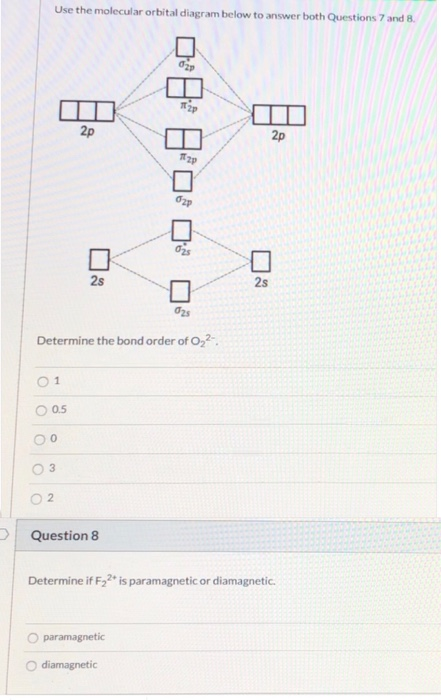
38 o22- molecular orbital diagram
Explanation: In a molecule, there are total 16 electrons. The molecular orbital configuration of molecule is as follows.. The formula for bond order is as follows. Bond order = There are 10 bonding and 6 non-bonding electrons in the orbitals according to the molecular orbital configuration. Use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which is most stable a o22 bf2 c f22 d f22 e ne22 a. A asdfasdf b asdfasdf c asdf d f2 2 e none of the above are paramagnetic.
Printable O2 molecular orbital diagram s are available for you to guide your study in the molecular orbital lesson.This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combinat ion of atomic orbital s (LCAO) molecular orbital method in particular.
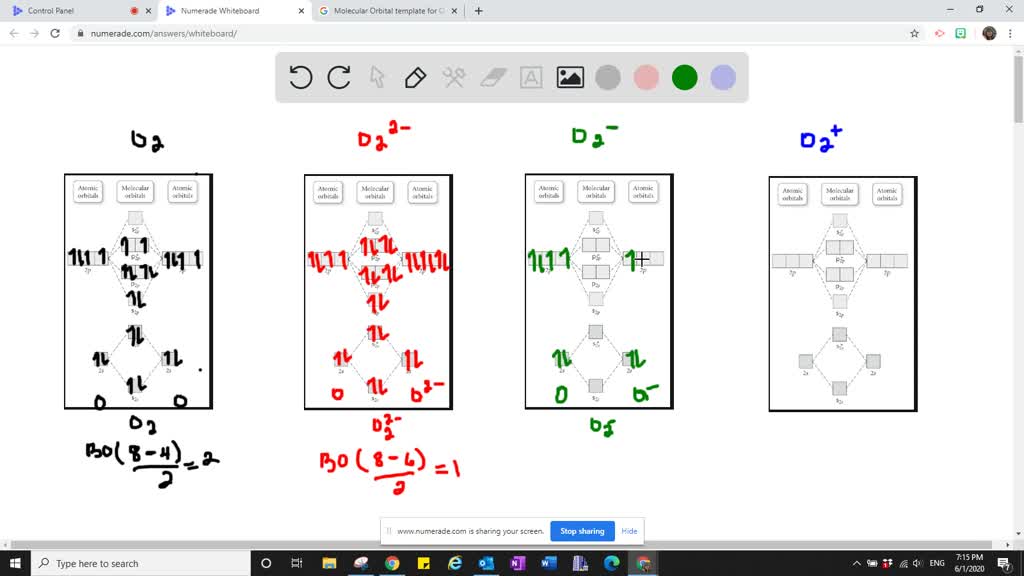
O22- molecular orbital diagram
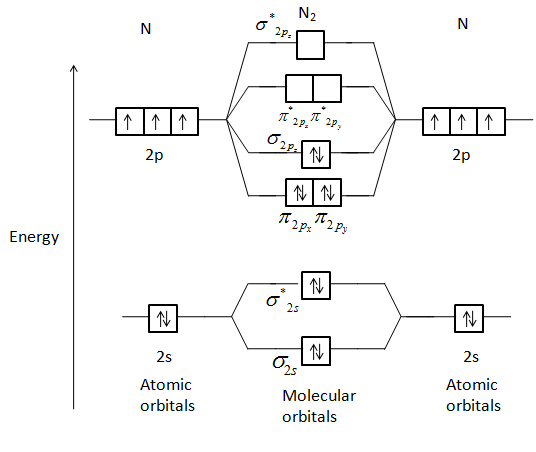
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ... As it can be seen from the given structures that in the molecular orbital diagram for O 2 + ion, the highest occupied orbital is π ∗ MO orbital. Video Explanation Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-
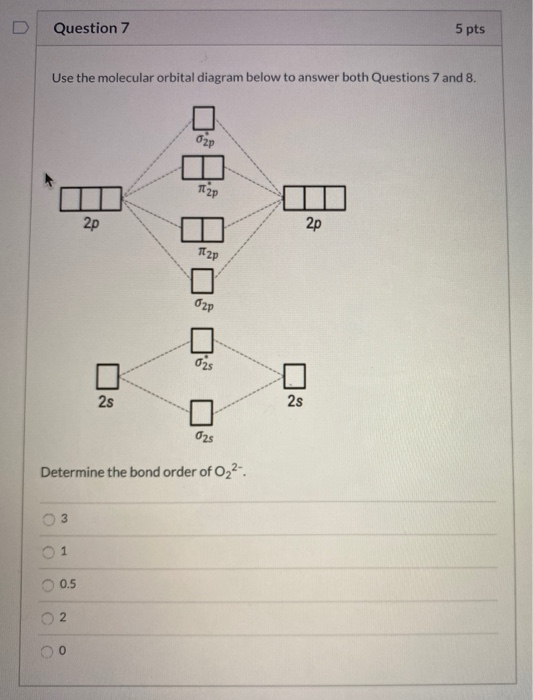
O22- molecular orbital diagram. Problem: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.a. F22+b. Ne22+c. F22-d. O22+e. F2 Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. Step 3: Calculate the bond order of the molecule/ion. Recall that the formula for bond order is: Bond Order = 1 2 [ # of