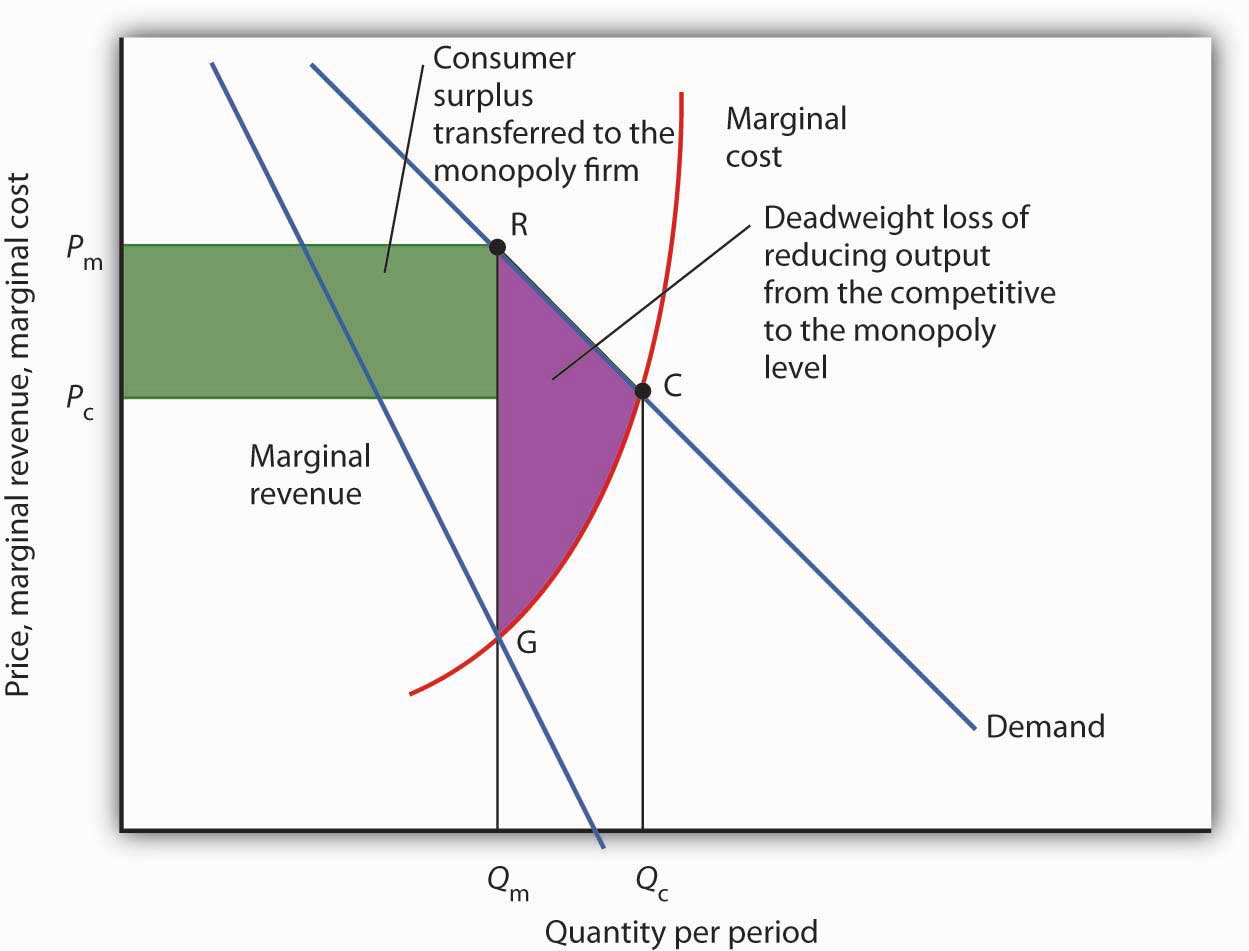
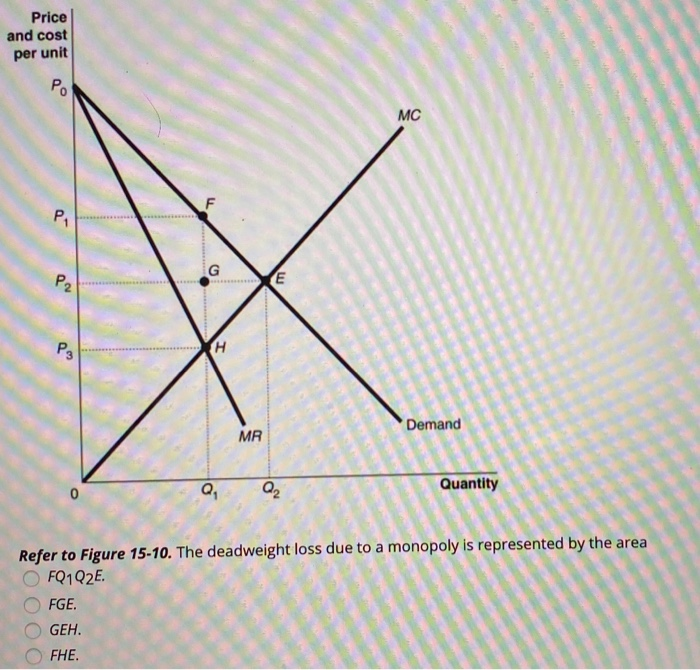
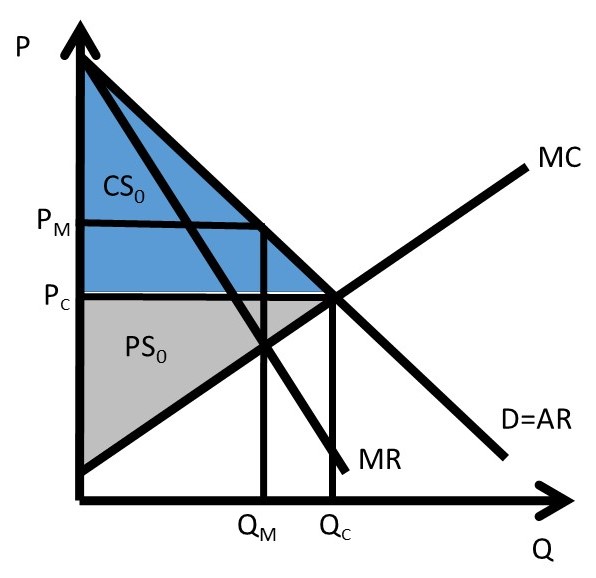
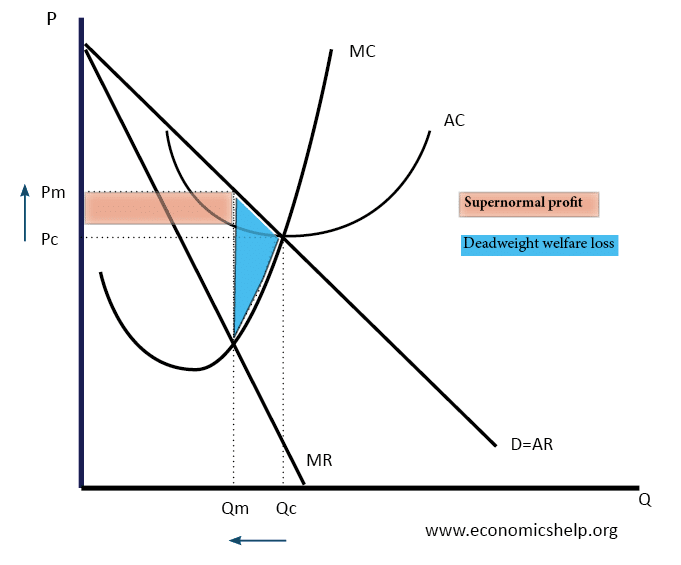
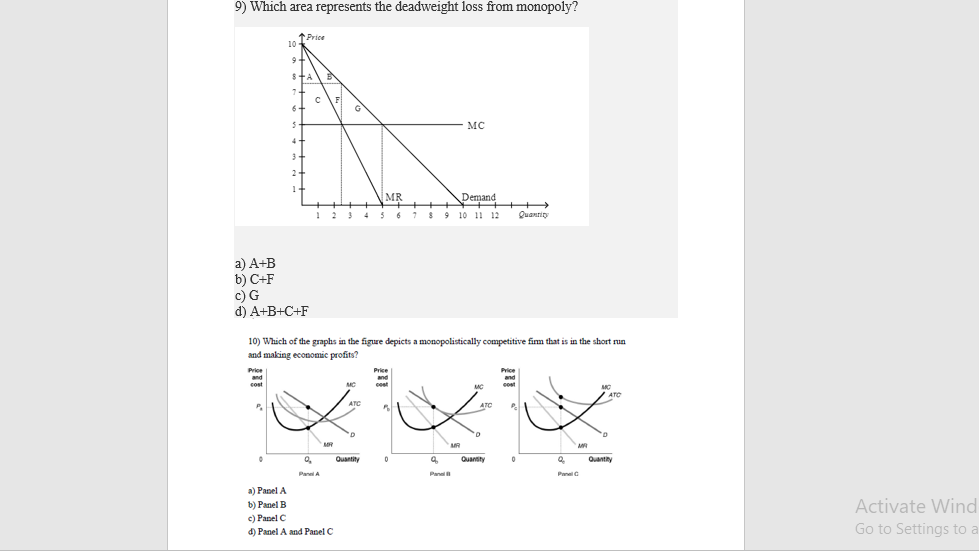
37 refer to the diagram to the right. the deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area
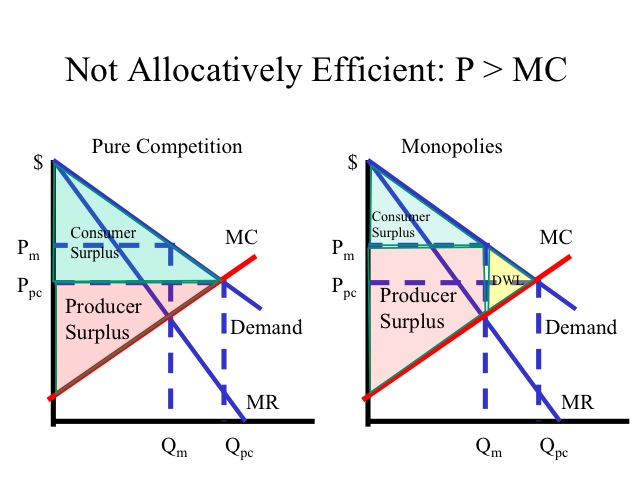
Chapter 8 Solutions | Principles Of Economics 7th ... - Chegg In the below diagram 1.2, it is shown that as price increases from P to Pc, which means consumers has to pay P C, thus, the area under consumer surplus will decrease. Whereas producer will receive P S and producer surplus will also decrease, here P C = P S + $1. (Get Answer) - Consider the natural monopoly depicted in ... Problem 4.3, Review the figure to the right on the inefficiency of monopoly.. the deadweight loss due to monopoly be larger if the demand is elastic or if it is inelastic? Briefly explain. \Then a monopoly. maximizes profit, deadweight loss WM be...
