35 cellular respiration detailed diagram
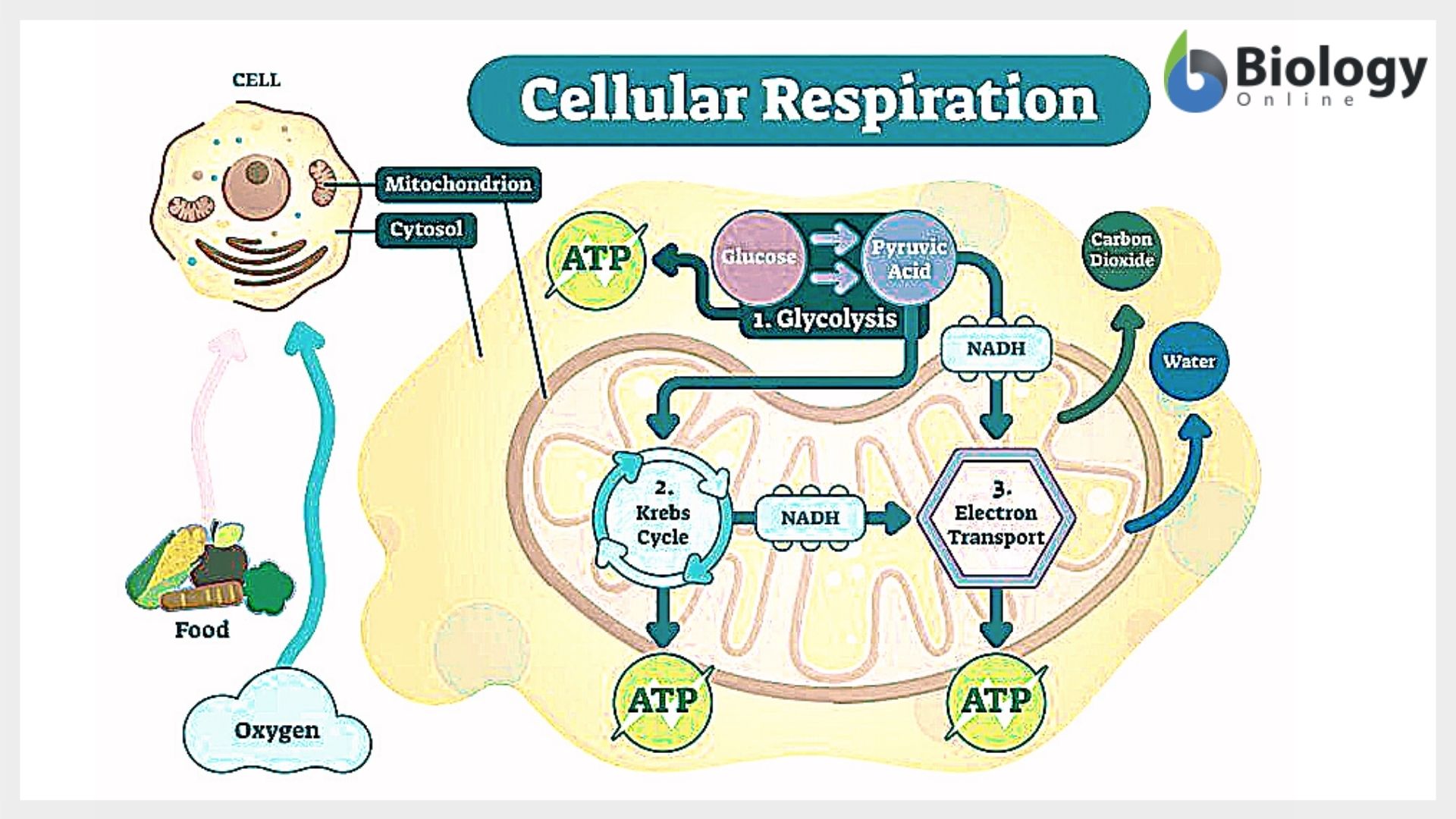
Cellular respiration. Glucose (blood sugar) is the body’s main energy source. Cellular respiration occurs in every body cell when oxygen reacts with glucose to free its energy in chemical form. The end products are carbon dioxide and water, which is known as metabolic water and amounts to about 300ml (10fl oz) daily throughout the body. Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.
