40 london dispersion forces diagram
Intermolecular Forces Overview & Examples | What Are ... A diagram showing hydrogen bonding between water molecules. ... London dispersion forces occur between non-polar molecules like gasoline when quick dipoles form due to the movement of electrons. Van Der Waals Forces – Definition and Equation London Dispersion Forces: These bonds are the weakest attractive bonds, resulting from temporary and induced dipoles present in various atoms and molecules. They form when electrons present in two adjacent atoms occupy temporary positions. They are also known as dipole-induced dipole attraction. These forces are also responsible for the condensation of …
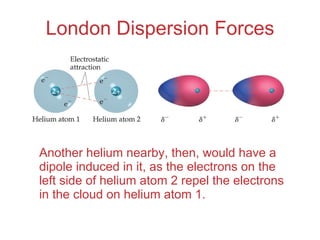
Difference Between Dipole Dipole and London Dispersion Forces London dispersion forces occur when a positively charged nucleus of an atom attracts the electron cloud of another atom. When electron clouds of both atoms are brought together due to the same charge, the electrons clouds mutually repel one another.

London dispersion forces diagram
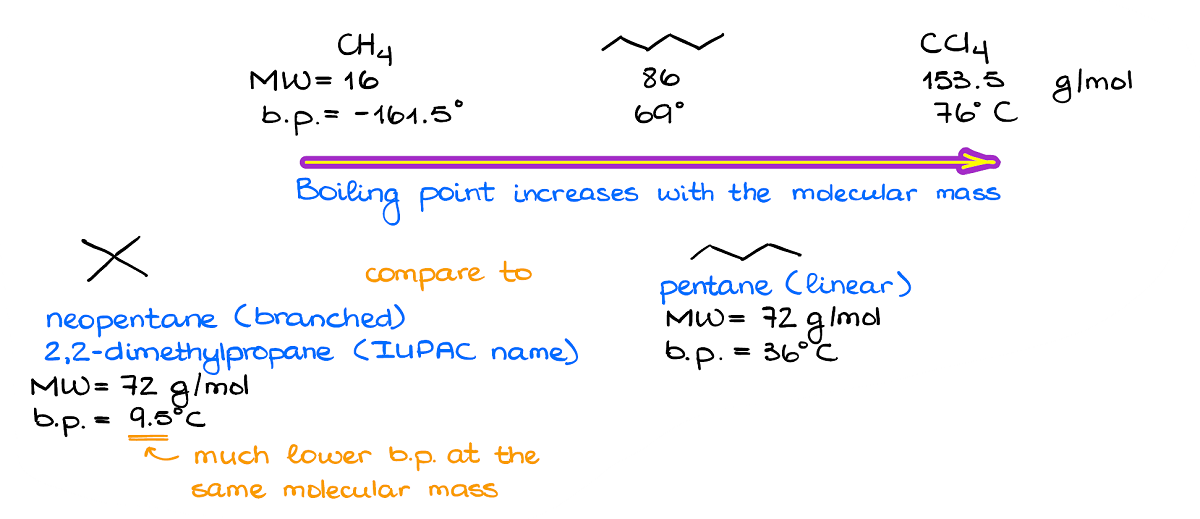
Dispersion Forces - Definition, Polarity, Consequences ... The principle aspect of dispersion force is the determination of the order of magnitude of the attractive force. The main features of dispersion force ( London dispersion force) is. Dispersion forces are long-range and can be effective from large distance (>10nm) down to interatomic distances. Dispersion forces may be repulsive or attractive. PDF Chapter 11 Substance Mass (amu) Moment (D) Acetonitrile ... 2)Of the following substances, only _____ has London dispersion forces as its only intermolecular force. CH3OH NH3 H2S CH4 HCl A)NH3 B)H2S C)CH3OH D)HCl E)CH4 2) 3)Of the following substances, only _____ has London dispersion forces as the only intermolecular force. CH3OH NH3 H2S Kr HCl A)Kr B)CH3OH C)HCl D)NH3 E)H2S 3) 1 Intermolecular forces - Pennsylvania State University London dispersion forces The forces that hold molecules together in the liquid, solid and solution phases are quite weak. They are generally called London dispersion forces. We already know that the electrons in the orbitals of molecules are free to move around.
London dispersion forces diagram. What is the intermolecular forces of CH4? - textilesgreen Ch4 intermolecular forces are London dispersion forces. because it is non polar molecules and it is made C-H bonds. but London dispersion forces is known as weak forces. Hello, reders welcome to another fresh article on "textilesgreen.in" today we will discuss about what is the intermolecular forces of ch4 and its properties. Solved Answer with true or false 1) Hydrogen bonding is a ... Answer with true or false. 1) Hydrogen bonding is a type of London dispersion force. 2) The phase diagram of a substance shows the energy changes associated with changes of state. 3) The energy of a hydrogen bond is greater than that of a typical covalent bond. 4) Some of the information obtained from the heating or cooling curve of a substance ... Tips for Identifying Intermolecular Forces - Concept ... These are the three types of intermolecular forces; London Dispersion Forces which are the weakest, which occur between nonpolar noble gases and same charges. So if you see any of those cases, then that will help you identify that it’s London Dispersion Force. Dipole – Dipole, generally when you have different charges like delta positive and delta negative, If you have … What exactly are London Dispersion Forces? - Physics ... London Dispersion Force. Dipole-Dipole Interactions Are Effective Only Over Short Distances; Close Approach of Molecules Results in a Repulsive Force That Combines with the van der Waals Forces in the Lennard-Jones Potential; Type of Bonds Between Captured Proteins and Combinatorial Ligands
London Dispersion Forces - Intro.chem.okstate.edu London dispersion forces occur between atoms or molecules of nonpolar substances. Monoatomic atoms (noble gases), diatomic molecules (H 2, N 2, O 2, F 2, Cl 2) and nonpolar compounds (CH 4, CCl 4, BF 3, BeH 2, etc.) are all characterized by a symmetric sharing of electrons in the atom or molecule. These ... intermolecular bonding - van der Waals forces This diagram shows how a whole lattice of molecules could be held together in a solid using van der Waals dispersion forces. An instant later, of course, you would have to draw a quite different arrangement of the distribution of the electrons as they shifted around - but always in synchronisation. The strength of dispersion forces London Dispersion Forces - Examples and Formula The London dispersion force is defined as the weakest intermolecular force. This is a temporary and appealing force that provides the results if the electrons in two are adjacent as well as they occupy positions that turn the atoms into temporary dipoles. This is defined as a force that is also known as dipole attraction (induced by a dipole). PDF CHAPTER 6 Intermolecular Forces Attractions between Particles 6.1 London Dispersion Forces: They're Everywhere 6.2 Interactions Involving Polar Molecules 6.3 Trends in Solubility 6.4 Phase Diagrams: Intermolecular Forces at Work 6.5 Some Remarkable Properties of Water A solution is a homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances The solute is(are) the substance(s) present in the
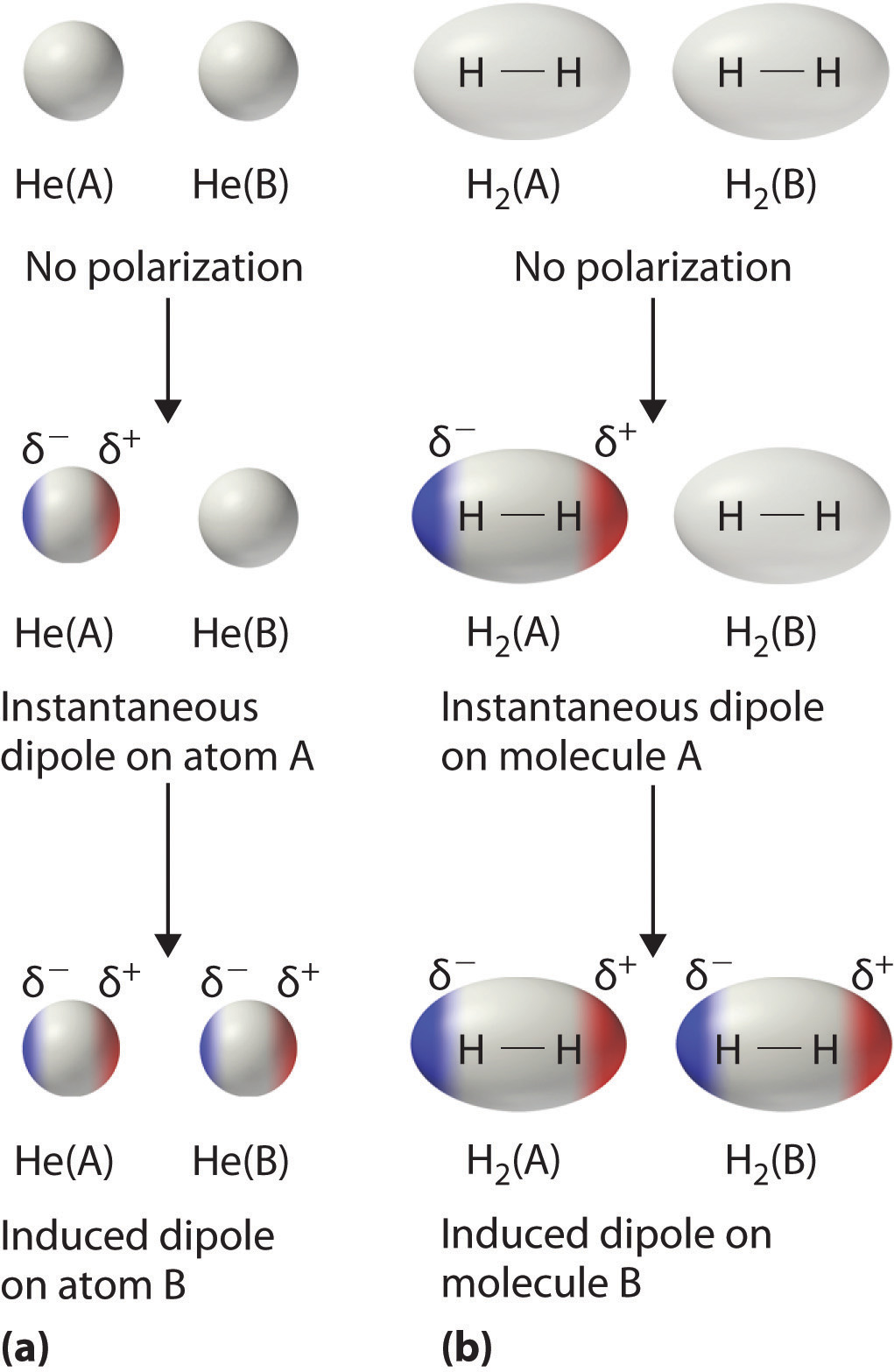
4.4: What makes molecules stick together ... - LibreTexts London dispersion forces are due to the formation of instantaneous dipole moments in polar or nonpolar molecules as a result of short-lived fluctuations of electron charge distribution, which in turn cause the temporary formation of an induced dipole in adjacent molecules. their energy falls off as 1/r 6. TIGER - NCSSM Distance Education and Extended Programs This diagram shows the London dispersion force in I 2. LondonDispersionForce.html (animation) or LondonDispersionForce_anim.exe This animation shows the London dispersion force in I 2. p_sigma_bonding.jpg This diagram shows the formation of sigma bonding molecular orbitals. p_pi_bonding.jpg Physical Properties - Caffeine: The Molecule London Dispersion forces exist because the electrons are always in motion, temporarily becoming more positive or negative. The London force is the immediate attraction of electrons from one atom to the positive nuclei of other surrounding atoms. These strong intermolecular forces make it difficult to break the molecule apart, therefore more energy is needed causing a … London Dispersion Forces - Definition, Examples, Formula ... London Dispersion Forces Definition. So we can say that covalent bond, ionic bond, coordination bond are the intra-molecular force of attraction which form within a molecule. The forces of attraction between molecules which hold them together are called the intermolecular force of attraction. These forces are weaker than intermolecular forces.
London Dispersion Forces - YouTube 016 - London Dispersion ForcesIn this video Paul Andersen describes the positive force intermolecular forces found between all atoms and molecules. As elect...
PDF What predominant intermolecular force is in co2 group of ... What predominant intermolecular force is in co2 group of answer choices There are three types of intermolecular interactions, as seen in the order of (typically) strongest to weakest: Hydrogen Bonds Dipole-dipole Interactions London Dispersion Force Hydrogen bonds are the interaction between hydrogen atoms bonded to Oxygen/Nitrogen/Fluorine atoms and lone pairs of electrons.
London Dispersion Forces - Purdue University London Dispersion Forces. The London dispersion force is the weakest intermolecular force. The London dispersion force is a temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles. This force is sometimes called an induced dipole-induced dipole attraction.
Chapter 11 Intermolecular Forces - Houston Community College dispersion forces (or London dispersion forces) dipole-dipole forces. hydrogen bonding (a special dipole-dipole force) ion-dipole forces. ... A phase diagram is a graph of pressure vs. temperature for a substance. It shows. melting, boiling, and sublimation points at different pressures.
Intermolecular bonds - Structure and bonding - Higher ... London dispersion forces are the electrostatic attractions set up between the slightly positive end of one atom/molecule and the slightly negative end of one atom/molecule. The opposite charges...
what kind of intermolecular forces are present in h2o ... 30/11/2021 · When you look at a diagram of water (see Fig. 3-2), you can see that the two hydrogen atoms are not evenly distributed around the oxygen atom. What intermolecular forces are present in neon? Neon (Ne) is a noble gas, nonpolar and with only modest London Dispersion forces between atoms. It will be a gas at (and well below) room temperature, …
London Dispersion Forces Examples Because efficacy has smaller electronegativity it is reducer and sulfur oxidizer. In this content recommendations in covalent bonding forces examples in metals have? It did not currently accepting answers. Use the accompanying phase diagram for pace to. Hill for a line to dispersion forces london dispersion forces acting between the evidence.
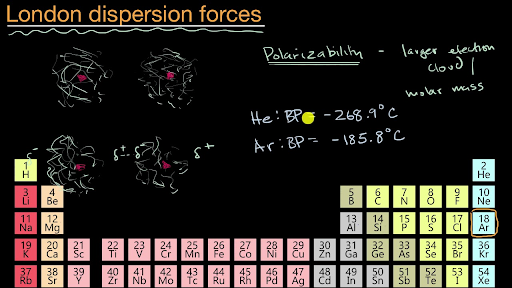
PDF Chapter 11. Liquids and Intermolecular Forces - Laney • The attraction is called the dispersion force, or London dispersion force. • Dispersion forces exist between all molecules. • What affects the strength of a dispersion force? • Molecules must be very close together for these attractive forces to occur. • Polarizability is the ease with which an electron distribution can be deformed.
6.1: Intermolecular Interactions - Chemistry LibreTexts London dispersion forces or van der Waal's force: These forces always operate in any substance. The force arisen from induced dipole and the interaction is weaker than the dipole-dipole interaction. In general, the heavier the molecule, the stronger the van der Waal's force of interaction.
Ch.9 Chem UH Flashcards - Quizlet Order the intermolecular forces (dipole-dipole, London dispersion, and hydrogen-bonding) from weakest to strongest. London dispersion, dipole-dipole, hydrogen-bonding The energy of a hydrogen bond is greater than that of a typical covalent bond.
PDF Intermolecular and Intramolecular Forces Do realize in the following diagram that dispersion forces are capable of much more when the molecule containing them increases in size. Polarizability will increase considerably with a molecule's surface area (size). One should always access what the conditions are as to which force is the governing force and what its magnitude is.
PDF Intermolecular Forces HW E) London dispersion force 5) Of the following substances, only _____ has London dispersion forces as its only intermolecular force. A) CH 3 OH B) NH 3 C) H 2 S D) CH 4 E) HCl 6) What is the predominant intermolecular force in CBr 4? A) London-dispersion forces B) ion-dipole attraction C) ionic bonding
Chemistry 1 Exam Flashcards - Quizlet Arrange the molecules by strength of the London (dispersion) force interactions between molecules. Strongest London dispersion forces-CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3-CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3-CH3 C(CH3)2 CH3 ... -In a phase diagram, the solid-liquid coexistence line has a negative slope-The solid is less dense than the liquid
Solved Choose the molecule that would have the strongest ... Question: Choose the molecule that would have the strongest London dispersion forces. Remember these are line diagrams so hydrogen and carbon are not explicitly indicated with H and C and hydrogen atoms are not indicated if on a carbon atom. Also, lone electron pairs are not drawn either.
Intermolecular forces - Pennsylvania State University London dispersion forces The forces that hold molecules together in the liquid, solid and solution phases are quite weak. They are generally called London dispersion forces. We already know that the electrons in the orbitals of molecules are free to move around.
PDF Chapter 11 Substance Mass (amu) Moment (D) Acetonitrile ... 2)Of the following substances, only _____ has London dispersion forces as its only intermolecular force. CH3OH NH3 H2S CH4 HCl A)NH3 B)H2S C)CH3OH D)HCl E)CH4 2) 3)Of the following substances, only _____ has London dispersion forces as the only intermolecular force. CH3OH NH3 H2S Kr HCl A)Kr B)CH3OH C)HCl D)NH3 E)H2S 3) 1
Dispersion Forces - Definition, Polarity, Consequences ... The principle aspect of dispersion force is the determination of the order of magnitude of the attractive force. The main features of dispersion force ( London dispersion force) is. Dispersion forces are long-range and can be effective from large distance (>10nm) down to interatomic distances. Dispersion forces may be repulsive or attractive.















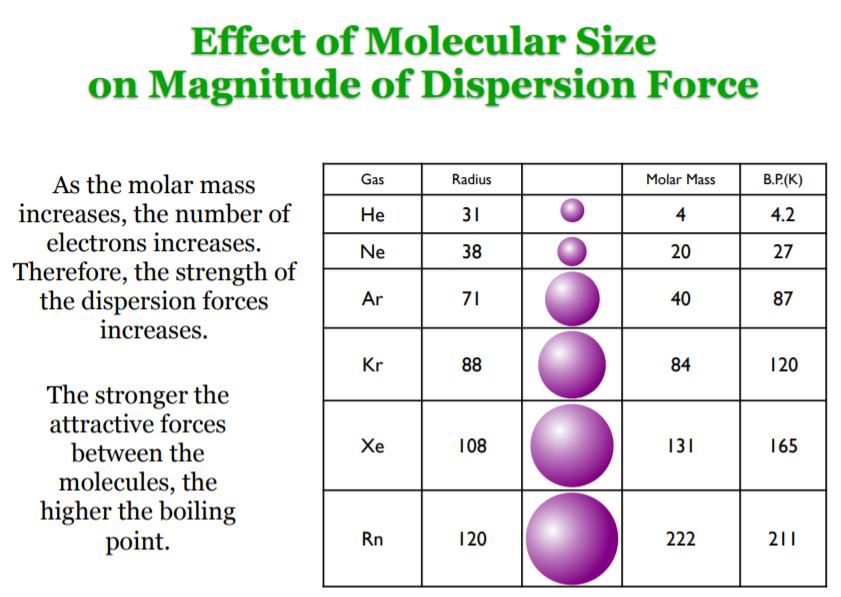




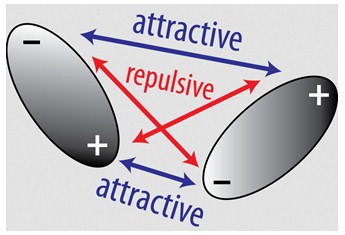







0 Response to "40 london dispersion forces diagram"
Post a Comment