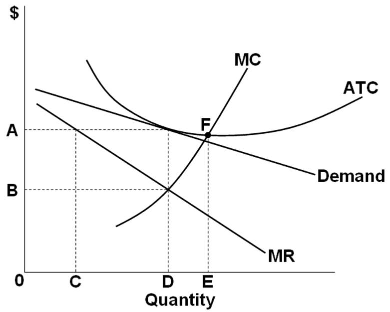
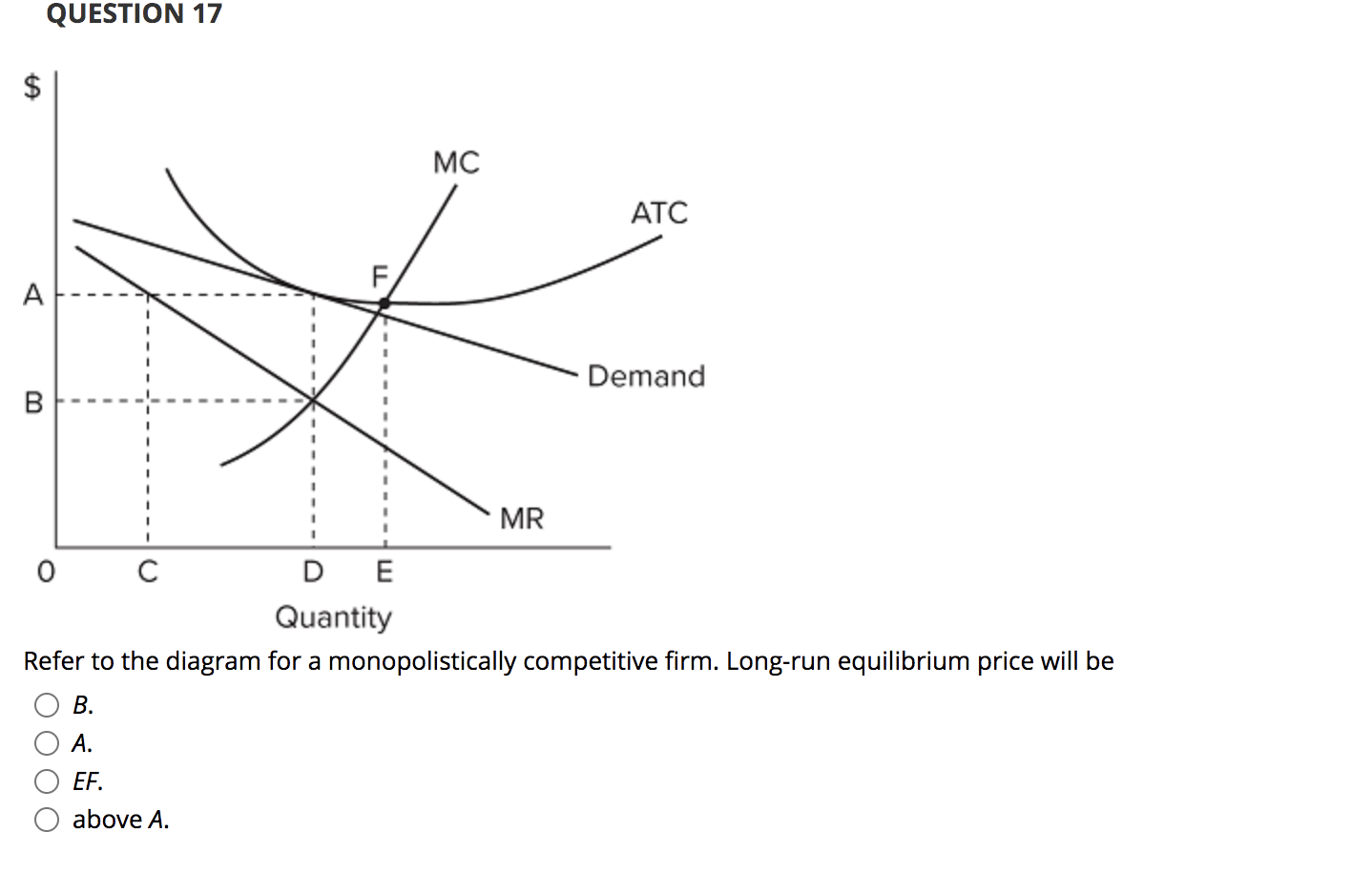
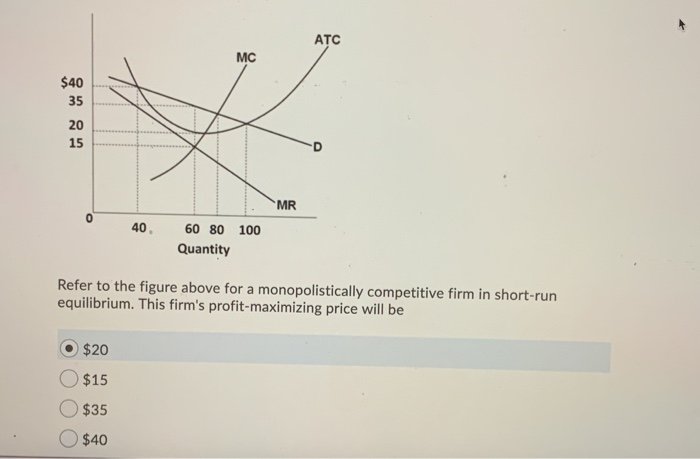
40 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
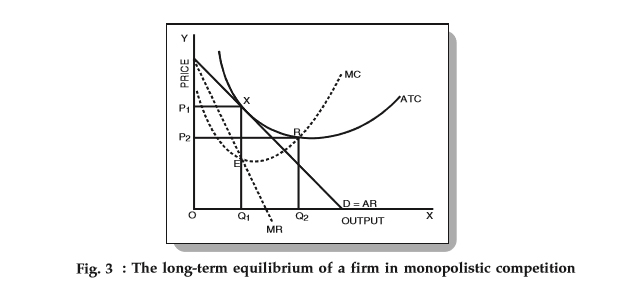
Solved 1.Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically Long-run equilibrium output will be: a. greater than E. 2.Refer to the diagram. In short-run equilibrium, the monopolistically competitive firm shown will set its price Long Run Equilibrium of Competitive Firm and Industry In the long run, a firm achieves equilibrium when it adjusts its plant/s to produce output at the minimum point of their long-run Average Cost (AC) curve. This leads to an increase in the quantity supplied, shifting the supply curve to the left and a fall in the price, until it reaches the point OP1.
10.1 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Economics A monopolistically competitive firm perceives a demand for its goods that is an intermediate case Monopolistic competition refers to an industry that has more than a few firms, each offering a The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price in much the...

Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be
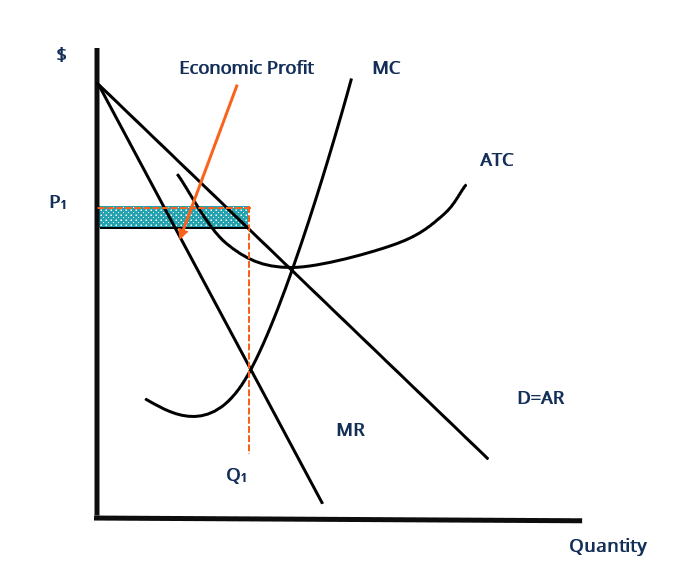
SOLVED:Make a case for why monopolistically competitive... The long-run equilibrium is considered when firms providing same products are having zero profits in long-run but in monopolistically competitive industries, the differentiation between But this action leads to fact that monopolistically competitive firms are not able to reach long-run equilibrium. IB Economics Syllabus 2020 (New) - Qurious Education Diagram: monopolistically competitive firm showing: • abnormal profit • normal profit • losses Diagram: monopolistic competition (with a • Macroeconomic equilibrium • Short-run equilibrium • Equilibrium in the monetarist/new classical model Determination of long-run equilibrium at full... Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive Firm... A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is 350 price is 300 marginal revenue is 150 and marginal cost is 150. If more firms would enter the industry and product differentiation would weaken. At the long run equilibrium level of...
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be. Monopolistic competition Monopolistically competitive firms are assumed to be profit maximisers because firms tend to be Equilibrium under monopolistic competition. In the short run supernormal profits are possible, but Super-normal profits attract in new entrants, which shifts the demand curve for existing firm to the left. Chapter 10: Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly Flashcards Monopolistically competitive firms ignore the effect of their decisions upon other firms in the industry because. a. each firm is large relative to the market. all firms follow the same known pricing rules. b. each firm is small relative to the market. 9. Monopolistic competition is different from perfect... Monopolistic Competition - Introduction to Microeconomics Monopolistic competition refers to a situation where firms have a monopoly on their own product but they must Thus, although a monopolistically competitive firm may earn positive economic profits in the short term, the The adjustment to long-run equilibrium is analogous to the previous example. Perfect Competition | Boundless Economics | Firm Revenues Perfect Competition in the Long Run: In the long-run, economic profit cannot be sustained. The arrival of new firms in the market causes the demand A perfectly competitive firm faces a demand curve is a horizontal line equal to the equilibrium price of the entire market. Learning Objectives.
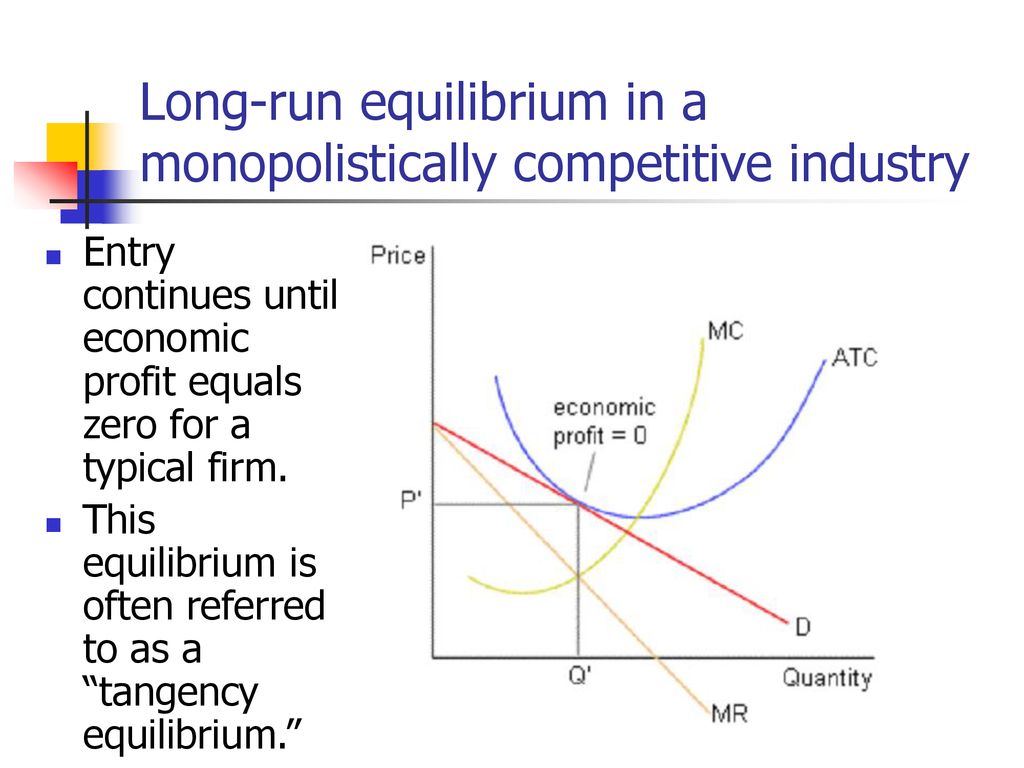
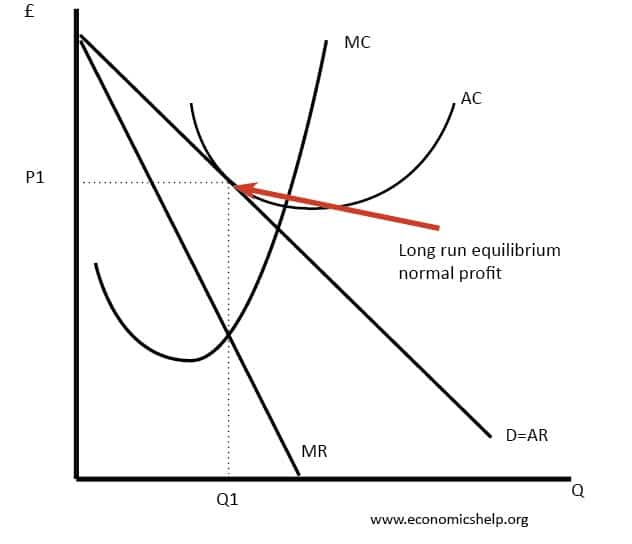
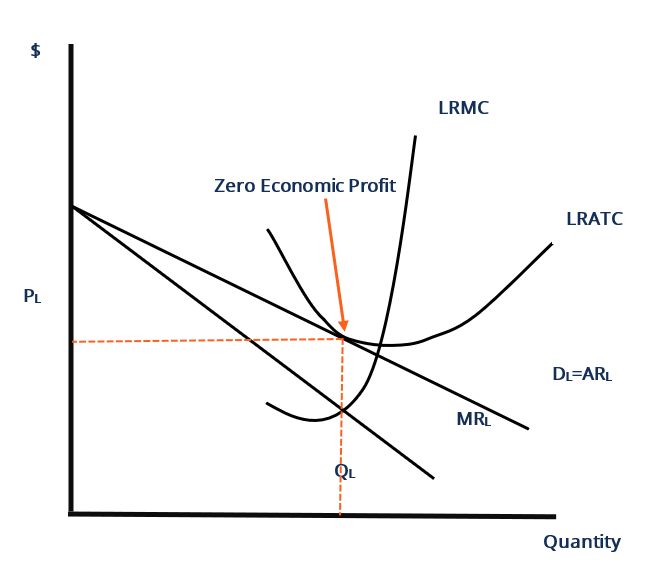
OneClass: How does the long-run equilibrium for a monopolistically... One way in which monopolistically competitive markets and perfectly competitive markets differ is that in long-run equilibrium, monopolistically competitive firms. A. charge a price greater than marginal cost. B. do not earn zero economic profits. PDF Chapter 12 What happens to the equilibrium price and quantity in such a market if one firm introduces a new, improved product? Suppose a monopolistically competitive firm is making a profit in the short run. What will happen to its demand curve in the long run? You are hired as the consultant to a monopolistically competitive firm. For long run equilibrium, price should be equal to average total cost. If price is greater than ATC, firms will be having profits which will attract other potential firms to enter the market. This will increase the supply, consequently price will fall and so will profit. This process continues till P=ATC. Different Market Structures - CAIE A-level Economics - PMT 2 Perfect competition - characteristics and long-run equilibrium. This video explains the characteristics of monopolistic competition and breaks down the long-run diagram of a monopolistically competitive firm earning normal profits.