e - in bonding MO - # of e - in antibonding MO] 89% (181 ratings) Problem Details. Explain the following. The O22+ ion has a stronger O-O bond than O2 itself. The valence electrons = 14; BO = 0.5* (8-6) = 1. The bond order is commonly used to signify the bond stability. Higher bond order indicates more stability and vice versa. Thus, is the most stable. is diamagnetic while and are paramagnetic in nature. Further Explanation: MO diagram: It is a tool used to describe the chemical bonding formed ... According to molecular orbital theory the o22 molecular ion should be. Construct the molecular orbital diagram for he2 and then identify the bond order complete this valence molecular orbital diagram for oxygen o2. What is the molecular orbital electron configuration for o2 and how many unpaired electrons would it have.
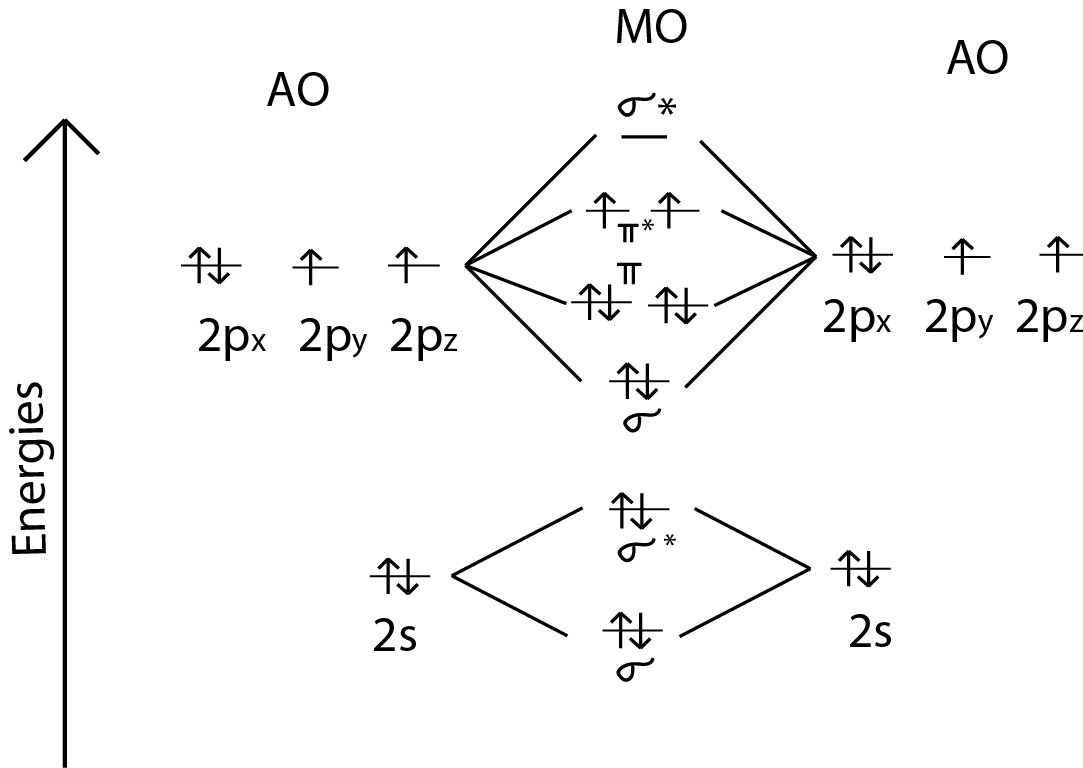
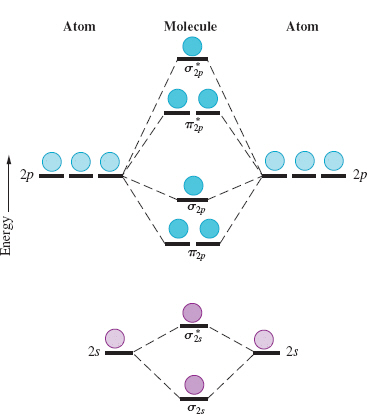
Hint: First draw a molecular orbital diagram (MOT) where the atomic orbitals combine to form molecular orbitals. The total electrons associated with the molecules are filled in the MOT diagram. To solve this question, we need to write the molecular orbital configuration. To find out the bond order from the molecular orbital configuration is: Molecular orbital theory describes the distribution of electrons in molecules in much the same way that the distribution of electrons in atoms is described using atomic orbitals. Using quantum mechanics, the behavior of an electron in a molecule is still described by a wave function, Ψ, analogous to the behavior in an atom.Just like electrons around isolated atoms, electrons around atoms in ... Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... 1 answerDraw the MO diagram for O22- and identify the following: Bond order, diamagnetic or paramagnetic, homo and lumo. ... Hey there! We will begin by drawing the ...
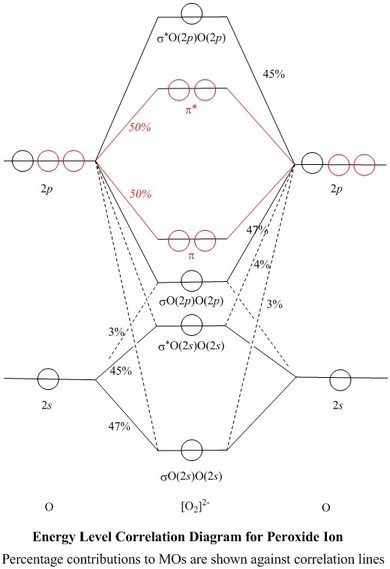
Answer: Yes O2 (2+) is diamagnetic. Explanation: We can work this out by looking at the molecular orbital diagram of O2 O2 (2+) has two fewer electrons than O2 which is what it gives it positive charge. And show diamagnetic behavior as have no unpaired electron. Molecular orbital diagram of ... Molecular orbital diagram for o2 2. This ion has been observed in the gas phase. O2 molecular orbital diagram oxygen has a similar setup to h 2 but now we consider 2s and 2p orbitals. This diagram is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of a molecular orbital theory in general and the linear ... It is sigma2s(2)sigma2s*(2)sigma2p(2)pi2p(4)pi2p*(4)Bond order 1. It is stable. In fact, it's the perioxide ion.Check me out: http://www.chemistnate.com Jmol Molecular Models Showing Orbitals for Peroxide. The MO models shown on this web page were obtained at the RMPW1PW91/6-311g(2df) level in a conventional ab initio calculation, using a Gaussian atomic basis set; The Gaussian atomic basis set is an approximation to Natural Atomic Orbitals, 2s, 2p z, etc., which are not very amenable to computation; A Natural Bond Orbital analysis of the ...