Mitochondrion & Cellular Respiration Diagram Worksheet. Two worksheets are included. The first is a simple worksheet that has students label the main parts of a mitochondrion. The second worksheet has students identify the main reactants and products of cellular respiration as they relate to the mitochondrion.
Cellular respiration detailed diagram
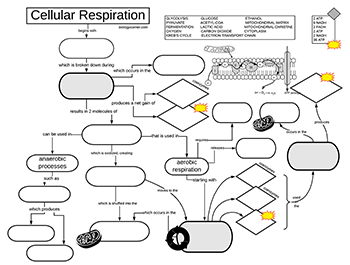
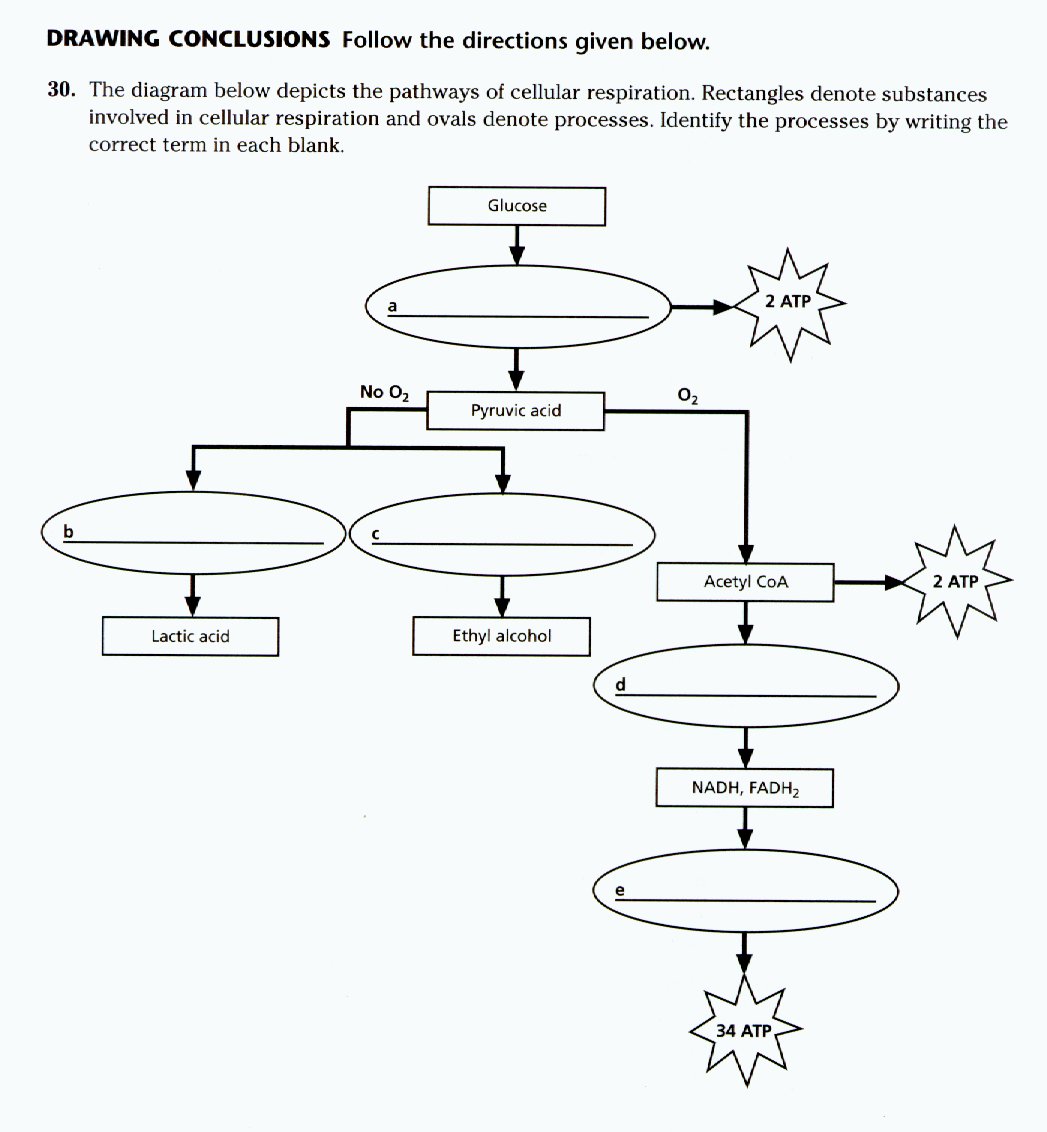
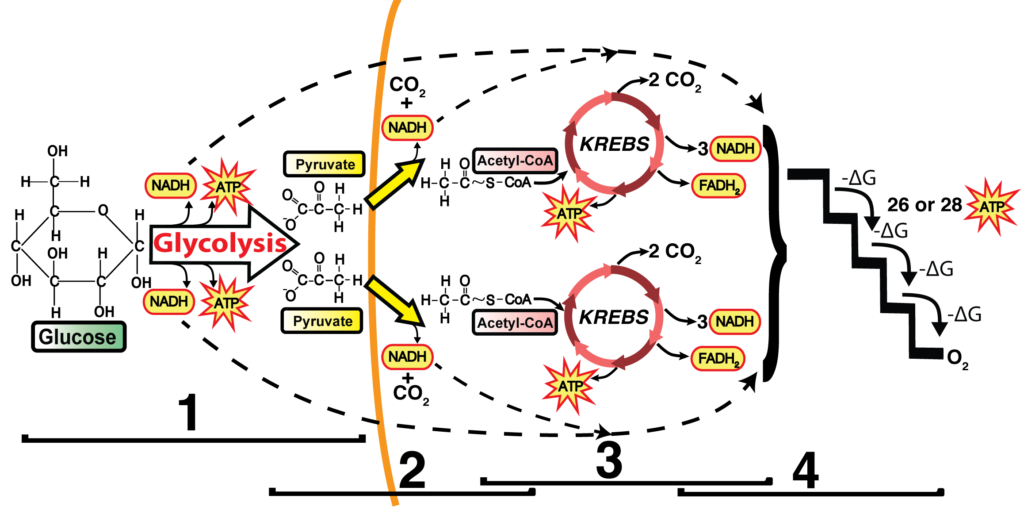
Detailed discussion on the steps of cellular respiration The reactants of the Electron Transport chain hold 10 NADH electron carrier molecules, 2FADH2, six oxygen atoms from the initial glucose molecule, and especially, 34 ADP and P to bond with ATP Synthase. Diagram; Steps; Key Points; Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals. in a separate box or draw a cell and mitochondria and add all steps to the diagram in the appropriate location(s). No matter which option you choose, number the boxed sections or the steps. Your numbered diagram or drawing of the steps much include the following: 2. glycolysis, kreb cycle and electron transport chain 3. the movement of electrons 4.
