35 octahedral molecular orbital diagram
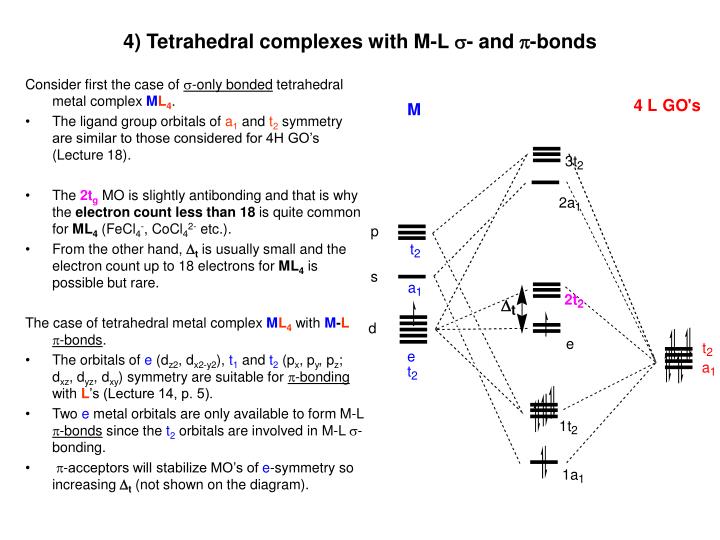
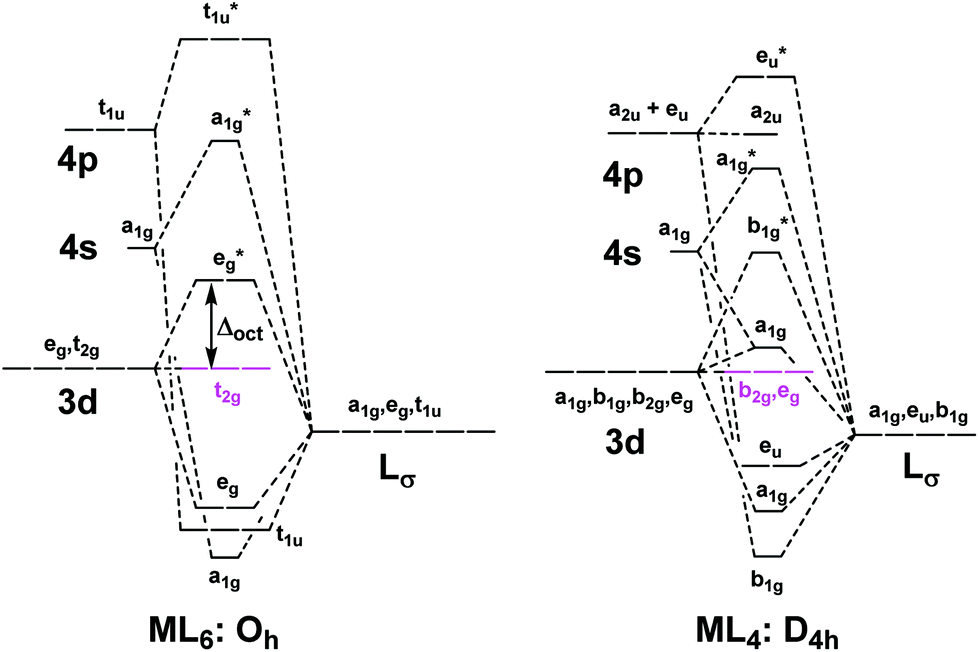
To describe the five bonding orbitals in a trigonal bipyramidal arrangement, we must use five of the valence shell atomic orbitals (the s orbital, the three p orbitals, and one of the d orbitals), which gives five sp 3 d hybrid orbitals. With an octahedral arrangement of six hybrid orbitals, we must use six valence shell atomic orbitals (the s ... The tetrahedral MO diagram is similar to the octahedral molecular orbital diagram. On the left, the metal ion orbitals are present, and on the right side are the ligand orbitals. The center depicts the orbitals of the metal complex. There are four ligands in tetrahedral complexes.
