37 terminal velocity free body diagram
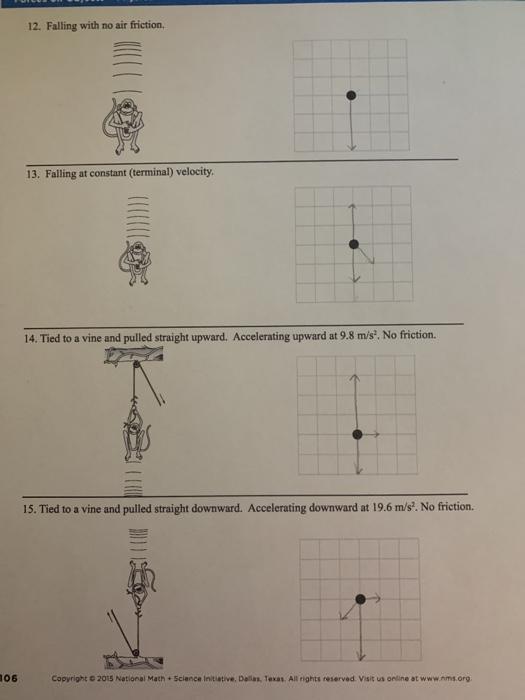
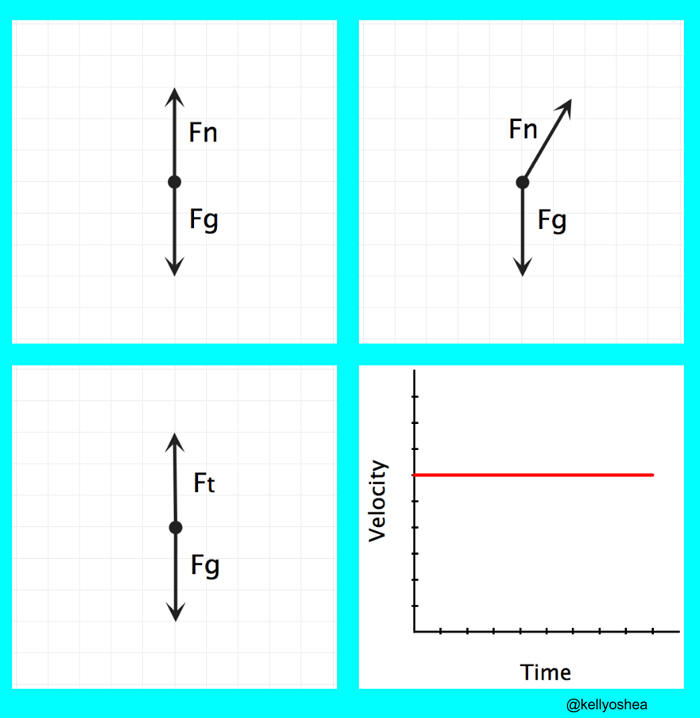
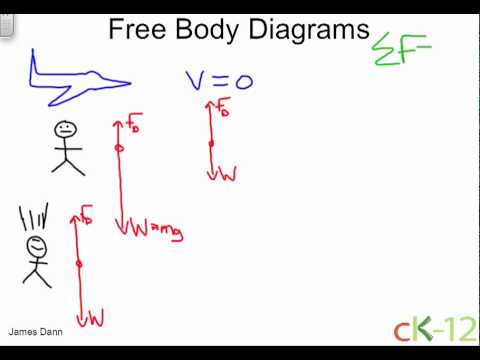
PDF SPH 3U: Representing Forces Free Body Diagrams A free body diagram (FBD) is a tool that helps us understand the total effect of all the forces acting on an object. There are a few steps that you should ... Terminal Velocity A rock is falling at a constant speed. This is called the object's terminal velocity. 1. Draw a FBD. Drawing Free-Body Diagrams - Physics Classroom A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram reflects the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow shows the direction that the force is acting.
PPT PowerPoint Presentation She has reached TERMINAL VELOCITY (air resistance =gravity) :acceleration and force Physics 12/16/04 * In order to understand this motion, we need to use a free body diagram 12/16/04 * Terminal Velocity of a human~180mph 12/16/04 :acceleration and force Physics 12/16/04 * In order to understand this motion, we need to use a free body diagram 12 ...
Terminal velocity free body diagram
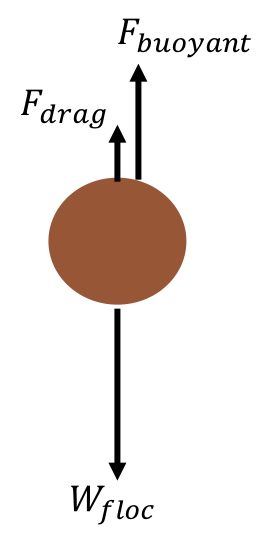
Terminal Velocity and Free Fall - ThoughtCo Terminal velocity and free fall are two related concepts that tend to get confusing because they depend on whether or not a body is in empty space or in a fluid (e.g., an atmosphere or even water). Take a look at the definitions and equations of the terms, how they are related, and how fast a body falls in free fall or at terminal velocity under different conditions. Air Resistance - StickMan Physics I can describe terminal velocity Free Body Diagrams A free body diagram shows all the vector forces and their direction acting on an object The dot in the middle represents the object Air Resistance Air resistance is a force that pushes backwards as an object moves through the air The faster an object falls the greater the opposing air resistance Terminal Velocity of a Body Falling Through a Fluid ... Suppose we are interested in finding the terminal velocity of a spherical object falling through a fluid. Assuming the only forces acting on the body are gravity and the viscous force, we can draw the free body diagram of the object as below. FBD of a falling Spherical Object. The net force acting on the body will be given by the follow equation
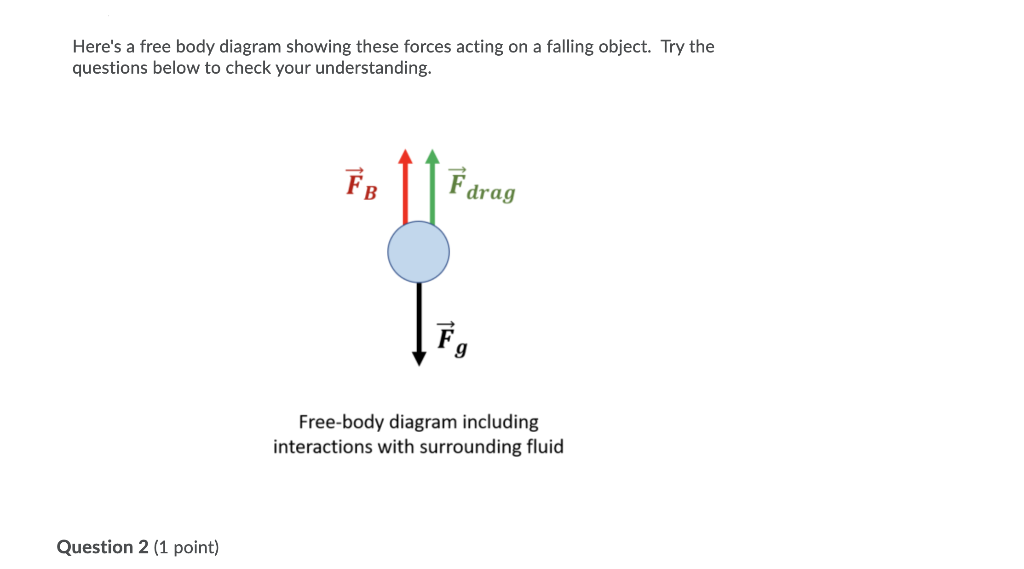
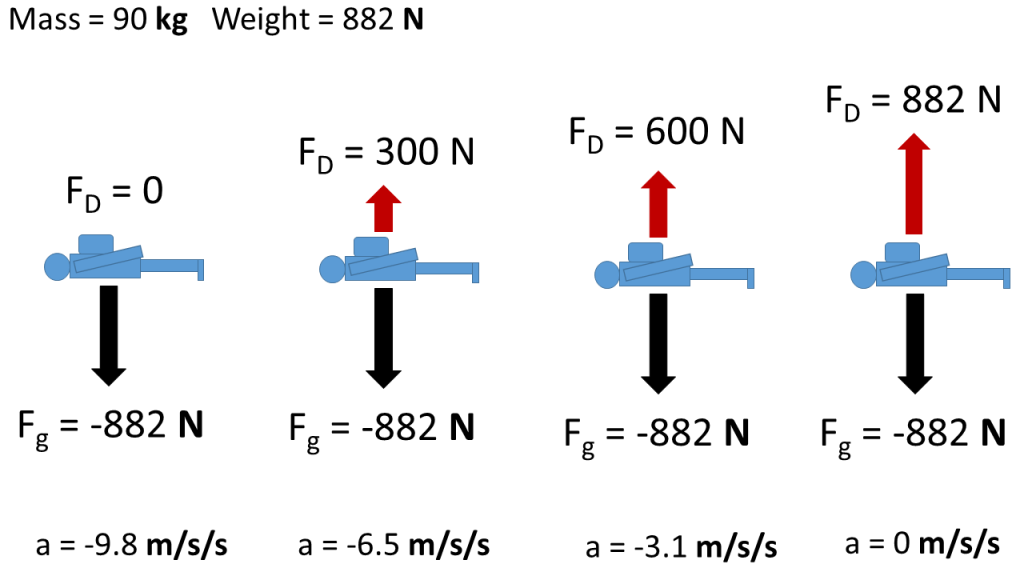
Terminal velocity free body diagram. Answered: A 95 kg paratrooper is falling at… | bartleby ASK. Science Physics Q&A Library A 95 kg paratrooper is falling at terminal velocity, a) Draw a free-body diagram of the paratrooper showing all of the forces involved. b) What is the upward force of air resistance on the paratrooper while at terminal velocity? Physical Model for Terminal Velocity – Body Physics: Motion ... Free body diagrams of a person with 90 kg mass during a skydive. The initial speed is zero, so drag force is zero. As speed increases, the drag force grows, eventually cancelling out the person’s weight. At that point acceleration is zero and