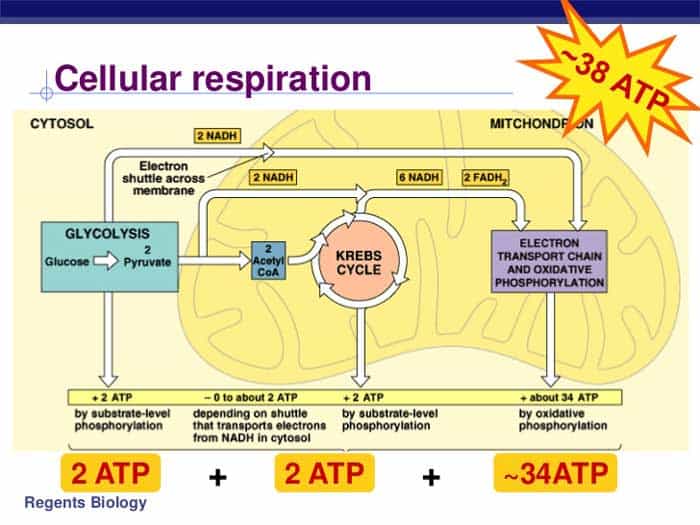
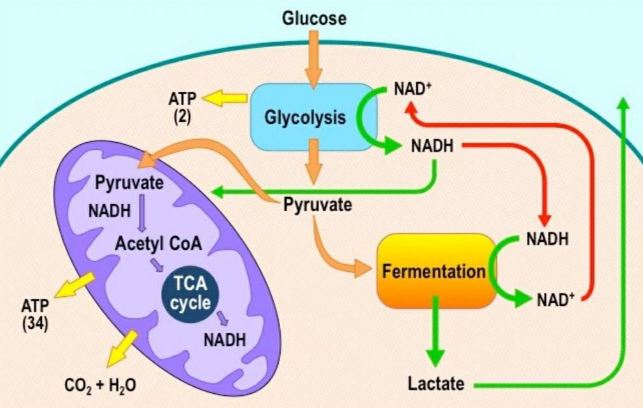
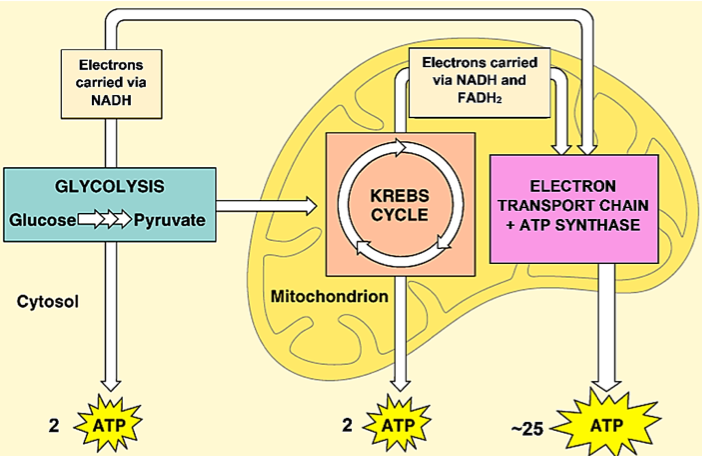
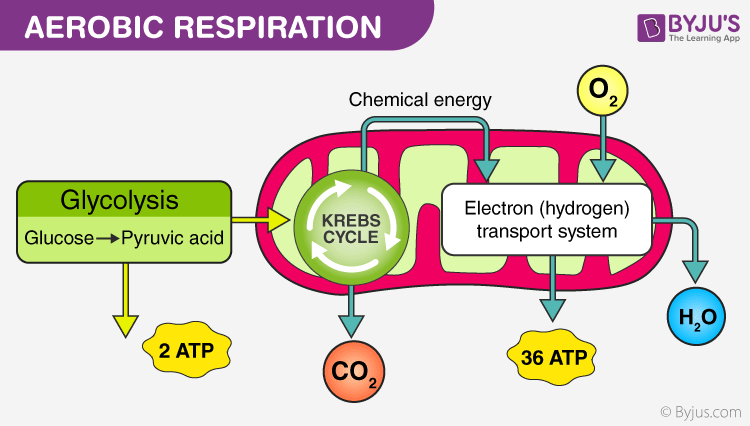
Cellular respiration detailed diagram. The cellular respiration can be classified into two types, depending upon the availability of oxygen: Aerobic Respiration: It is the process in which the oxidation of the carbohydrate molecule, glucose, takes place in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic Respiration: It is the process in which the oxidation of glucose takes place in the absence of ... Glycolysis. The name glycolysis means "sugar-splitting," and sure enough, this metabolic pathway splits glucose into two three-carbon molecules. Learn more about the steps of glycolysis and how it is used in both cellular respiration and fermentation. What is Cellular Respiration? It is the process by which organisms use energy from "food" (e.g., glucose, fatty acids) to fuel the endergonic synthesis of ATP. • requires (O 2), occurs in most organisms (plants, too!) • provides a supply of usable energy for cells (ATP) C 6 H 12 O 6 6HCO 2 2 OATPs Glucose Oxygen gas Carbon dioxide 6 ... The energy released is in the form of ATP molecules that are used to carry out various functions of the cell. The cellular respiration equation is as follows: C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 ――> H 2 O + CO 2 + 36ATP . The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process. Diagram of Cellular Respiration. The following diagram of cellular respiration will give a better understanding of this process.
Cellular Respiration ( Flowchart) Use Creately's easy online diagram editor to edit this diagram, collaborate with others and export results to multiple image formats. We were unable to load the diagram. You can edit this template on Creately's Visual Workspace to get started quickly. Adapt it to suit your needs by changing text and adding ... Feb 12, 2020 · Cellular Respiration. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. process by which cells turn nutrients into useful energy. relating to organisms whose cells have a nuceleus. natural or artificial process of changing a food's sugars into alcohols. Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration – an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C6H12O6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O2 = 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy. 2) Description of the molecules: created in all three stages of cellular respiration: Cellular Respiration. Glycolysis. Krebs Cycle. Electron Transport Chain. Fermentation. Ch. 7 Diagrams. Overview of Cellular Respiration - Complete the diagram using Figure 7-13 (p.146) & Fig. 7-16 (p.148). Glycolysis - Complete the diagram using Figure 7-17 (p.149). Also label the energy phases. Krebs Cycle - Complete the diagram using ...
Cellular Respiration needs Oxygen to occur. Cellular Respiration takes place in the mitochondria; the powerhouse of the cell. Glycolysis. Glycolysis is the first step of cellular respiration and commonly begins with the simple sugar glucose. Through a series of steps a single molecule of glucose is broken down into 2 molecules of Pyruvic Acid ... This video discusses Glycolysis, Krebs Cycle, and the Electron Transport Chain.Teachers: You can purchase this PowerPoint from my online store. Follow the li... Understanding Cellular Respiration Here are three visual depictions of cellular respiration – an equation, an output description and an illustration. 1) Equation: C 6 H 12 O 6 (1 glucose molecule) + 6 O 2 = 6 CO 2 + 6 H 2 O + 36 ATP (ENERGY) carbohydrate + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water + ATP energy 2) Description of the molecules created in all three stages of cellular respiration: Tree respiration is similar to respiration in animals. In animals, glucose (6C sugar) is the primary respiration substance. In trees, sucrose (12C double sugar) is the primary transport and initial respiration substance. Sucrose is broken into 6C* units once in a cell. Complete respiration of one sucrose mol-

Cellular Respiration Chemistry Concept Flowchart Diagram Png 1205x743px Cellular Respiration Area Biology Chart Chemical Reaction Download
The detailed glycolysis diagrams are illustrated in clear pictures. ... Glycolysis is the first of the main metabolic pathways of cellular respiration to produce energy in the form of ATP. Through two distinct phases, the six-carbon ring of glucose is cleaved into two three-carbon sugars of pyruvate through a series of enzymatic reactions ...

Cellular Respiration Medical Vector Illustration Diagram Respiration Process Scheme Stock Vector Illustration Of Diagram Life 125302632
Cellular respiration involves four main steps in converting glucose molecules to harvest energy in one's body cells. These are: 1. Glycolysis - The glucose undergoes chemical processes where it gets converted into pyruvate. The energy released in these reactions is ATP.
Cellular respiration is a collection of three unique metabolic pathways: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis is an anaerobic process, while the other two pathways are aerobic. In order to move from glycolysis to the citric acid cycle, pyruvate molecules (the output of glycolysis) must be oxidized in a ...
Detailed Diagram of Cellular Respiration Poster A diagram of cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine ...
Mitochondria are a double-membrane-bound cell organelle found in most eukaryotic organisms. In all living cells, these cell organelles are found freely floating within the cytoplasm of the cell. The diagram of Mitochondria is useful for both Class 10 and 12.
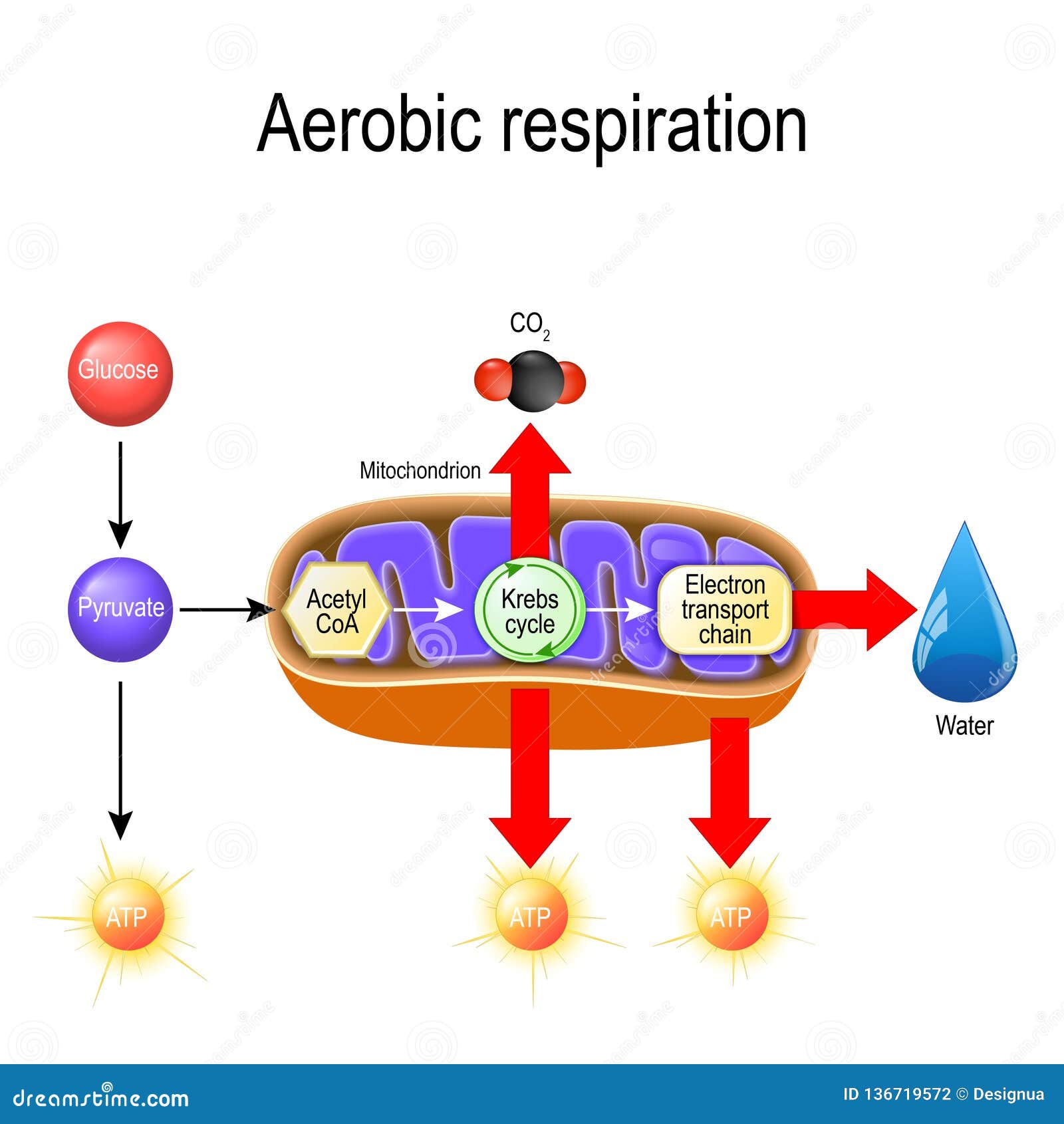
Aerobic Respiration Cellular Respiration Stock Vector Illustration Of Oxidation Educational 136719572
Respiration. What is the overall purpose of cellular respiration? Write the equation for cellular respiration below. Label the reactants and the products. What are the 3 phases of the cellular respiration process? Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? Label the location on the cell diagram (Where in the cell does the Krebs (Citric Acid ...
Detailed Diagram of Cellular Respiration Poster. A diagram of cellular respiration including glycolysis, Krebs cycle, citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain Cellular respiration is the set of the metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine ...
Oct 19, 2018 - Cellular respiration is essential for sustaining life at a cellular level. This BiologyWise article provides you with its diagram and some brief information. Have a look!
Start studying Respiration Diagram, Cellular Respiration. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools.
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of the steps of cellular respiration. Glycolysis. Six-carbon glucose is converted into two pyruvates (three carbons each). ATP and NADH are made. These reactions take place in the cytosol. Pyruvate oxidation. Pyruvate travels into the mitochondrial matrix and is converted to a two-carbon molecule bound to ...
Metabolic pathways that contribute to the production of ATP molecules in cells are collectively referred to as cellular respiration. When a molecule of glucose undergoes aerobic cellular respiration, 36 molecules of ATP are produced. Glucose is an energy-rich molecule. The breakdown of glucose results in the formation of low-energy molecules and energy.
Cellular Respiration Equation: Every machine needs specific parts and fuel in order to function. Likewise, “biological machines” also require well engineered parts and good energy source in order to work.Perhaps the second most important molecule (DNA is the first) is adenosine triphosphate (also known as ATP).Basically, ATP serves as the main energy currency of the cell.
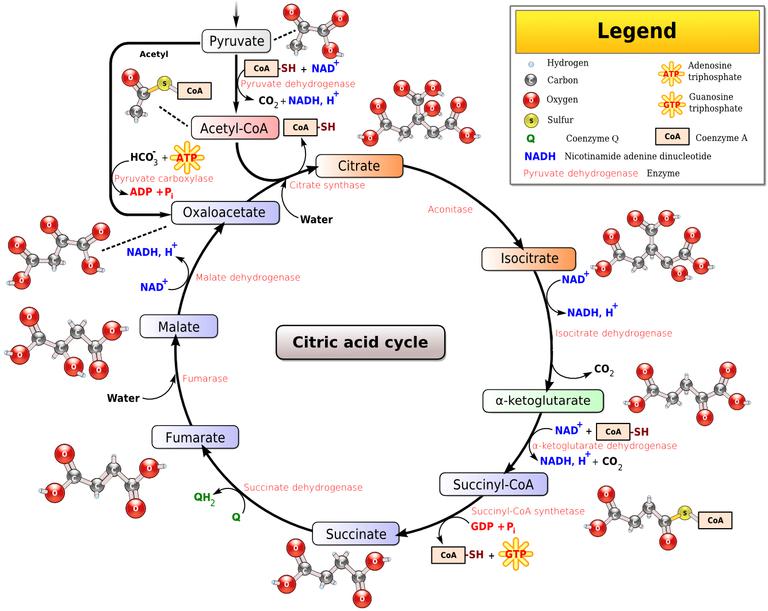
Krebs Cycle and Link Reaction: Interactive Tutorial. 1. Introduction. If oxygen is present in a cell where respiration is occurring, then glycolysis is followed by a series of reactions that completely oxidize pyruvate (pyruvic acid) and the molecules it gets broken down into. You can see this in steps “2” and “3” in the diagram below.
In the mean time we talk concerning Cellular Respiration Diagram Worksheet, we have collected several related pictures to complete your ideas. cellular respiration diagram worksheet blank, comparing photosynthesis and cellular respiration diagram and photosynthesis and cellular respiration concept map are some main things we want to show you ...
in a separate box or draw a cell and mitochondria and add all steps to the diagram in the appropriate location(s). No matter which option you choose, number the boxed sections or the steps. Your numbered diagram or drawing of the steps much include the following: 2. glycolysis, kreb cycle and electron transport chain 3. the movement of electrons 4.
Diagram; Steps; Key Points; Respiration is of two types, aerobic respiration, and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic Respiration: It is the process of cellular respiration that takes place in the presence of oxygen gas to produce energy from food. This type of respiration is common in most of the plants and animals, birds, humans, and other mammals.
Detailed discussion on the steps of cellular respiration The reactants of the Electron Transport chain hold 10 NADH electron carrier molecules, 2FADH2, six oxygen atoms from the initial glucose molecule, and especially, 34 ADP and P to bond with ATP Synthase.
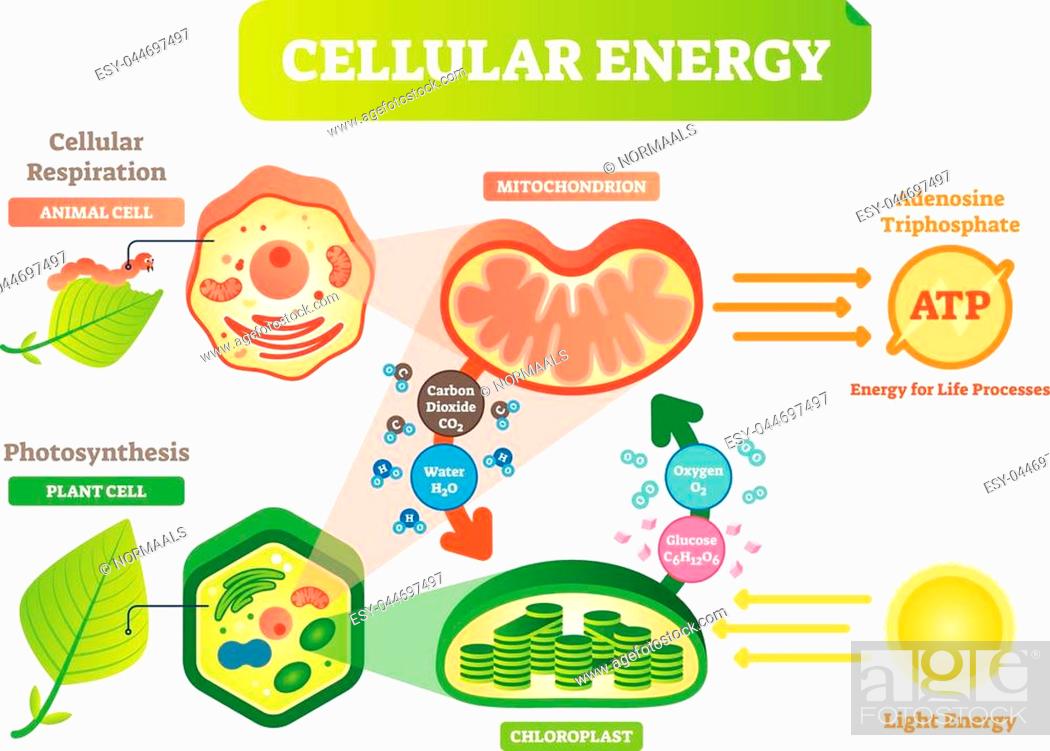
Animal And Plant Cell Energy Cycle Vector Illustration Diagram With Mitochondrion And Chloroplast Stock Vector Vector And Low Budget Royalty Free Image Pic Esy 044697497 Agefotostock

5 Clear Simple Diagrams With A Concise Study Guide Will Help Your Biology Students Visualize The Cellular Respiration Study Guide Cellular Respiration Biology

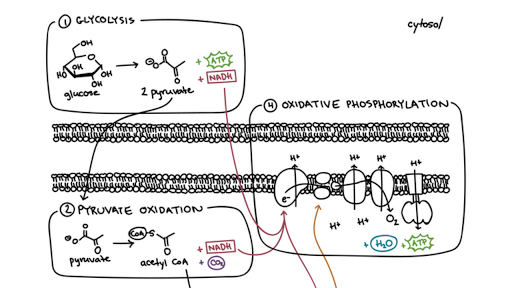












/Cellular-Respiration-58e52b113df78c5162b38dca.jpg)


0 Response to "35 cellular respiration detailed diagram"
Post a Comment