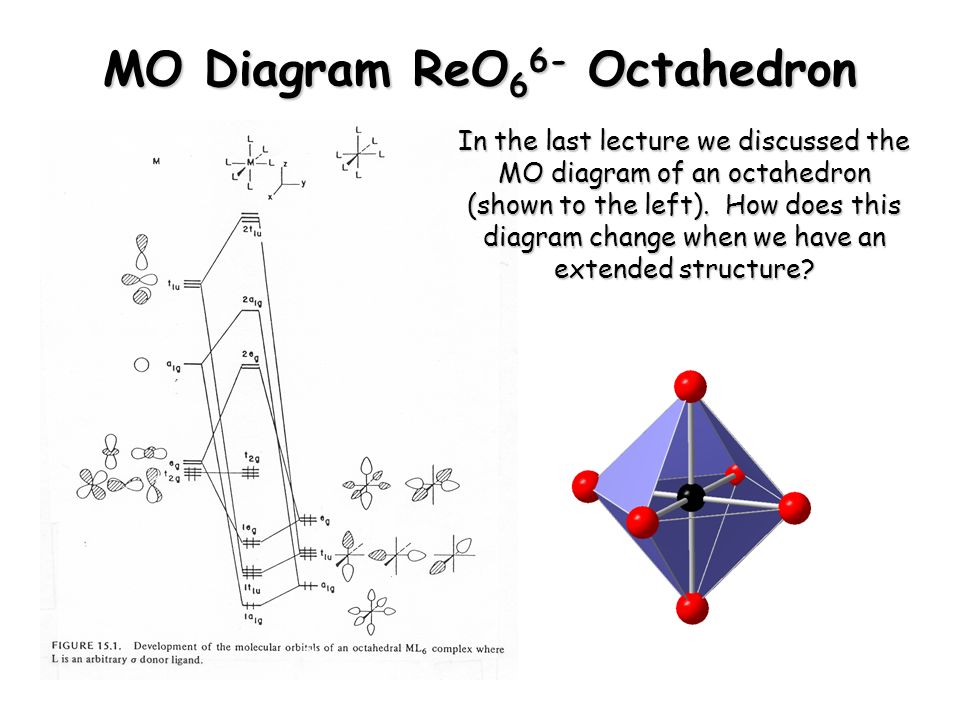
Molecular orbital diagram for a simple octahedral complex. This is qualitatively equivalent to the results of the simpler crystal field theory, which ignores orbital overlap with the ligand orbitals and uses just the electrostatic repulsion of the metal d-orbitals and the negative charges of the ligands.
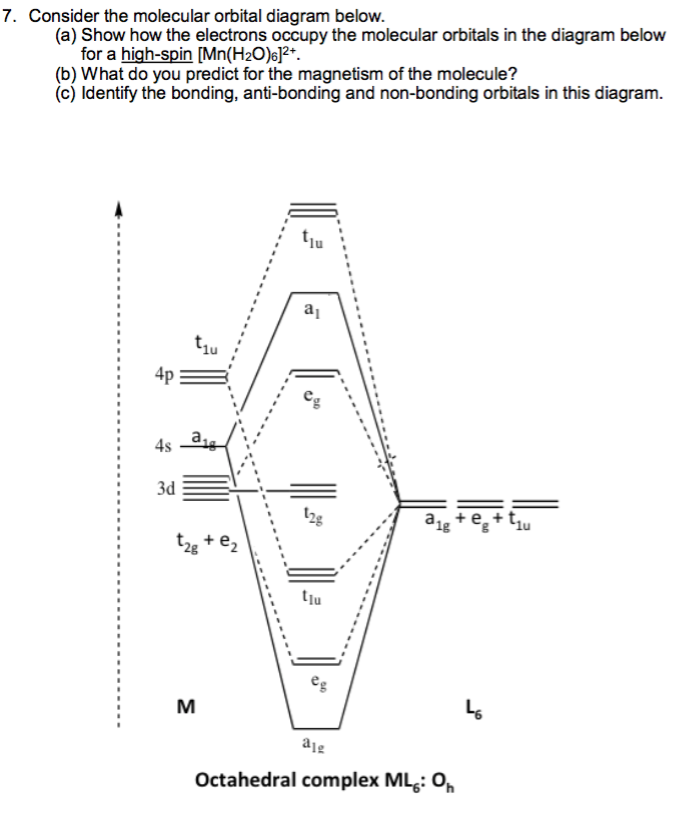
Octahedral molecular orbital diagram
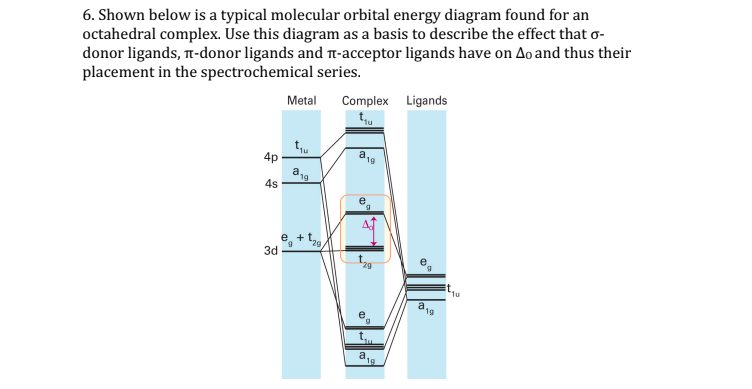
Molecular orbital theory Octahedral complexesDiagrams with examplesExplainedThanks for watching!!!!!#chemistry In octahedral complexes, the molecular orbitals created by the coordination of metal center can be seen as resulting from the donation of two electrons by each of six σ-donor ligands to the d-orbitals on the metal. The metal orbitals taking part in this type of bonding are nd, (n+1)p and (n+1)s. It should be noted down The orbitals responsible for -bonding are not shown. The energy scale is expanded relative to the -complex MO diagram. Determine which diagram is for the -donor and -acceptor cases. Label the MOs with the appropriate symmetry labels and the o. ... Molecular Orbital Theory of Octahedral Complexes ...
Octahedral molecular orbital diagram. High‐Spin and Low‐Spin Configurations • In an octahedral complex, electrons fill the t 2g and e g orbitals in an aufbau manner, but for configurations d4 - d7 there are two possible fillingschemesdependingon the magnitudeof o. • The relative magnitudes of o and the mean pairing energy, P, determine whether a high spin or low spinstate isobserved inoctahedralcomplexes. Please use Internet Explorer web browser for site best experience or Click here · e-PG Pathshala is an initiative of the MHRD under its National Mission on Education through ICT (NME-ICT) being executed by the UGC. The content and its quality being the key component of education d orbitals •l = 2, so there are 2l + 1 = 5 d-orbitals per shell, enough room for 10 electrons. •This is why there are 10 elements in each row of the d-block. σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes 1. Point group Oh 2. The six ligands can interact with the metal in a sigma or pi fashion. Let's consider only sigma interactions for now. September 16, 2020 - Thus, the electrons can fill the lowest energy molecular orbitals available to them. However, the electron pairing may be different if the electrons were allowed to fill the lowest energy atomic orbitals available to them. ... This diagram shows the field splitting of a metal with ligands in an octahedral ...
In this video I have explained SALC (Symmetry adopted linear combination) of transition metal valence orbitals and LGO'S (ligand group orbitals) to construct... This video shows molecular orbital theory ,its basics , and molecular orbital diagrams for diatomic molecules and coordinaion complexes. The three lower-energy orbitals ... labels are based on the theory of molecular symmetry: they are the names of irreducible representations of the octahedral point group, Oh.(see the Oh character table) Typical orbital energy diagrams are given below in the section High-spin ... Prof. Marcetta Y. Darensbourg myd@mail.chem.tamu.edu 408 Chemistry Bldg. (979) 845-5417 Office Hours: Th 11-12; M 11-12. Or any afternoon · Admin. Coord.: Abbey Kunkle darensbourg_asst@chem.tamu.edu 407 Chemistry Bldg. (979) 845-5417
π‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes The reducible representation for the π‐ligand orbitals in O h: E 8C3 6C2 6C4 3C2′ i 6S4 8S6 3σh 6σd Γπ 12000-400000T1g + T2g + T1u + T2u irreducible representations x and y axes on each ligand The non-bonding t2gorbitals of an octahedral metal complex are oriented perfectly to form π-bonds with ligands Molecular orbital diagram corresponding to an octahedral MX N complex. Atomic levels of the transition-metal impurity, M, (ligand anions, X) are depicted on the left-hand (right-hand) side of the ... The original version of this website (2003) was created back when I was at University, as a place to store my Chemistry notes for others - particularly later year groups - to have a little bit of help if they need it. I've recently (2019) brought the website up to date as it was showing serious ... CONNECT WITH TEAM CHEMISTRY UNTOLD :- CHANNEL MEMBERSHIP :- https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCUumszIie8-D0LXi9AbvYCg/joinChemistry untold face book link :- h...
A qualitative molecular orbital diagram for octahedral compounds like W0 3. Electrons Per Shell, 2 8 18 32 12 2. Electron Configuration, [Xe] 4f14 5d4 6s2. 1s 2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s2 5p6 4f14 5d4 6s2. Orbital Diagram. manual for problem e states that the electron configuration for Tungsten is [ Xe] 4f^14 5d^4 6s^2.
1. Molecular orbital theory and the octahedron 2. The MO energy diagram and Δo 1. Octahedral transition metal complexes utilize s, p and d-orbitals in their bonding. For a first row transition metal, these are the 3d, 4s and 4p orbitals (the valence orbitals). Here we will create a molecular
Show below is a molecular orbital diagram for an octahedral ML 6 complex and the O h character table. From the ligand pi orbitals, only the t 2g set is considered. All ligand orbitals are fully filled. Guiding lines connecting atomic orbitals to their corresponding molecular orbitals have been omitted.
For this we need to picture atomic and molecular orbitals. l = 0 2. ATOMIC ORBITALS 2p x 2p y 2p z l = 1 x y z n = 2 This is an accurate representation of a 2p x orbital. This is a common picture of a p x orbital This simplifi ed p x orbital is often useful. A hand drawn version does not have to be exact.
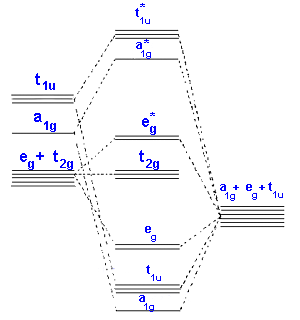
Fig. 2. Simplified molecular orbital diagram for a low spia octahedral complex, such as [Co(NH3 )g, where A = energy difference a, e, and t may be antisymmetric (subscript ungerade) or centrosymmetric (subscript, gerade) symmetry orbitals.
In an octahedral complex, the molecular orbitals created by coordination can be seen as resulting from the donation of two electrons by each of six σ-donor ligands to the d-orbitals on the metal. In octahedral complexes, ligands approach along the x-, y- and z-axes, so their σ-symmetry orbitals ...
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals.
New bifunctional TCNQ-based material · New bifunctional TCNQ based material: [Co(terpy)2](TCNQ)3·CH3CN exhibits a high room temperature conductivity of 0.13 S cm−1 and an anomaly in conductivity at ∼190 K as evidenced by variable temperature structural, magnetic and conductivity studies
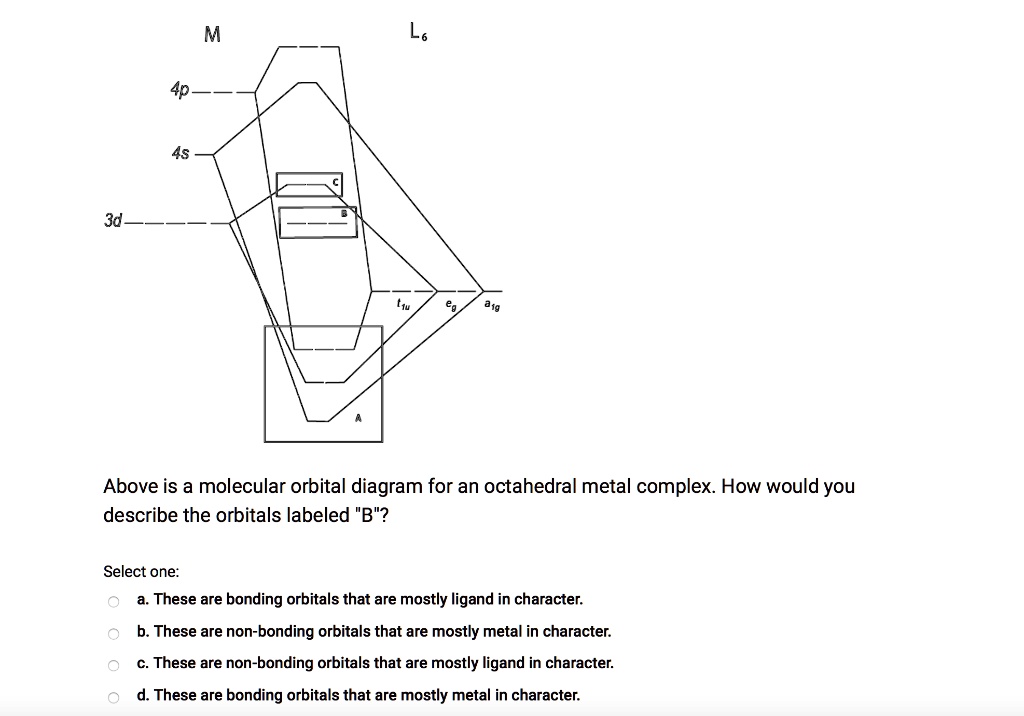
Ligand Field Theory The molecular orbital diagram is consistent with the crystal field approach. Note that the t2g set of orbitals is non-bonding, and the eg set of orbitals is antibonding. 27. Ligand Field Theory The electrons from the ligands (12 electrons from 6 ligands in octahedral complexes) will fill the lower bonding orbitals. { 28.
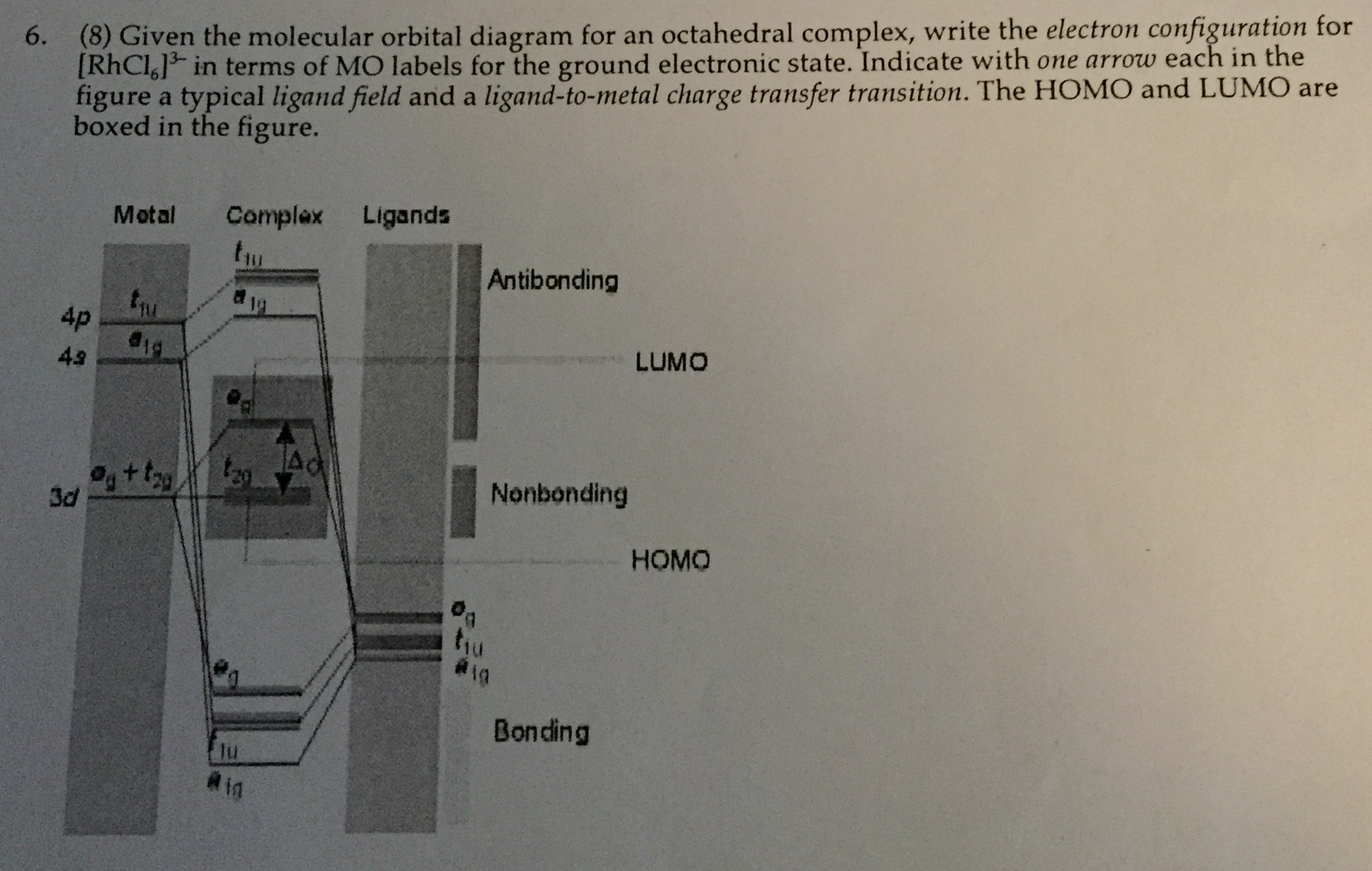
Molecular orbital theory of transition metal complexes. The characteristics of transition metal-ligand bonds become clear by an analysis of the molecular orbitals of a 3d metal coordinated by six identical ligands in octahedral complexes [ML 6].As the result of the interaction between the metal d and ligand orbitals, bonding, non-bonding and anti-bonding complex molecular orbitals are formed.
A molecular orbital diagram which estimates the energies of the bonding (show above) antibonding and non-bonding orbitals is shown below. Since there is a large disparity in energy between the ligand orbitals and the metal orbitals, the lower lying molecular orbitals in the diagram are essentially ligand orbitals.
AboutPressCopyrightContact usCreatorsAdvertiseDevelopersTermsPrivacyPolicy & SafetyHow YouTube worksTest new features · © 2021 Google LLC
Draw the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable. O22+ ... Identify the number of electron groups around a molecule with an : octahedral shape. 6. Give the approximate bond angle for a molecule with an : octahedral shape. 90. The bond angle in NH3 is. 107. Give the major force between acetone and ...
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes a molecular geometry in which 6 ligands are symmetrically arranged around a central atom in an octahedral geometry. All six ligands are chemically equivalent. The central atom is often a transition metal.The octahedron has eight faces (hence the prefix octa) and thus is one of the Platonic solids (although octahedral molecules typically ...
On the other hand, the bonding molecular orbitals of t2g are higher in energy than all σ bonding molecular orbitals. The overall molecular orbital energy level diagram for this type of π-bonding in octahedral complexes can be shown as: Figure 21. The generation of π and σ-molecular orbitals in octahedral complexes.
Self‐consistent charge and configuration (SCCC) molecular orbital calculations are reported for 32 selected octahedral and tetrahedral first‐row transition‐metal complexes containing halide and chalcogenide ligands. It is found that for the range of metal oxidation states II through IV, F σ, chosen to fit the experimental Δ, is a function of only the metal atomic number for constant F π.
Molecular orbitals for Octahedral complexes The combination of the ligand and metal orbitals (4s, 4p x, 4p y, 4p z, 3d z2, and 3d x2-y2) form six bonding and six antibonding with a 1g, e g, t 1u symmetries. The metal T 2g orbitals do not have appropriate symmetry - nonbonding Electron in bonding orbitals provide the potential energy that holds ...
In chemistry, octahedral molecular geometry describes the shape of compounds with six atoms or groups of atoms or ligands symmetrically arranged around a central atom, defining the vertices of an octahedron.The octahedron has eight faces, hence the prefix octa.The octahedron is one of the Platonic solids, although octahedral molecules typically have an atom in their centre and no bonds between ...
February 3, 2021 - 20.4: Molecular Orbital Theory - Octahedral Complexes
Give the approximate bond angle for a molecule with an octahedral shape. A) 109.5° ... Use molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which is most stable a) O22-b)F2 c) F22+ d) F22-e) Ne22-a. Use the molecular orbital diagram shown to determine which of the following is most stable.
Theoretical chemistry research group focusing on development of methods, and calculations in the areas of ionic liquids, photochemistry and catalysis
November 22, 2019 - Self-consistent charge and configuration (SCCC) molecular orbital calculations are reported for 32 selected octahedral and tetrahedral first-row transition-metal complexes containing halide and chalcogenide ligands. It is found that for the range of metal oxidation states II through IV, Fsigma, ...
May 7, 2021 - Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\): (a) Tetraheral ligand field surrounding a central transition metal (blue sphere). (b) Splitting of the degenerate d-orbitals (without a ligand field) due to an octahedral ligand field (left diagram) and the tetrahedral field (right diagram).
This molecule is made up of six equally spaced sp 3 d 2 (or d 2 sp 3) hybrid orbitals arranged at 90° angles. The shape of the orbitals is octahedral. Two orbitals contain lone pairs of electrons on opposite sides of the central atom. The remaining four atoms connected to the central atom give the molecule a square planar shape.
The orbitals responsible for -bonding are not shown. The energy scale is expanded relative to the -complex MO diagram. Determine which diagram is for the -donor and -acceptor cases. Label the MOs with the appropriate symmetry labels and the o. ... Molecular Orbital Theory of Octahedral Complexes ...
In octahedral complexes, the molecular orbitals created by the coordination of metal center can be seen as resulting from the donation of two electrons by each of six σ-donor ligands to the d-orbitals on the metal. The metal orbitals taking part in this type of bonding are nd, (n+1)p and (n+1)s. It should be noted down
Molecular orbital theory Octahedral complexesDiagrams with examplesExplainedThanks for watching!!!!!#chemistry



















0 Response to "35 octahedral molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment