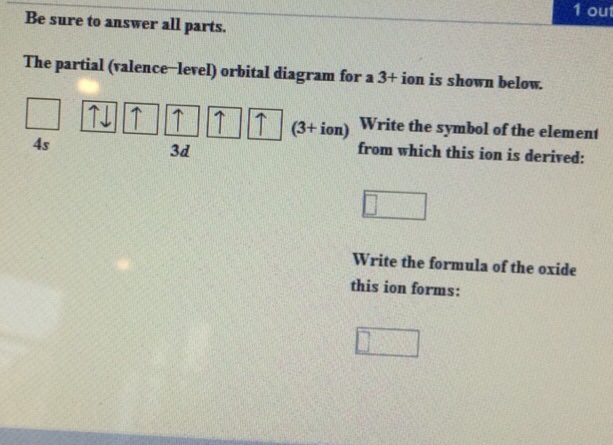
35 the partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.
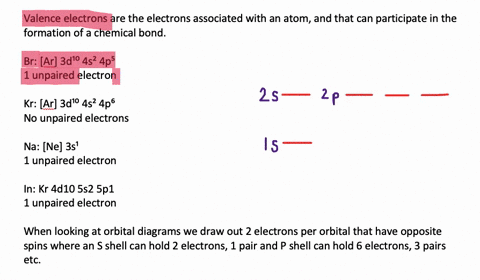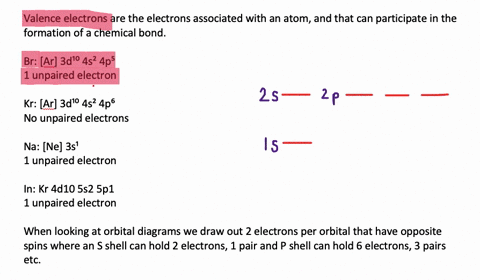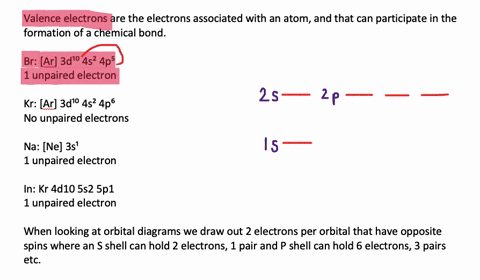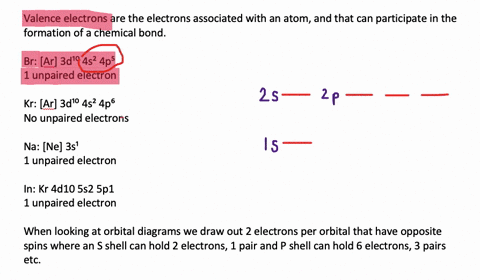
- electrons in the highest energy level that contains electrons Valence electrons ... this energy is a measure of how easily the element forms an ion with a ____ charge. ... Which sub levels may be utilized in constructing a partial orbital diagram for a period 3 element? select all that apply - 3p Construct the molecular orbital diagram for dichlorine. x y z z y 3 x y z z y 4 Showing the p orbital s. Showing the s and p orbital s. ORBITAL S AND MOLECULAR REPRESENTATION 11. CARBON ORBITAL S Methane Ethane METHANE AND ETHANE C H H H H CH4 C C H H H H H H C2H6 1 2 Color conventions: Hydrogen atoms are shown in gray.
Solved Using The Molecular Orbital Diagram Depicted Below Which Species Have Bond Order Of 3 2p 2p 02p 72p Energy 2s Oa B2 B 02 2 C C22 D N2 Oeco Of Cn G . Molecular orbital diagram for b2. This interaction introduces an element of s p mixing or hybridization into the molecular orbital theory. When p s mixing is allowed the energies of the σ2p and π2p orbitals are reversed. The two electrons ...
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.
Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3-ion is shown below. What is the symbol of the element from which this ion is ... Chemistry questions and answers. The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms: Question: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. 5.13 The energy level diagram for SH- is shown below. A bond order of 1 is predicted. The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.. Molecular Orbitals for Larger Molecules 1. Determine point group of molecule (if linear, use D2h and C2v instead of D∞h or C∞v) 2. Assign x, y, z coordinates (z axis is principal axis; if non-linear, y axes of outer atoms point to central atom)3. Find the characters of the reducible representationfor the combination of Consider the following portion of the energy-level diagram for hydrogen: n = 4-0.1361 × 10-18 J n = 3-0.2420 × 10-18 J n = 2-0.5445 × 10-18 J n = 1-2.178 × 10-18 J For which of the following transitions does the light emitted have the longest wavelength? Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 4+ ion is shown below. What is the symbol of the element from which this ion is ... So the formal it'll be cobalt thio, oxygen three. So here and see were given an empty five s orbital and a completely filled in 40 orbital with 10 electrons in it. And we're told that the iron has a charge of plus one. This one's a little tricky because usually want the s orbital be completely filled before you fill in the d orbital.
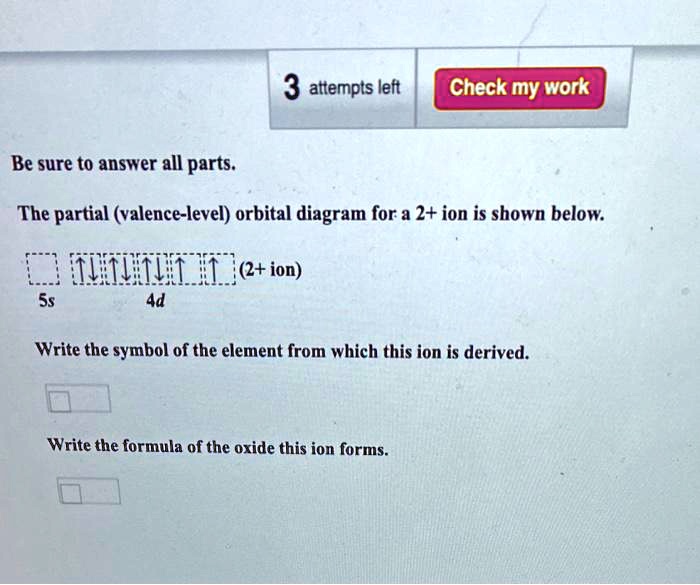
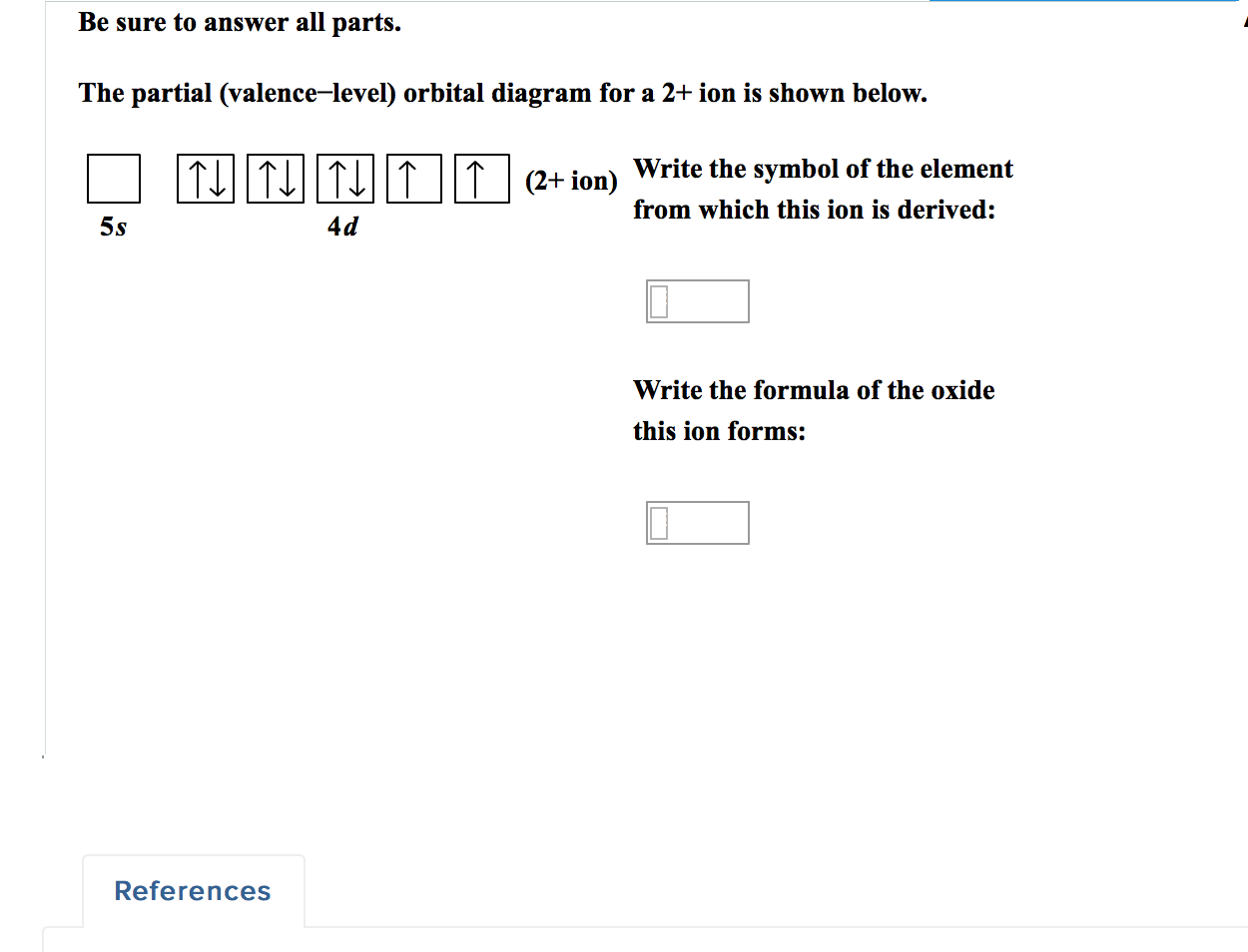
Figure 8.10 or Table 8.3), give the full and condensed electron configurations, partial orbital diagrams showing valence electrons only, and number of inner electrons for the following elements: (a) potassium (K; Z = 19) (b) technetium (Tc; Z = 43) (c) lead (Pb; Z = 82) PLAN: The atomic number gives the number of electrons, and the The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. quifditu1 (2+ion) 5s 4d Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived. 2-methylbutan-2-ol, (CH3)2C (OH)CH2CH3 (C H 3) 2 C (OH)C H 2 C H 3, is a liquid with a smell of camphor that was formerly used as a sedative. One way of producing it starts with 2-methylbut-2-ene. As well as 2-methylbutan-2-ol, the reaction also produces a small quantity of an optically active isomer, X. The d orbital splitting diagram for a tetrahedral coordination environment is shown below. Given this diagram, and the axes in the accompanying picture, identify which d orbitals are found at which level. In the picture, the metal atom is at the centre of the cube, and the circle represent the ligands. Problem CC8.3.
a. Mg 1s22s22p63s13p1 b. Cl 1s22s22p63s23p44s1 c. Mn 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d 44p1 d. Ne 1s22s22p53s1 8.46 Given the following partial (valence‐level) electron configurations, a. identify each element, A Si B F C Sr D S b. rank the four elements in order of increasing atomic size, and F, S, Si, Sr Here we will get you the information with the valence electrons that nitrogen has. There are 5 valence electrons in Nitrogen Electron Configuration and it lies at the top of group 15 in the periodic table. Apart from that one more thing is unique about the element, i.e, nitrogen can have either ... The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms: Question: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the ... molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule.
required and write a partial orbital diagram. PROBLEM: Use partial orbital diagrams to describe how mixing of the atomic orbitals of the central atom(s) leads to hybrid orbitals in each of the following: (a) Methanol, CH. 3. OH (b) Sulfur tetrafluoride, SF. 4 (a) CH. 3. OH. The electron- group arrangement is tetrahedral around both the C and ...
