas and liquid regions. (b) Graphite is the most stable phase of carbon at normal conditions. On the phase diagram, label the graphite phase. Portions of the ternary phase diagram were determined by titrating a PEO solution in the polar solvent with heptane under visual inspection, in a temperature controlled environment (within 1 degree for experiments at - 50ºC and within 0.1 degree for the other temperatures). 1. Roughly sketch the phase diagram, using units of atmosphere and Kelvin. Answer. 1-solid, 2-liquid, 3-gas, 4-supercritical fluid, point O-triple point, C-critical point -78.5 °C (The phase of dry ice changes from solid to gas at -78.5 °C) 2. Rank the states with respect to increasing density and increasing energy. The figure below shows the consequences of the fact that solutes lower the vapor pressure of a solvent. The solid line connecting points B and C in this phase diagram contains the combinations of temperature and pressure at which the pure solvent and its vapor are in equilibrium.
Chemistry questions and answers. The phase diagrams for a pure solvent and the solvent in a solution are shown. Identify the normal freezing (fpsoly) and boiling (bpsolv) points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing (fpsoln) and boiling (bpsoln) points of the solution at 1 atm. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that ... May 16, 2019 · Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. The vaporization curve for the solution lies below the curve for pure water at all temperatures which results in an increase in the boiling point and a decrease in the freezing point of the solution. This is the case for many solutions comprising liquid solvents and nonvolatile solutes. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Shown above is a phase diagram for water. Well look now at the phase diagram for sodium chloride solution in some detail. Phase diagrams of pure water and an aqueous solution of a nonvolatile solute. Pure a and pure b are also considered to be α and β phases respectively. October 25, 2013 - Skip to Main content Skip to Navigation · menu-label-0 · Contact · Support · Resources · Documentation · OAI-PMH · AuréHAL · Information · Personal data and privacy
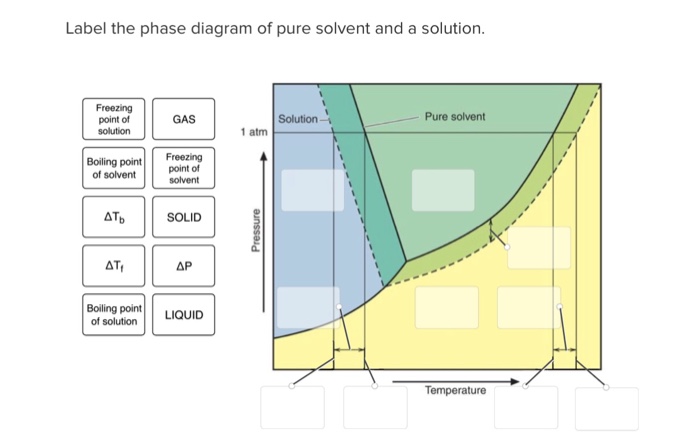
Phase diagrams for polystyrene solutions in poor solvents and theta-solvents have been determined as functions of concentration, molecular weight and polydispersity, pressure, temperature, and H/D... Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution Freezing point of solution GAS Solution Pure solvent 1 atm Boiling pointFreezing point of of solvent solvent ??? 11 SOLID AT AP Boiling pointLIQUID of solution Temperature. Recall that a phase diagram shows the transition of matter between solid, liquid, and gas phases as temperature and pressure changes. In a phase diagram, the different phases can be identified by their location: • Solid → high pressure and low temperature. • Liquid → between the solid and gas regions. • Gas → low pressure and high temperature. Chapter 1: Chemistry: Matter and Measurement · Chapter 2: Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
June 10, 2017 - Consider the following general phase diagram: Now, consider the pure substance, whose phase diagram was represented by the black curves. The normal freezing point of the pure substance at constant pressure is indicated by B, and its reduced normal freezing point (due to addition of nonvolatile ...
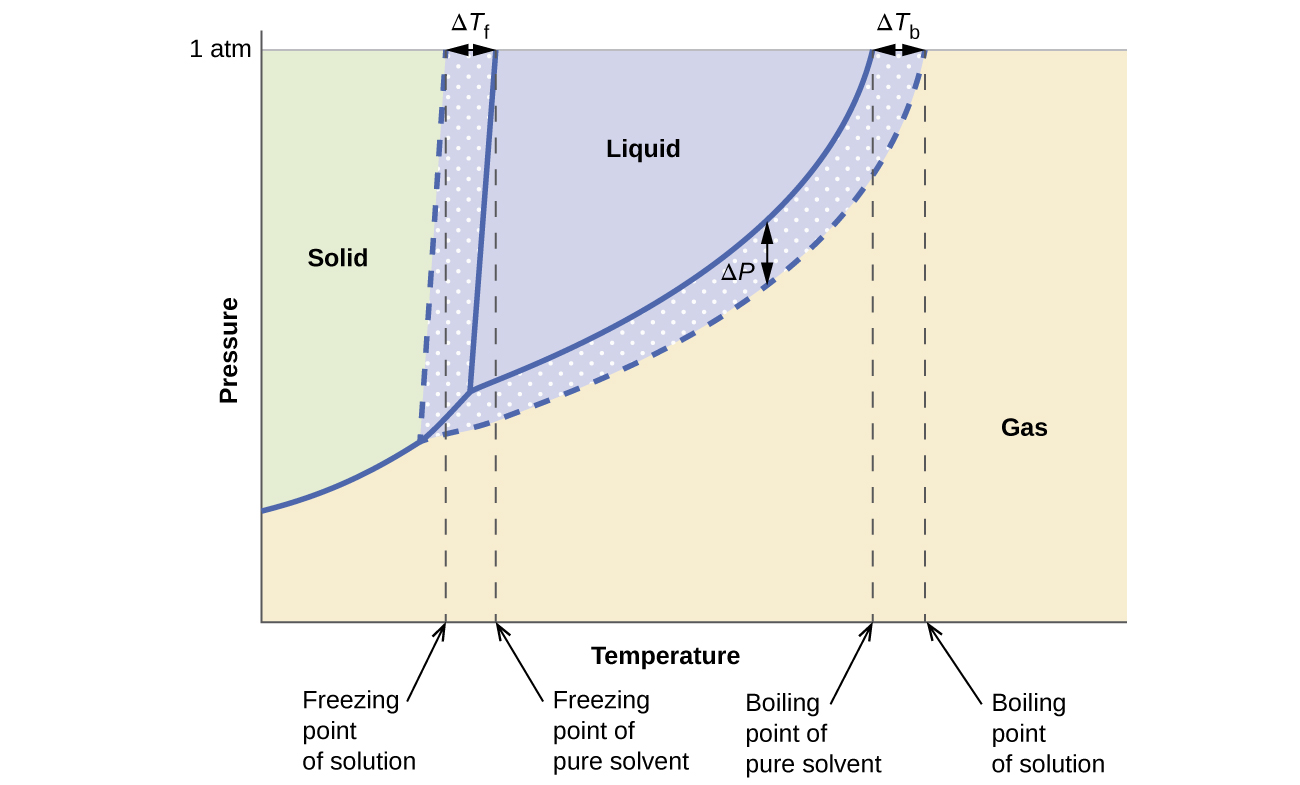
Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Freezing point of solution ΔΤ, Solution Pure solvent 1 atm Boiling point of solution SOLID LIQUID AP Pressure AT) GAS Boiling point of solvent Freezing point of solvent Temperature.
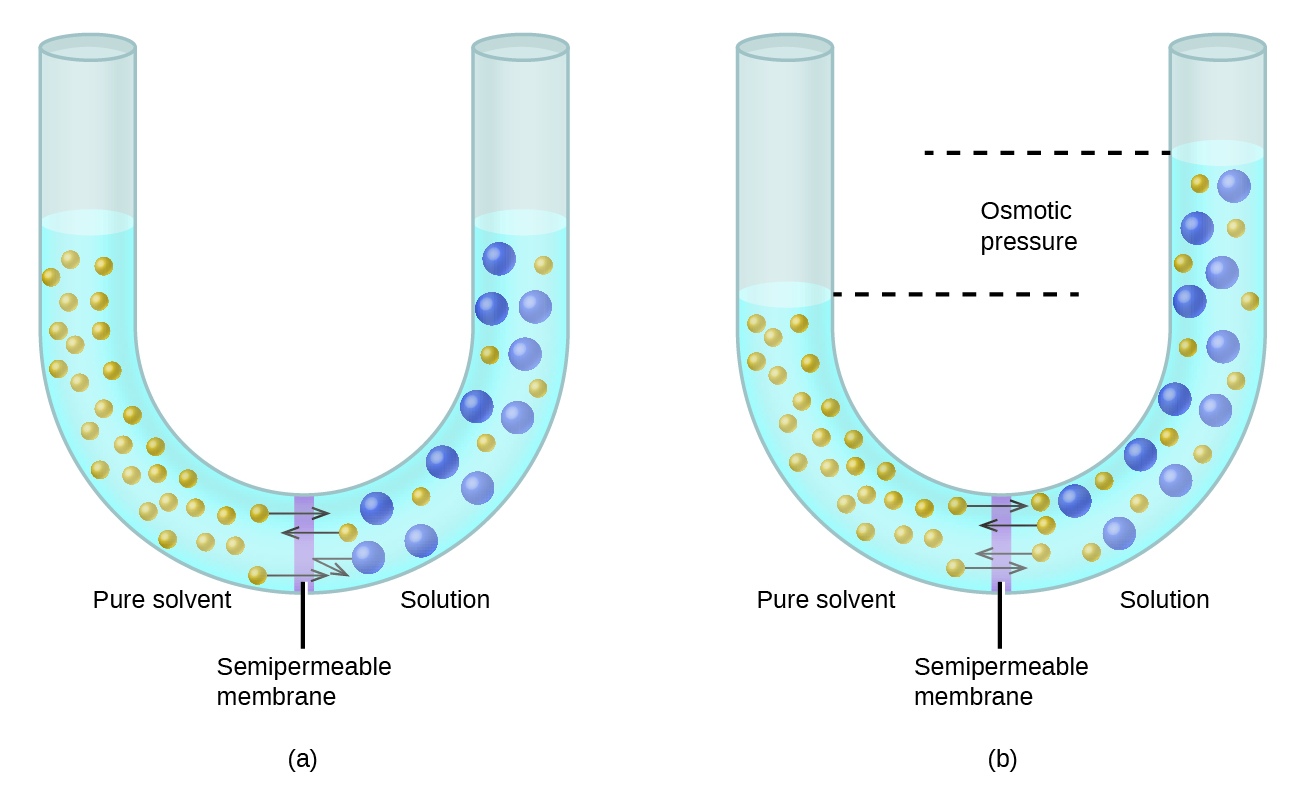
February 28, 2021 - Colligative properties of a solution depend on only the total number of dissolved particles in solution, not on their chemical identity. Colligative properties include vapor pressure, boiling point, …
September 21, 2018 - We study fluid-fluid equilibrium in the simplest model of ionic solutions where the solvent is explicitly included, i.e., a binary mixture consisting of a restricted primitive model (RPM) and neutral hard-spheres (RPM-HS mixture). First, using the collective variable method we find free energy, ...
– Solutions – solid solutions, single phase – Mixtures – more than one phase • Solubility Limit : Max concentration for which only a single phase solution occurs. Question: What is the solubility limit at 20°C? Answer: 65 wt% sugar . If Co < 65 wt% sugar: syrup If Co > 65 wt% sugar: syrup + sugar. 65 Sucrose/Water Phase Diagram Pure ...
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. This is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
May 26, 2014 · Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution freezing point of solution gas solution pure solvent 1 atm boiling pointfreezing point of of solvent solvent. Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Assume the solute is nonvolatile and that the solid that freezes from solution is pure solvent. 12716 3 the phase diagram in figure 1 is for a pure compound.
January 31, 2018 - Export articles to Mendeley · Get article recommendations from ACS based on references in your Mendeley library
As suggested by the Gibbs Phase Rule, the most important variables describing a mixture are pressure, temperature and composition. In the case of single component systems, composition is not …
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below. The quantity indicated by L in t














0 Response to "37 label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution"
Post a Comment