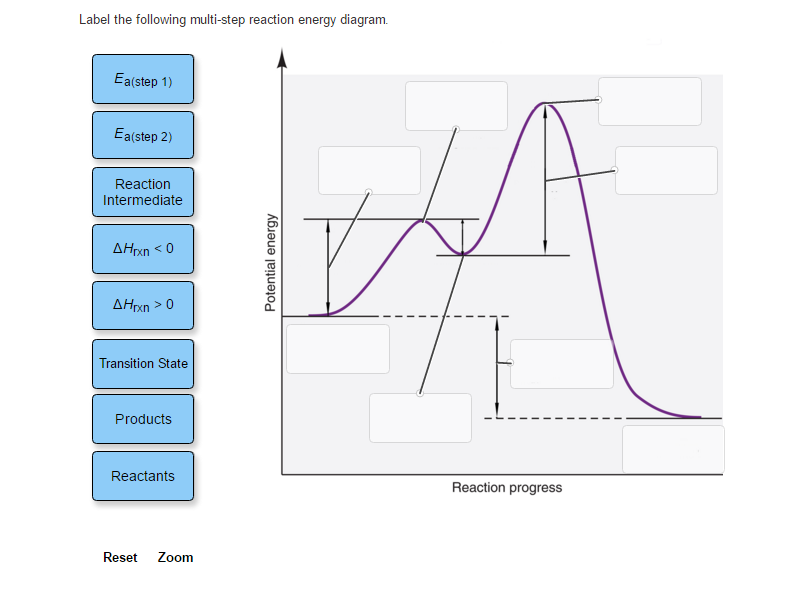
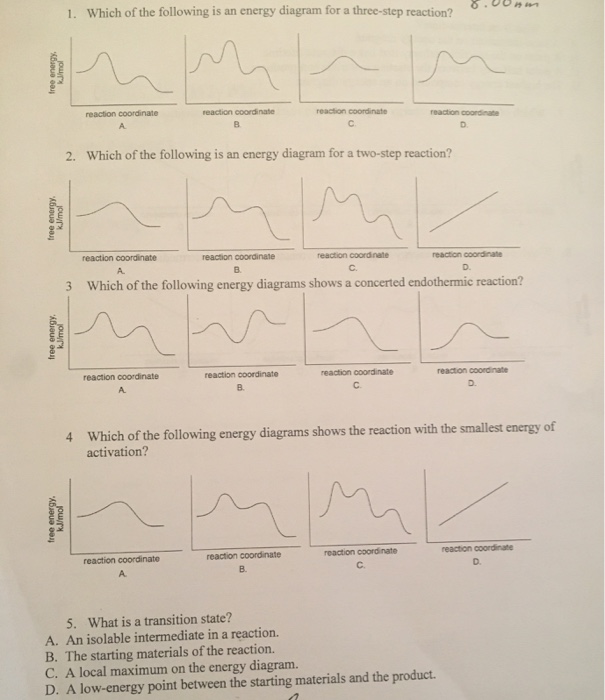
37 label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.
PDF Rates, Temperature and Potential Energy Diagrams Worksheet 2. Draw a potential energy (E p ) diagram for a reaction in which ∆H = 80 kJ/mol and E a = +28kJ/mol. Label the axes, activation energy, ∆H, site of the activated complex, reactants and products. 3. Using the potential energy diagrams for an endothermic and PDF 5.12 Spring 2003 Review Session: Exam #2 reaction. Use fishhook arrows! • Draw and completely label a reaction-energy diagram. • Deter min e th ra te-d ter ing sp of a ulti- ep re act ion-energy d gram. • Differentiate between transition states and intermediates. • Differentiate between kinetic and thermodynamic control. • Use the Hammond postulate to predict whether a
OneClass: Label the following multi-step reaction energy ... 11. Label numbers 1-4 on the energy diagram: Label the activation energies on the diagram. Is the overall reaction endothermic or exothermic? 3. What is the reactant for the rate determining step? Reaction Path 27. Calculate the pH of a 0.0sS M solution of CHCNa (K,(C)-18x10)

Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.
viii__reaction_mechanisms.pdf - VIII) Reaction Mechanisms ... Reactions are expressed using a reaction equation. The equation gives information about the reactants and products, but very little information about the process that occurs to get from reactants to products. An equation suggests a one step process, which is in reality seldom the case. Most reactions involve a series of steps, called a reaction mechanism. Chapter 14 B Flashcards - Quizlet The reaction is exothermic because the energy of the products is less than the energy of the reactants Intermediates are dips (2) in this case, and they are formed at different rates Consider the following multi-step reaction: DOC 1 - bohr.winthrop.edu a. For each reaction: 1) Draw in all non-bonding electrons in the reactants and products. 2) Label each reactant as either nucleophile or electrophile. 3) Draw the curved arrows needed to show each reaction mechanism. b. Draw a free energy diagram for the reaction of ethanol with HBr to give bromoethane.
Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.. Welcome to CK-12 Foundation | CK-12 Foundation Draw the potential energy diagram for the following multi-step reaction . Properly label the diagram. Solution: Rate of Reaction is Determined by Slowest Step In a series of reactions that make up a multi-step reaction, each individual reaction step has its own reaction rate that is determined by the factors that have been discussed in this ... Energy Diagrams: Describing Chemical Reactions Specifically, energy diagrams tell you about the relative rate of a reaction, or of any step in a reaction, and they tell you about thethermodynamic favorability of a reaction, or of any step in a reaction. Take a few minutes to review the four basic types of single-step processes that can occur, shown in Fig.2: 12.6 Reaction Mechanisms - Chemistry Because a reaction cannot proceed faster than its slowest step, this step will limit the rate at which the overall reaction occurs. The slowest step is therefore called the rate-limiting step (or rate-determining step) of the reaction Figure 2. Figure 2. A cattle chute is a nonchemical example of a rate-determining step. DOC 1 - Winthrop University Draw a free energy diagram for the acid-catalyzed hydration of 2-butene (the last step is very fast.) Label all reactants, products and intermediates using structures. 3. Reactions. a. Draw the major product or products of each of reaction in the boxes provided. ... Be explicit when showing multi-step reactions. 4. Mechanisms.
Reaction Mechanisms | Boundless Chemistry Every chemical reaction proceeds according to a reaction mechanism, which is a step-by-step description of what occurs during a reaction on the molecular level. Each step of the mechanism is known as an elementary process, which describes a single moment during a reaction in which molecules break and/or form new bonds. Solved Label the following multi-step reaction energy - Chegg Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (4 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram AHn> 0 Reaction Intermediate Ealstep 2) Products Ea (step 1) Reactants Reaction progress. Cellular Respiration Diagram - Biology Wise The energy released is in the form of ATP molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. The cellular respiration equation is as follows: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 ――> H 2 O + CO 2 + 36ATP . The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. Diagram of Cellular Respiration PDF 5.111 F14 Final Exam Solutions - MIT OpenCourseWare 406 M-1 min-1 and the rate constant for the reverse reaction is 244 M-1 min-1. The activation energy for the forward reaction is 26.2 kJ mol-1 and that for the reverse reaction is 42.4 kJ mol-1. (a) (5 points) On the axes below, draw a reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction, showing the
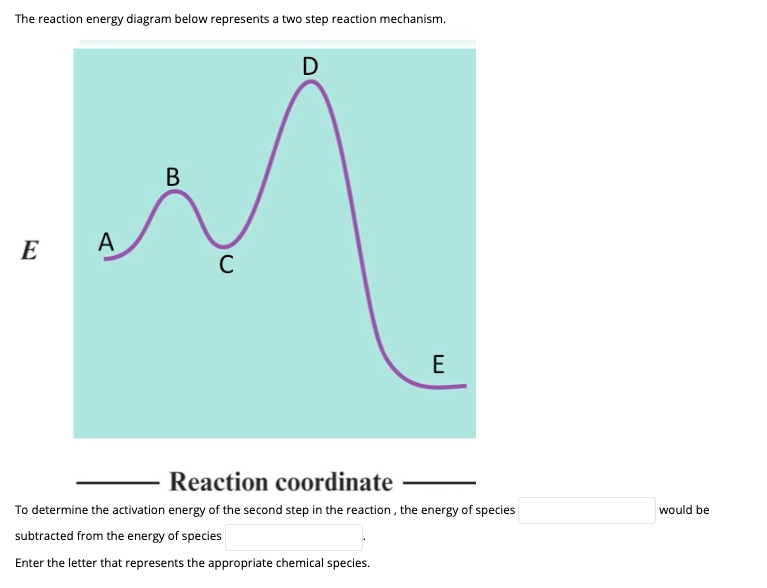
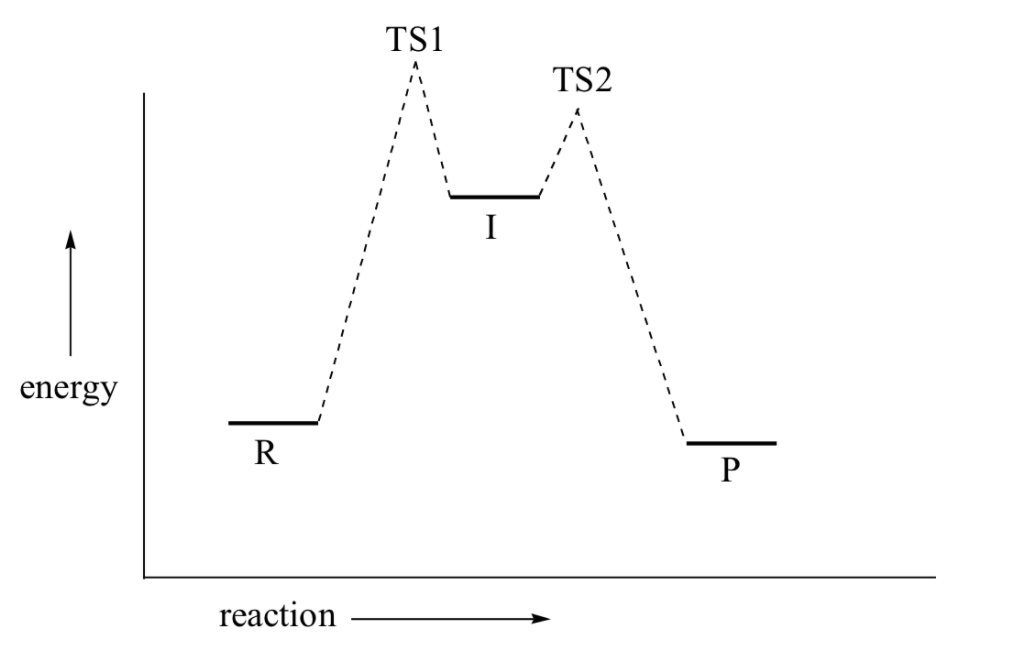
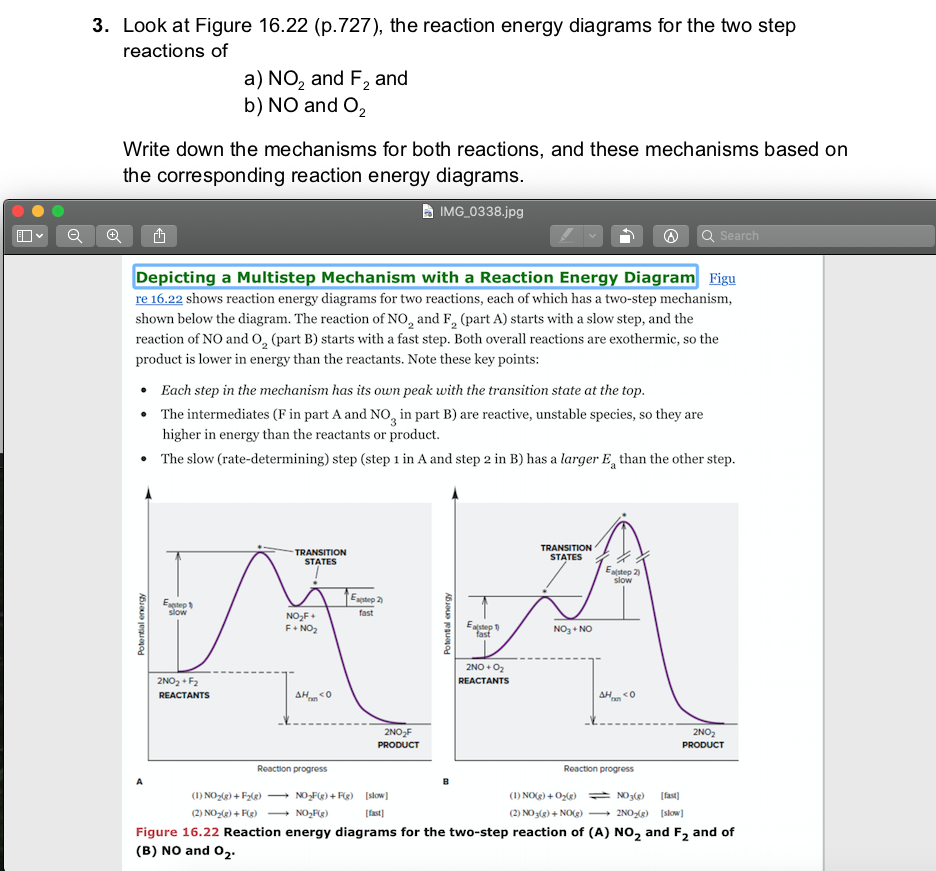
Energy level diagrams - Why are there energy changes in ... The reaction shown by the second diagram is more exothermic. There is a greater difference in energy between the reactants and products. The green arrow is longer. ENERGY PROFILES FOR SIMPLE REACTIONS - chemguide Diagrams like this are described as energy profiles.In the diagram above, you can clearly see that you need an input of energy to get the reaction going. Once the activation energy barrier has been passed, you can also see that you get even more energy released, and so the reaction is overall exothermic. Energy Diagram Module Series- Part Three: Intermediates ... This is part 3 of a four part series in the Energy Diagram Module. Stay tuned for Part 4! Click on the following links to see earlier parts: Part 1. Part 2. Sometimes reactions are more complex than simply a transition state (Graph 3), which would represent a single step in the reaction mechanism. Mechanisms and Potential Energy Diagrams | Chemistry for ... The reaction whose potential energy diagram is shown in the figure is a two-step reaction. The activation energy for each step is labeled E a1 and E a2 .Each elementary step has its own activated complex, labeled AC 1 and AC 2 .Note that the overall enthalpy change of the reaction is unaffected by the individual steps, since it depends only on the initial and final states.

How to Draw Multi-Steps Energy Profile Diagrams: Reactant, Product, ∆H, Activation Energy, Slow Step
Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism by Ashima Singh Energy Diagram for a Two-Step Reaction Mechanism Complete Energy Diagram for Two-Step Reaction A Two-Step Reaction Mechanism The transition states are located at energy maxima. The reactive intermediate B+ is located at an energy minimum. Each step has its own delta H and
Energy Diagrams of Two Step Reactions - YouTube Watch Complete videos @ Organic Chemistry 1
Solved Label the following multi-step reaction energy - Chegg Label the following multi-step reaction diagram. Show transcribed image text. Expert Answer. Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 99% (114 ratings) Transcribed image text: Label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram.
This review was not prepared by your professor or school ... UCONN - GENERAL CHEMISTRY - PROF. CADY UCONN CHEM 1128Q CADY EXAM 1 REVIEW* PRACTICE: Label the multi-step reaction energy diagram below using the letters corresponding to the labels on the left. There are more labels than needed; each label can be used only once. A) Reaction intermediate B) E a (step 2) C) Reactants D) Products E) Transition state F) E a (step 1) G) Catalyst H) Equilibrium I ...
MCB: Exam 4 Sapling Flashcards - Quizlet Label the diagram with the appropriate terms to describe glycogen synthase regulation. ... The multi‑step activation of a fatty acid involves the hydrolysis of the equivalent of two molecules of ATP. The overall free energy change for the reaction includes the free energy change for the hydrolysis of ATP and the subsequent hydrolysis of PPi.
Labeling an Energy Diagram Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Labeling an Energy Diagram. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
PDF Organic Chemistry 32-235 Practice Questions for Exam #2 ONE 2) Draw an energy diagram (using the ∆H° for each step to set appropriate energy levels) for the two propagation steps, and decide which step is more likely the rate-determining step? (label this step as rds) see the textbook for chlorination of methane and apply it to this case. energy reaction coordinate (progress) CH4 + Br2 CH3Br + HBr
PDF time (s) conc. (M) 0 1.284 1.4 1.135 2.8 0.986 4.2 0.837 7.0 0 6. (6.5 points) Assume a certain chemical reaction releases 57kJ/mol of heat. Use the following diagram to show the energy change during the reaction. Make sure to label: products, E a, ∆H (change in heat energy). Extra Credit (2 points): What is the chemical species at the highest point in the energy curve called? Label it on the diagram.
12.7 Catalysis - Chemistry - opentextbc.ca This potential energy diagram shows the effect of a catalyst on the activation energy. The catalyst provides a different reaction path with a lower activation energy. As shown, the catalyzed pathway involves a two-step mechanism (note the presence of two transition states) and an intermediate species (represented by the valley between the two ...
Energy Profiles (Energy Diagrams) Chemistry Tutorial An energy profile is a diagram representing the energy changes that take place during a chemical reaction. Enthalpy change , ΔH, is the amount of energy absorbed or released by a chemical reaction. On an energy profile, the enthalpy change for the reaction is measured from the energy of the reactants to the energy of the products.
PDF Rates, Temperature and Potential Energy Diagrams Worksheet Use the multistep reaction shown to the right to answer the following: ... E a = +28kJ/mol. Label the axes, activation energy, ∆H, site of the activated complex, reactants and products. ... Draw a potential energy diagram for the the reaction. ...
Reaction Mechanisms - Chem1 2 Multi-step (consecutive) reactions. Mechanisms in which one elementary step is followed by another are very common. step 1: A + B → Q. step 2: B + Q → C. net reaction: A + 2B → C. (As must always be the case, the net reaction is just the sum of its elementary steps.) In this example, the species Q is an intermediate, usually an unstable ...
Answer: Label the multi-step reaction ener... | Clutch Prep Problem: Label the multi-step reaction energy diagram below using the letters corresponding to the labels on the left.There are more labels than needed; each label can be used only once.A) Reaction intermediateB) Ea (step 2)C) ReactantsD) ProductsE) Transition stateF) Ea (step 1)G) CatalystH) EquilibriumI) kfJ) krK) Reaction coordinateL) Energy
DOC 1 - bohr.winthrop.edu a. For each reaction: 1) Draw in all non-bonding electrons in the reactants and products. 2) Label each reactant as either nucleophile or electrophile. 3) Draw the curved arrows needed to show each reaction mechanism. b. Draw a free energy diagram for the reaction of ethanol with HBr to give bromoethane.
Chapter 14 B Flashcards - Quizlet The reaction is exothermic because the energy of the products is less than the energy of the reactants Intermediates are dips (2) in this case, and they are formed at different rates Consider the following multi-step reaction:
viii__reaction_mechanisms.pdf - VIII) Reaction Mechanisms ... Reactions are expressed using a reaction equation. The equation gives information about the reactants and products, but very little information about the process that occurs to get from reactants to products. An equation suggests a one step process, which is in reality seldom the case. Most reactions involve a series of steps, called a reaction mechanism.
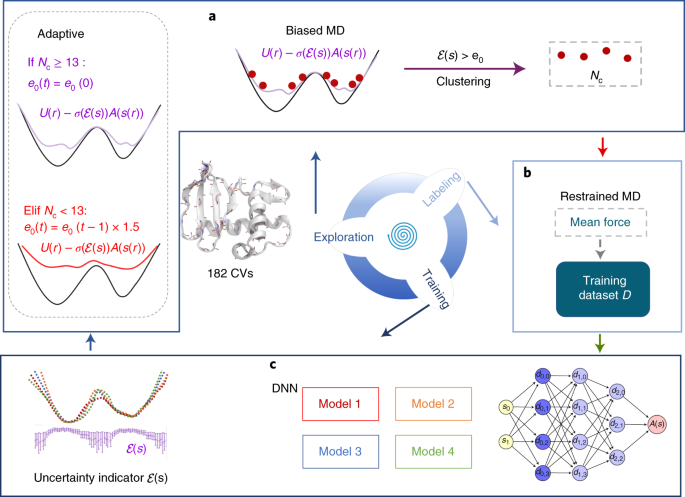
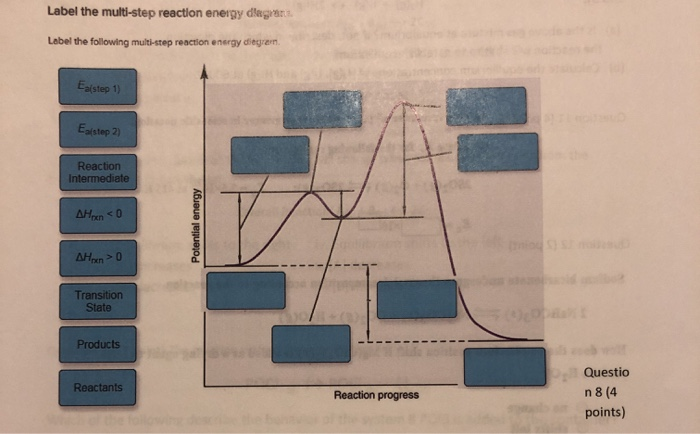
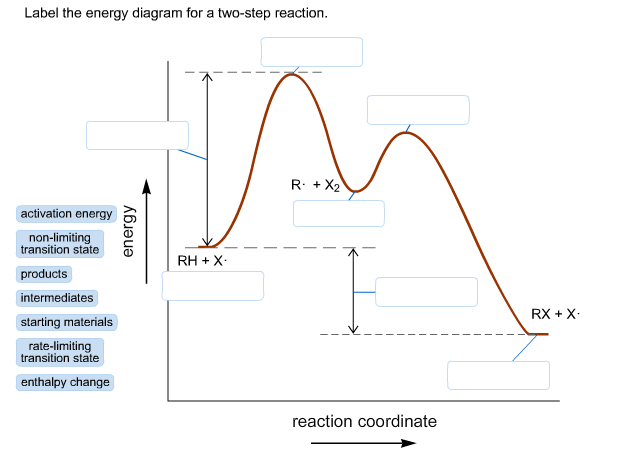


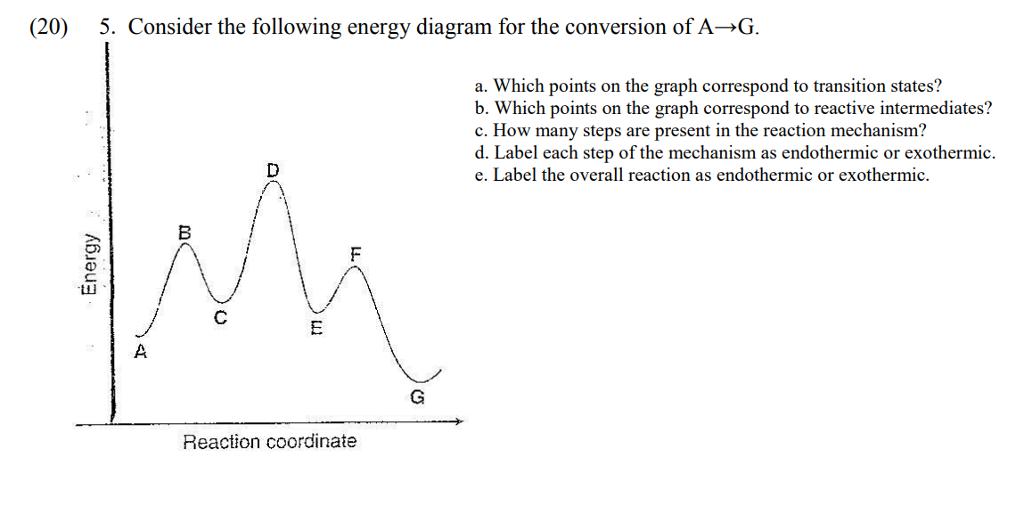






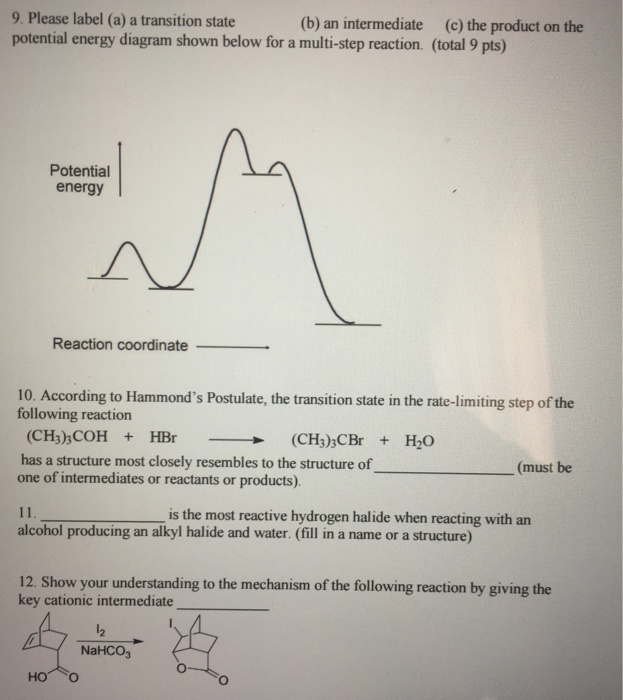







0 Response to "37 label the following multi-step reaction energy diagram."
Post a Comment