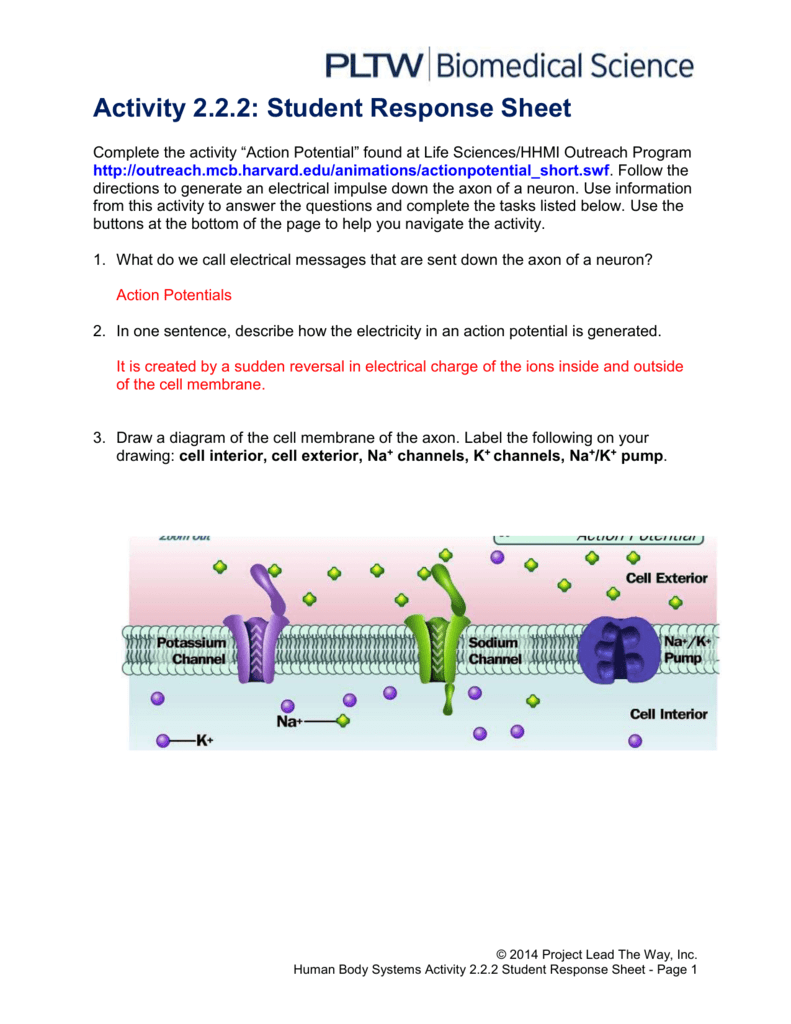
38 diagram of the cell membrane of the axon
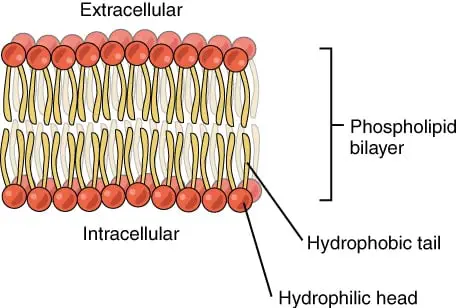
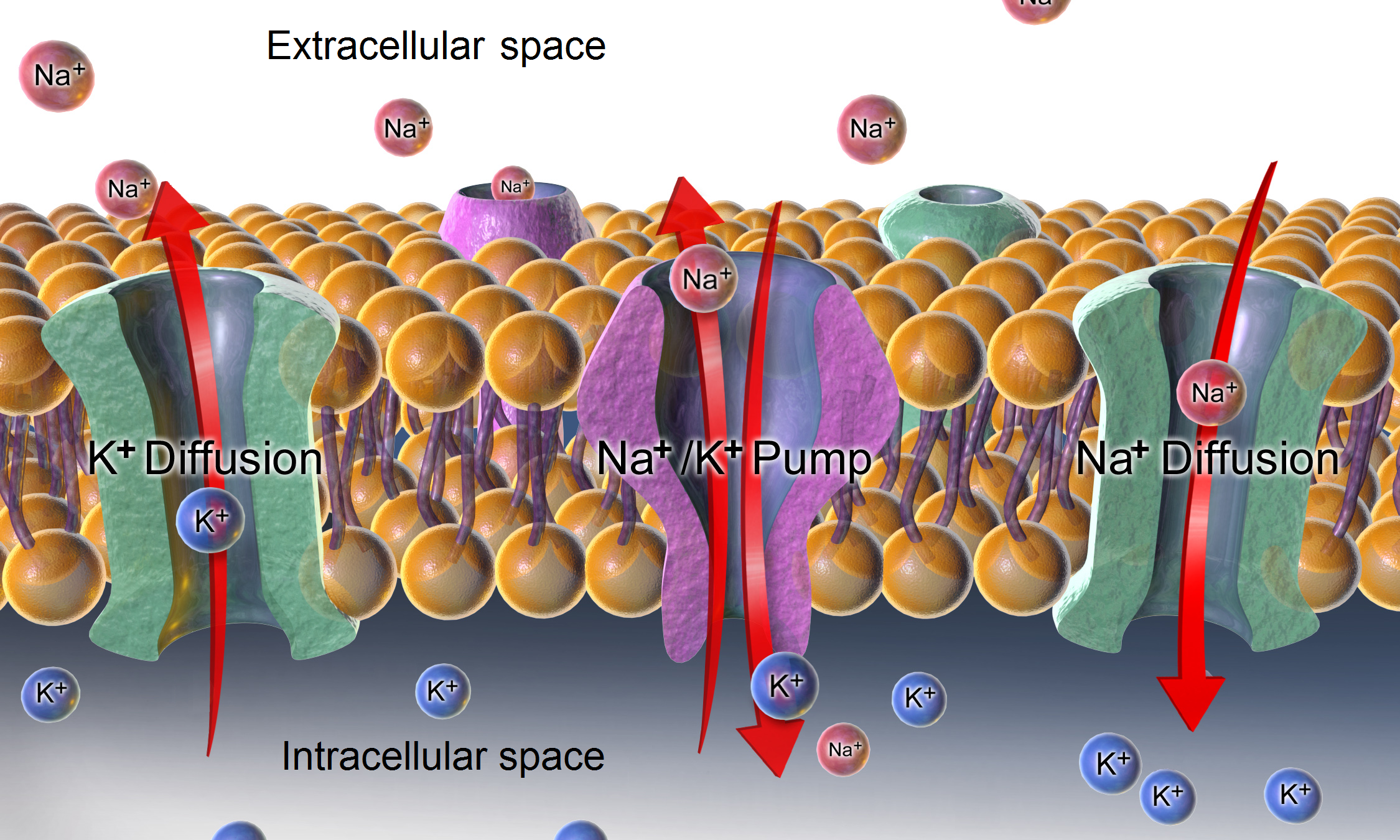
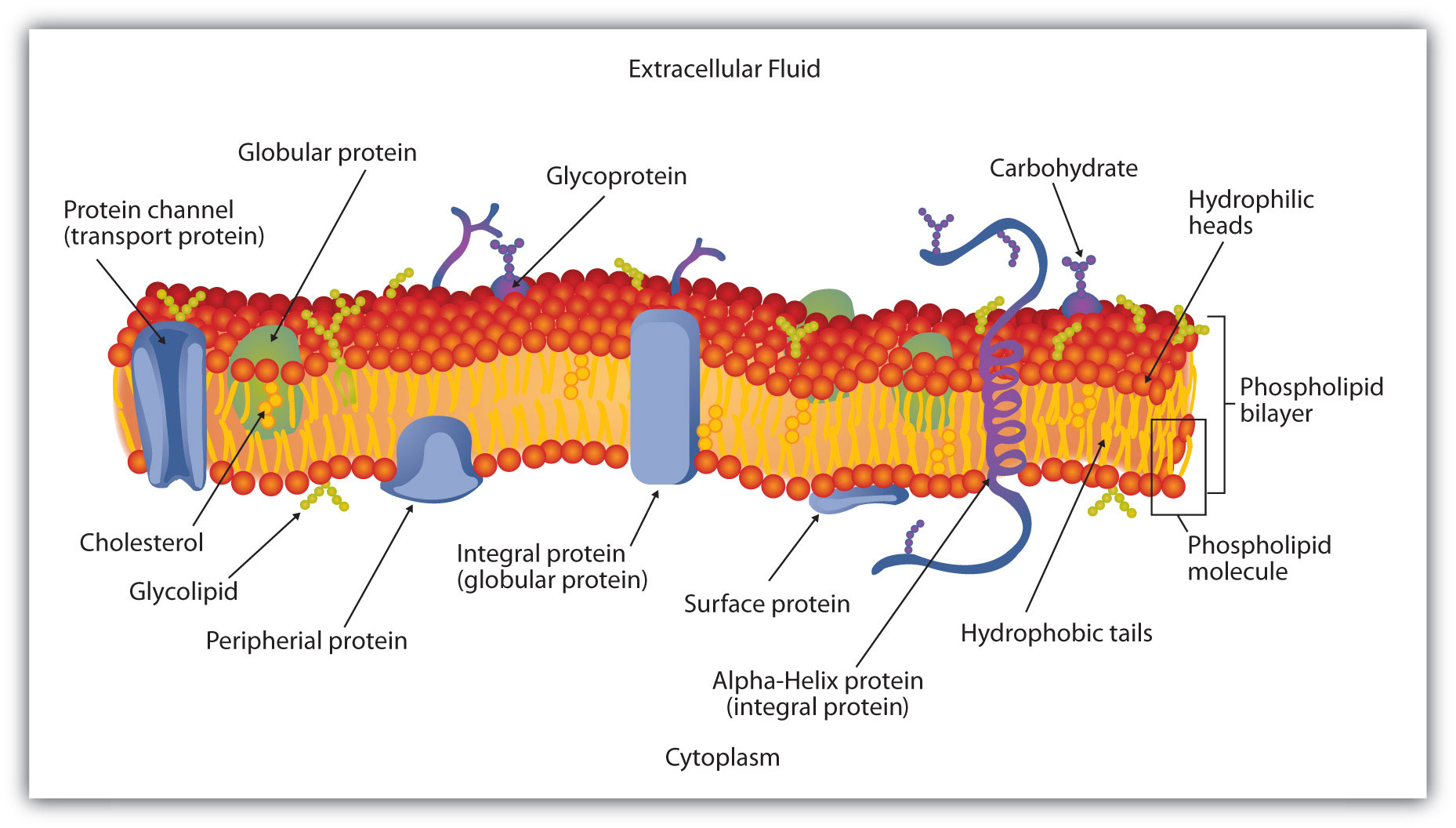
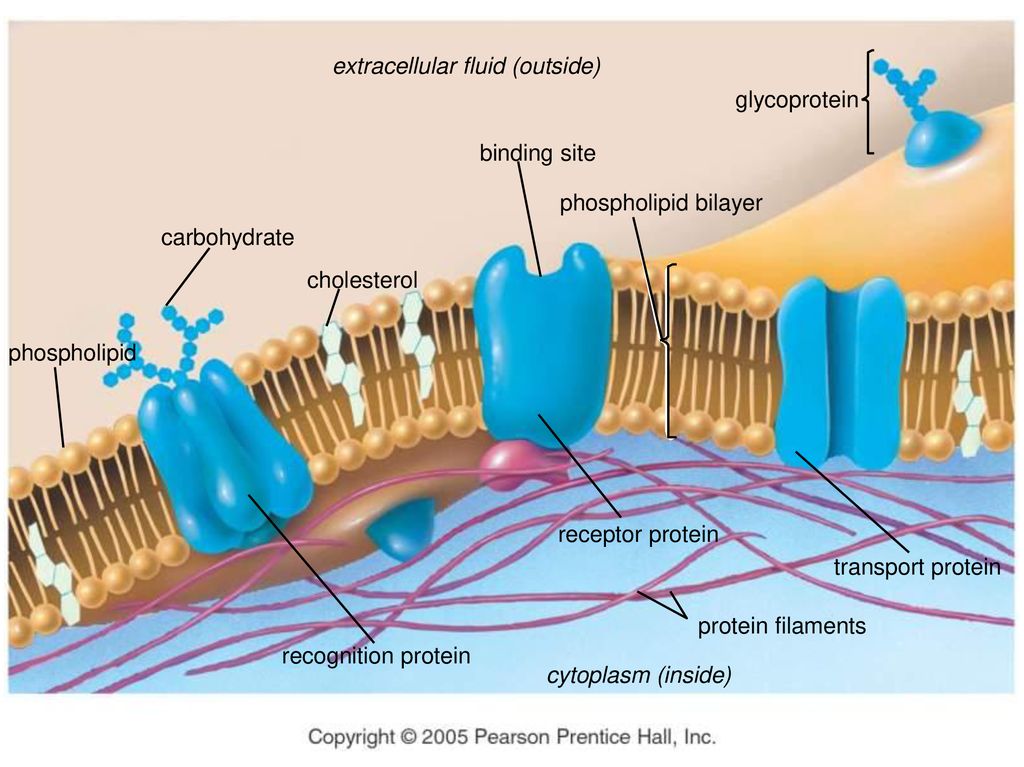
teachmephysiology.com › cell-membraneThe Cell Membrane - Structure - TeachMePhysiology In a cell, different parts of the membrane have different functions and therefore their structure is specialised for this. An example of this specialisation can be seen in the different parts of a nerve; the cell membrane in the axon is specialised for electrical conduction whereas the end of the nerve is specialised for synapsing, meaning the ... DOCX A2.2.2.StudentResponse - Weebly Draw a diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Label the following on your drawing: cell interi: or, cell exterior, Na + channels, K + channels, Na + /K + pump. The main component of cell membranes are fats called phospholipids. Use the Internet to research the structure of a phospholipid. Label a phospholipid on your diagram.
39 diagram of the cell membrane of the axon - Wiring ... Diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Cell Structure | The Cell Surface Membrane The RER consists of interconnected membranous sacs (cisternae) - unit membrane enclosing a fluid-filled lumen. The function of the RER is the synthesis, storage and transport of proteins around the cell.
Diagram of the cell membrane of the axon
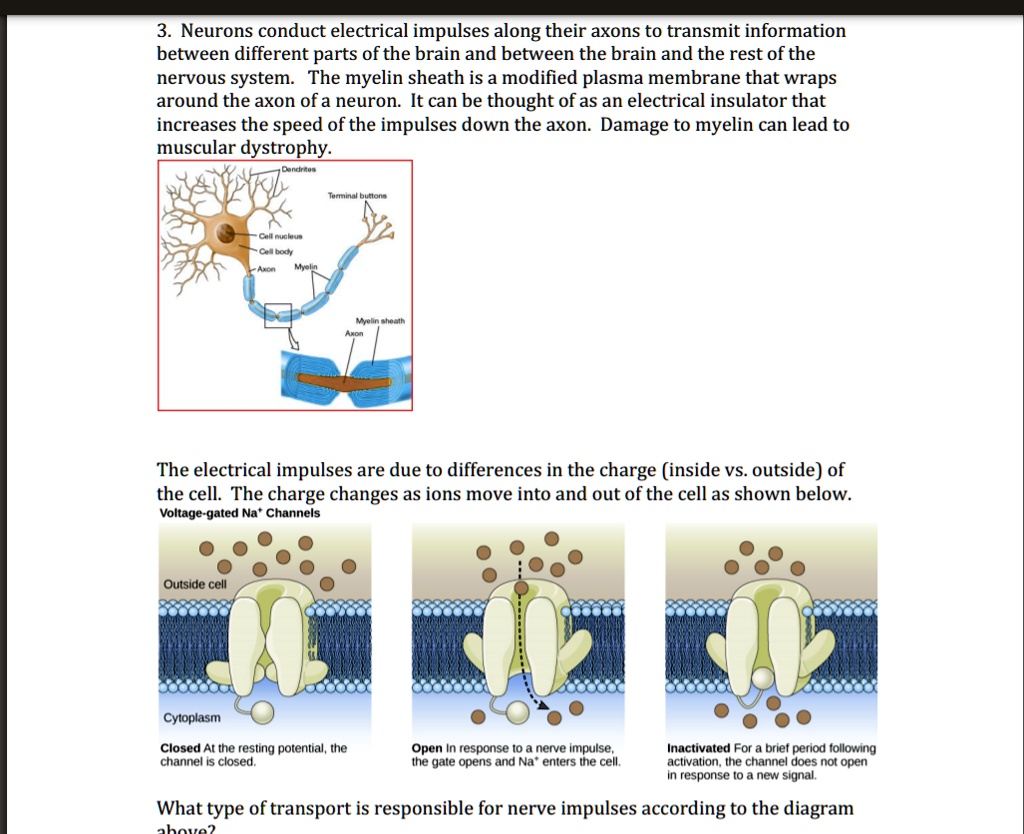
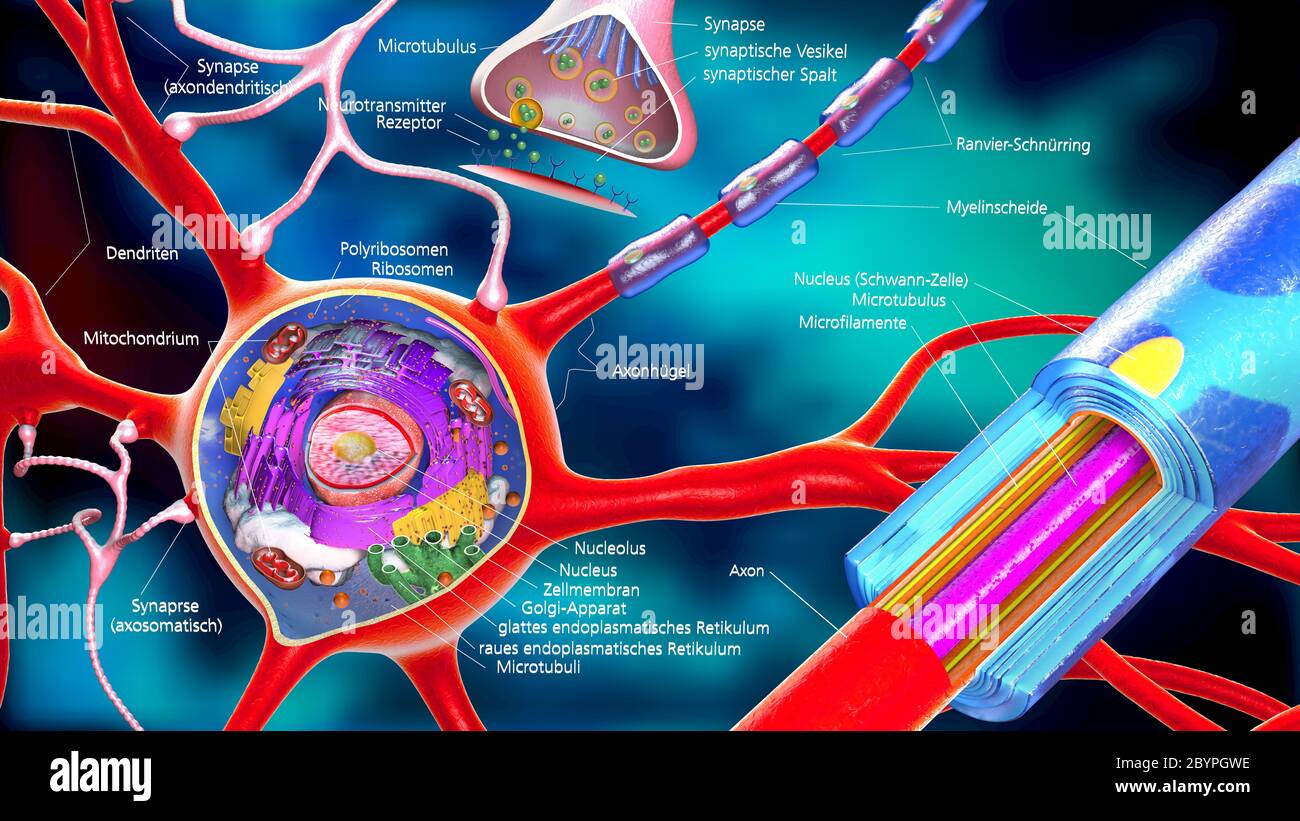
Neuron Diagram, Structure & Function | What Is a Neuron ... In the axon diagram shown below, ... The cell membrane of the neuron creates a charge imbalance across the membrane by pumping sodium ions out of the cell, and potassium ions into the cell. Every ... What Is an Axon Membrane? (with pictures) - Info Bloom The structure and chemical properties of the axon membrane is what enables it to contain an electrical charge, to force its flow in one direction, and to transfer the signal to other cells of the body. For the most part, for most types of nerve cells, the axon is insulated within a protective sheath called myelin. Developmental mechanism of the periodic membrane skeleton ... The brain contains hundred types of neurons, but they are all variations on the same basic structure. Each neuron consists of a cell body that is covered in short protrusions called dendrites and a long thin structure called the axon. The dendrites receive incoming signals from neighboring neurons and they transmit these signals via the cell body to the axon, which in turn relays them to the ...
Diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Plasma membrane structure at the axon hillock, initial ... Plasma membrane structure at the axon hillock, initial segment and cell body of frog dorsal root ganglion cells J Neurocytol . 1985 Oct;14(5):731-47. doi: 10.1007/BF01170825. Synapse Structure - Foundations of Neuroscience But synapses can also be located between the terminal and the cell body of the postsynaptic cell, called axosomatic, or even between the terminal and the axon of the postsynaptic cell, called axoaxonic. Figure 8.3. A) Axodendritic synapses occur when the presynaptic terminal makes a synaptic connection with the dendrite of a postsynaptic neuron. PDF The Action Potential • Positive charge flows along the axon, depolarizing adjacent areas of membrane, which reach threshold and generate an action potential. The action potential thus moves along the axon as a wave of depolarization traveling away from the cell body. • Label where the action potential is in these two diagrams: Page 17. DOCX A2.2.2.StudentResponse - Weebly Draw a diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Label the following on your drawing: cell interi. or, cell exterior, Na + channels, K + channels, Na + /K + pump. The main component of cell membranes are fats called phospholipids. Use the Internet to research the structure of a phospholipid. Label a phospholipid on your diagram.
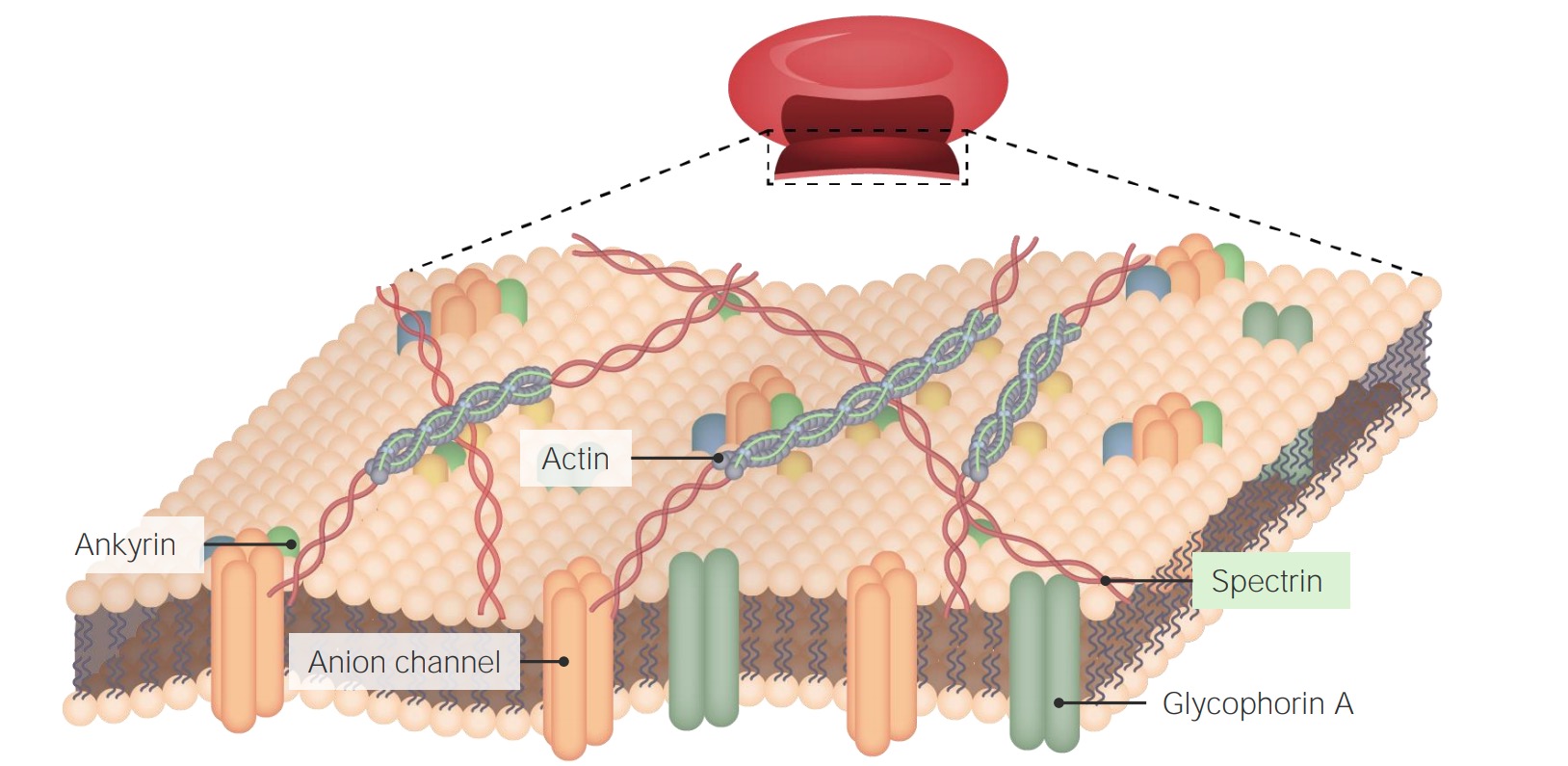
Chapter 12 Lecture Presentation - Houston Community College axon. Basement. membrane. Capillary. A diagram of nervous tissue in the CNS showing relationships between neuroglia and neurons. Internode. Node. 12-3 Neuroglia. Ependymalcells. Form epitheliumthat lines central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain. ... membrane. Schwann. cell. Axon. Myelin. Schwann cell. cytoplasm. Stages . Modeling of the axon plasma membrane structure and its ... Author summary The axon plasma membrane skeleton consists of repeated periodic actin ring-like structures along its length connected via spectrin tetramers and anchored to the lipid bilayer at least via ankyrin. However, it is currently unclear whether this structure controls diffusion of lipids and proteins in the axon. Here, we developed a coarse-grain molecular dynamics computational model ... DOCX A2.2.2.StudentResponse - Rose Millay Draw a diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Label the following on your drawing: cell interi. or, cell exterior, Na + channels, K + channels, Na + /K + pump. The main component of cell membranes are fats called phospholipids. Use the Internet to research the structure of a phospholipid. Label a phospholipid on your diagram. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › NeuronNeuron - Wikipedia The cell membrane of the axon and soma contain voltage-gated ion channels that allow the neuron to generate and propagate an electrical signal (an action potential). Some neurons also generate subthreshold membrane potential oscillations .
byjus.com › biology › diagram-of-neuronA Labelled Diagram Of Neuron with Detailed Explanations Cell Body–Each neuron has a cell body with a nucleus, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and other components. Axon– Axon is a tube-like structure that functions by carrying an electrical impulse from the cell body to the axon terminals for passing the impulse to another neuron. DOC BiologyMad A-Level Biology The diagram shows some of the pump and channel proteins in the cell surface membrane of a neurone. (a) (i) What evidence is there in the diagram that structure . A. ... The effect of this lateral inhibition is shown in the diagram. (i) Explain how one axon of a neurone can be stimulatory, while another axon of the same neurone can be inhibitory. DOCX A2.2.2.StudentResponse - HBS portfolio 2015-16 Draw a diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Label the following on your drawing: cell interi. or, cell exterior, Na + channels, K + channels, Na + /K + pump. The main component of cell membranes are fats called phospholipids. Use the Internet to research the structure of a phospholipid. Label a phospholipid on your diagram. Axon - Wikipedia An axon (from Greek ἄξων áxōn, axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action potentials away from the nerve cell body.The function of the axon is to transmit information to different neurons, muscles, and glands.
Axon Structure And Function - Nerve Cell - MCAT Content Axon is a tube-like structure that carries neural signals away from the cell body via the axon terminals. The cell body contains the axon hillock that collects signals from many synapses. The axon hillock serves as a junction between the cell body and an axon. The axon then delivers these collected signals to specialized endings called axon ...
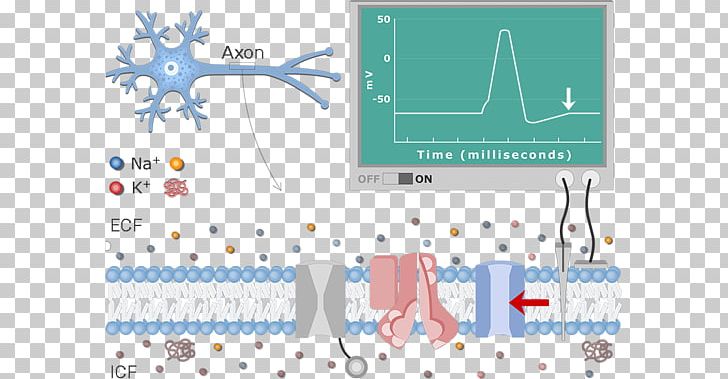
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Membrane_potentialMembrane potential - Wikipedia Membrane potential (also transmembrane potential or membrane voltage) is the difference in electric potential between the interior and the exterior of a biological cell.That is, there is a difference in the energy required for electric charges to move from the internal to exterior cellular environments and vice versa, as long as there is no acquisition of kinetic energy or the production of ...
axon An axon is a typically long outgrowth, or process, of a neuron that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body (soma) toward target cells. Axons are the main transmission lines of the nervous system, and as bundles they help make up nerves.. Individual axons have a diameter of only about one micrometer but may extend to macroscopic lengths.
Axon - Structure and Functions - GetBodySmart Axon - Structure and Functions. All neurons have a cytoplasmic process called an axon (nerve fiber), which conducts electrochemical impulses or action potentials. Axons most commonly attach to one side a neuron cell body (soma, perikaryon), at a cone-shaped region called the axon hillock. Electrochemical events in the cell body summate in the ...
How does the structure of an axon relate to its function? Describe the structure of a neuron with the help of a neat, labelled diagram. Structure of neuron: Nerve cells or neurons are the structural and functional units of the nervous system. It consists of three major parts namely, Cell body, dendrites, Axon. Cell Body: It is irregular in shape or polyhedral.
Chapter 2 Notes.docx - Chapter 2: Structure and Function ... Chapter 2: Structure and Function of Cells of the Nervous System Section 1 CELLS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM I. Neurons - info processing and info transmitting element of the nervous system A. Basic Structure of a Neuron 1. Soma - contains the nucleus and provides for the life processes of the cell 2. Dendrites-tree-like structures attached to the soma which serve as important recipients of these ...
Human Body Axon Diagram - Studying Diagrams No need to register buy now. Axon terminals dendrites cell body axon chandelier axon terminals dendritic tree cell body axon A B FIGURE 1-7A and B Chandelier neurons. Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Posted on June 7 2016 by admin. Draw a diagram of the cell membrane of the axon. Find the perfect human body organs diagram stock photo.
biologydictionary.net › axon-terminalAxon Terminal - The Definitive Guide | Biology Dictionary May 22, 2020 · The axon terminal, also known as the synaptic bouton and terminal bouton, is the most distal portion of a neuron’s axon and is critical for neural communication. When action potentials reach the axon terminal, calcium floods the neuron, allowing synaptic vesicles to fuse with the membrane and release stored neurotransmitters to target cells.
Schwann cell - Wikipedia The vertebrate nervous system relies on the myelin sheath for insulation and as a method of decreasing membrane capacitance in the axon. The action potential jumps from node to node, in a process called saltatory conduction, which can increase conduction velocity up to 10 times, without an increase in axonal diameter. In this sense, Schwann cells are the PNS's analogues …
2.2 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Terms in this set (32) Describe the path of an electrical impulse as it moves through a neuron. Electrical impulses from other neurons come from neurotransmitters. The impulses start at the dendrites, travel through the axon. the myelin sheath and the nodes of Ranvier speed up the process. The impulse then goes through the synapse, until it ...
The Myelin Sheath - Basic Neurochemistry - NCBI Bookshelf The myelin sheath is a greatly extended and modified plasma membrane wrapped around the nerve axon in a spiral fashion [].The myelin membranes originate from and are a part of the Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system and the oligodendroglial cells in the central nervous system (see Chap. 1).Each myelin-generating cell furnishes myelin for only one segment of any given axon.
Action potential - Definition, Steps, Phases - Kenhub An action potential propagates along the cell membrane of an axon until it reaches the terminal button. Once the terminal button is depolarized, it releases a neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. The neurotransmitter binds to its receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of the target cell, causing its response either in terms of stimulation ...
Neprilysin - Wikipedia Neprilysin (/ ˌ n ɛ p r ɪ ˈ l aɪ s ɪ n /), also known as membrane metallo-endopeptidase (MME), neutral endopeptidase (NEP), cluster of differentiation 10 (CD10), and common acute lymphoblastic leukemia antigen (CALLA) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MME gene. Neprilysin is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease that cleaves peptides at the amino side …
Histology, Axon - PubMed The cell membrane of Schwann cells is arranged around the axon, forming a double membrane structure (mesaxon), which elongates and wraps itself in a spiral, in concentric layers, around the axon itself.
Neurons (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The cell membrane of the axon is called axolemma and its cytoplasm is known as axoplasm. The axon ends in a group of branches, the terminal arborizations (= axon terminals or telodendria). When terminal arborizations of the axon meet the dendrites of another neuron to form a synapse they form synaptic knobs (= end plates).
