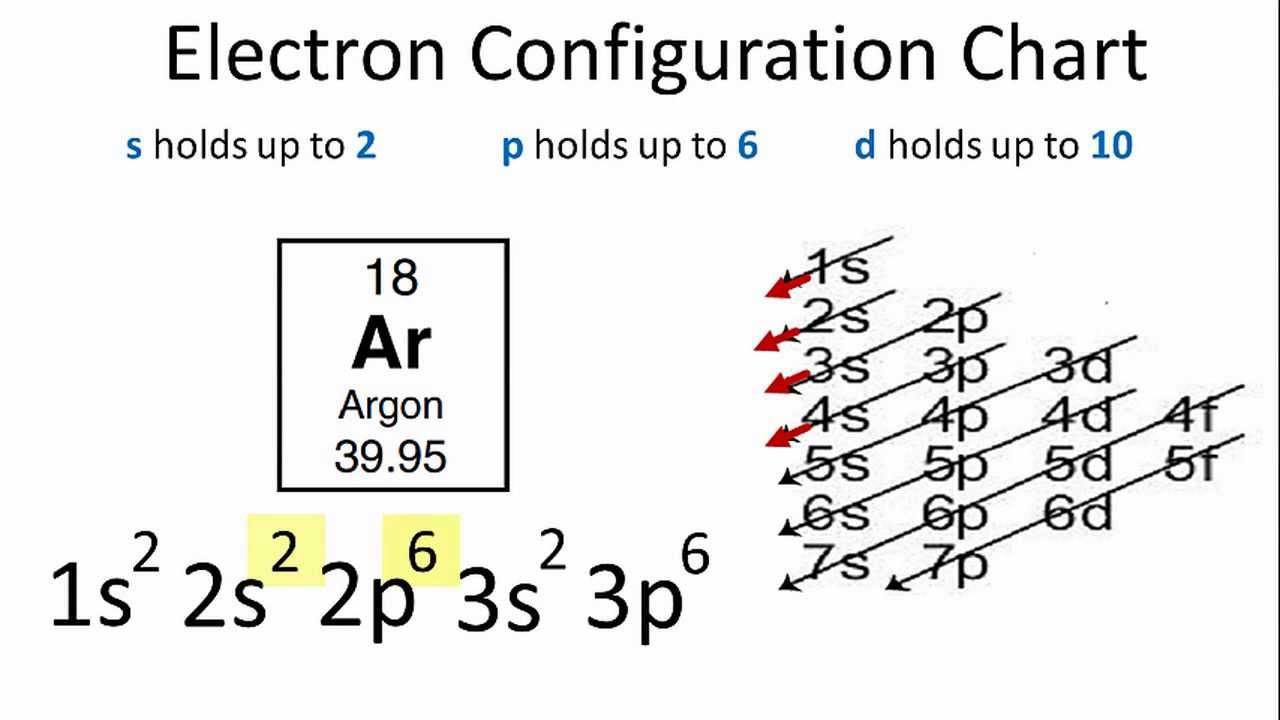
39 orbital diagram for s
Jan 26, 2021 — when we the electron configuration of Sulfur the first two electrons go in the 1s orbital. As 1s only hold two electrons and the next two ... Orbital diagrams are like the configuration notation just introduced, except with the spins of electrons indicated. Use the Pauli exclusion principle and Hund';s rule to work out how to fill shells. The exclusion principle states that no two electrons can share the same four quantum numbers, which basically results in pairs of states ...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11.