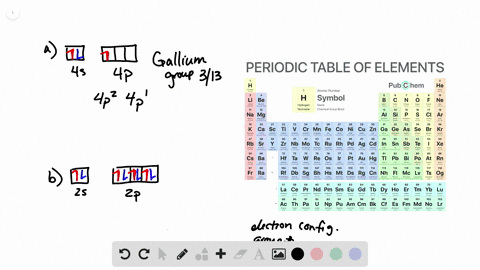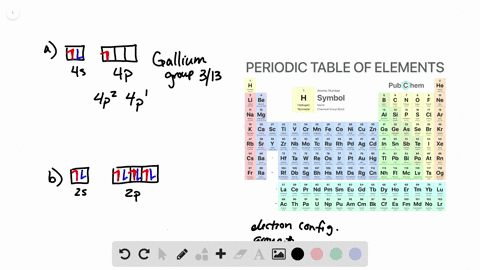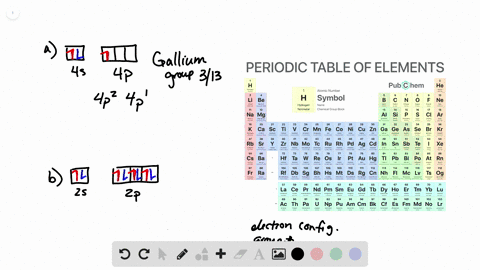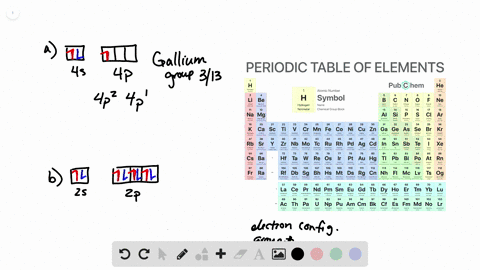
Solved From Each Partial Valence Level Orbital Diagram Write The Condensed Electron Configuration And Group Number A B
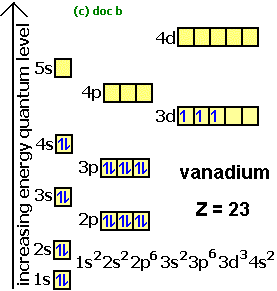
An atom of vanadium (Z=23) in its ground state has _____ valence electrons. 5. Rank the following elements in order of increasing metallic character (from least metallic at the top of the list to most metallic at the bottom). Al, P, Cs, Zn.

Draw The Partial Valence Level Orbital Diagram And Write The Symbol Group Number And Period Number Of The Element Ar 4s 2 3d 10 4p 3 Image Src Orbital9195593143458043682 Jpg Alt Orbital C Study Com
Draw a partial (valence-level) orbital diagram, and write the condensed ground-state electron configuration for each: $$ \begin{array}{llll}{\text { (a) Ti }} & {\text { (b) } \mathrm{Cl}} & {\text { (c) } \mathrm{V}}\end{array} ... Period 4 transition element that forms $3+$ diamagnetic ion (n) Period 4 transition element that forms $2+$ ion ...
a. the n = 3 shell has no f subshell b. there are three p orbitals in every shell of an atom except the n = 1 shell c. all s orbitals have spherical shapes d. each d subshell has five d orbitals e. the energies of subshell in the shells (energy levels) of a hydrogen atom vary as s < p < d, etc.