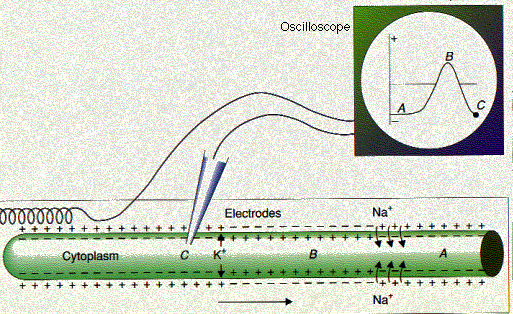
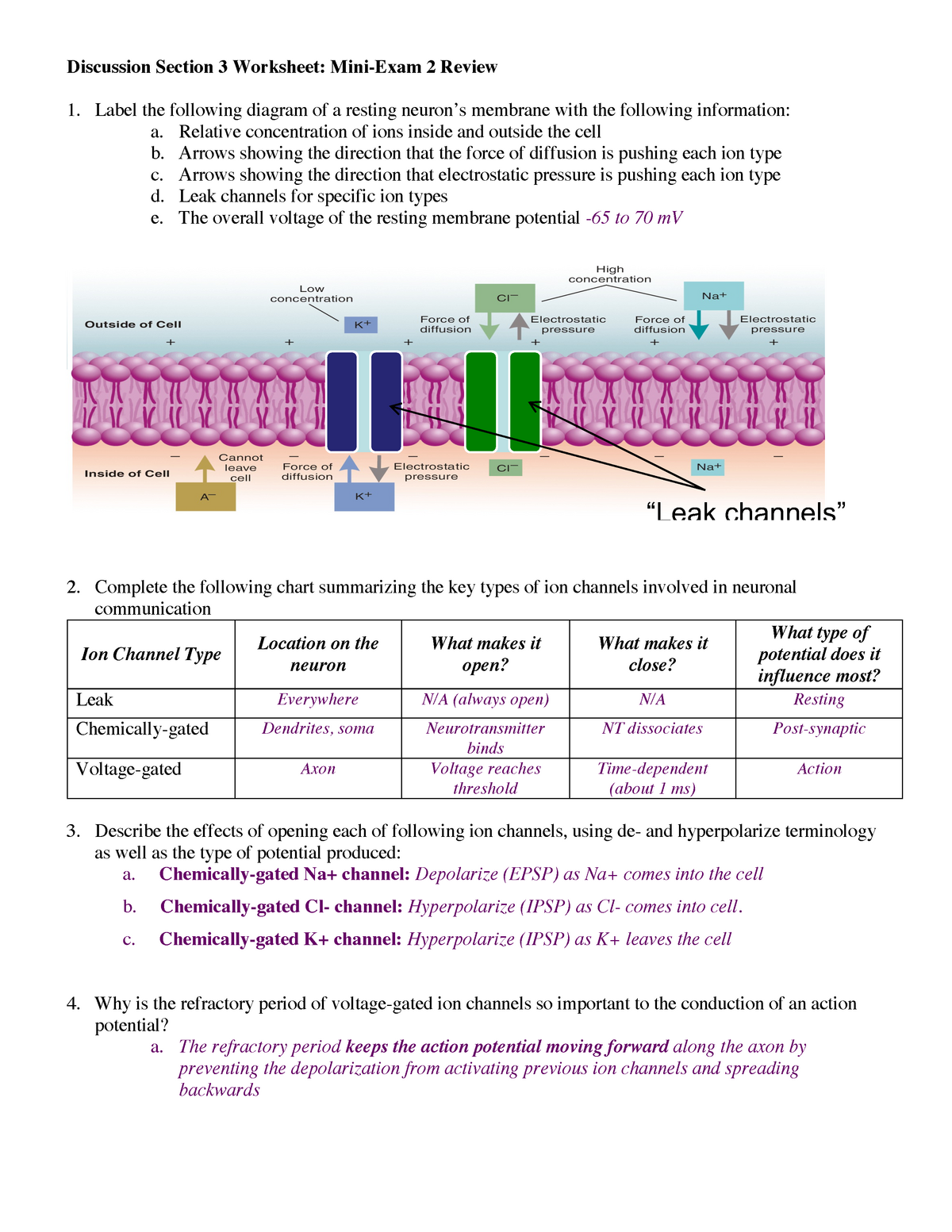
Action Potential - The Resting Membrane Potential ... During the resting state, the membrane potential arises because the membrane is predominantly permeable to K+. An action potential begins at the axon hillock as a result of depolarisation. During depolarisation voltage-gated sodium ion channels open due to an electrical stimulus. As the sodium ions rush back into the cell, their positive charge ...
aqa biology - ch15 nervous coordination and muscles - Quizlet 14. During an action potential, the permeability of the cell-surface membrane of an axon changes. The graph shows changes in permeability of the membrane to sodium ions and to potassium ions during a single action potential. Explain the shape of the curve for sodium ions between 0.5 ms and 0.7ms.
Developmental mechanism of the periodic membrane skeleton ... The brain contains hundred types of neurons, but they are all variations on the same basic structure. Each neuron consists of a cell body that is covered in short protrusions called dendrites and a long thin structure called the axon. The dendrites receive incoming signals from neighboring neurons and they transmit these signals via the cell body to the axon, which in turn relays them to the ...
What Is an Axon Membrane? (with pictures) - Info Bloom The structure and chemical properties of the axon membrane is what enables it to contain an electrical charge, to force its flow in one direction, and to transfer the signal to other cells of the body. For the most part, for most types of nerve cells, the axon is insulated within a protective sheath called myelin.
Neuron Diagram, Structure & Function | What Is a Neuron ... In the axon diagram shown below, ... The cell membrane of the neuron creates a charge imbalance across the membrane by pumping sodium ions out of the cell, and potassium ions into the cell. Every ...




















0 Response to "38 diagram of the cell membrane of the axon"
Post a Comment