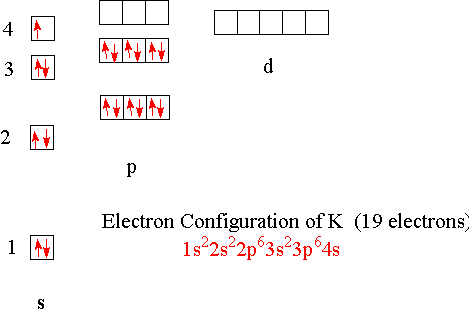
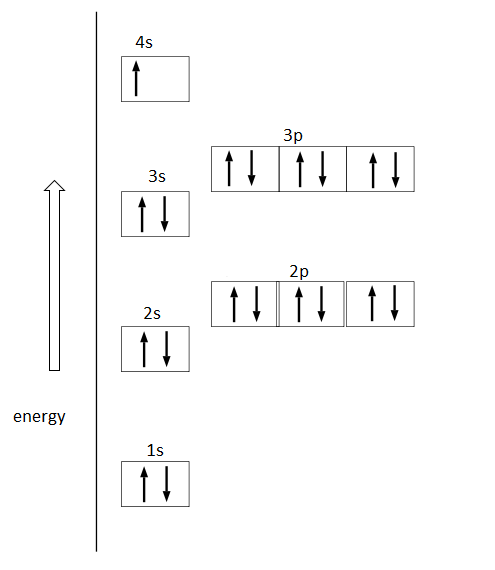
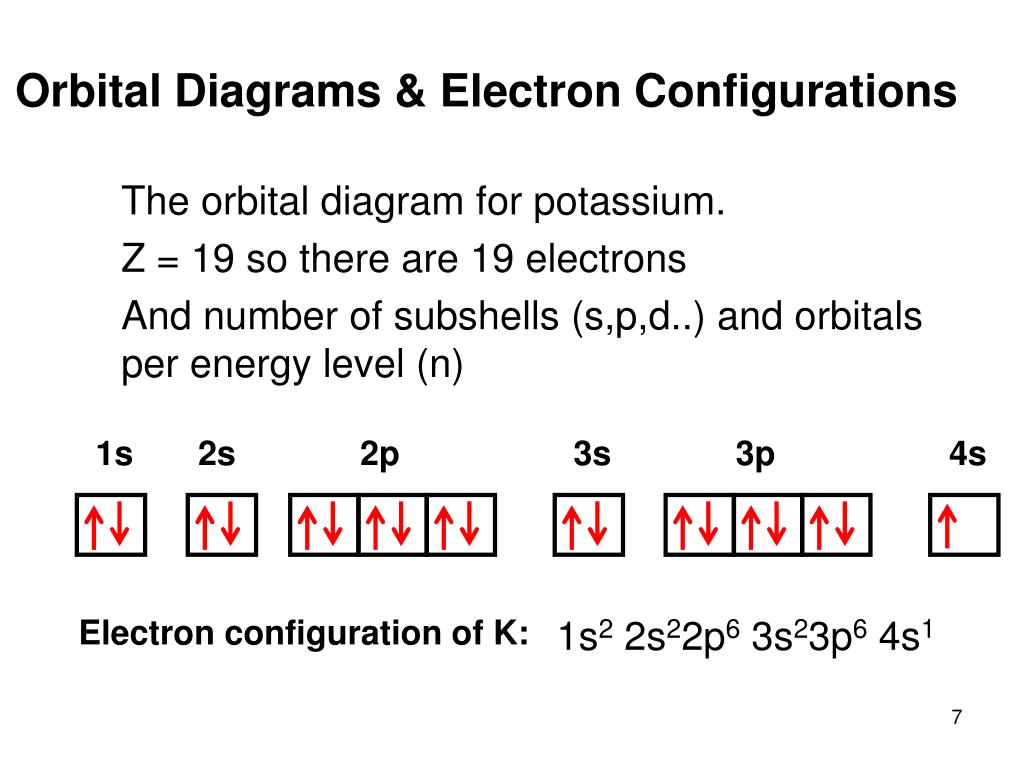
38 orbital diagram for k
To write the orbital diagram for the Potassium atom (K) first we need to write the electron configuration for just K. To do that we need to find the number o...
Orbital diagram of Potassium (K) 20: Orbital diagram of Calcium (Ca) 21: Orbital diagram of Scandium (Sc) 22: Orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti) 23: Orbital diagram of Vanadium (V) 24: Orbital diagram of Chromium (Cr) 25: Orbital diagram of Manganese (Mn) 26: Orbital diagram of Iron (Fe) 27: Orbital diagram of Cobalt (Co) 28: Orbital diagram of ...
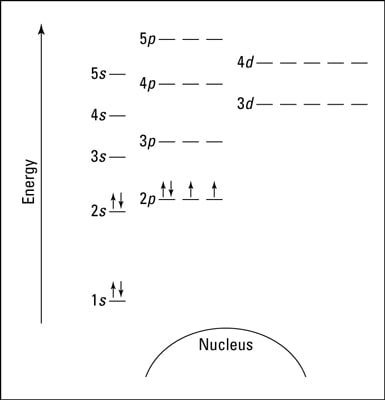
The energy of an electron in an orbital with quantum number nfor an atom with atomic number Zis given by: E n = ... There is a simple way of remembering how electrons fill up orbitals, shown in the accompanying diagrams: 6d 1s 2s 3s 4s 5s 6s 2p 3p 4p 5p 6p 3d 4d 5d 4f 5f 2. Materials 100A: Orbitals, bonding, etc. 19 20 K Ca 1 2 H He 3 4 Li Be ...
Orbital diagram for k
In atomic theory and quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus.The term atomic orbital may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be ...
The orbital filling diagram for helium. The electron configuration for helium is 1s². This means that we have two electrons in the 1s orbital, which looks like this: This diagram is exactly the same as the one for hydrogen, except that there's a second arrow added to the 1s orbital. This represents the second electron in the 1s orbital, and ...
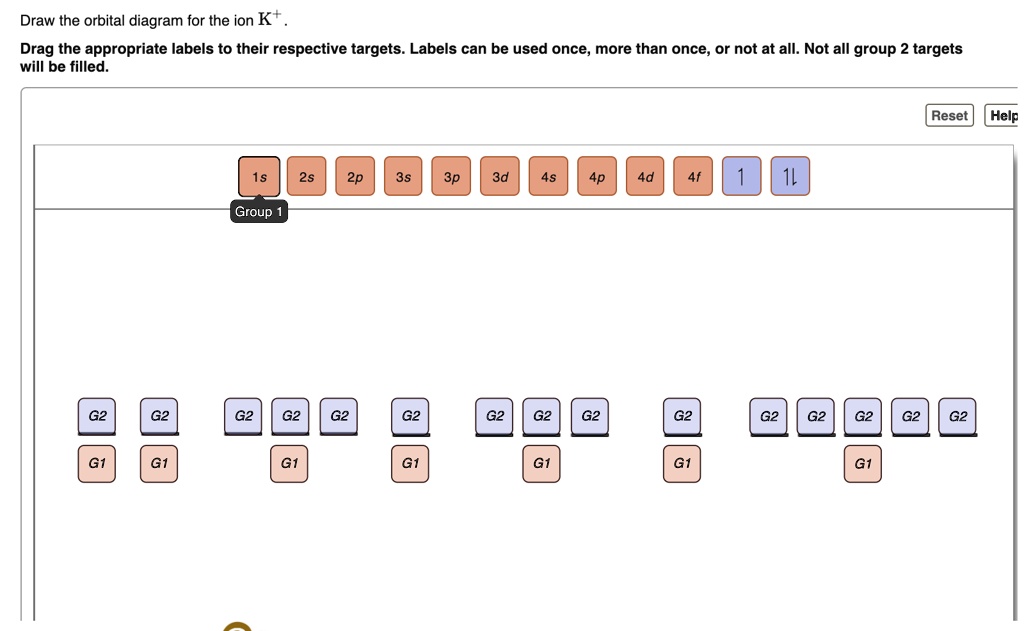
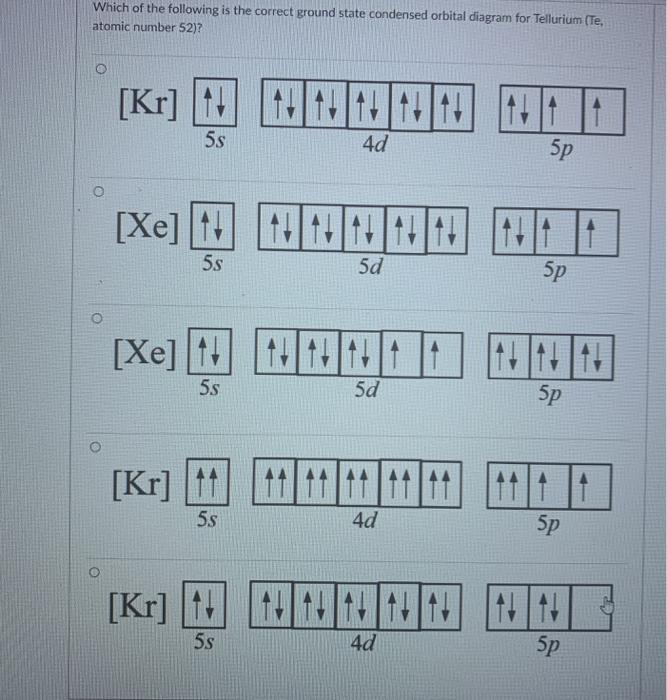
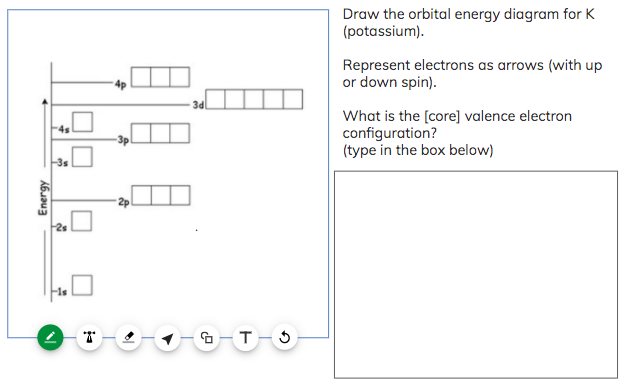
Draw the orbital energy diagram for K (potassium). Represent electrons as arrows (with up or down spin). What is the core] valence electron configuration? (type in the box below) -45 Energy 2p 2s is *** -T-5 ; Question: Draw the orbital energy diagram for K (potassium). Represent electrons as arrows (with up or down spin).
Orbital diagram for k.
Orbital Diagram For Chromium Xanes Data For The Crvi Reference Compounds K 2 Cr 2 O 7 Na 2. Orbital Diagram For Chromium 35 Atomic Structure And The Periodic Table Creating. Orbital Diagram For Chromium Media Portfolio. Orbital Diagram For Chromium Chromium Orbital Diagram Circular Flow Diagram.
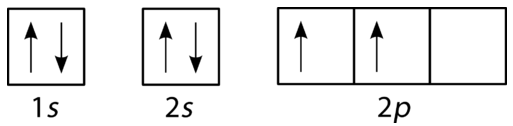
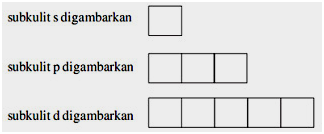
An orbital diagram, or orbital box diagram, is a way of representing the electron configuration of an atom. A box, line, or circle, is drawn to represent each orbital in the electron configuration. (using the Aufau Principle to order the orbitals and hence the boxes, lines or circles, as shown below) 1s. →. 2s.
Orbital Filling Diagrams •Each box represents an orbital which can hold a max of 2 e- •Aufbau principal -each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available; German for "build up" •Electrons are notated with an arrow -Up arrow goes first then, down arrow -Arrows represent the opposing spin of electrons 5.2 Quantum Theory & The Atom
Krypton Orbital Diagram. Diagram of the nuclear composition, electron configuration, chemical data, and valence orbitals of an atom of krypton (atomic number: 36), the most common . Box spin diagram of outer electron orbitals for the electron configuration of the atom . 36 Krypton, Kr, [Ar]3ds24p6 = [Kr] (), [Ar]3d 4s 4p v. stable, Kr .
Phosphorus (P) atom electron configuration (Bohr model) K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, N is the name of the fourth orbit. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n 2. For example, n = 1 for K orbit. The electron holding capacity of K orbit is 2n 2 = 2 × 1 2 = 2 electrons.
Electron orbital diagrams and written configurations tell you which orbitals are filled and which are partially filled for any atom. The number of valence electrons impacts on their chemical properties, and the specific ordering and properties of the orbitals are important in physics, so many students have to get to grips with the basics.
Orbital Diagram. 1s ... Formerly called kalium (K). Vital to function of nerve and muscle tissures. Sources Found in minerals like carnallite [(KMgCl3).6H2O] & sylvite (potassium chloride, KCL). Pure metal is produced by the reaction of hot potassium chloride and sodium vapors in a special retort.
(10 pts) Element, K 19) Your answer Full electron configuration Condensed electron configuration Partial orbital diagram 7. What are the Lewis electron-dot symbol for the following elements? (10 pts) Lewis electron-dot symbol Element Lewis electron-dot symbol Element Mg Na.
Chapter 11: Modern Atomic Theory. Orbital Diagrams. Back to Chapter 11. Orbital Diagrams. Orbital (box) Diagram: Orbitals are represented by boxes grouped by sub levels (subdivision of the principal energy level) with small rows indicating the the electrons.
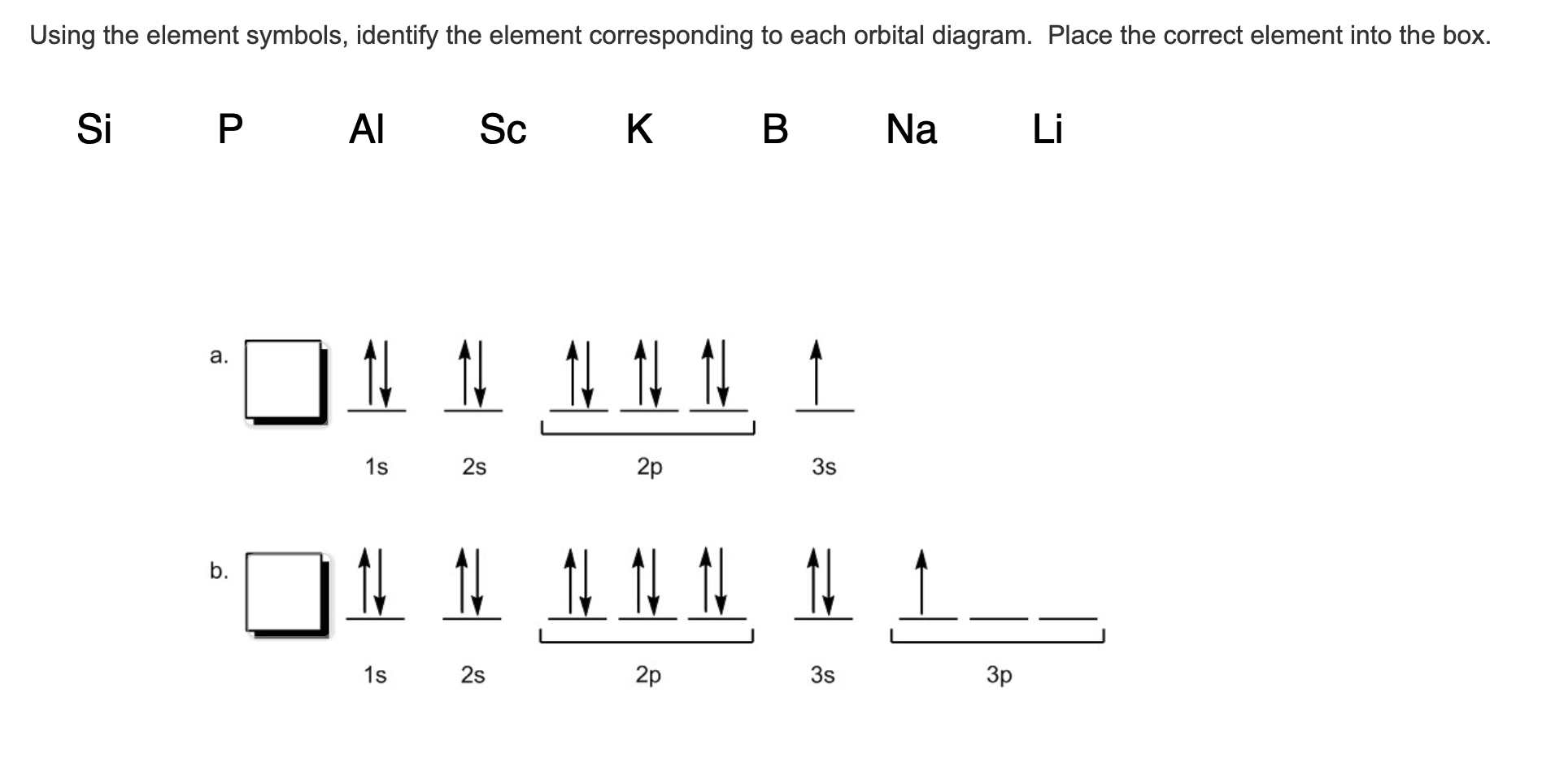
To write the orbital diagram of silicon(Si), you have to do the electron configuration of silicon. Which has been discussed in detail above. 1s is the closest and lowest energy orbital to the nucleus. Therefore, the electron will first enter the 1s orbital. According to Hund's principle, the first electron will enter in the clockwise ...
Orbital notation shows the number of electronics in an orbit. The orbital notation of Hydrogen is a circle with one slash through it. The electron configuration of Hydrogen is 1(s^1).
A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular.
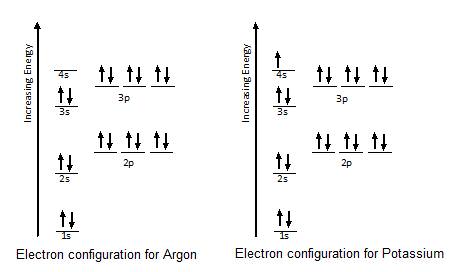
In writing the electron configuration for Potassium the first two electrons will go in the 1s orbital. Since 1s can only hold two electrons the next 2 electrons for Potassium go in the 2s orbital. The next six electrons will go in the 2p orbital. The p orbital can hold up to six electrons. We'll put six in the 2p orbital and then put the next ...
As shown in Figure2, at k= 0 the orbitals are all in phase with each other leading to no nodes between them and an infinite crystal orbital wavelength. As kmoves from 0, nodes are introduced into the chain when some orbitals switch phases until k= ˇ=aat which every orbital is out of phase with its neighbors.
Angular momentum l (orbital shape) Magnetic m l (orbital orientation) These 3 quantum numbers are the spatial quantum numbers. ⇒ together, they describe the 3D appearance of the orbital in space ⇒ the spatial probability distribution of an e-described by that orbital The 4th quantum number is necessary to fully describe an e-in an orbital.
orbital diagram for potassium qaswers the bohr diagram is the diagram of the electrons on the orbital layers of the nucleus of an atom for potassium you would put 2 electrons on the first layer 8 on the second … layer and 9 on the third layer this is because the atomic number of potassium k is 19 therefore has 19 protons and 19 electrons
Orbital Diagram For Arsenic. Because the 4p section has 3 orbitals, but Arsenic ends with 4p3. It'll want to leave as few orbitals empty, so you have three arrows pointing up. The orbital diagram of arsenic can be written as 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s23p6 4s2 3d10 4p3. Arsenic has 33 electrons, including 3 in itsoutermost shell. schematron.org!
In this video we will write the electron configuration for N 3-, the Nitride ion. We'll also look at why Nitrite forms a 3- ion and how the electron configur...
Answer (1 of 3): Orbital Diagrams Many times it is necessary to see all the quantum numbers in an electron configuration, this the purpose of the orbital diagram. In addition to listing the principle quantum number, n, and the subshell, ℓℓ, the orbital diagram shows all the different orientation...
Molecular Orbital Diagrams, Bond Order, and Number of Unpaired Electrons Draw the molecular orbital diagram for the oxygen molecule, O 2. From this diagram, calculate the bond order for O 2. How does this diagram account for the paramagnetism of O 2? Solution. We draw a molecular orbital energy diagram similar to that shown in Figure 11.
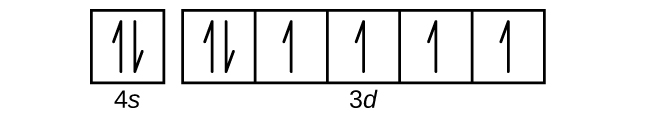
So the electron configuration of potassium will involve 19 electrons. The full electron configuration of potassium is "1s"^2"2s"^2"2p"^6"3s"^2"3p"^6"4s"^1". The noble gas notation is "[Ar]4s"^1". The following orbital diagram shows the increase in energy from one energy sublevel to the next, but you can write them on the same level horizontally,
The third electron goes into the next orbital in the energy diagram, the 2s orbital. Li (Z = 3): 1s 2 2s 1. The fourth electron fills this orbital. Be (Z = 4): 1s 2 2s 2. After the 1s and 2s orbitals have been filled, the next lowest energy orbitals are the three 2p orbitals. The fifth electron therefore goes into one of these orbitals.
Orbital Filling Diagram Electron Configuration Electron Dot Diagram a. Boron b. Silicon c. Sulfur d. Calcium e. Iodine f. Rubidium g. Chromium h. Gallium Where are the Electrons? Write the full electron configuration, short-hand electron configuration, and fill in the orbital diagrams, for the following elements. 1.





/800px-Orbital_representation_diagram.svg-589bd6285f9b58819cfd8460.png)












0 Response to "38 orbital diagram for k"
Post a Comment