• The molecular orbital energy level diagrams for F 2 and B 2 are shown below. Fill in the valence electrons for each species in its ground state. Hence calculate the bond order for F 2 and B 2 and indicate whether these molecules are paramagnetic or diamagnetic. Marks 3 F 2 B 2 Bond order ½ (8 – 6) = 1 ½ (4 – 2) = 1 Paramagnetic or ...
Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
Hello. My name is Margaret. And today I'm gonna be helping you with problem 33 from Chapter eight of chemistry. Molecular nature of matter and change. 2016. Ah, and we're going to draw the partial orbital diagram on and then identify the symbol group number of period number for two different ...
A 4s orbital is higher in energy than a 3s orbital. As increases, orbital energy increases. In the n = 3 shell, 3s < 3p < 3d. As n increases, the subshell energies become more closely spaced and overlapping occurs. The 4f orbital is higher in energy than the 5s orbital, despite its lower n value. 7.3 Electron Configuration of Elements

Wadsley Roth Crystallographic Shear Structure Niobium Based Oxides Promising Anode Materials For High Safety Lithium Ion Batteries Yang 2021 Advanced Science Wiley Online Library
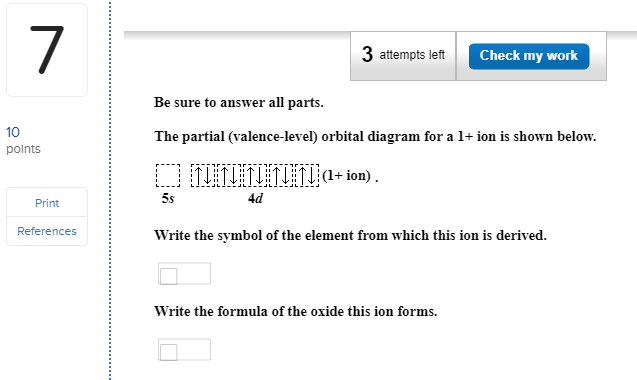
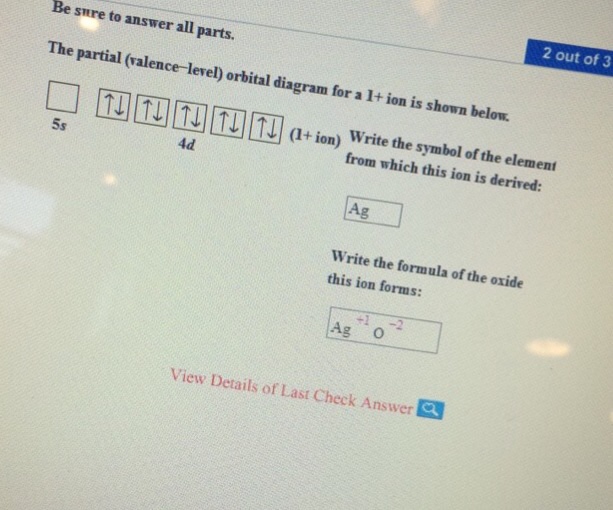
10 polnts The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 1+ ion is shown below. + ion 4d Print References Write the symbol of the element from which this ion ...
Solved The Orbital Diagram That Follows Shows The Valence Electrons For A 2 Ion Of An Element A What Is The Element B What Is The Electron Configuration Of An Atom Of This
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. __ 4s (no arrows) __ __ __ __ __ 3d (two arrows in the first box, up and down) (One up arrows in the rest of the boxes, 6 arrows total) Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived. Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms. The answer is not Fe or Cr.
The Aufbau principle tells you that the lowest-energy orbitals fill first, but the specific order isn't sequential in a way that's easy to memorize. See Resources for a diagram showing the filling order. Note that the n = 1 level only has s orbitals, the n = 2 level only has s and p orbitals, and the n = 3 level only has s, p and d orbitals.
(a) Use the “Frost circle” approach to generate an approximate valence π-MO energy level diagram (energy levels only!) for cyclic hydrocarbon species of the form [C 5H 5]x. Be sure to label each molecular energy level on your diagram with the correct label.
Electron Configurations How To Write Out The S P D F Electronic Arrangements Of Atoms Ions Periodic Table Oxidation States Using Orbital Notation Gce A Level Revision Notes
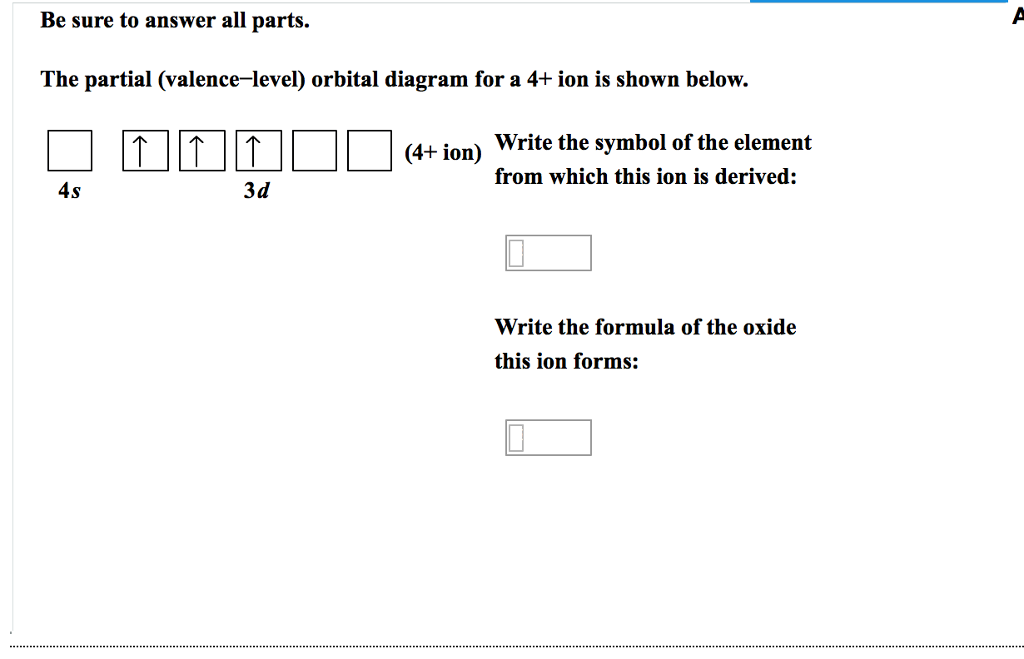
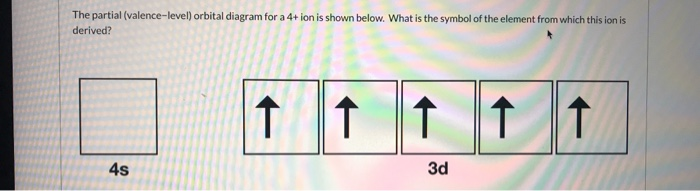
A. the partial valence-level orbital diagram for a 4+ ion is 4s __ 3d 1 1 1 _ _ What is the element from which the ion is derived? Question : A. the partial valence-level orbital diagram for a 4+ ion is 4s __ 3d 1 1 1 _ _ What is the element from which the ion is derived?
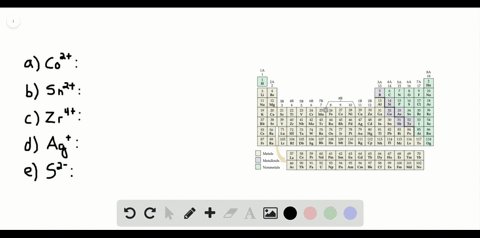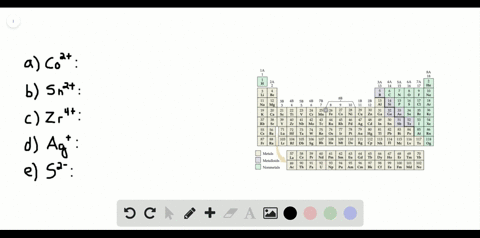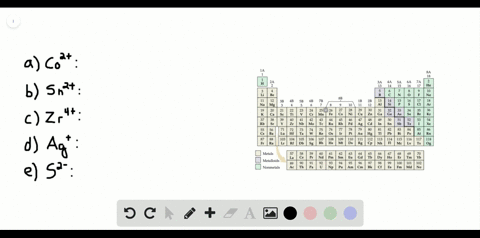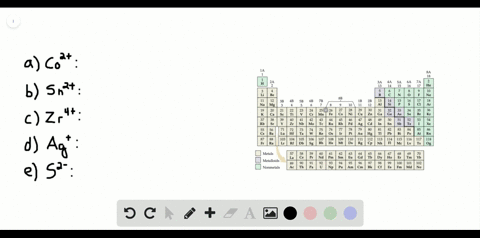
Solved Partial Valence Level Electron Configurations For Four Different Ions Are Shown Below Identify The Elements From Which The Ions Are Derived And Write The Formula Of The Oxide Each Ion Forms
Best Answer: look at the number of valence electron here. it's on the orbital number 5, having a total of 4 valence electrons (outermost shell electrons) that will contribute to bonding. So with F having a -1 charge. And E will have to be a cation of +4. So total is EF4.

Be Sure To Answer All Parts Draw The Partial Valence Level Orbital Diagram And Write The Symbol Homeworklib
Procedure for Construct ing Molecular Orbital Diagram s Based on Hybrid Orbital s 1. Begin with the Lewis structure. 2. Decide how many orbital s each atom needs to make its sigma bonds and to hold its non-bonding electrons. Draw the atomic and hybrid orbital s on on side of the page. 3. For each sigma bond, take a hybrid (or atomic) orbital ...
The molecular, sp 3 orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedron, with bond angles of 109.5 o. Each of the 1s orbitals of H will overlap with one of these hybrid orbitals to give the predicted tetrahedral geometry and shape of methane, CH 4. Hybridization also changes the energy levels of the orbitals. The 2s orbital of carbon is lower in energy than the 2p orbitals, since it is more penetrating.
Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is ...
The valence molecular orbital diagram for the cation f2+ is shown. which of the following options correctly interpret this diagram? * F2+ has a stronger bond than F2 *The olecular orbital bond order is equal to 3/2
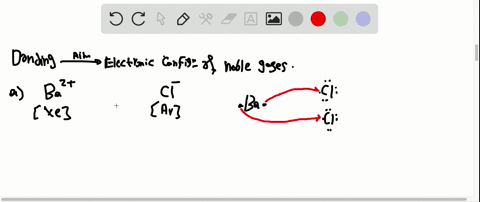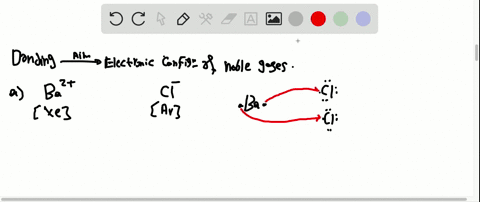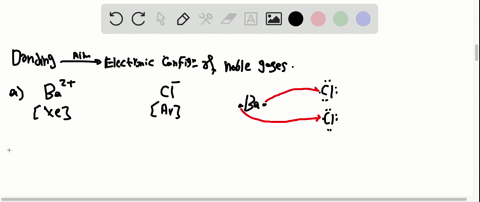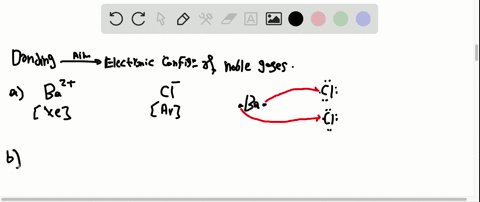
Solved Partial Valence Level Electron Configurations For Four Different Ions Are Shown Below Identify The Elements From Which The Ions Are Derived And Write The Formula Of The Oxide Each Ion Forms
a. The n = 3 shell has no f subshell b. There are three p orbitals in every shell of an atom except the n = 1 shell c. All s orbitals have spherical shapes d. Each d subshell has five d orbitals e. The energies of subshell in the shells (energy levels) of a hydrogen atom vary as s < p < d, etc.