Orbital diagram for s
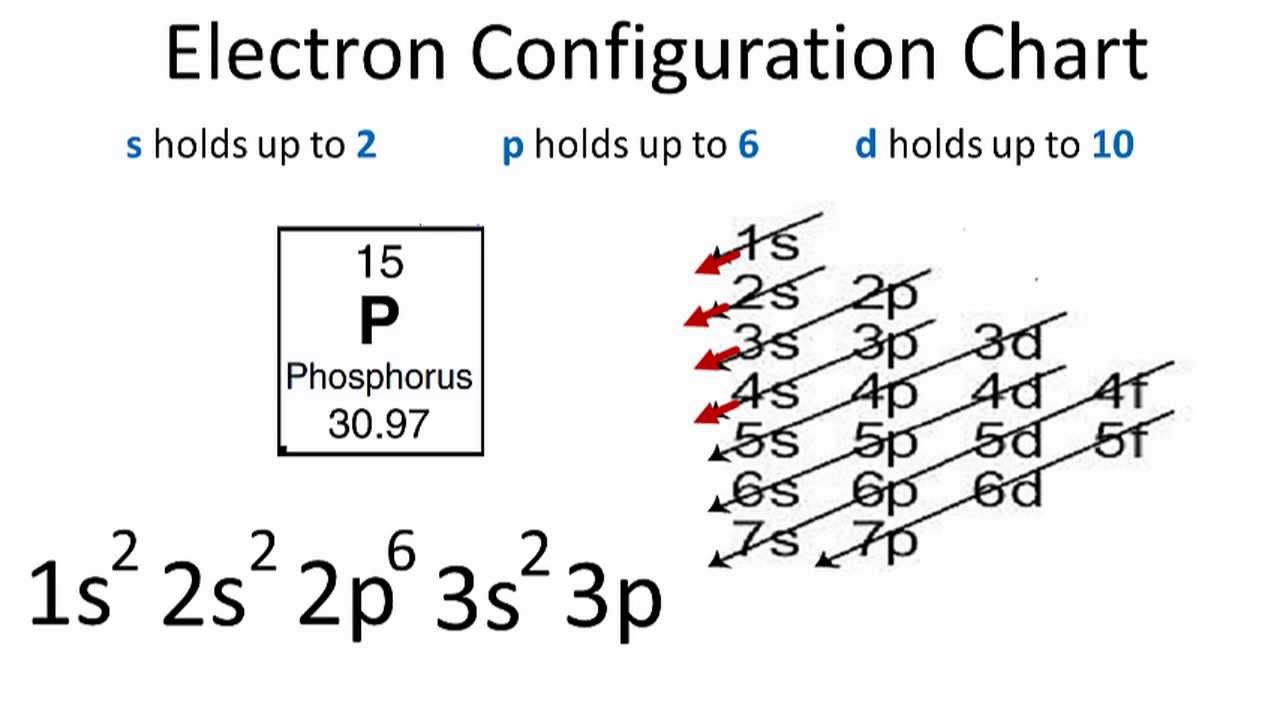
Carbon electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2.Carbon(C) is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of carbon(C) and the orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of carbon, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.. The nucleus is located in the center of the atom. MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
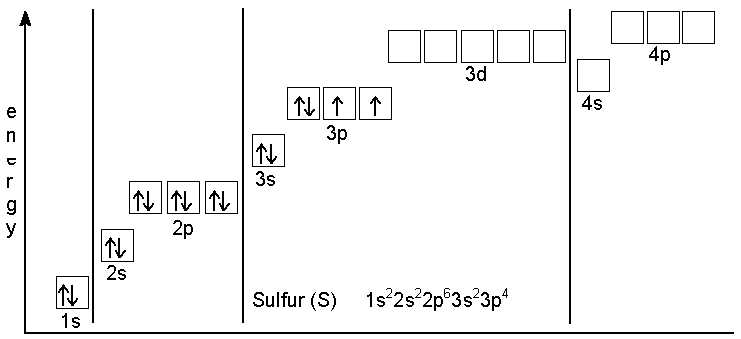
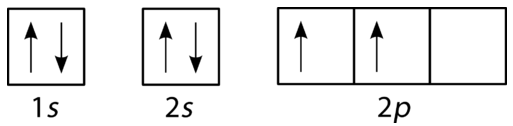
Orbital diagram for s. In writing the electron configuration for Sulfur the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons ...Oct 24, 2016 · Uploaded by Wayne Breslyn required and write a partial orbital diagram. PROBLEM: Use partial orbital diagrams to describe how mixing of the atomic orbitals of the central atom(s) leads to hybrid orbitals in each of the following: (a) Methanol, CH. 3. OH (b) Sulfur tetrafluoride, SF. 4 (a) CH. 3. OH. The electron- group arrangement is tetrahedral around both the C and ... S Orbital Versus P Orbital . While orbital numbers (e.g., n = 1, 2, 3) indicate the energy level of an electron, the letters (s, p, d, f) describe the orbital shape. The s orbital is a sphere around the atomic nucleus. Within the sphere there are shells in which an electron is more likely to be found at any given time. The smallest sphere is 1s. May 30, 2020 — The electron configuration for sulfur is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s2 3p4 and can be represented using the orbital diagram below. orbital diag sulfur.png ...
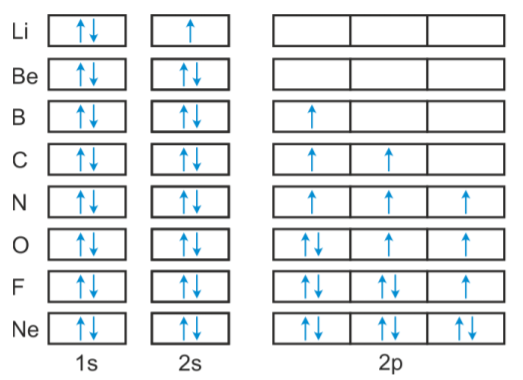
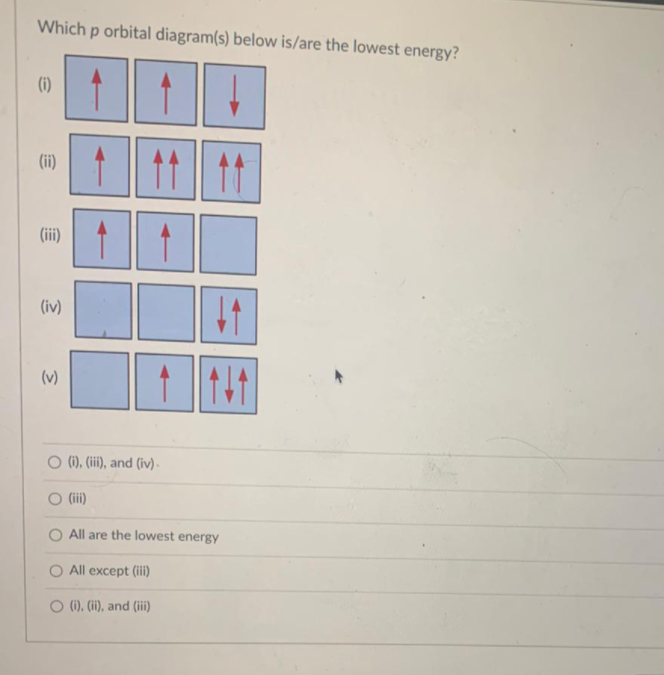
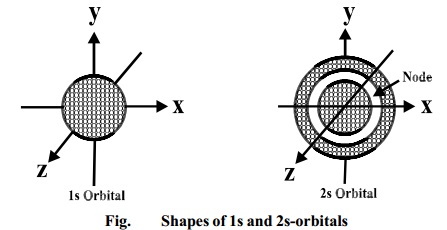
The orbital diagram shows how the electrons are arranged within each sublevel. The maximum number of electrons allowed in an orbital is 2, each with opposite spins (Pauli';s exclusion principle). In a neutral carbon atom, the 1s sublevel has one orbital with two electrons with opposite spins, represented by the arrows pointing in opposite ... The orbital diagram for sulfur has seven boxes with two arrows pointing in opposite directions and two boxes with one arrow pointing up in each. The arrows represent the 16 electrons of the sulfur atom, and the directions represent their spins. The boxes represent sulfur's orbitals. Sulfur's electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 4 ... The Shape of s Orbitals. The boundary surface diagram for the s orbital looks like a sphere having the nucleus as its centre which in two dimensions can be seen as a circle. Hence, we can say that s-orbitals are spherically symmetric having the probability of finding the electron at a given distance equal in all the directions. What element is represented by this orbital diagram? Pauli Exclusion Principle. 2 electrons in the same orbital must have opposite spins. Hund';s Rule. Electrons don't pair up in orbitals of equal energy until they have to, and all electrons in singly occupied orbitals have the same spin.