› 37077456 › Instructors_Manual(PDF) Instructor's Manual with Solutions ... - Academia.edu Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Refer to the diagram to the right. the deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area
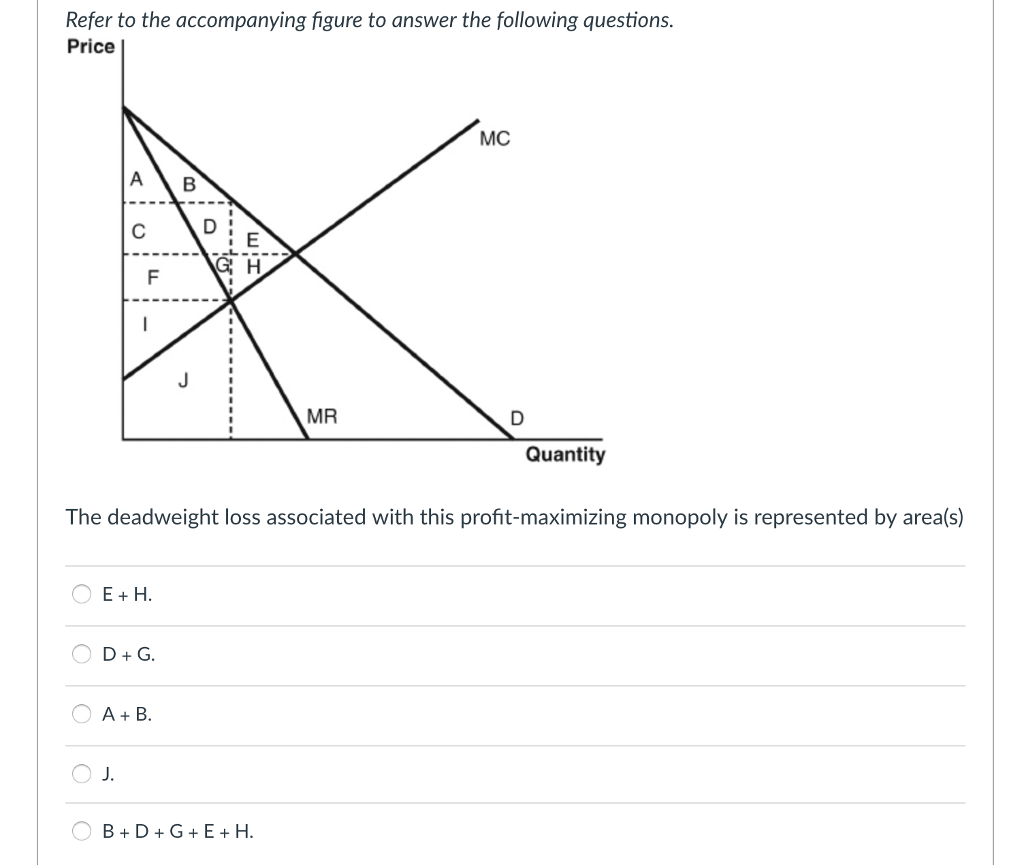
Deadweight Loss Definition - Investopedia A deadweight loss is a cost to society created by market inefficiency, which occurs when supply and demand are out of equilibrium. Mainly used in economics, deadweight loss can be applied to any ... Solved Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight ... Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area MC Po C O A. FHE B. FQ,Q, F C. FGE. Price and cost per unit ($) G D. GEH H MR D 0 2 Q2 Quantity This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics At a price of $70/month, ATC is only $60 and Rogers' profit is $36 million. ($10 profit/subscriber) Notice that this market creates a deadweight loss equal to the red area since the equilibrium quantity is less than what would occur in competitive equilibrium (5 million subscriptions).
Refer to the diagram to the right. the deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area. PDF Study Questions (with Answers) - University of Michigan deadweight losses that they cause. c. The deadweight loss due to protection consists primarily of lost quota rents. d. The deadweight loss due to U.S. protection is large, more than 7% of U.S. GDP. e. The losses to foreigners due to U.S. protection are negligible, and can be ignored in estimating the global effects of U.S. trade policies. Ans: a 6. Stanford University UNK the , . of and in " a to was is ) ( for as on by he with 's that at from his it an were are which this also be has or : had first one their its new after but who not they have – ; her she ' two been other when there all % during into school time may years more most only over city some world would where later up such used many can state about national out known university united … History of microeconomics - Wikipedia He states that as an individual wealth increases so will his utility increase in inverse proportion to quantity of goods already possessed. This is called diminishing marginal utility in microeconomics textbooks. He also describes the following problem. "My most honorable cousin the celebrated Nicolas Bernoulli, Professor utriusque iuris at the University of Basle, once submitted five … PDF Chapter 10 Market Power: Monopoly and Monopsony The social gain arises from the elimination of deadweight loss. Deadweight loss in this case is equal to the triangle above the constant marginal cost curve, below the demand curve, and between the quantities 5.67 and 11.3, or numerically (18.5-10)(11.3-5.67)(.5)=$24.10. Consumers gain this deadweight loss plus the monopolist's profit of $48.17.
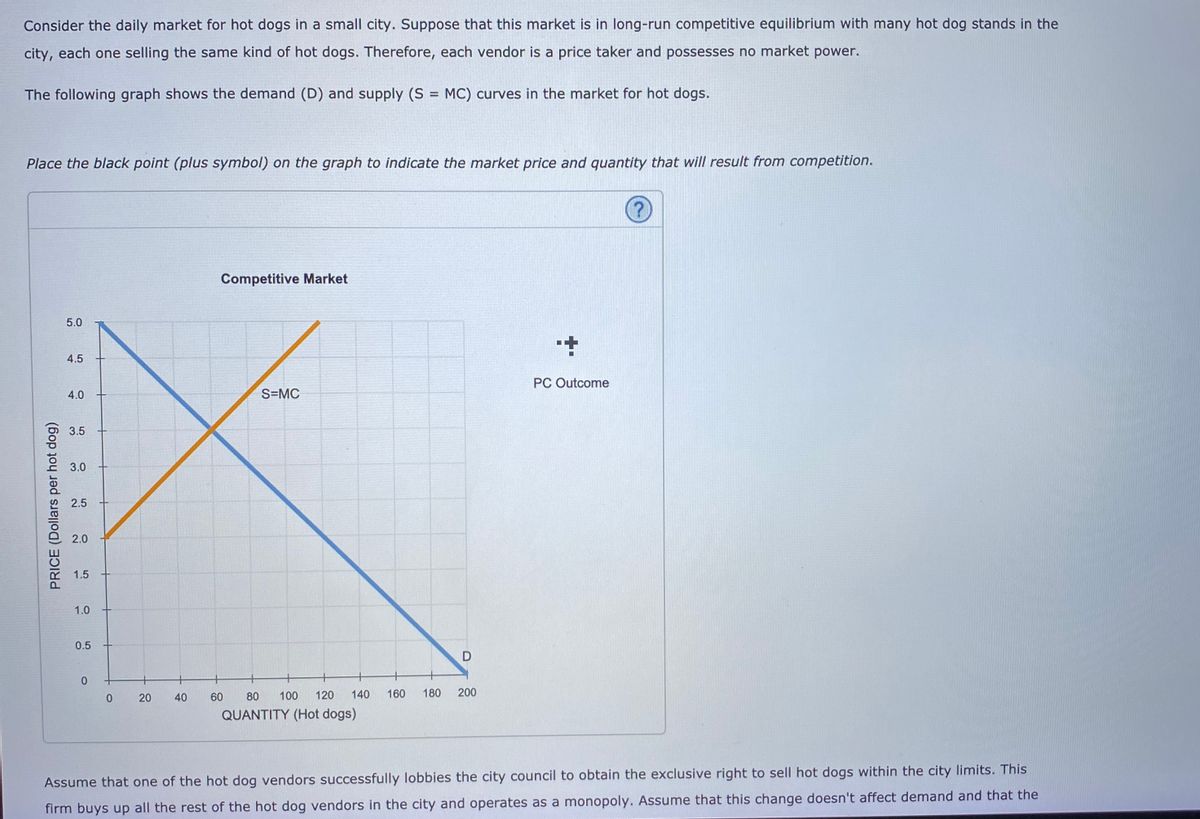
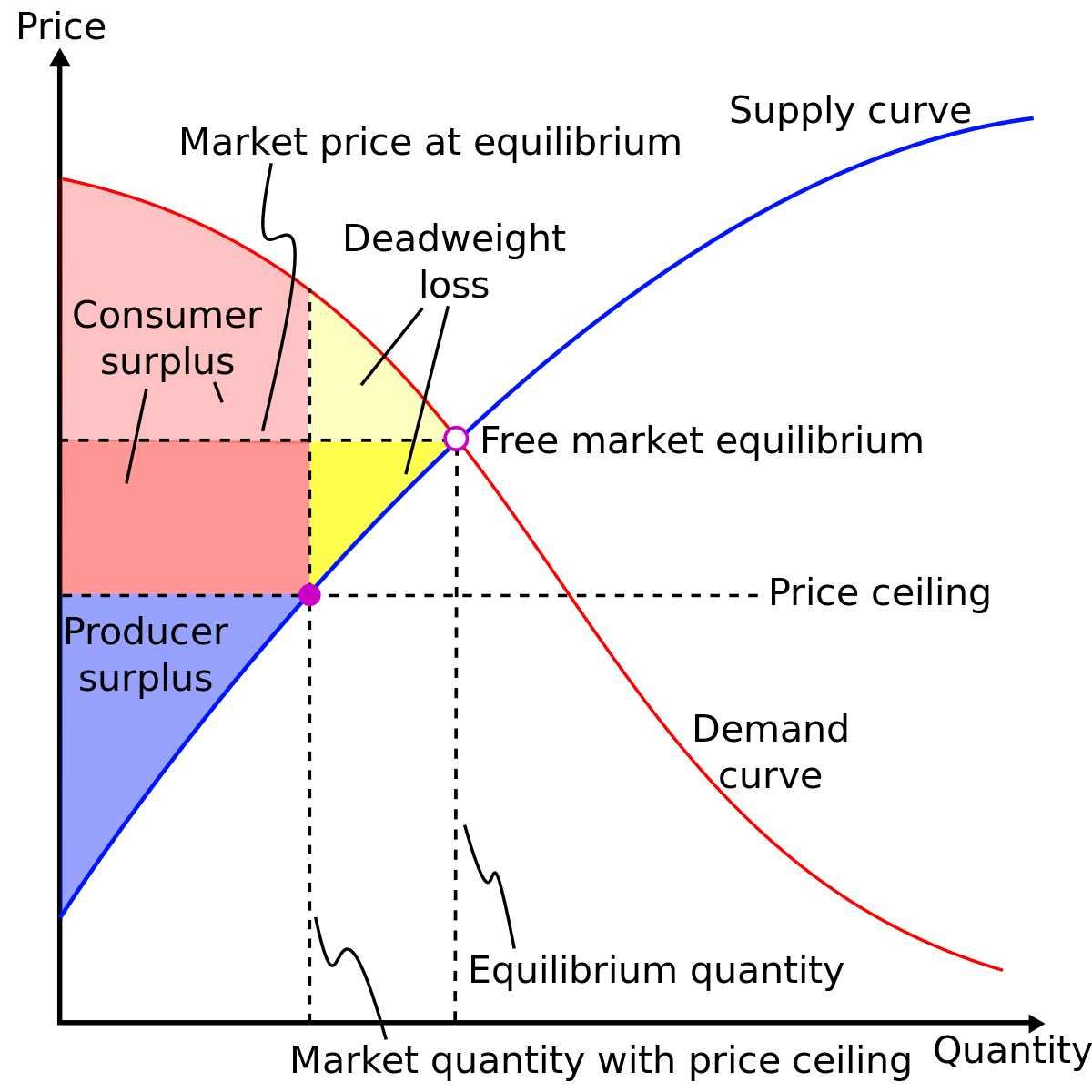
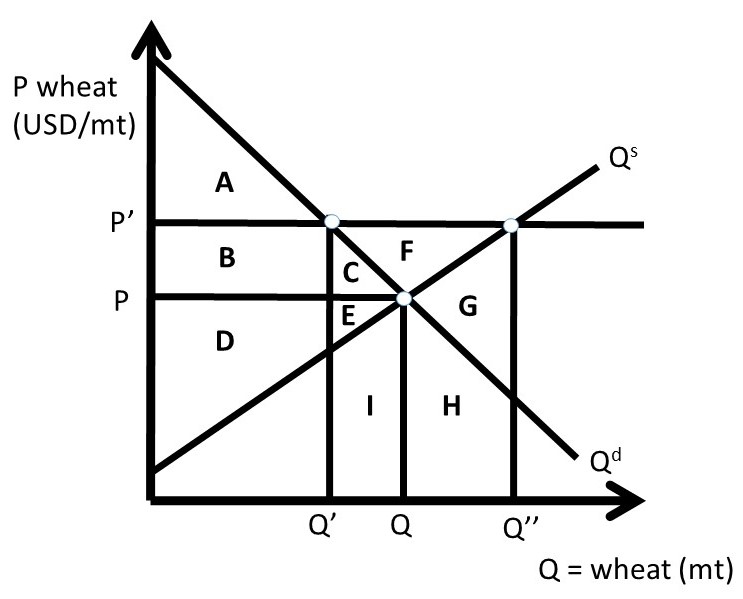
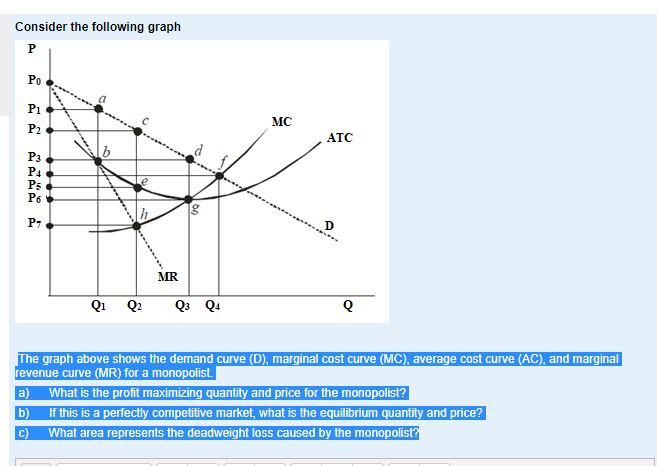
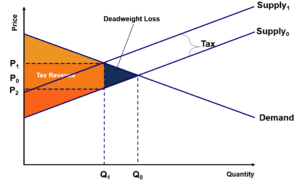
3.5 Demand, Supply, and Efficiency - Principles of Economics The loss in social surplus that occurs when the economy produces at an inefficient quantity is called deadweight loss. In a very real sense, it is like money thrown away that benefits no one. In Figure 2 (a), the deadweight loss is the area U + W. 5.1 Externalities - Principles of Microeconomics Market equilibrium in this diagram occurs at the intersection of supply and demand, or the intersection of MPC and MSB (which is equivalent to MPB). This occurs at Q 1. Now we know that total private benefits at the market equilibrium are equal to a+b+c+e+f and we know that total private cost at the market equilibrium equals c+f. ECN 202 Final Exam Flashcards | Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right. The dead weight loss due to the externality is represented by the area abf. The fumes from dry cleaners can contribute to air pollution. Suppose the following diagram illustrates the situation in the dry cleaning market. Microeconomics: Chapter 15 Flashcards - Quizlet The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Act divided authority to police mergers between the FTC and the Department of Justice. Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist. If the firm's average total cost curve is ATC3 , the firm will suffer a loss.
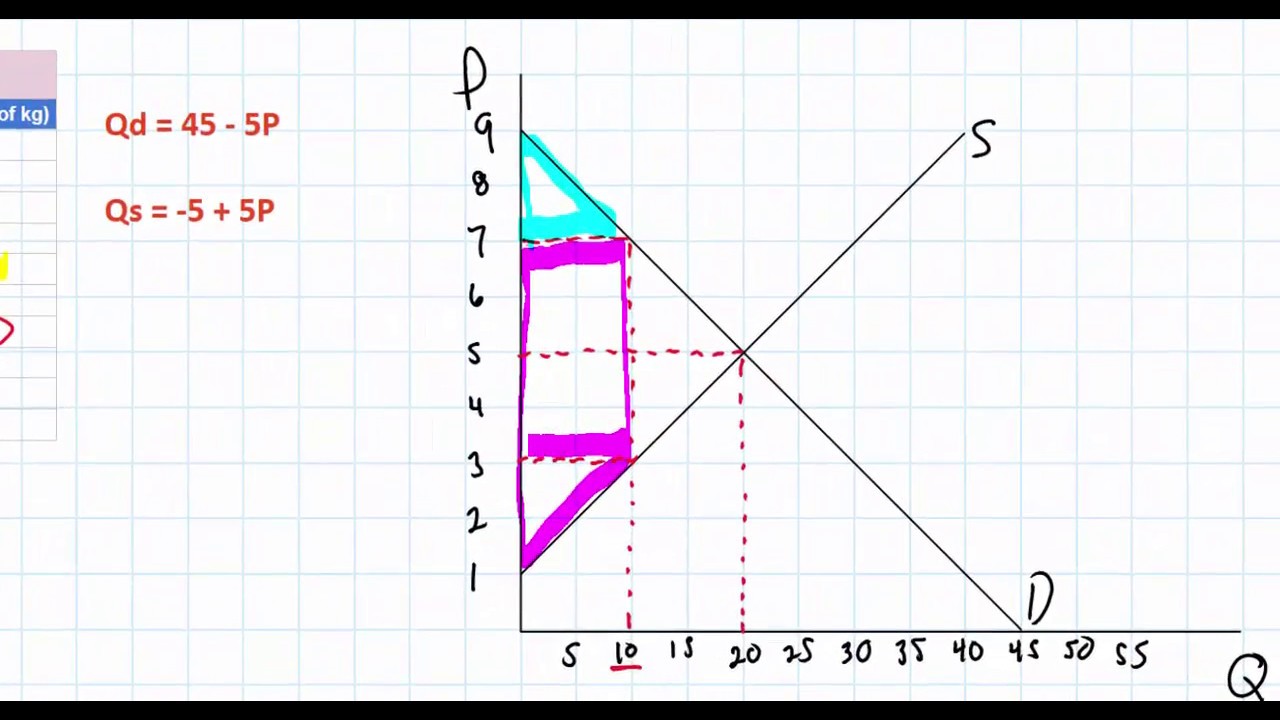
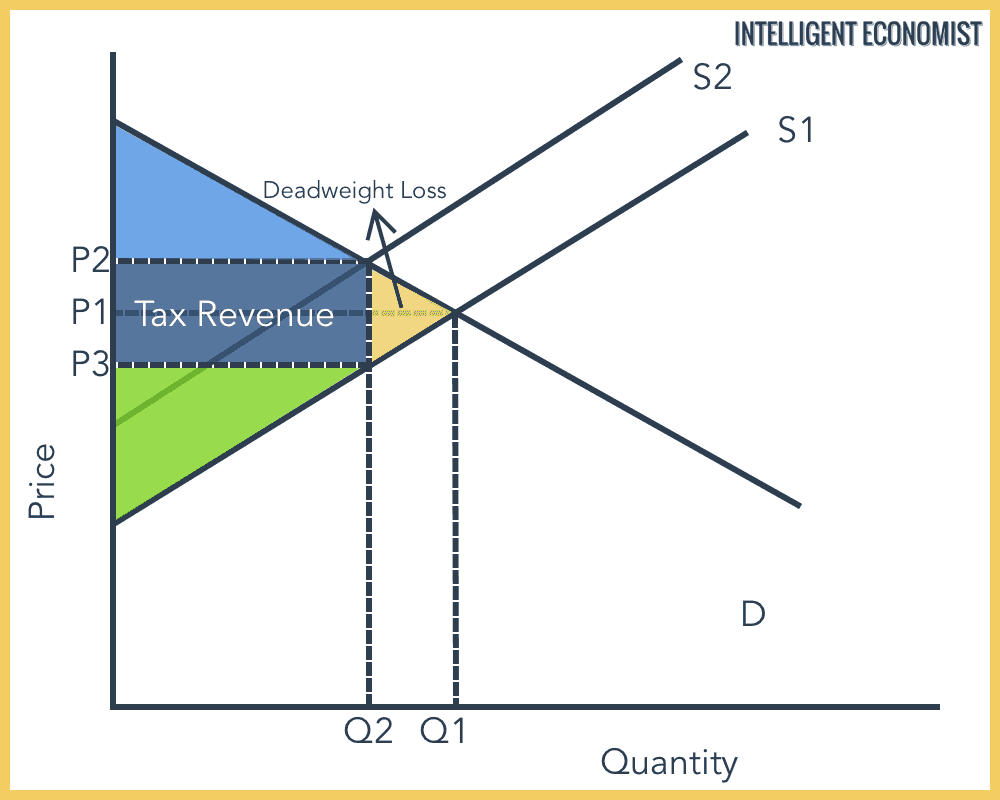
Consumer & Producer Surplus | Microeconomics The area of a triangle. Let's apply the calculation for the area of a triangle to our example market to see the added value that consumers will get for this item at the equilibrium price in our sample market. Step 1: Define the base and height of the consumer surplus triangle. The base of the consumer surplus triangle is 3 units long. 9.1 How Monopolies Form: Barriers to Entry - Principles of ... Because of the lack of competition, monopolies tend to earn significant economic profits. These profits should attract vigorous competition as described in Perfect Competition, and yet, because of one particular characteristic of monopoly, they do not. Barriers to entry are the legal, technological, or market forces that discourage or prevent potential competitors from entering a market. Chapter 3. Monopoly and Market Power - The Economics of ... The second term, (∂P/∂Q)Q, is equal to area A in the diagram. This area represents the change in price given a small change in quantity (∂P/∂Q), multiplied by the quantity (Q). For a competitive firm, (∂P/∂Q) = 0, since the competitive firm is a price taker. For a competitive firm, AE = ME, as shown in the left of Figure 3.17. PDF Economics 101 Fall 2011 Homework #3 Due 10/11/11 before ... find the deadweight loss. DWL = $500 - $325 = $125. This is also the area of the triangle to the right of the quota quantity (10) which has base 20 - 10 = 10 and height $30 - $5 = $25. ½ * 10 * $25 = $125. (h) Based on your calculations, do think the quota policy is a good idea? Why or why not?
fountainessays.comFountain Essays - Your grades could look better! It is very easy. Click on the order now tab. You will be directed to another page. Here there is a form to fill. Filling the forms involves giving instructions to your assignment. The information needed include: topic, subject area, number of pages, spacing, urgency, academic level, number of sources, style, and preferred language style.
(PDF) Economics of the Public Sector - Joseph E. Stiglitz ... Economics of the Public Sector - Joseph E. Stiglitz
quizlet.com › 144045961 › chapter-4-flash-cardsCHAPTER 4 Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram. If actual production and consumption occur at Q1: A. efficiency is achieved. B. consumer surplus is maximized. C. an efficiency loss (or deadweight loss) of b + d occurs. D. an efficiency loss (or deadweight loss) of e + d occurs.
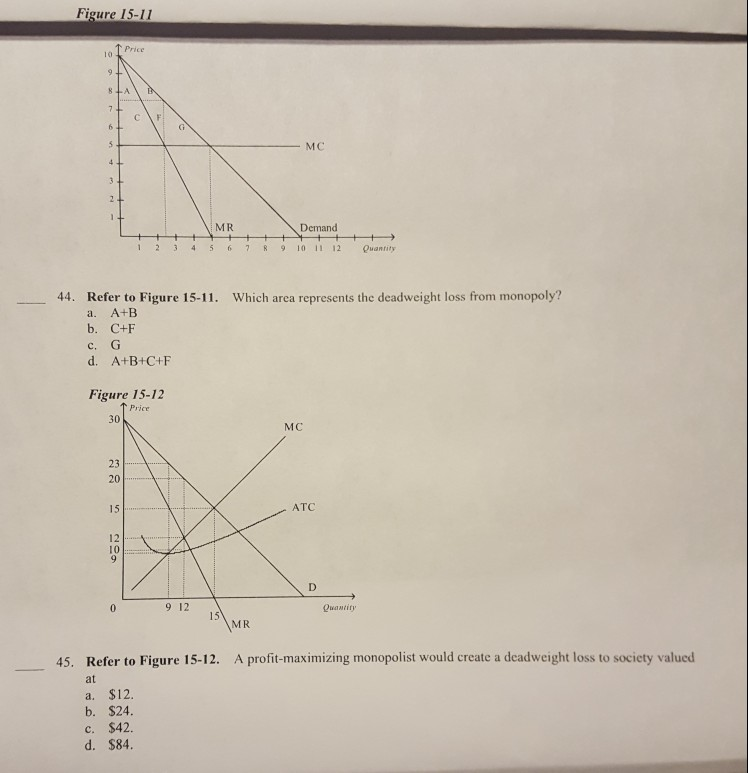
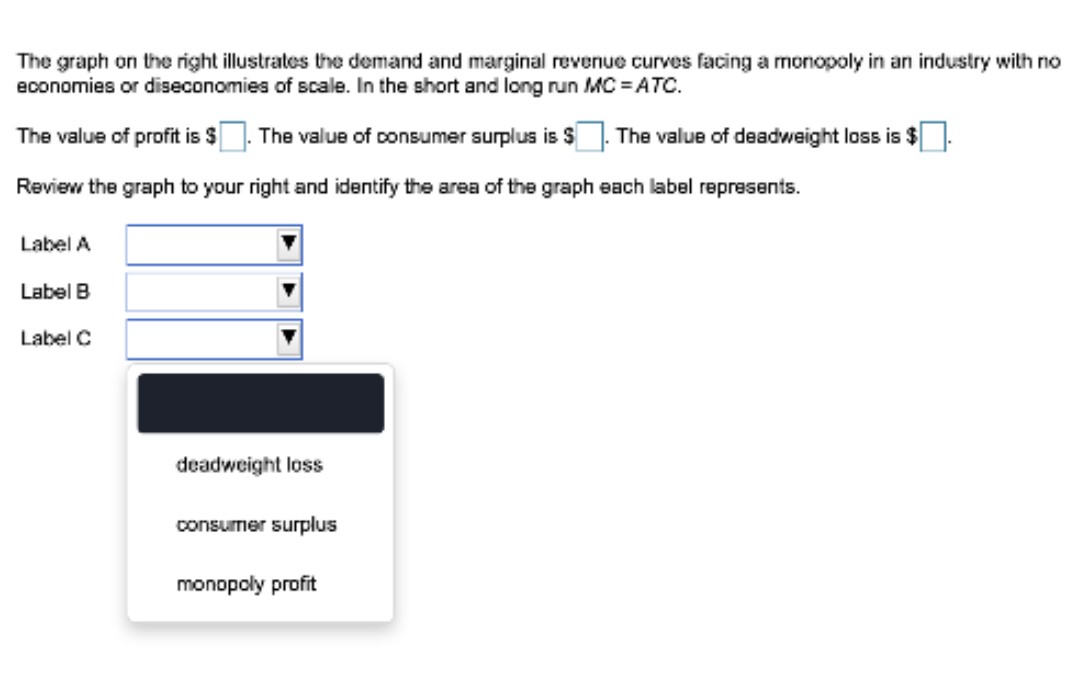
PDF before your name, TA name, and section number staple Part ... deadweight loss (DWL). In a well-labeled graph illustrate this monopolist: be sure to include the areas that represent CS, PS, and DWL in your graph. 3) Suppose demand increases by 90 units at every price. Find the equation for the monopolist's new demand curve. Then, calculate the new profit maximizing price
ECO 2023 CHAPTER 15 HW.docx - 1) Refer to Figure 15-6. The ... View full document 1) Refer to Figure 15-6. The deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area FHE 2) Economic efficiency in a free market occurs when the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized. the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized . 3) Refer to Figure 13-2.
dokumen.pub › microeconomic-theory-basicMicroeconomic Theory: Basic Principles and Extensions [12th ... The loss of approximately 2.1 units of y is a measure of the cost of the labor market inefficiency. Alternatively, if the labor supply of 180 were allocated evenly between the production of the two goods, then we would have x 9.5 and y 19, and the inefficiency would show up in both goods’ production—more of both goods could be produced if ...
Deadweight Loss - Examples, How to Calculate Deadweight Loss The deadweight loss is the value of the trips to Vancouver that do not happen because of the tax imposed by the government. Graphically Representing Deadweight Loss Consider the graph below: At equilibrium, the price would be $5 with a quantity demand of 500. Equilibrium price = $5 Equilibrium demand = 500
Chapter 5. Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly - The ... Monopolistic competition is a market structure defined by free entry and exit, like competition, and differentiated products, like monopoly. Differentiated products provide each firm with some market power. Advertising and marketing of each individual product provide uniqueness that causes the demand curve of each good to be downward sloping.
Solved Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight ... Question:Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area MCQ O A FO,F O B. GEH OC. FHE OD. FGE Price and cost per unit ($) Q1 Q2 Quantity This problem has been solved! See the answerSee the answerSee the answerdone loading Show transcribed image text Expert Answer Who are the experts?
› 43024032 › _Paul_Krugman_Robin[Paul Krugman, Robin Wells] Microeconomics(z ... - Academia.edu Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
DOC Chapter 14: SOLUTIONS TO TEXT PROBLEMS: - Geneseo The deadweight loss from monopoly is the triangular area between Qc and Qm that is above the marginal-cost curve and below the demand curve. It represents deadweight loss, since society loses total surplus because of monopoly, equal to the value of the good (measured by the height of the demand curve) less the cost of production (given by the ...
(PDF) Exercise Book Series: Microeconomics. Ist Edition ... Academia.edu is a platform for academics to share research papers.
Micro: Econ 202 Ch. 1 - 13 : Ole Miss Flashcards - Quizlet When new firms are encouraged to enter a monopolistically competitive market, some existing firms must be earning economic profits. Figure 9-1 shows the U.S. demand and supply for leather footwear. Refer to Figure 9-1. Suppose the government allows imports of leather footwear into the United States. The market price falls to $18.
Subsidies - Economics Online In the diagram below, the subsidy per unit is A - B, and the new quantity consumed is Q1. However, the price the consumer pays does not fall by the full amount of the subsidy - instead it falls from P to P1.
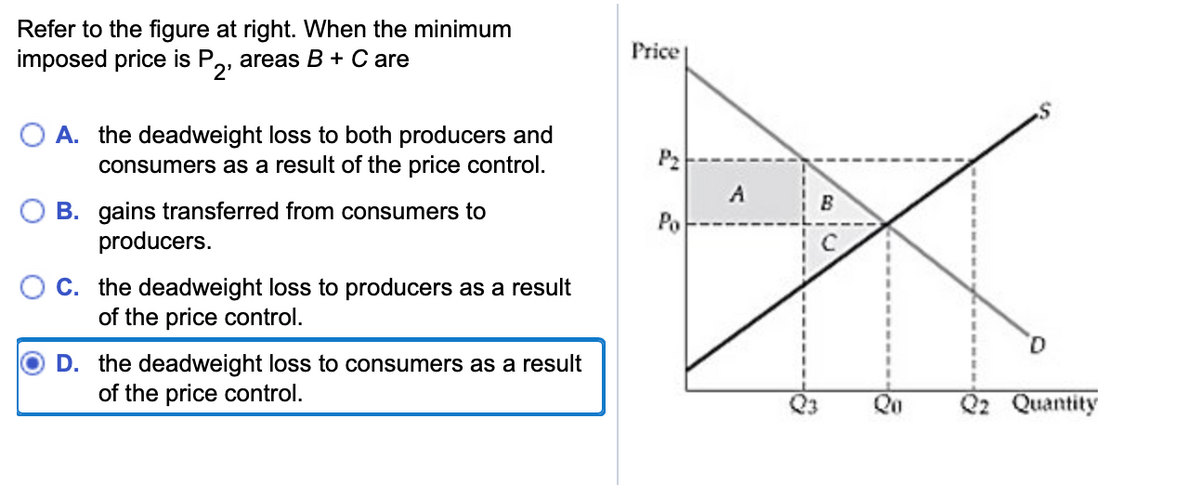
PDF Economics 103 Final exam ANSWER KEY - Simon Fraser University 17) Refer to Figure 7.2.3. The graph shows the market for shoes in Canada. The world price of a pair of shoes is $20. With free international trade, Canadian consumer surplus _____ and Canadian producer surplus _____. A) increases by area A + B; decreases by area B B) increases by area B; decreases by area B
Chapter 10 Flashcards - Quizlet The first important federal law passed to regulate monopolies in the United States was the Sherman Act Refer to the diagram to the right which shows the demand and cost curves facing a monopolist. The firm's profit maximizing price is P3 Governments grant patents to encourage research and development on new products The U.S. government patent last
PS9 Graphs Flashcards - Quizlet Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area A. FQ1Q2E. B. GEH. C. FGE. D. FHE. A In 2011, Verizon was granted permission to enter the market for cable TV in Upstate New York, ending the virtual monopoly that Time Warner Cable had in most local communities in the region.
study.com › learn › price-ceiling-questions-andPrice Ceiling Questions and Answers | Study.com Price Ceiling Questions and Answers. Get help with your Price ceiling homework. Access the answers to hundreds of Price ceiling questions that are explained in a way that's easy for you to understand.
Producer Surplus Formula | Calculator (Examples with Excel ... Producer Surplus = (Market Price - Minimum Price to Sell) * Quantity Sold. On the other hand, the formula for the producer surplus for the market as a whole can be derived by using the following steps: Step 1: Firstly, draw the Demand curve and Supply curve with quantity on the X-axis and price on the Y-axis.
PDF Economics 101 Fall 2011 before - Social Science Computing ... 1 Economics 101 Fall 2011 Homework #6 Due: 12/13/2010 in lecture Directions: The homework will be collected in a box before the lecture.Please place your name, TA name and section number on top of the homework (legibly).
8.4 Monopolistic Competition - Principles of Microeconomics At a price of $70/month, ATC is only $60 and Rogers' profit is $36 million. ($10 profit/subscriber) Notice that this market creates a deadweight loss equal to the red area since the equilibrium quantity is less than what would occur in competitive equilibrium (5 million subscriptions).
Solved Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight ... Question: Refer to the diagram to the right. The deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area MC Po C O A. FHE B. FQ,Q, F C. FGE. Price and cost per unit ($) G D. GEH H MR D 0 2 Q2 Quantity This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer
Deadweight Loss Definition - Investopedia A deadweight loss is a cost to society created by market inefficiency, which occurs when supply and demand are out of equilibrium. Mainly used in economics, deadweight loss can be applied to any ...












0 Response to "37 refer to the diagram to the right. the deadweight loss due to a monopoly is represented by the area"
Post a Comment