terminal velocity is reached. Dynamic Equilibrium With a net force of zero the skydiver must be in Free Body Diagrams - people.springfield.k12.or.us Draw a free body diagram of a meteor that is falling towards earth at terminal velocity. F air F gravity Net Force = 0 N The meteor is falling down, but its net force is 0 N! There is no acceleration! 5.7 Drawing Free-Body Diagrams – General Physics Using Calculus I Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
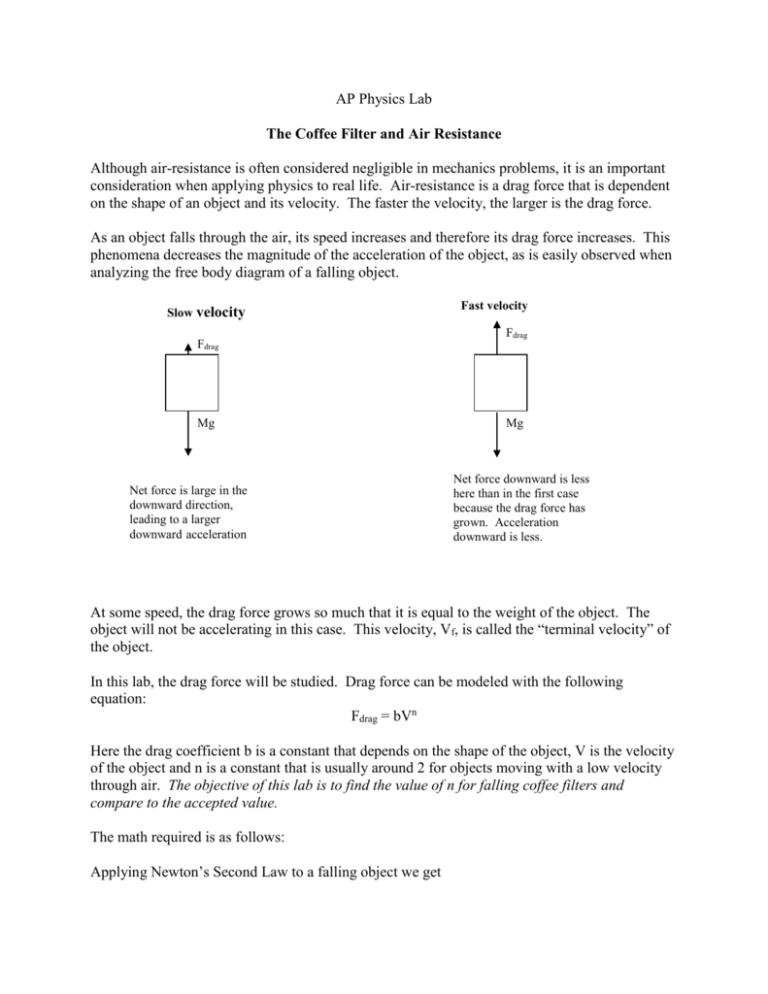
6.4 Drag Force and Terminal Speed - University Physics ... The terminal velocity is the same as the limiting velocity, which is the velocity of the falling object after a (relatively) long time has passed. Similarly, the limiting distance of the boat is the distance the boat will travel after a long amount of time has passed. ... Draw a free-body diagram of the forces to see what the angle . should be.) Free Fall and Air Resistance - Physics Classroom In a previous unit, it was stated that all objects (regardless of their mass) free fall with the same acceleration - 9.8 m/s/s. This particular acceleration value is so important in physics that it has its own peculiar name - the acceleration of gravity - and its own peculiar symbol - g. But why do all objects free fall at the same rate of acceleration regardless of their mass? Is it because they all weigh the same? ... because they all have the same gravity? ... because the air resistance is the same for each? Why? These questions will be explored in this section of Lesson 3. [Expert Answer] A ball is falling at terminal velocity ... Terminal velocity occurs when the ball is in equilibrium and the forces are balanced. Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at terminal velocity? A free body diagram with one force pointing downward labeled F Subscript g Baseline 20 N. PDF With Buoyancy As previously shown the forces can be balanced to nd terminal velocity. Figure 2: Free Body Diagram of Circle without Buoyant Forces From the free body diagram the following equation is created D= W (1) The full equation is given as 1 2 c dˆv 2A= ˆ sgV (2) where c d is the drag coe cient of the object, ˆis uid density (kg/m2), vis the speed ...
Answered: A 95 kg paratrooper is falling at a… | bartleby Homework help starts here! Science Physics Q&A Library A 95 kg paratrooper is falling at a terminal velocity. a)Draw a free body diagram of the paratrooper showing all of the forces involved. b) what is the upward force of air resistance on the paratrooper while at terminal velocity? A 95 kg paratrooper is falling at a terminal velocity. a)Draw ... PDF Free-Body Diagrams and Forces - Weebly A free-body diagram shows objects in equilibrium, or a steady state. In contrast, this diagram shows a car accelerating as it leaves a stop sign. ... • A skydiver eventually reaches a constant terminal velocity of 50 m/s. • A parked car pushes down on the pavement with a force of 8,000 N, and the pavement pushes up with Terminal Velocity, Equations, Free Fall, Drag Force - Fact ... Terminal Velocity =V = [ (2 * W) / (K*r*A)] 1/2[formula for Terminal Velocity] here K = Drag Coefficient of the falling object (it depends on the inclination of the shape and some other criteria like airflow) r = air density. W = weight of the falling object. A = cross sectional area of the object falling. PhysicsLAB: Freebody Diagrams #2 Refer to the following information for the next four questions. True or False: The magnitude of the normal, , is smaller than the object's weight. True. False. A 5 kg mass is being pushed across a rough table at a constant velocity by a constant force, F = 15 N, which acts at an angle θ = 37º to the horizontal.
(14%) Problem 7: A ball is dropped from a tall build ... (14%) Problem 7: A ball is dropped from a tall building and has reached terminal velocity (i.e. it is now falling at a constant velocity). Use Fd to denote the drag force due to air resistance. L. 1 > A Please use the interactive area below to draw the Free Body Diagram for the ball.
Terminal Velocity Derivation With Simple Step By Step ... Deriving terminal velocity using mathematical terms according to the drag equation as follows: F = bv2 F = b v 2 Where b is the constant depending on the type of drag ∑F = ma ∑ F = m a (free fall of an object) mg−bv2 = ma m g − b v 2 = m a (assuming that the free fall is happening in positive direction) mg−bv2 = mdv dt m g − b v 2 = m d v d t
PDF Project 3: Mission to Mars - Edutopia approaching terminal velocity. Students will be able to draw free-body diagrams for objects falling in the presence of air objects approaching terminal velocity, and objects falling at terminal velocity. Students will be able to draw free-body diagrams depicting that a greater force of air resistance is required to balance out the greater
Terminal Velocity - IIT JEE Study Material For Mains and ... Terminal Velocity is the highest velocity that is achieved by an object as it falls through a fluid or a gas. Terminal force occurs when an object is subjected to a resistance that increases with the increase in velocity and when its resistance equals the driving force. An object that is moving downwards with a higher speed compared to terminal velocity will eventually slow down with the ...
Lab 2: Kinematics and Terminal Velocity - Harvard University Figure 1: Free body diagram of an object falling with drag. The object is dropped at time t 0, then proceeds through t 1 and t 2 before reaching terminal velocity at time t 3. drag force in your experiment. Later in the course, when we study motion in fluids in more detail,
Speed of a Skydiver (Terminal Velocity) - The Physics Factbook "The terminal velocity of a falling human being with arms and legs outstretched is about 120 miles per hour (192 km per hour) — slower than a lead balloon, but a good deal faster than a feather!" 53 m/s: The terminal velocity of a falling body occurs during free fall when a falling body experiences zero acceleration. This is because of the ...
Solved Nora has just parachuted out of an airplane(t), and ... Transcribed image text: Nora has just parachuted out of an airplane(t), and she and her parachute have reached a constant terminal velocity. The free-body diagram for Nora and the parachute shown below is correct, and includes the weight force and a drag force due to air resistance (which acts a lot like friction).
Terminal velocity - Forces and movement - KS3 Physics ... Free fall. Terminal Velocity. ... In this diagram, the object is accelerating, or speeding up. ... Terminal velocity is the maximum speed achieved by an object freely falling through a gas or liquid.
A ball is falling at terminal velocity. Which free body ... A ball is falling at terminal velocity. Which free body diagram shows the ball falling at termainal velocity 2 See answers Advertisement Advertisement Heyitsdaedae Heyitsdaedae so I hope that diagram gives u a great view at it Advertisement Advertisement nessa314 nessa314 Hey guys! I just took the quiz and the correct answer is the picture below!
PDF Free-Body Diagrams - Ms. Poulton's Science & Math Class ... Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. Label all forces (e.g, Fgrav, Fnorm, Fapp, Ffrict, Fair, Ftens, etc. ). a. A physics book rests upon a level table. b. A skydiver is falling and has reached a terminal velocity. c. A large crate is being pushed leftward at a constant velocity. d. A sledder has reached
Terminal Velocity - NASA The constant vertical velocity is called the terminal velocity . Using algebra, we can determine the value of the terminal velocity. At terminal velocity: D = W Cd * r * V ^2 * A / 2 = W Solving for the vertical velocity V, we obtain the equation V = sqrt ( (2 * W) / (Cd * r * A) where sqrt denotes the square root function.
Terminal Velocity of a Body Falling Through a Fluid ... Suppose we are interested in finding the terminal velocity of a spherical object falling through a fluid. Assuming the only forces acting on the body are gravity and the viscous force, we can draw the free body diagram of the object as below. FBD of a falling Spherical Object. The net force acting on the body will be given by the follow equation
Air Resistance - StickMan Physics I can describe terminal velocity Free Body Diagrams A free body diagram shows all the vector forces and their direction acting on an object The dot in the middle represents the object Air Resistance Air resistance is a force that pushes backwards as an object moves through the air The faster an object falls the greater the opposing air resistance
Terminal Velocity and Free Fall - ThoughtCo Terminal velocity and free fall are two related concepts that tend to get confusing because they depend on whether or not a body is in empty space or in a fluid (e.g., an atmosphere or even water). Take a look at the definitions and equations of the terms, how they are related, and how fast a body falls in free fall or at terminal velocity under different conditions.























0 Response to "37 terminal velocity free body diagram"
Post a Comment