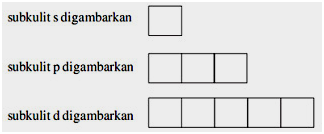
This chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. It explains how to write the orbital diagram n... Orbital diagrams are pictorial descriptions of the electrons in an atom. Three rules are useful in forming orbital diagrams. According to the Auf Bau Principle, each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital. The Pauli Exclusion Principle says that only two electrons can fit into an single orbital. Hund s rule states that electrons go into ... Carbon Electron Dot Diagram. If we talked about the electronic configuration of the element then, carbon is an element whose electronic configuration is given as 1s22s22p2. Now the main thing here is what electronic configuration actually means, so the solution/ answer is that in simple words, by knowing the electronic configuration of any ... Review •Sublevels are made of orbitals. •s-type sublevels are made of 1 orbital. •p-type sublevels are made of 3 orbitals. •d-type sublevels are made of 5 orbitals. •f-type sublevels are made of 7 orbitals. •Every orbital can hold up to 2 electrons.

Difference Between Orbital Diagram And Electron Configuration Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms
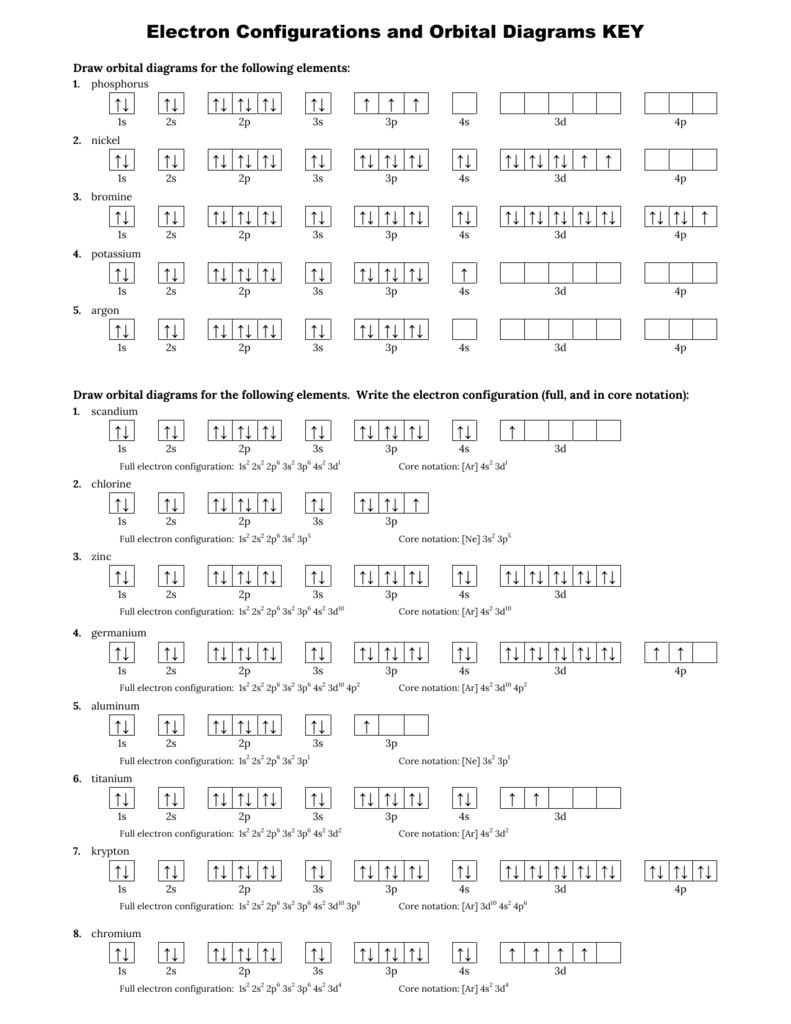
Start studying Electron Configurations and Orbital Diagrams. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom

Which Of The Orbital Diagrams Represent S The Ground State Electron Configuration Of An Oxygen Cation O Homeworklib
An orbital diagram illustrates how the electrons pair off in each orbital. Now that you've mastered the world of electron configurations, it';s time to write orbital filling diagrams. This sounds like something that would be tough, but orbital filling diagrams are really just pictures that show you the same thing as electron configurations.
A 3s orbital is even larger, and it has three nodes. p ORBITALS. Not all electrons inhabit s orbitals. At the first energy level, the only orbital available to electrons is the 1s orbital. However, at the second level, there are also orbitals called 2p orbitals in addition to the 2s orbital.
According to Hund';s rule, as electrons are added to a set of orbitals of equal energy, one electron enters each orbital before any orbital receives a second electron. Orbital Filling Diagrams An orbital filling diagram is the more visual way to represent the arrangement of all the electrons in a particular atom.
The orbital diagrams below show the"ground state" before bonding, the"excited state" where the 2s electron has been promoted to the 2p, and the "hybridized state" where the two single electrons now reside in equivalent orbitals. Note that any left-over "p" orbitals are referred
This video goes over how to properly draw orbital diagrams for an element, after determining the electron configuration. You will also learn how to use hund'...
3 days ago — Writing electron configurations & orbital diagrams for elements on ... has two electrons occupying an s orbital at the first energy level, ...
Write Electronic Configuration Of Following Elements In Form Of Orbital Notation And Orbital Diagram C Chemistry Topperlearning Com N0khl8gg
orbital diagram (orbital box diagram) : Pairs of electrons occupy the 1s, 2s, 2p x, 2p y, 2p z, 3s, 3p x, 3p y, 3p z, 4s orbital and three of the 3d orbitals, with only 1 electron occupying each of the other 3d orbitals and these electrons have parallel spin (arrows pointing in the same direction) in accordance with Hund';s Rule.
Electron Orbital Diagrams s, p, and d block elements. Introduction. Electron orbital diagrams are a way of illustrating what energy level and orbital shape ...3 pages
Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified. Megan Lim. Oct 26, 2016 · 3 min read. Drawing molecular orbital diagrams is one of the trickier concepts in chemistry. The first major step is understanding ...
These are s, p, d and f. The shapes of these orbitals are discussed below: s-orbitals. The s-orbitals are solid spherical shape around the nucleus. When principal quantum number n = 1 and azimuthal quantum number l = 0, that is 1s orbital which is closest to the nucleus. When n = 2 and l = 0 , i.e 2s orbital which contains one node.
Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 11 1 15 2s 2p 3s 3p G1 G1 G1 G1G1 G1 G1 G1 | G1 G2 G2 G2 G2 G2 Submit Part D Show the orbital-filling diagram for Br (bromine).
What is the Orbital Diagram For Nitrogen? When we talk about the orbital diagram, we first need to understand what exactly it means. Therefore, during exams, the student can expect questions related to this topic so it is important that the students must go through it.
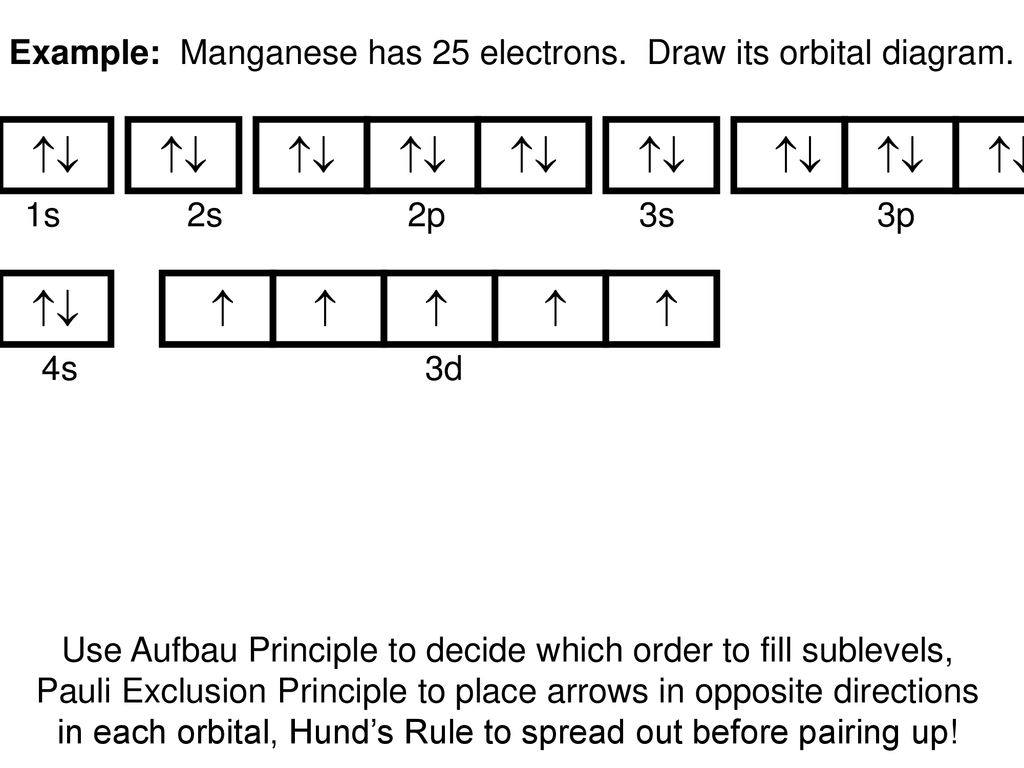
Orbital diagram of Sulfur (S) 17: Orbital diagram of Chlorine (Cl) 18: Orbital diagram of Argon (Ar) 19: Orbital diagram of Potassium (K) 20: Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca) 21: Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc) 22: Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti) 23: Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V) 24: Orbital diagram of Chromium (Cr) 25: Orbital diagram of ...
Diagram of the S and P orbitals The s subshells are shaped like spheres. Both the 1n and 2n principal shells have an s orbital, but the size of the sphere is larger in the 2n orbital. Each sphere is a single orbital. p subshells are made up of three dumbbell-shaped orbitals. Principal shell 2n has a p subshell, but shell 1 does not.
Show the orbital-filling diagram for (bromine).Status: Resolved. Show the orbital-filling diagram for S (sulfur). Stack the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top%(15). 1. Describe the two differences between a 2p x orbital and a 3p y orbital.
... you need 2 electrons to fill an s orbital, 6 electrons to fill a p orbital, 10 electrons to ... Image result for electron configuration periodic table ...
The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the 3s orbital of sulfur interact only weakly; this is shown in the diagram by a slight stabilization of
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
Carbon electron configuration is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 2.Carbon(C) is a p-block element. This article gives an idea about the electron configuration of carbon(C) and the orbital diagram, period and groups, valency and valence electrons of carbon, bond formation, compound formation, application of different principles.. The nucleus is located in the center of the atom.










/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)








0 Response to "39 orbital diagram for s"
Post a Comment