Solved The Superoxide Ion O2 Is A Reactive Species That May Play A Role In The Chemistry Of Aging Use A Molecular Orbital Diagram To Determine The Bond Order Of The Superoxide Ion
Bond order (B.O) 1/2 × [Number of an electron in antibonding molecular orbitals] - [Number of electrons in bonding molecular orbitals] The higher the order of the bond the greater the pull between the two atoms and the shorter the length of the bond. (1) B.O for O 2 = 1/2 × [10 - 6] B.O for O 2 = 2
Molecular Orbital Theory -- Homodiatomics use the molecular orbital model to fully describe the bonding in O2+, O2, O2-, and O22-. Determine which of the following statements are true and which ...
O 2 − , O 2. and. O 2 2 −. molecular species, the total number of antibonding electrons are 7,6,8 respectively. Hence, the correct option is the option (A). Note: From the molecular orbital electronic configuration of a species, you can determine the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons.
Remember: When two oxygen atoms bond, the pi(2p) bonding molecular orbitals are lower in energy than the sigma(2p) bonding orbitals. They are flipped compare...
C o22 use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following are paramagnetic. Molecular orbital diagram. Periodic trends determine. A n22 b b2 c b22 d c22 e c22. Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is paramagnetic. Molecular Orbital Theory
Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F, Ne Ne22 F₂2. F2 . 022- • F22 ; Question: Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable based on their bond order. Atomic orbitals Molecular orbitals Atomic orbitals O, F, Ne Ne22 F₂2. F2 . 022- • F22
Draw molecular orbital diagrams for O2-, O22-, and O2. Which has the highest bond order? Which would be paramagnetic, and which would be diamagnetic? Can you draw good dot structures that correspond to each of these ions or molecules? Draw a molecular orbital diagram lor Arz*. This ion has been observed in the gas phase.
The first photo is straight from a 2006 edition Pearson general chemistry textbook, and it shows you what the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for O2 is.5 answers · 31 votes: Hello! I actually just covered this question in my gen chem class this week. I have attached ...
Molecular Orbital Theory Chemistry Encyclopedia Structure Number Molecule Atom Bond Order Multiple Bonds
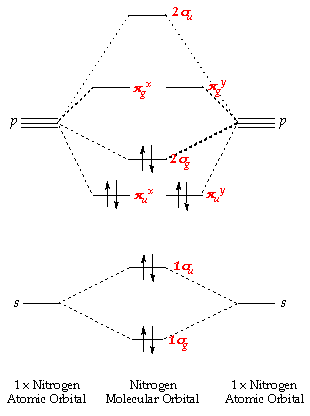
Molecular orbital diagram for hydrogen: For a diatomic molecule, an MO diagram effectively shows the energetics of the bond between the two atoms, whose AO unbonded energies are shown on the sides. The unbonded energy levels are higher than those of the bound molecule, which is the energetically-favored configuration.
Question: Complete the molecular orbital diagram for CN. Note that the 1s orbitals are not shown. Identify the bond order of CN. O2 01 OOOOO 25- 0 2s Answer Bank The atomic orbitals on the left side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of The atomic orbitals on the right side of the molecular orbital diagram are those of.
Oct 28, 2014 — Ans: The stabilities of these can be best explained using Molecular orbital theory. ... Atomic orbitals of oxygen combine to form molecular ...
(a) Sketch the molecular orbitals of the H 2 - ion and draw its energy-level diagram. (b) Write the electron configuration of the ion in terms of its MOs.(c) Calculate the bond order in H 2-.(d) Suppose that the ion is excited by light, so that an electron moves from a lower-energy to a higher-energy molecular orbital.Would you expect the excited-state H 2-ion to be stable?
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
The molecular orbital energy level diagram of oxygen molecule is given as follows : Bond order 2 N b − N a = 2 8 − 4 = 2 Thus, oxygen molecule has two bonds. i.e., one is bond and one p bond.
As it can be seen from the given structures that in the molecular orbital diagram for O 2 + ion, the highest occupied orbital is π ∗ MO orbital. Video Explanation Solve any question of Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure with:-
Electronic structure of oxygen atom is Leaving out the 4 electrons in the 1s orbitals of two oxygen atoms constituting the molecule (represented as KK), the molecular orbital energy diagram for remaining 12 electrons of oxygen as molecule is shown: (i) Electronic configuration: (ii) Bond order: Here N b = 8; N a = 4 The two oxygen atoms in a molecule of oxygen are united through two covalent ...

Based On The Mo Diagrams For O 2 O 2 And O 2 Answer The Following 1 Is O 2 Paramagnetic Or Diamagnetic 2 Which Will Have The Shortest Bond Length 3 Which Will Have The
Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in

Molecular Orbital Theory Homodiatomics Use The Molecular Orbital Model To Fully Describe The Bonding In O2 O2 O2 And O22 Determine Which Of The Following Statements Are True And Which Are





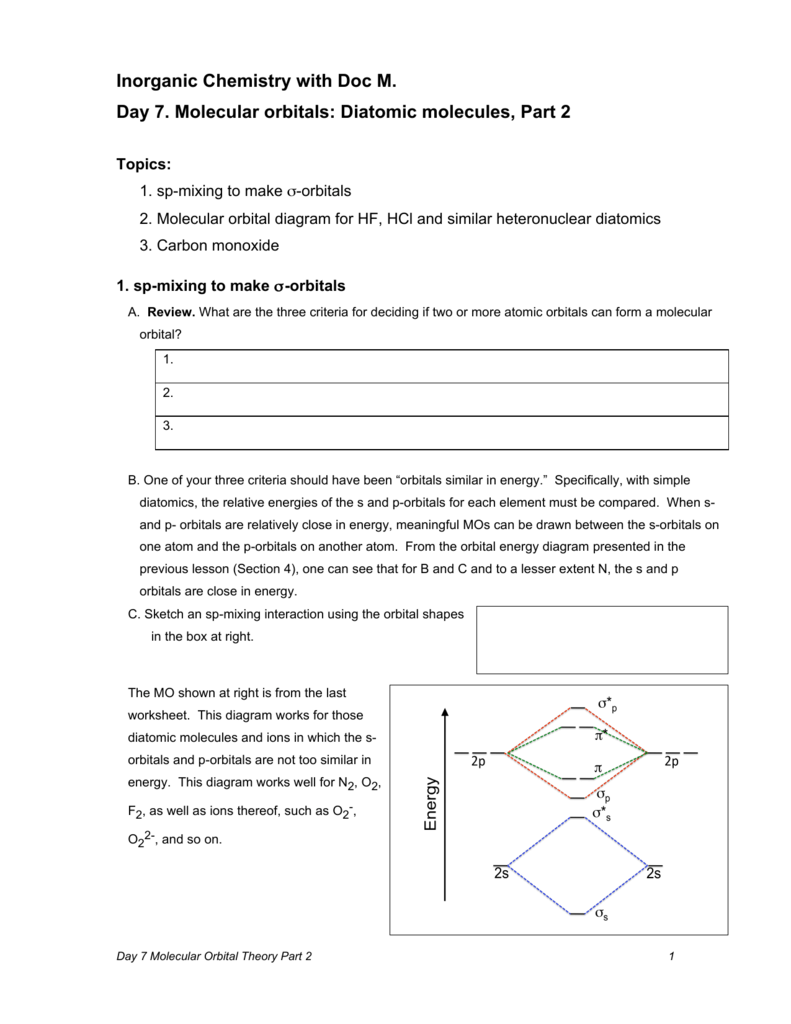
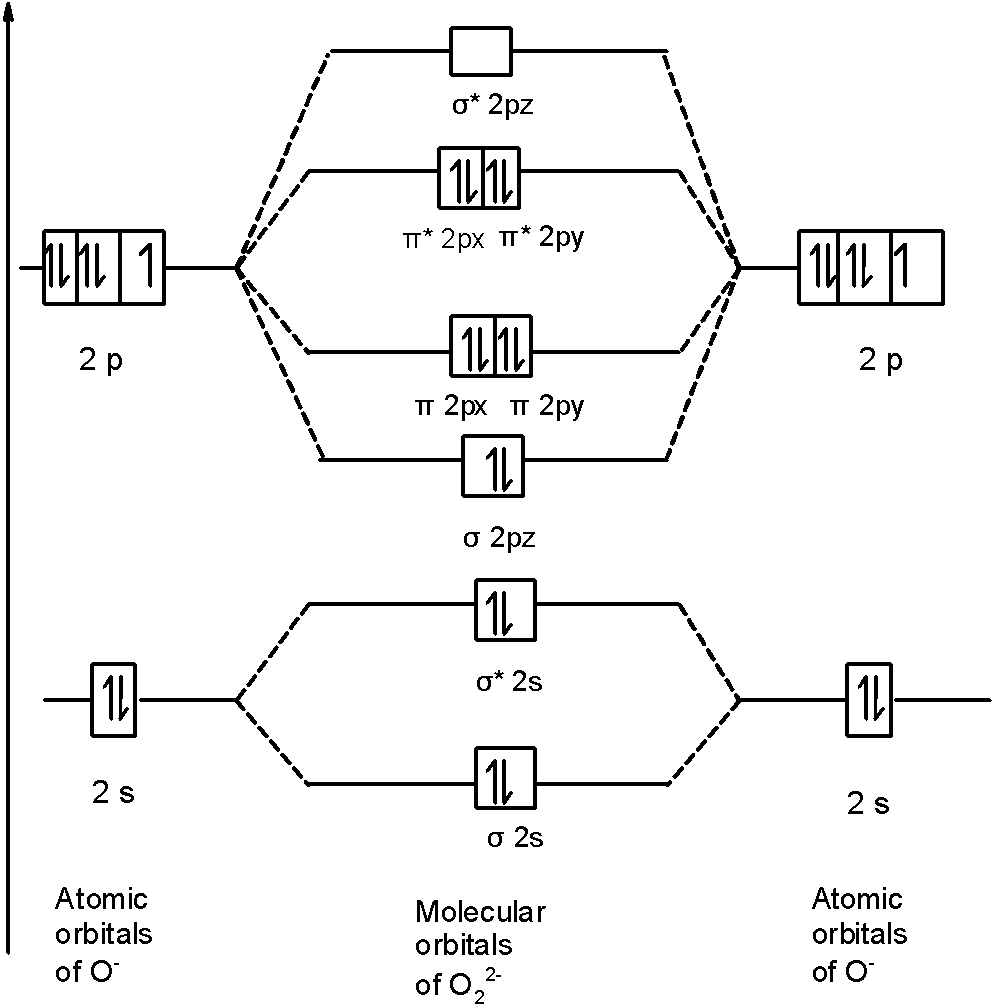

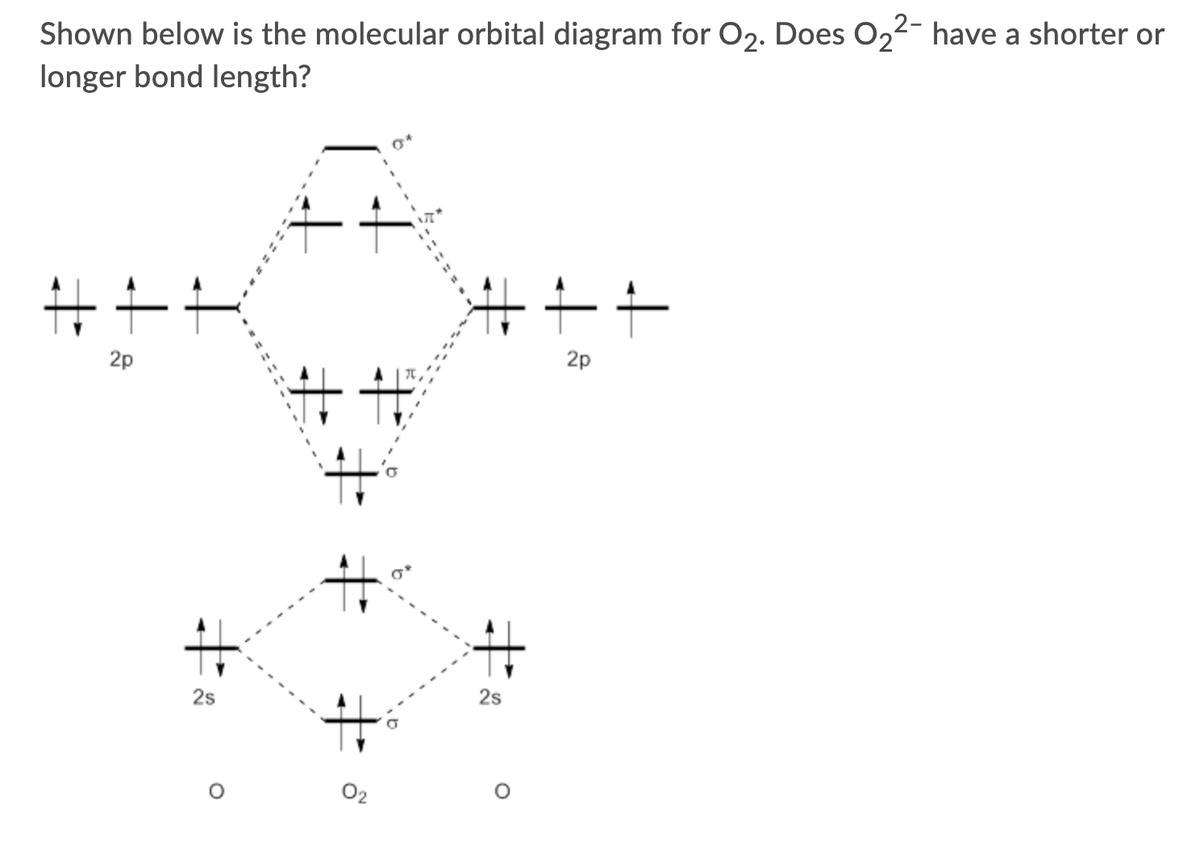






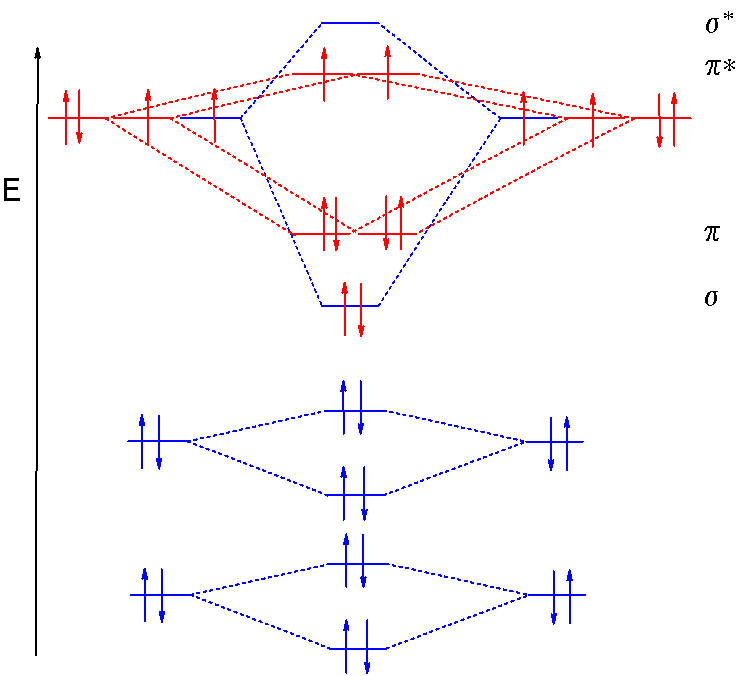
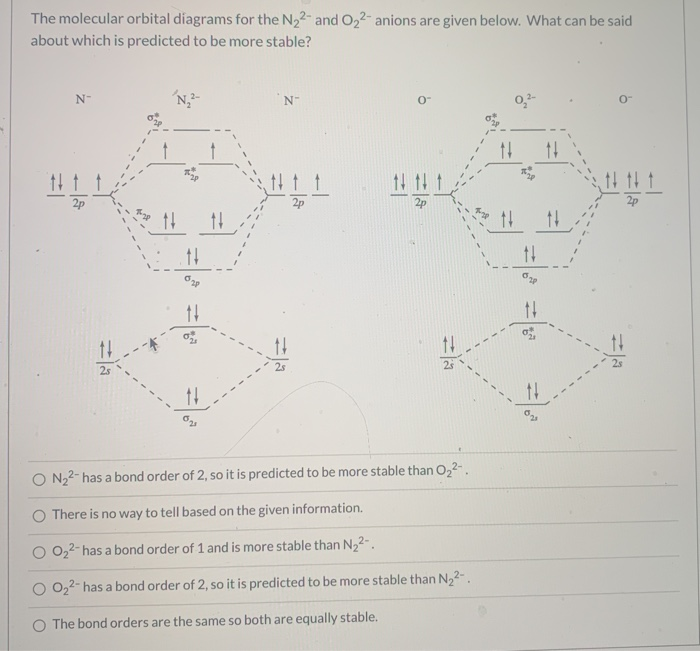

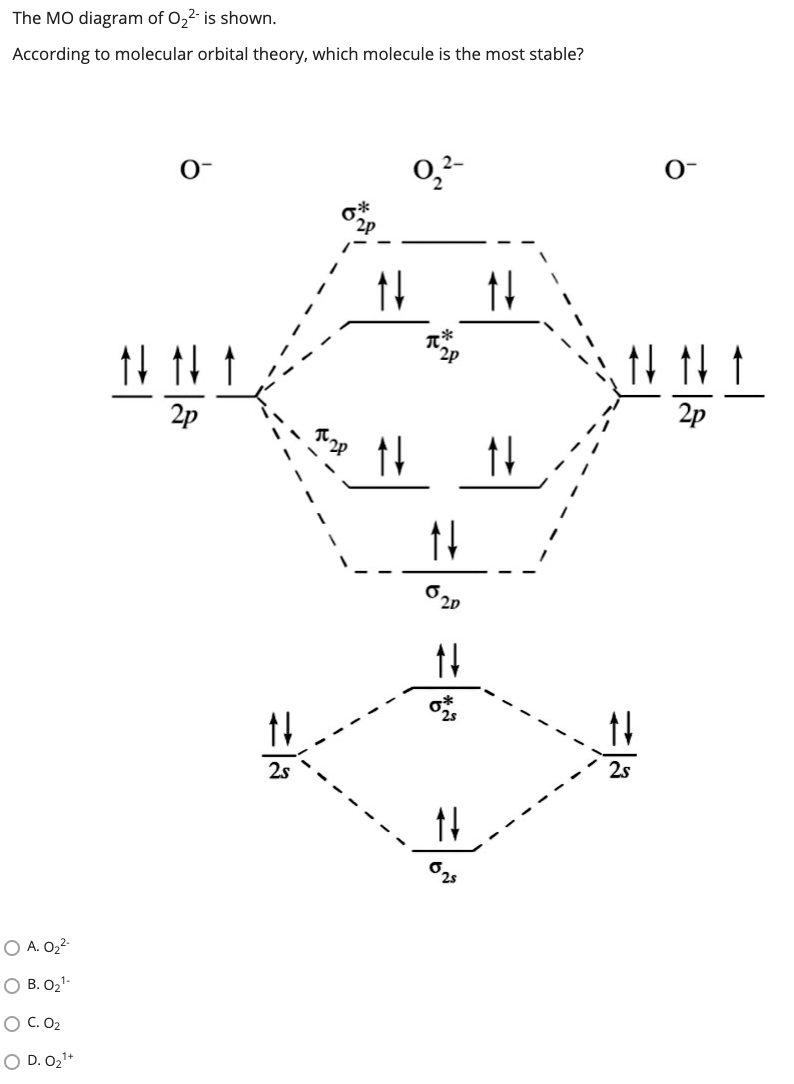
0 Response to "38 o22- molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment