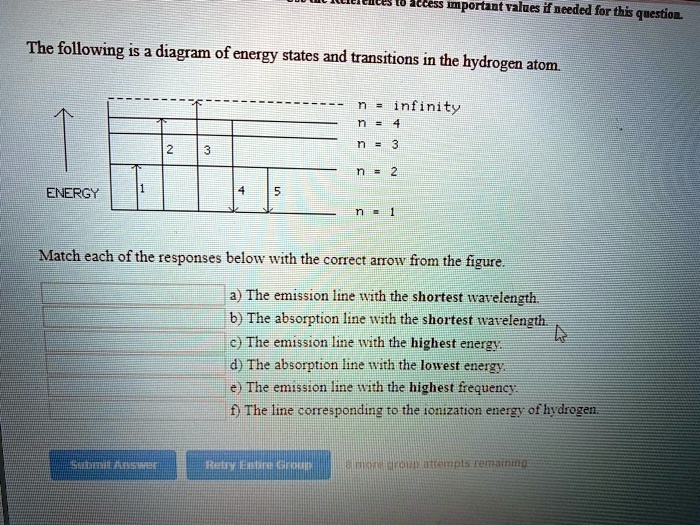
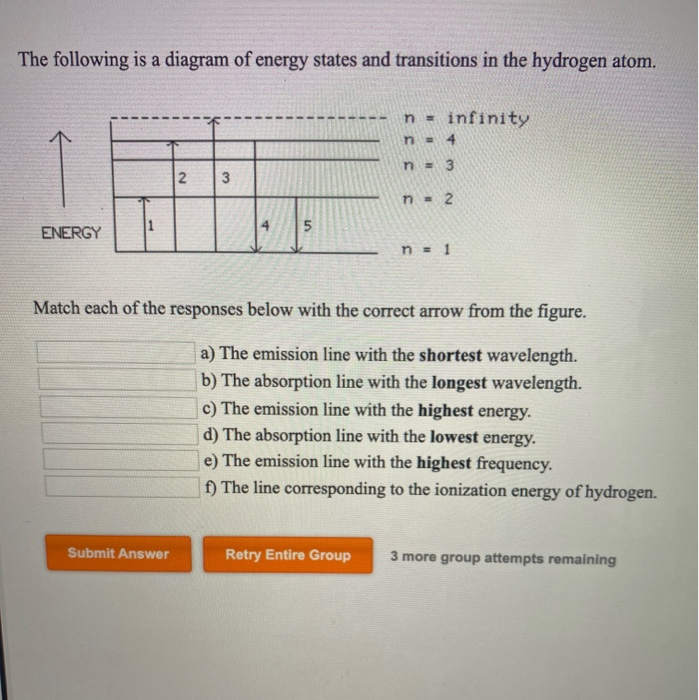
39 the following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom.
In this section we will discuss the energy level of the electron of a hydrogen atom, and how it changes as the electron undergoes transition. According to Bohr's theory, electrons of an atom revolve around the nucleus on certain orbits, or electron shells. Each orbit has its specific energy level, which is expressed as a negative value. This is because the electrons on the orbit are "captured ...
B. The following diagram represents energy levels in a hydrogen atom. The labeled transitions (A through E) represent an electron moving between energy levels. If an electron at level 1 in a hydrogen atom absorbs 10.2 eV of energy, it moves to level 2.
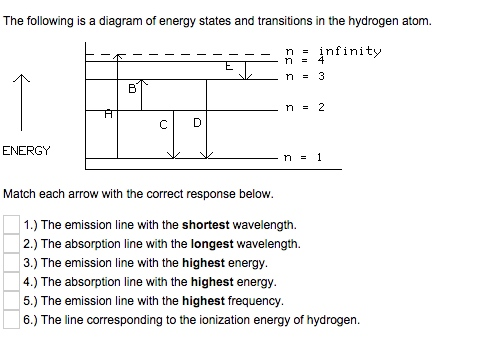
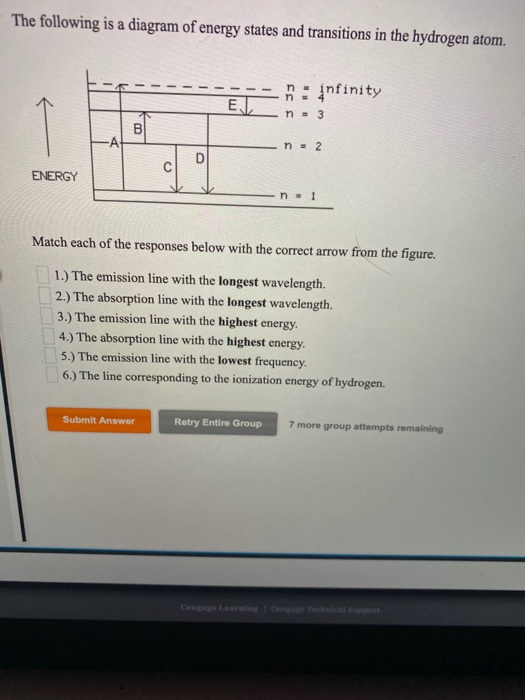
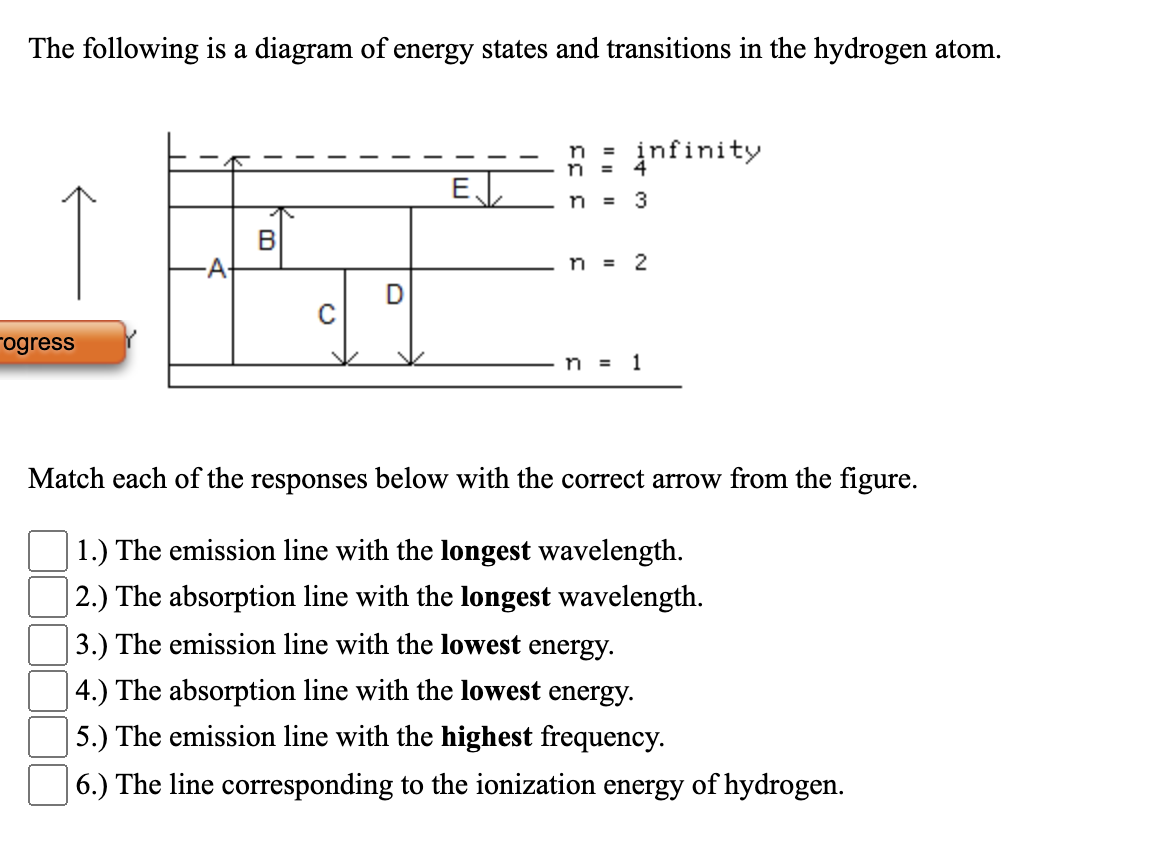
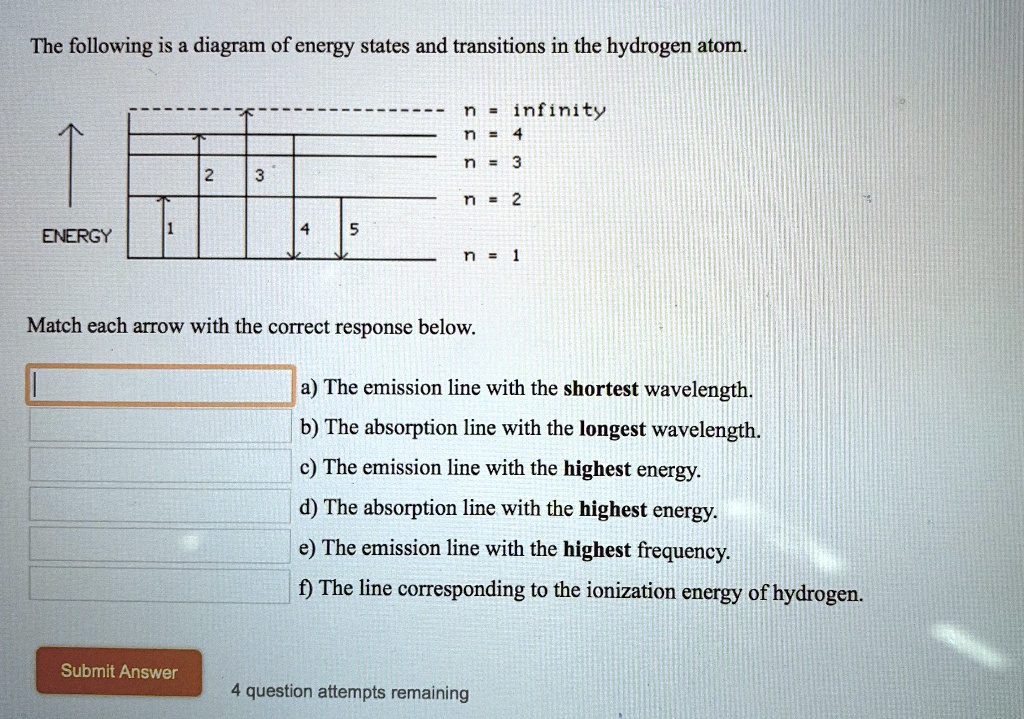
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each arrow with the correct response below. a) The emission line with the longest wavelength. b) The absorption line with the shortest wavelength. c) The emission line with the lowest energy. d) The absorption line with the highest energy. e) The emission line with the highest frequency.
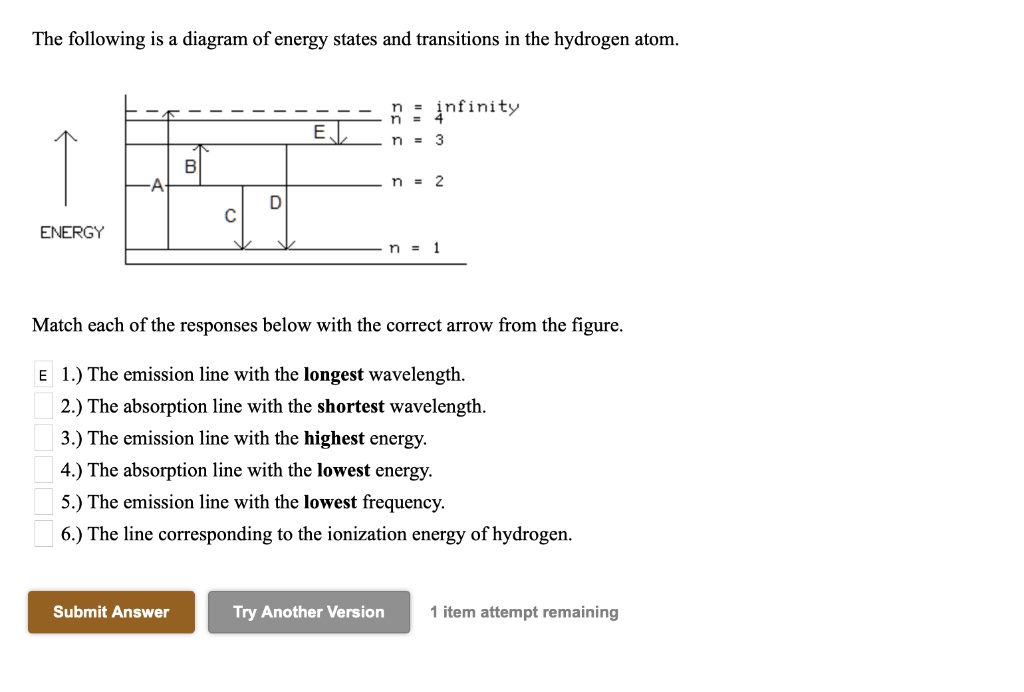
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom.
The diagram shows some atomic energy levels of hydrogen. A photon of energy 2.86 eV is emitted from a hydrogen atom. Using the diagram, draw an arrow to indicate the electron transitions that results in the emission of this photon.
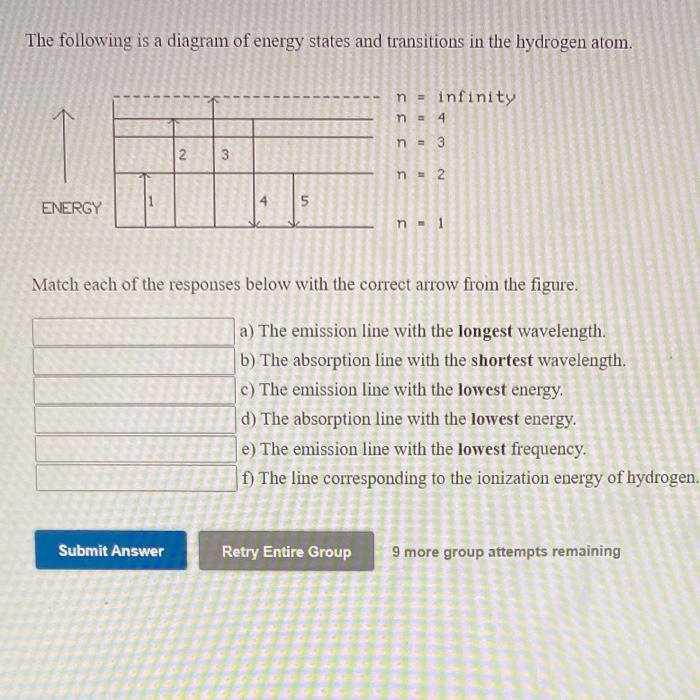
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each of the responses below with the correct arrow from the figure. a) The emission line with the longest wavelength. b) The absorption line with the shortest wavelength. c) The emission line with the lowest energy. d) The absorption line with the highest ...
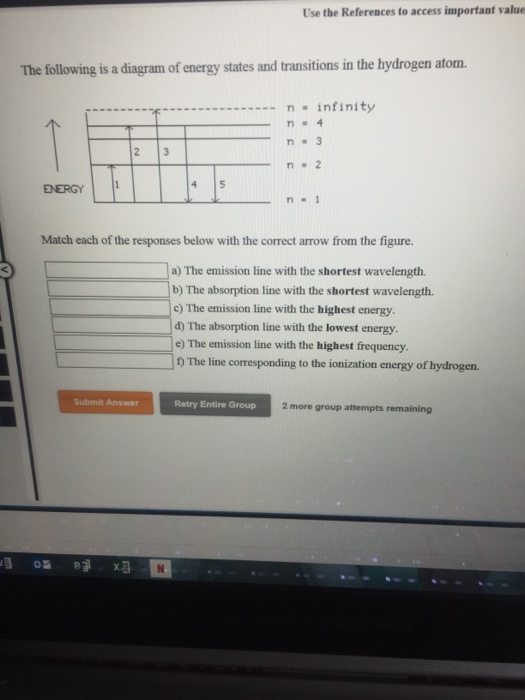
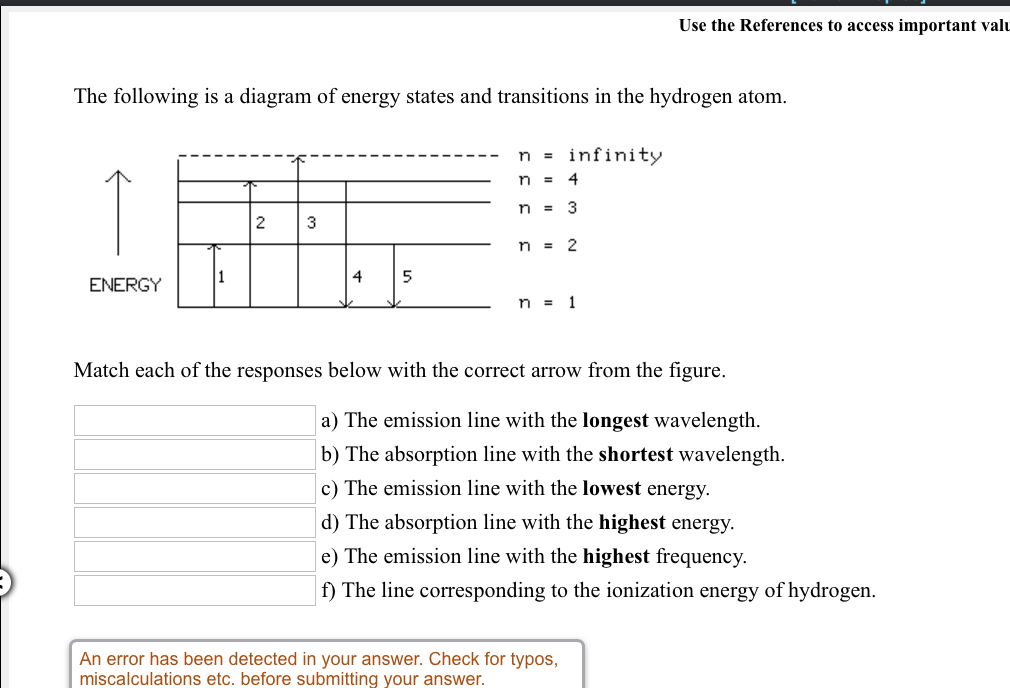
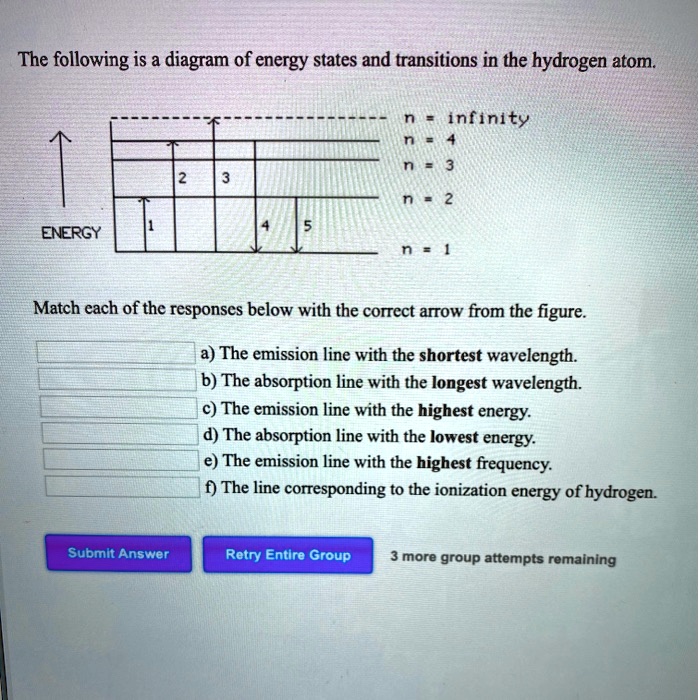
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. n = infinity 4 n = 3 3 n = 2 ENERGY 4 n = 1 Match each arrow with the correct response below. a) The emission line with the shortest wavelength. b) The absorption line with the shortest wavelength. c) The emission line with the lowest energy.
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom..
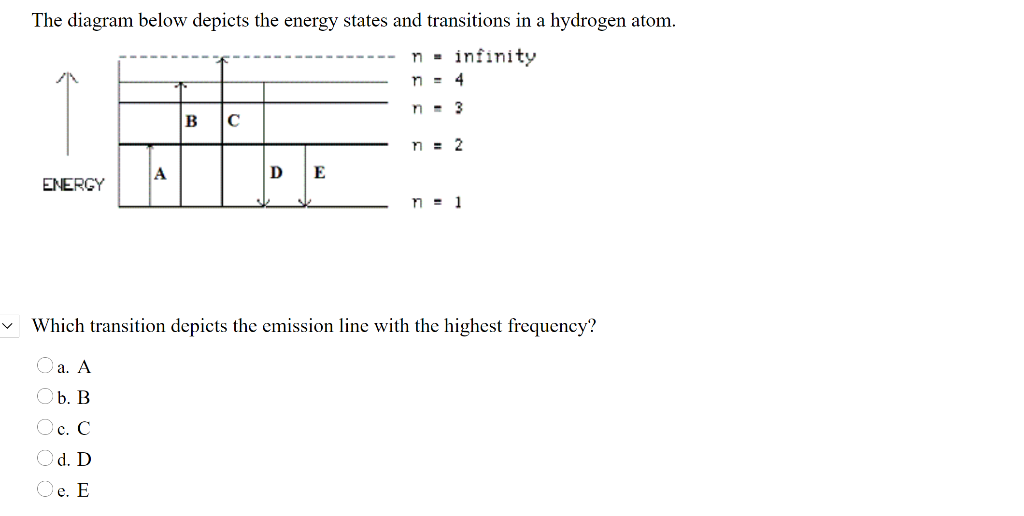
19. Identi9 the drawing in Model 3 that depicts a hydrogen atom with an electron moving from energy level 5 to energy level 2. Refer to Models I and 2 for the following questions. a. Label the picture with "n=5 to n=2" and list the corresponding color of light emitted. b. This electron transition (absorbs e eases) ergy. c. This electron moves ...
An energy-level diagram of a possible transition is given in . The absorption spectrum for such transitions in hydrogen chloride (HCl) is shown in . The absorption peaks are due to transitions from the to vibrational states. Energy differences for the band of peaks at the left and right are, respectively, and
the energy of the light absorbed when an electron in . a hydrogen. atom. makes the . following transitions: (a) n = 1 to n = 4; (b) n = 3 to n = 8; (c) n = 2 to n = 4. Give. your . answers . to. 3 significant . figures. (d) Draw an energy level diagram for hydrogen, and . draw vertical arrows to indicate each of these three electron transitions ...
enerw level 5 to energy level 2. Refer to Models 1 and 2 for the following questions. a. Label the picture with "n=5 to n=2" and list the corresponding color of light emitted. b. This electron transition (absorbs release energy. c. This electron moves from a (low [higher energy state to a lowe igher) energy state. d.
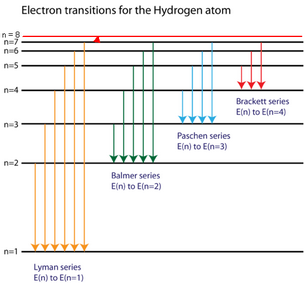
What are the degeneracies of the Hydrogen atom energy levels? Recall they are dependent on the principle quantum number only. III. Spectroscopy of the Hydrogen Atom Transitions between the energy states (levels) of individual atoms give rise to characteristic atomic spectra. These spectra can be used as analytical tools to assess composition of ...
Energy is absorbed. III. Electrons lose energy. IV. Electrons gain energy. I and III. The wave characteristics of a large, moving object, such as an automobile, are difficult to observe because the. wavelength is very small. What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron (m = 9.11 × 10-31 kg) moving at a velocity of 3.0 × 107 m/s (10% of ...
Energy level diagram . The energy of the electron in the n th orbit of the hydrogen atom is given by, En = -13.6 /n 2 eV. Energy associated with the first orbit of the hydrogen atom is, E 1 = -13.6 /1 2 = -13.6 eV. It is called ground state energy of the hydrogen atom. Energy associated with the second orbit is given by, E 2 = -13.6 /2 2 = -3.4 eV
Suppose the following energy level diagram represents electronic energy states in some atom where Eo is the lowest possible energy level. Several transitions between energy lev- els are shown. Assume the transitions occur by the absorption or emission of photons.
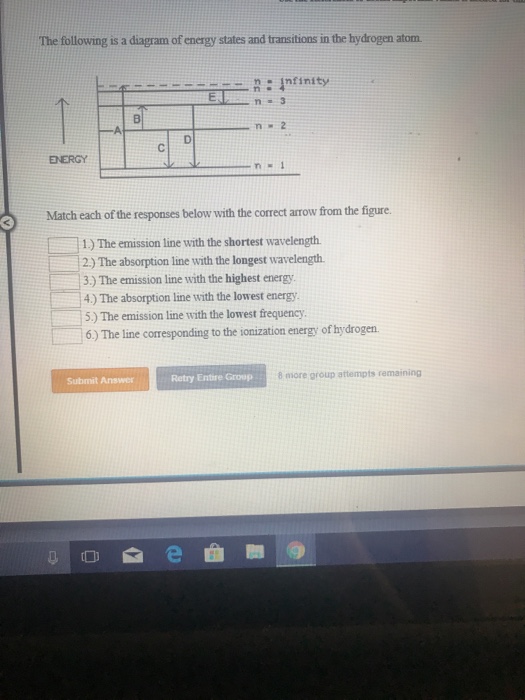
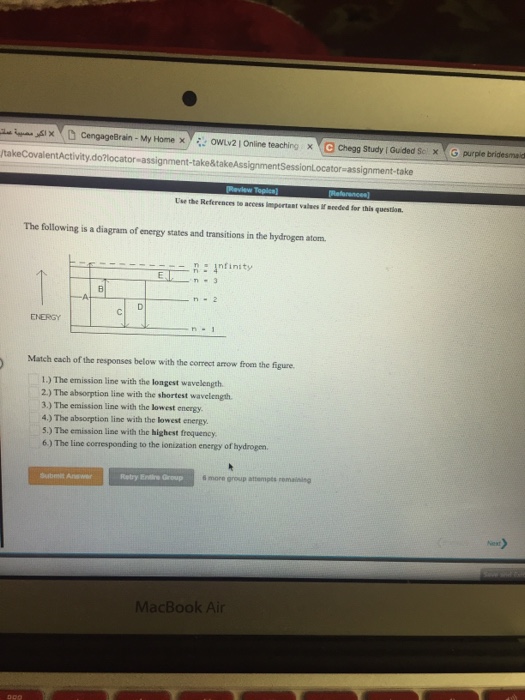
Question: The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each arrow with the correct response below. The emission line with the longest wavelength. The absorption line with the longest wavelength. The emission line with the highest energy.
Electron Transitions The Bohr model for an electron transition in hydrogen between quantized energy levels with different quantum numbers n yields a photon by emission with quantum energy: This is often expressed in terms of the inverse wavelength or "wave number" as follows: The reason for the variation of R is that for hydrogen the mass of the orbiting electron is not negligible compared to ...
The energy required to make the transition is 12.09 eV (or 1.9 × 10 −18 J ). The energy of incident electron is only 10.63 eV (or 1.7 × 10 −18 J) so it is of too low an energy for the transfer of energy required. (2 marks) (b) When electrons in the ground state of hydrogen atoms are excited to the n = 3 energy level, photons of more than ...
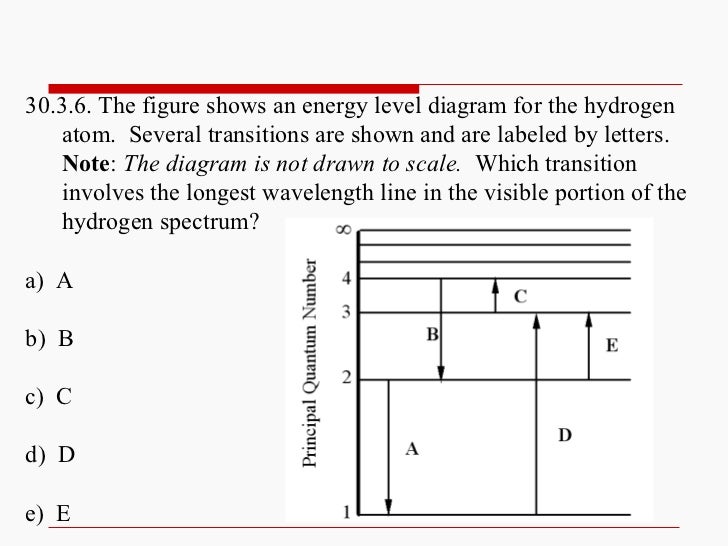
The figure shows an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. Several transitions are shown and are labeled by letters.Note: The diagram is not drawn to scale. Which transition corresponds to the absorption of the photon with the longest wavelength?
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each of the responses below with the correct arrow from the figure. a) The emission line with the shortest ...
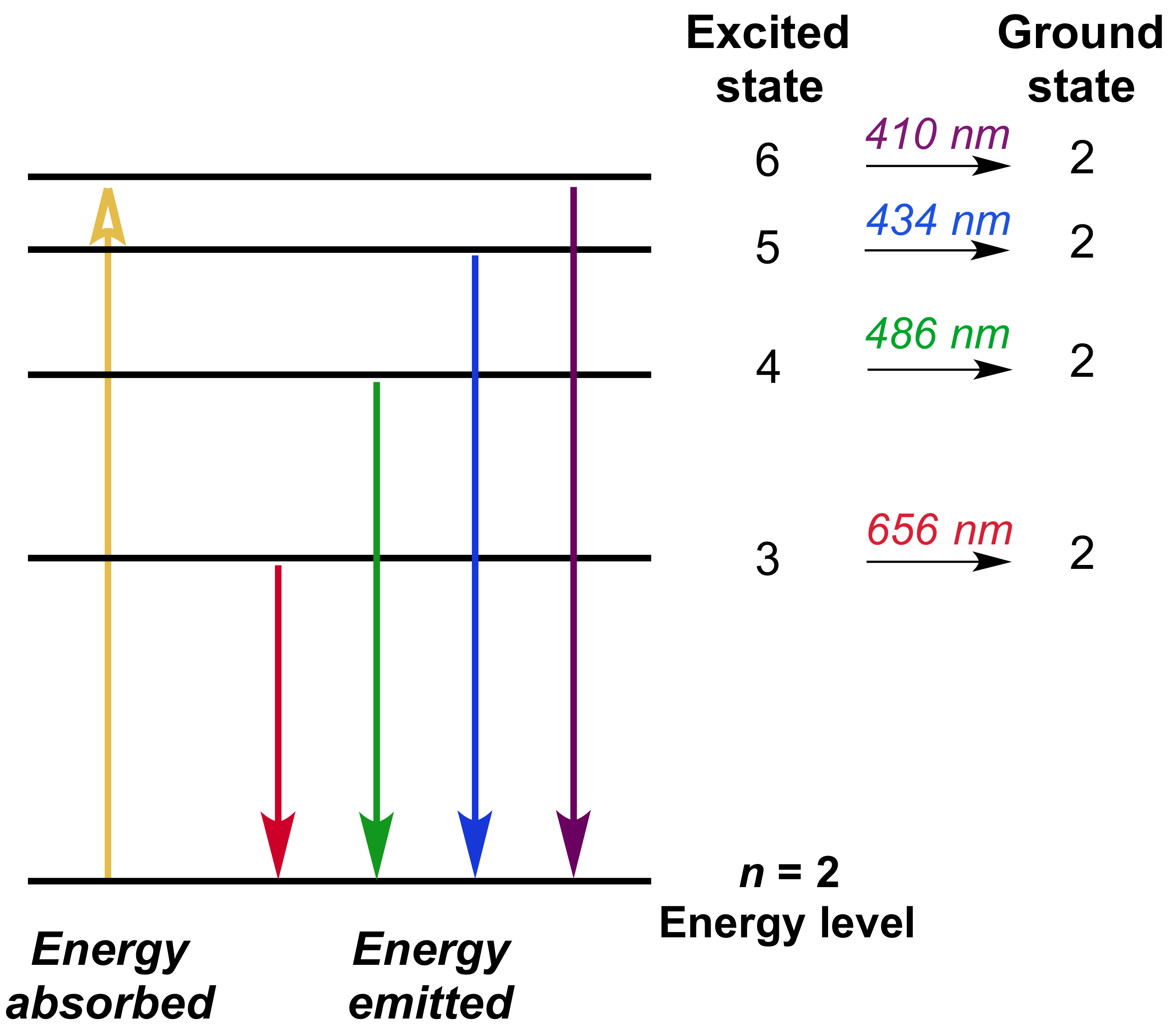
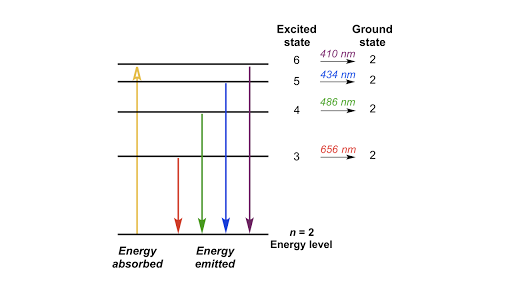
The n = 2 to n = 6 transition in the Bohr hydrogen atom corresponds to the _____ of a photon with a wavelength of _____ nm. absorption, 410 Indicate whether energy is emitted or absorbed when the following electronic transitions occur in hydrogen.
The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from a particular state to a lower state, it is losing energy. To conserve energy, a photon with an energy equal to the energy difference between the states will ...
Which of the transitions in the hydrogen atom energy-level diagram shown here is notpossible? d Determine the wavelength of the line in the hydrogen atom spectrum corresponding to the n 1 = 2 to n 2 = 6 transition.
Below is a simplified energy level diagram for atomic hydrogen. _____ 0 eV . first excited state _____ -3.4 eV . ground state _____ -13.6 eV (a) A free electron with 12 eV of kinetic energy collides with an atom of hydrogen. As a result the atom is raised to its first excited state.
The following is an energy-level diagram for electronic transitions in the Bohr hydrogen atom a. Explain why the energy levels get closer together as they increase. Provide mathematical support for this. b. Verify that the colors given in the diagram are correct. Provide mathematical support.
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each of the responses below with the correct arrow from the figure. Learn this topic by watching Bohr Model Concept Videos. All Chemistry Practice Problems Bohr Model Practice Problems. See all problems in Bohr Model.
The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match each of the responses below with the correct arrow from the figure. 1.) The emission line with the longest wavelength._____ 2.) The absorption line with the; Question: The following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom. Match ...
This states that the energy scale of hydrogen bound states is a factor of α2 smaller than the rest energy of the electron, that is, about 19000 times smaller. We can thus rewrite the possible energies as: En = −1 2α 2 mc2 1 n. (2.1.6) The typical momentum in the hydrogen atom is p≃ ~ a 0 = me2 ~ = e2 ~c mc → p≃ α(mc), (2.1.7)
Which of the transitions in the hydrogen atom energy-level diagram shown here requires the absorption of the longest wavelength photon? transition a b. ransition b c transition c d. ransition d n 5 a. e. None of these are correct, because photons are emitted, not absorbed, by these transitions 15.
39.50. Model: Photons are emitted when an atom undergoes a quantum jump from a higher energy level to a lower energy level. On the other hand, photons are absorbed in a quantum jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. Because most of the atoms are in the n = 1 ground state, the only quantum jumps in the absorption spectrum start from the n = 1 state.







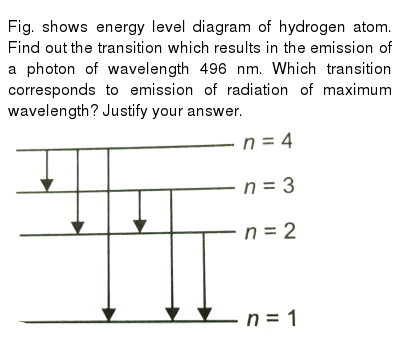












0 Response to "39 the following is a diagram of energy states and transitions in the hydrogen atom."
Post a Comment