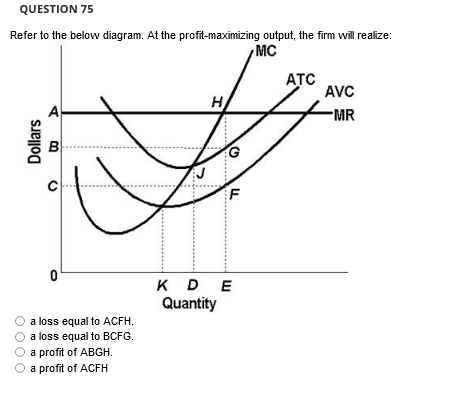
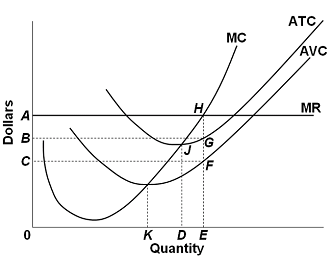
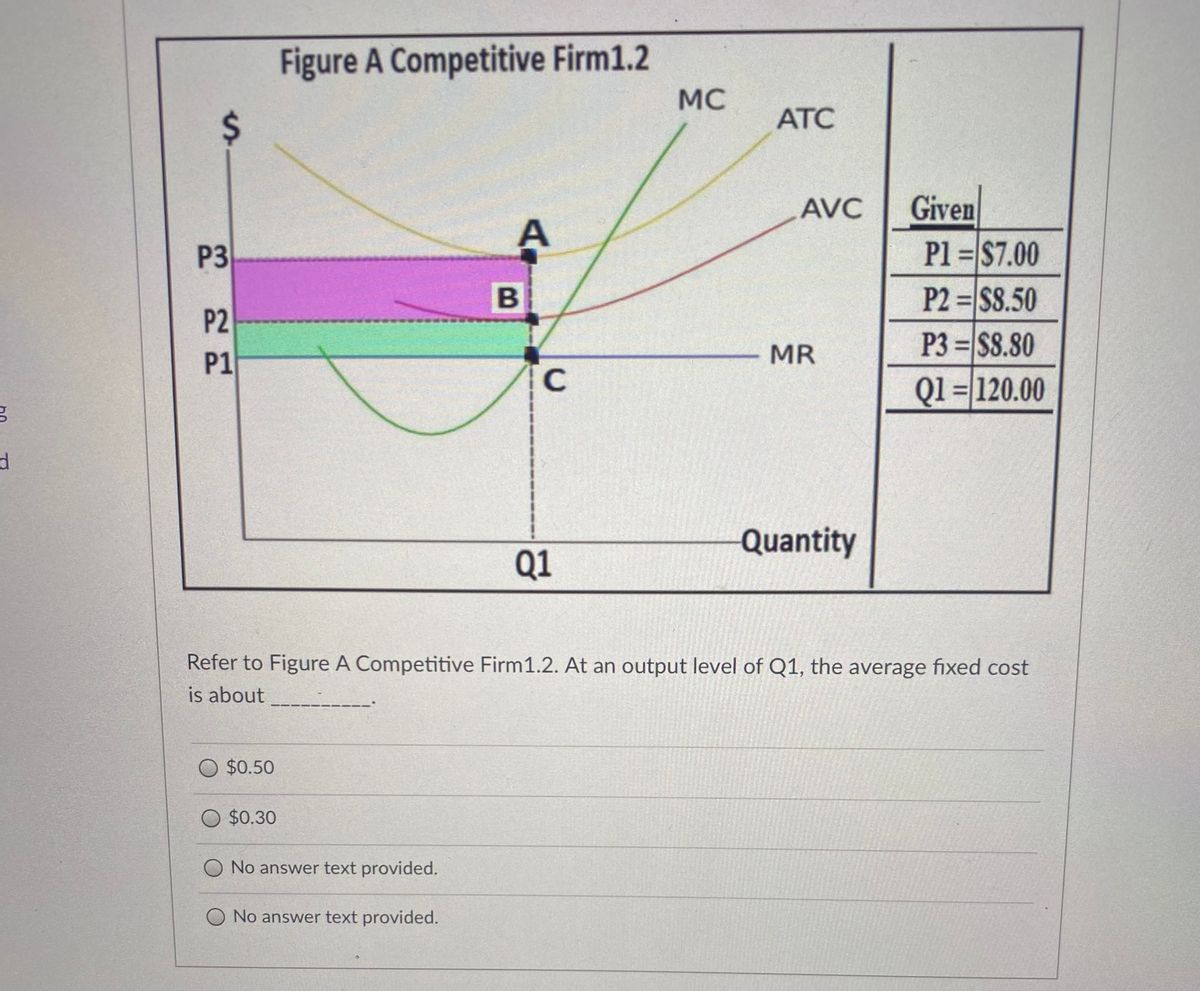
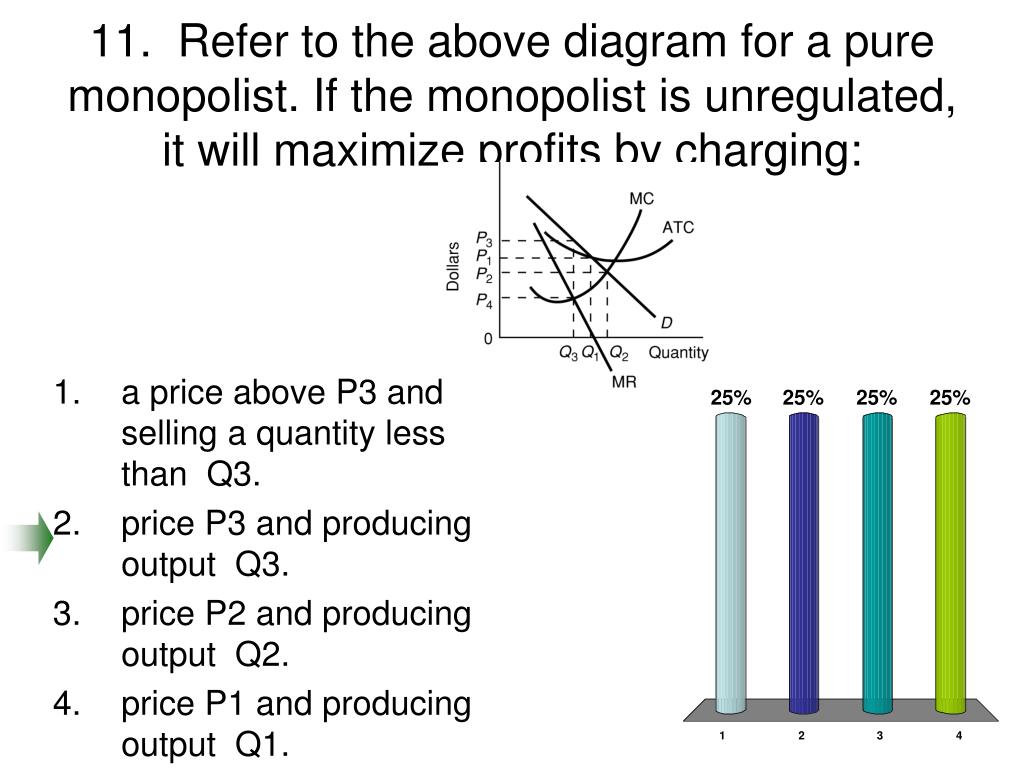
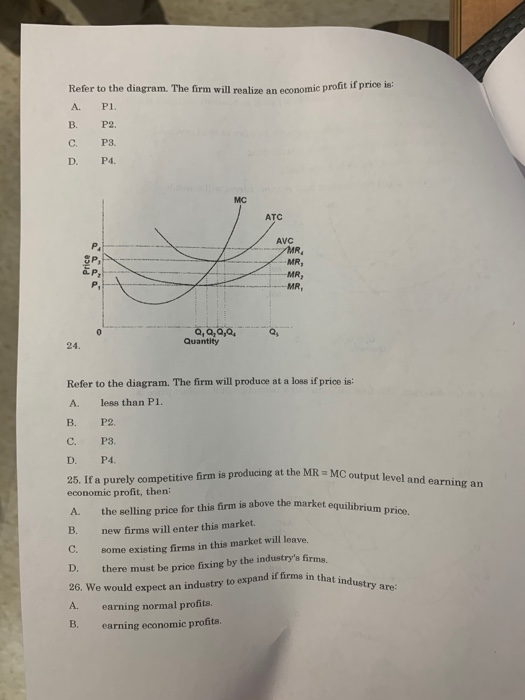
37 refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,
Chapter 8 (questions&answers) - ECON-1102 - Introduction... - StuDocu 4. In pure competition, the demand for the product of a single firm is perfectly 10. I n a t y pical graph for a purel y competitive firm, the intersection of the tot al cost and total. 22. A purely competitive firm will be willing to produce at a loss in the short run provided Ans: B. 25. Refer to the above diagram. PDF sol_02.PDF With a price ceiling of $80, consumers would like to buy 20 million, but producers will supply only 16 2. Refer to Example 2.4 on the market for wheat. At the end of 1998, both Brazil and Indonesia 3. A vegetable fiber is traded in a competitive world market, and the world price is $9 per pound.
PDF Are You suprised ? (a) (i) For a perfectly competitive firm price is always equal to marginal revenue. The reason for this is that a firm operating under the conditions of perfect competition constitutes a tiny part of the market, which allows it to sell as much of its output at the going market price as it wants.

Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,
Eco practice 4 | Economics homework help 18. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is: A. P1. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero. The table shows cost data of a purely competitive firm. - HomeworkLib Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. Next > Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce with an economic profit at all price Assume the following cost data are for a purely competitive producer: Average Product Fixed Cost Variable... Introduction to Marketing Coursera Quiz Answer Competitive Points of Difference. 7. According to the Weber Fechner Law, consumers react to prices in _____ as opposed to _____. The thought process for a _-centric company is "What combination of products is best for this customer?"
Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,. Refer To The Diagram For A Purely Competitive Producer If... Refer to the diagram. If product price is p 3. An increase in the steepness of curve 3 an upward shift in curve 2 and an upward shift in curve 1. Price and quantity will be. Purely competitive firms monopolistically competitive firms and pure monopolies all earn positive economic profits in the long... PDF homework 1998-2 econ 103 a. At a product price of $56, will this firm produce in the short run? Explain why price can be substituted for marginal revenue in the MR = MC rule when an industry is purely competitive. WRITE: The figure to the right shows Bob's demand for pizzas and the market price. a. What is the... Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly Flashcards - Cram.com Study Flashcards On Test Bank Chapter 24 Pure Monopoly at Cram.com. Quickly memorize the terms, phrases and much more. Cram.com makes it easy to get the grade you 19. For a nondiscriminating imperfectly competitive firm: A) the marginal revenue curve lies above the demand curve. Help with #8-11 please. For questions 8-11, refer to this ... For questions 8-11, refer to this diagram for 2 purely competitive producer. ... If product price is P3: A. The firm will maximize profit at point d.1 answer · 0 votes: 8. C Minimum price is the price where ATC intersects MC. 9. D Between P2 and P3 firm incurs loss. 10. B If the price is P3 it is equal to ATC meaning ...
4.7 Taxes and Subsidies - Principles of Microeconomics Like with price and quantity controls, one must compare the market surplus before and after a price change Due to the tax's effect on price, areas A and C are transferred from consumer and producer surplus Refer to the supply and demand curves illustrated below for the following THREE questions. ch 14 Flashcards 1. Refer to Table 14-1. The price and quantity relationship in the table is most likely that faced by a firm in a. Whenever a perfectly competitive firm chooses to change its level of output, holding the price of the product 18. When price is greater than marginal cost for a firm in a competitive market Profit-maximizing Output Chapter 10 - ProProfs Quiz Change in product price associated with the sale of one more unit of output. B. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. The firm will maximize profit at point d. Untitled 1 Technological advances that reduce the cost of producing computer chips represent a decline in an input price for producing a computer. The result is a shift to the right in the supply of computers, as shown in Figure. The equilibrium price falls and the equilibrium quantity rises, as the figure shows.
Practice MCQ topic 6 Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero. D. new firms will enter this industry. 16. If a purely competitive firm is producing at some level less... Chapter 10 | Business Quiz - Quizizz Refer to the diagram. Other things equal, an increase of product price would be shown as. Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is. PDF Microsoft Word - AP Micro Unit 4 MC Questions 6. Nonprice competition refers to: A) competition between products of different industries, for example, competition between aluminum and steel E) charges a price where MR=MC. 17. Refer to the above diagram for a natural monopolist. If the monopolist is unregulated, it will maximize profits... Answered: Assume that the cost data in the… | bartleby Business Economics Q&A Library Assume that the cost data in the following table are for a purely competitive producer: Average Fixed Average Loss per unit = $ 6.50 8 c. At a product price of $32.00 (i) Will this firm produce in the short run? No (ii) If it is preferable to produce, what will be the...
Econ Test Answers | PDF | Oligopoly | Perfect Competition Nonprice competition refers to: A.competition between products of different industries, for example, competition between aluminum and steel in the manufacture of automobile parts. 38. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer.
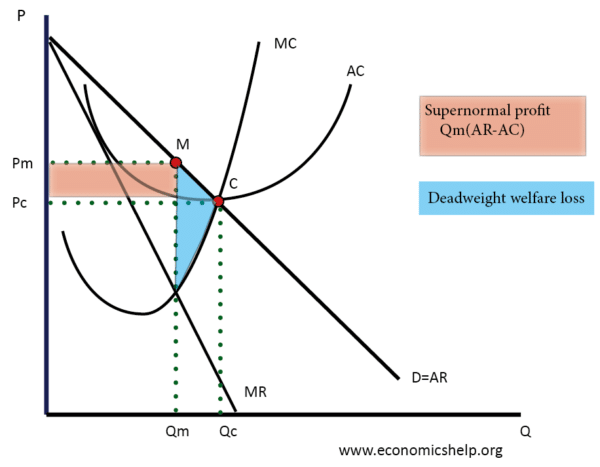
Pricing in Theory (With Diagram) | (b) Homogeneity of products The phrase competitive structure refers to the nature and extent of the monopolistic elements, if Purely Competitive Firm and Industry: A perfectly competitive market has the following features (b) Homogeneity of products: The product of any seller is identical to that of any other in the market.
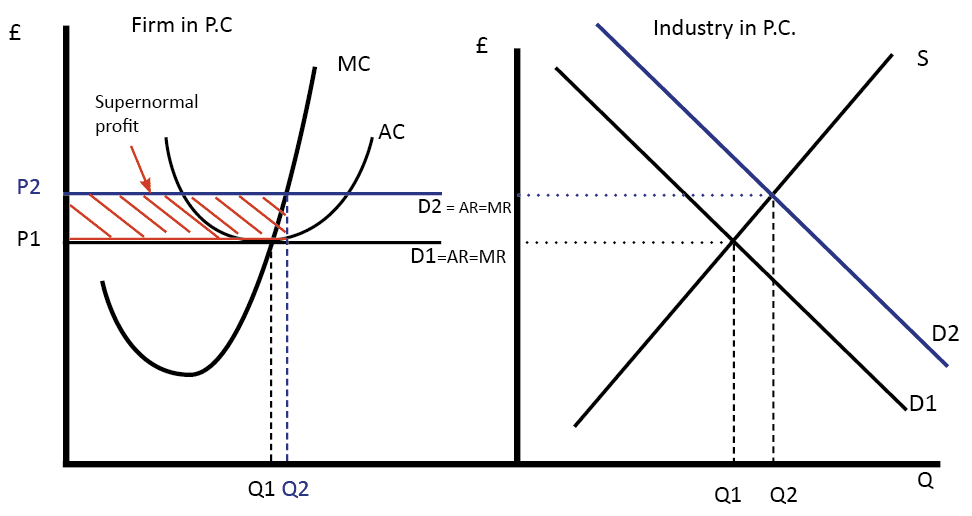
MICROECONOMICS Review for Exam Three (Chapters ) Fall ppt... Refer to the diagram below. Refer to the above diagrams which pertain to a purely competitive firm producing output q and the industry in which it operates. In the long run we should expect: A. firms to enter the industry, market supply to rise, and product price to fall.
ECON 150: Microeconomics | Comparing to Pure Competition Comparing to Pure Competition. Recall that purely competitive firms produce where MC is equal to price and that industry supply is obtained by Certain conditions must hold in order for a firm to charge different prices for the same product. First, a firm must be able to set the price (i.e. it must...
OneClass: Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The mr = mc rule can be restated for a purely competitive seller as p = mc because: Each additional unit of output adds exactly its price to total revenue. The firm's average revenue curve is downsloping. The market demand curve is down sloping. The firm's marginal revenue and total revenue curves will...
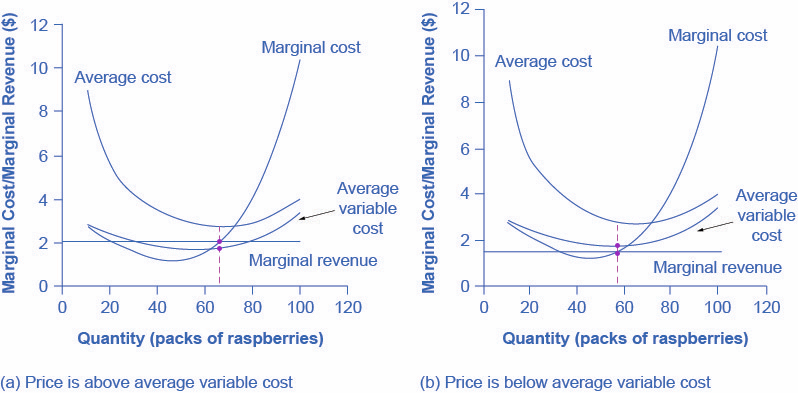
Pure Competition in the Short Run 4. 10-4 Pure Competition: Characteristics • Very large numbers of sellers • Standardized product Total revenue refers to the total amount of money that the firm collects for the sale of all of the units Examine the MC for the competitive firm. If price is below AVC, then the firm should shut down and...
Chapter 10 Flashcards | Chegg.com 45. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is: A. P1. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero.
30 Refer To The Diagram For A Purely Competitive Producer. If... If product price is p 3. The lowest point on a purely competitive firms short run supply curve corresponds to. The lowest price at which the firm Refer to the diagram at output level q the total variable cost is 0beq if a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price...
Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer If... In the short run a purely competitive seller will shut down if:Use the following to answer questions 77-81:77. D) is less than ATC.Answer: C118. Refer to the above diagram. This firm will earn only a normal profit if product price is:A) P1.
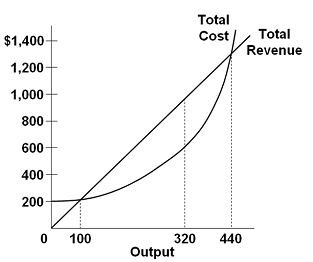
8.2 How Perfectly Competitive Firms Make Output Decisions If the price of the product increases for every unit sold, then total revenue also increases. As an example of how a perfectly competitive firm decides what quantity to produce Total revenue for a perfectly competitive firm is a straight line sloping up. The slope is equal to the price of the good.
Pure Competition Pure Competition. A perfectly competitive market is rare, but those that exist are very large, such Because, for purely competitive firms, marginal revenue = price, maximum revenue is also earned This diagram of the short-run supply curve shows the relationship among average variable cost...
Perfect Competition Definition | Produce Pure or perfect competition is a theoretical market structure in which a number of criteria such as perfect information and resource mobility are met. The average revenue and marginal revenue for firms in a perfectly competitive market are equal to the product's price to the buyer. As a result, the...
Micro CH 9 Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. If product price is P3 Refer to the diagram. To maximize profit or minimize losses, this firm will produce: E units at price A. The Ajax Manufacturing Company is selling in a purely competitive market.
Introduction to Marketing Coursera Quiz Answer Competitive Points of Difference. 7. According to the Weber Fechner Law, consumers react to prices in _____ as opposed to _____. The thought process for a _-centric company is "What combination of products is best for this customer?"
The table shows cost data of a purely competitive firm. - HomeworkLib Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. Next > Refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. The firm will produce with an economic profit at all price Assume the following cost data are for a purely competitive producer: Average Product Fixed Cost Variable...
Eco practice 4 | Economics homework help 18. Refer to the above diagram for a purely competitive producer. The lowest price at which the firm should produce (as opposed to shutting down) is: A. P1. If product price is P3: A. the firm will maximize profit at point d. B. the firm will earn an economic profit. C. economic profits will be zero.

















0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram for a purely competitive producer. if product price is p3,"
Post a Comment