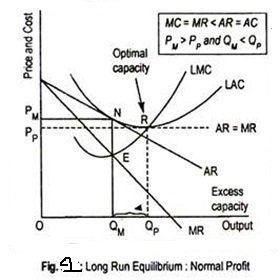
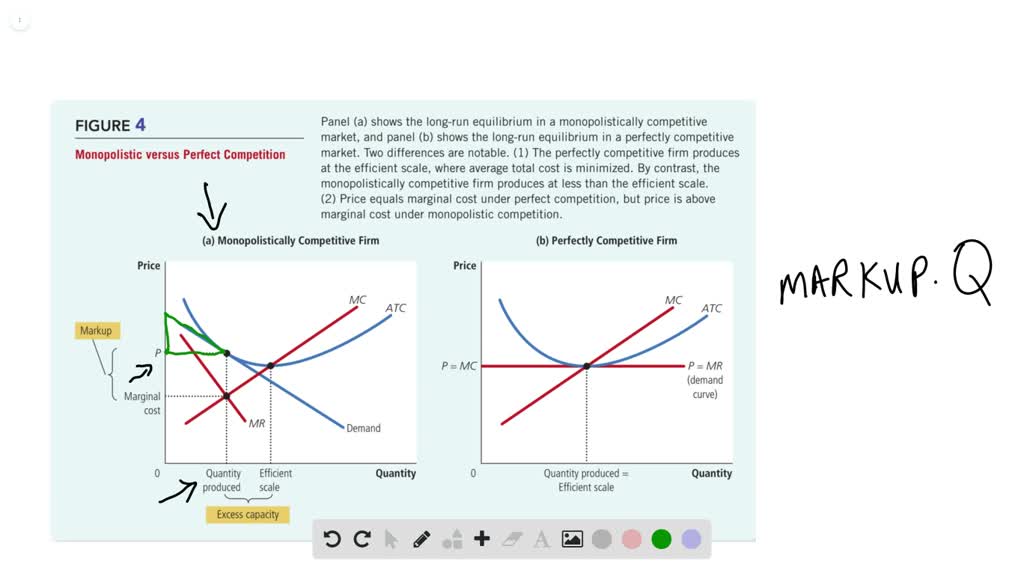
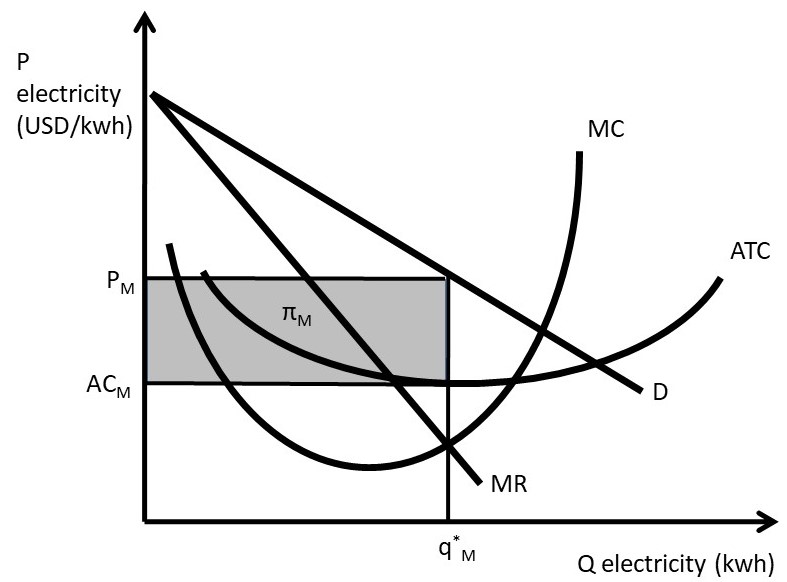
TESTING FOR "MONOPOLY" EQUILIBRIUM* | Semantic Scholar The authors develop simple models of oligopolistic, competitive, and monopolistically-competitive markets for which this test statistic may take on @article{Panzar1987TESTINGF, title={TESTING FOR "MONOPOLY" EQUILIBRIUM*}, author={John C. Panzar and James N. Rosse}, journal... Monopolistic Competition - Overview, How It Works, Limitations Companies are not price takersPrice TakerA price taker, in economics, refers to a market participant that is not The short-run equilibrium under monopolistic competition is illustrated in the diagram below Long-Run Decisions on Output and Price. In the long run, companies in monopolistic... Monopolistic Competition [ch. 16] - ProProfs Quiz In the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm produces at the efficient scale while a competitive firm has excess capacity. Monopolistically competitive firms charge prices equal to the minimum of their average total cost just like competitive firms. Equilibrium of a Firm under Monopolistic Competition Long run equilibrium is achieved at point E where LMC equals MR (Fig. 5.16). The equilibrium output thus determined is OQM. The firm gets normal profit by selling OQM output at the price OPM. Note that a monopolistically competitive firm always operates somewhere to the left of the minimum...
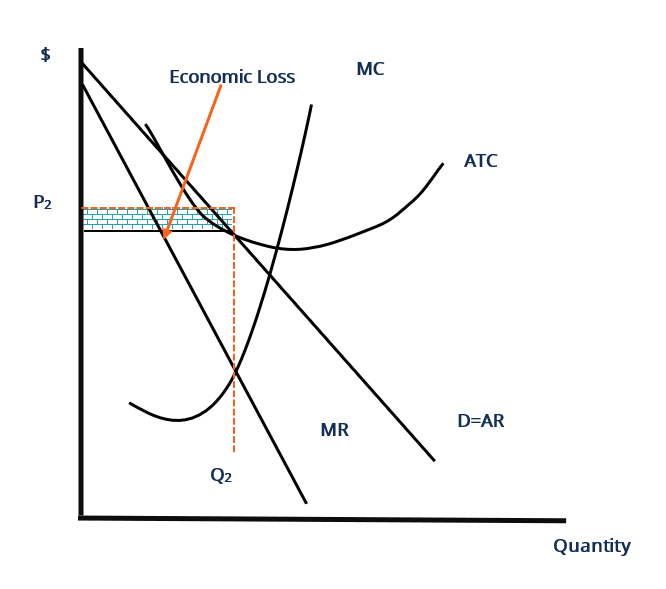
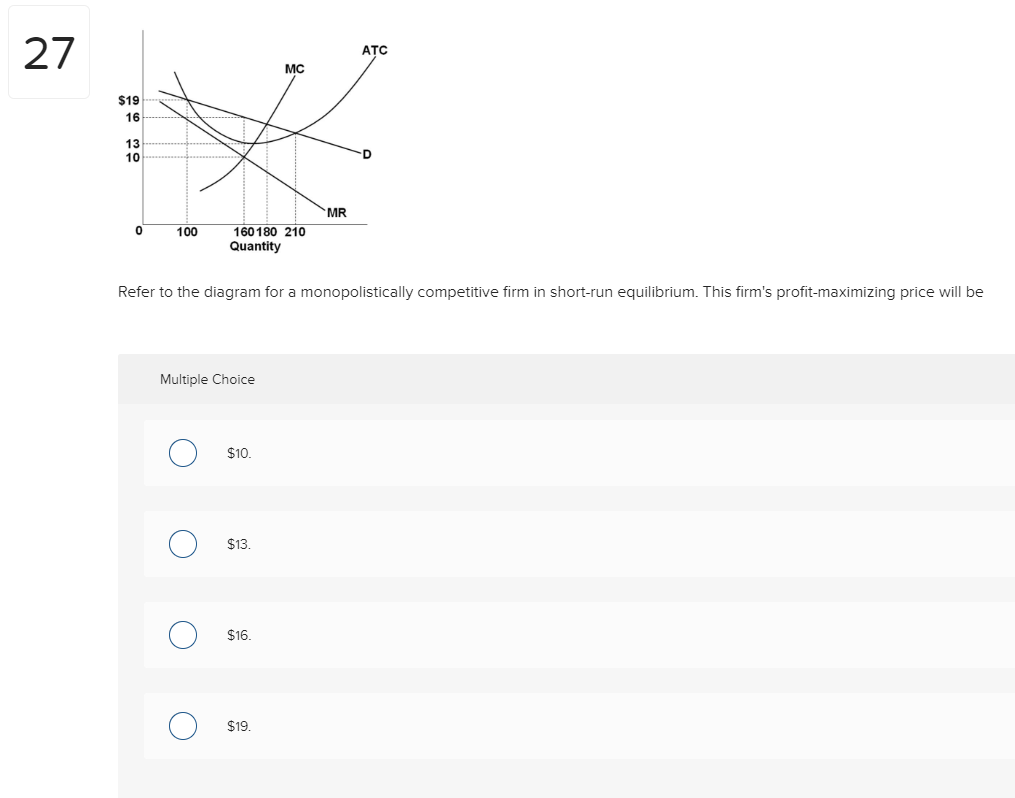
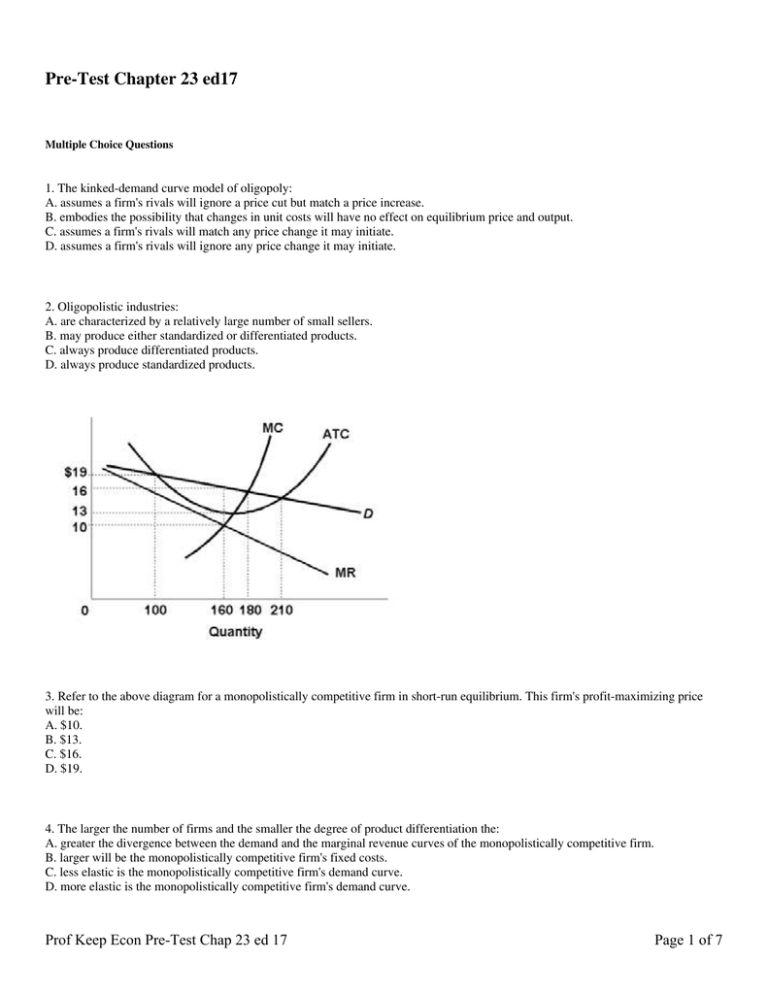
Econ 212-Micro Chapter 13 Quiz Flashcards | Quizlet Purely competitive firms, monopolistically competitive firms, and pure monopolies all earn positive economic profits in the long run. Refer to the above graphs. A short-run equilibrium that would result in losses for a monopolistically competitive firm would be represented by graph A. B. C. D.
Suppose that a typical firm in a monopolistically competitive industry... 1. How much will the firm produce in the short run? 2. What price will it charge? 51. A monopolistically competitive firm is producing an output level where marginal revenue. perfectly competitive industry. Each firm having identical cost structures. long-run average cost is minimized...
Econmentor.com - Market Equilibrium in Monopolistic Competition Long run equilibrium under perfect competition. MR is below AR (price) because the monopolistically competitive firm has to lower price in order to sell more. We draw a vertical from the equilibrium output Q, all the way up-to the demand curve.
Free Business Flashcards about ECON 201 (Micro) long-run average total cost is decreasing. A monopolistically competitive industry combines elements of both competition and monopoly. Refer to the figure about, which is the output schedule of a firm using input X. Under pure competition, the market price of output is $3.
PDF Lab 12: Perfectly Competitive Market Once the equilibrium price is determined, all the buyers and sellers have to accept it if they want to 2. Profit maximization in the short run 1) For a firm in a perfectly competitive market, price is equal to both average revenue and marginal revenue. firms will be attracted to this market in the long run.
Monopolistic competition - Wikipedia Long-run equilibrium of the firm under monopolistic competition. The firm still produces where This means in the long run, a monopolistically competitive firm will make zero economic profit. It will reduce the supply due to which price would rise and the existing firms will be left only with...
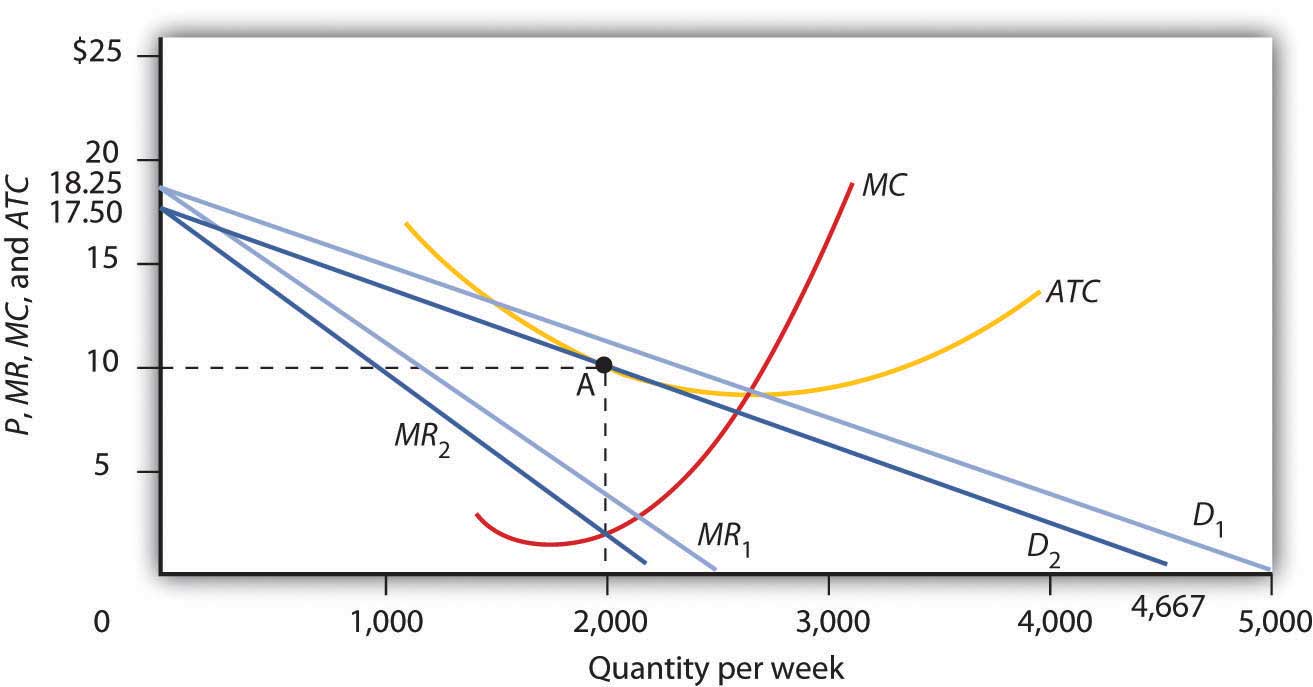
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics A monopolistically competitive firm faces a demand for its goods that is between monopoly and The monopolistically competitive firm decides on its profit-maximizing quantity and price similar to the Monopolistic Competitors and Entry. Consider the profits of Rogers at equilibrium quantity of...
Excess Capacity under Monopolistic or Imperfect Competition... Long-run equilibrium of a firm under monopolistic competition is achieved when the demand Thus a monopolistically competitive firm produces less than the socially optimum or ideal output, that is It is due to the existence of excess capacity that average cost of production and price of product are...
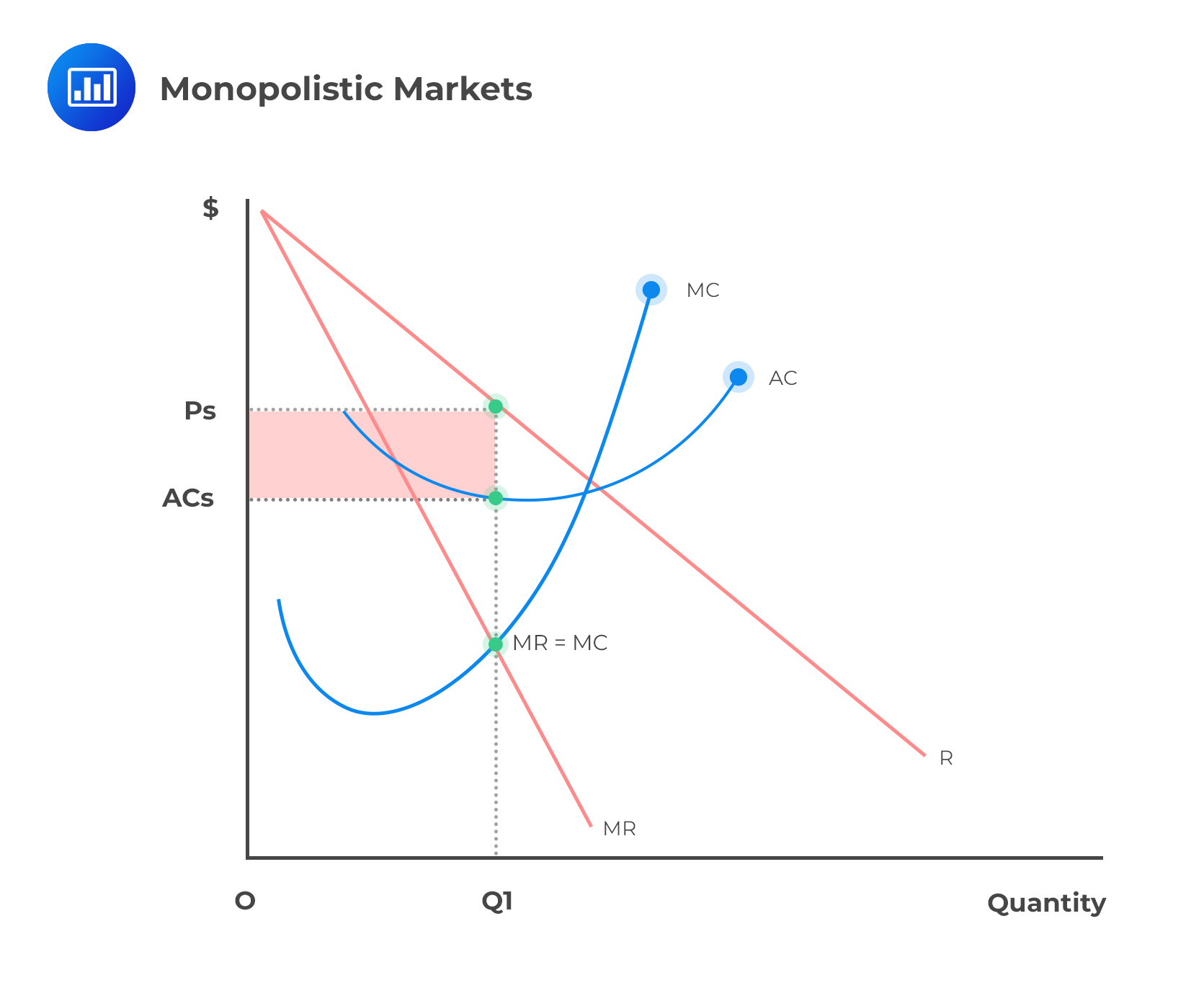
Refer to Figure 11 3 A monopolistically competitive firm is allocatively ...competitive firm is allocatively inefficient because in the long - run equilibrium 59) competition in the long run Skill: Applied 60) Refer to Figure 11 - 3. A monopolistically The diagram below shows selected cost and revenue curves for a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry.
Microeconomics Yellow Pages ANSWERS Unit 3 - Harper ... price will be: 1. above A. 2. EF. 3. A. 4. B. 8. Refer to the above diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. Long-run equilibrium output will be:.51 pages
Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive... The selling price for this firm is above the market equilibrium price. Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. Show transcribed image text minimizing losses in the long run. Refer to the above diagram where the numerical data show profits in millions of dollars.
Profit, Optimal Price, Optimal Output | CFA Level 1 - AnalystPrep Optimal Price and Output in Monopolistically Competitive Markets. Moreover, when we have a Cournot model (in which companies compete on the amount of output they will produce), every firm assumes that the other firms cannot alter their price levels of output with respect to the dominant firm.
Test: Microeconomics Final Multiple Choice | Quizlet In long run equilibrium, a monopolistically competitive firm is producing at a point on its average total cost curve where A. Firms have excess capacity. B. Firms spend too much on product development. C. Firms are too small relative to the market.
Refer To The Diagram For A Monopolistically Competitive Firm... A monopolistically competitive firm is producing at an output level in the short run where average total cost is 350 price is 300 marginal revenue is 150 and marginal cost is 150. If more firms would enter the industry and product differentiation would weaken. At the long run equilibrium level of...
IB Economics Syllabus 2020 (New) - Qurious Education Diagram: monopolistically competitive firm showing: • abnormal profit • normal profit • losses Diagram: monopolistic competition (with a • Macroeconomic equilibrium • Short-run equilibrium • Equilibrium in the monetarist/new classical model Determination of long-run equilibrium at full...
SOLVED:Make a case for why monopolistically competitive... The long-run equilibrium is considered when firms providing same products are having zero profits in long-run but in monopolistically competitive industries, the differentiation between But this action leads to fact that monopolistically competitive firms are not able to reach long-run equilibrium.







![Solved] The Diagram Below Shows Demand and Cost Curves for a ...](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5441/11ea71cb_f380_68da_91e5_a7c4098536ab_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00_TB5441_00.jpg)





0 Response to "40 refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive firm. long-run equilibrium price will be"
Post a Comment