Am C5me4h 3 An Organometallic Americium Complex Goodwin 2019 Angewandte Chemie International Edition Wiley Online Library
Chemistry questions and answers. Be sure to answer all parts. Re The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 1+ ion is shown below. 5s 4d Gu Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms. Question: Be sure to answer all parts.
The placement of the next electron must follow Hund's rule. The orbital diagram shows three unpaired electrons. The electron configuration for nitrogen is 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. For oxygen the eighth electron must pair with one of the electrons in the 2p orbitals. The orbital diagram for oxygen is shown on the left.
M.O.Energy Level Diagram for A2 (A = Li, Be) Li2 Only two valence electrons, i.e. σs 2σ*s 0. Bond order = 1. Diamagnetic Li2 exists in gas phase over metallic lithium. "Be2" σ s 2σ* s 2 B o ndr e= 0 - t b i g energy, so molecule does not exist. Beryllium in gas phase is monatomic. Use Aufbau, Pauli, Hund - just as in filling atomic orbitals
Partial (valence-level) electron configurations for four different ions are shown below: Identify the elements from which the ions are derived, and write the formula of the oxide each ion forms. Step-by-step solution. 100% (10 ratings) for this solution. Step 1 of 3.

Comprehensive Understanding Of The Roles Of Water Molecules In Aqueous Zn Ion Batteries From Electrolytes To Electrode Materials Energy Environmental Science Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 D1ee00030f
Valence electrons. Orbital diagram. Orbital diagram for titanium. Answer to: Fill in the orbital energy diagram for titanium. The lowest E levels are already filled in for you. This video shows how to draw the orbital diagram of Titanium (Ti). It also shows how to write the electron configuration of titanium and the shorthand noble...
Solved Attempts Ieft Check My Work Be Sure To Answer All Parts The Partial Valence Level Orbital Diagram For A 2 Ion Is Shown Below Ihihwi Hile Ion Write The Symbol Of The Element From Which
According to the Aufbau process, sublevels and orbitals are filled with electrons in order of increasing energy. Since the s sublevel consists of just one orbital, the second electron simply pairs up with the first electron as in helium. The next element is lithium and necessitates the use of the next available sublevel, the 2s.. The filling diagram for carbon is shown in the Figure below.
Atomic Orbital Diagram: Atoms contain electrons, and they are arranged, based on different rules, in various available orbitals. This is shown in the atomic orbital diagram.
The partial (valence level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below... Then it shows a box with no arrows for the 5s orbital (aka no electrons) then it shows the 4d orbital with five boxes the first 3 boxes have an up and down arrow in each box (indicating the electrons spin (spin up spin down)) and the last 2 boxes only have spin up arrows.
If you're working with an ion, adjust the valence electron count according to the charge. 2. Identify the valence shell for each atom. You will need to use all the atomic orbitals (AOs) in the valence shell of each atom to build your molecular orbital (MO) energy level diagram. 3. Draw a Lewis diagram for the molecule.
Answer to The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 4+ ion is shown below....
The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms: Question: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 2+ ion is shown below.
5.13 The energy level diagram for SH- is shown below. A bond order of 1 is predicted. The S orbital energies are -22.7 eV (3s) and -11.6 eV (3p); the 1s of H has an energy of -13.6 eV. Because of the difference in their atomic orbital energies, the 1s orbital of hydrogen and the
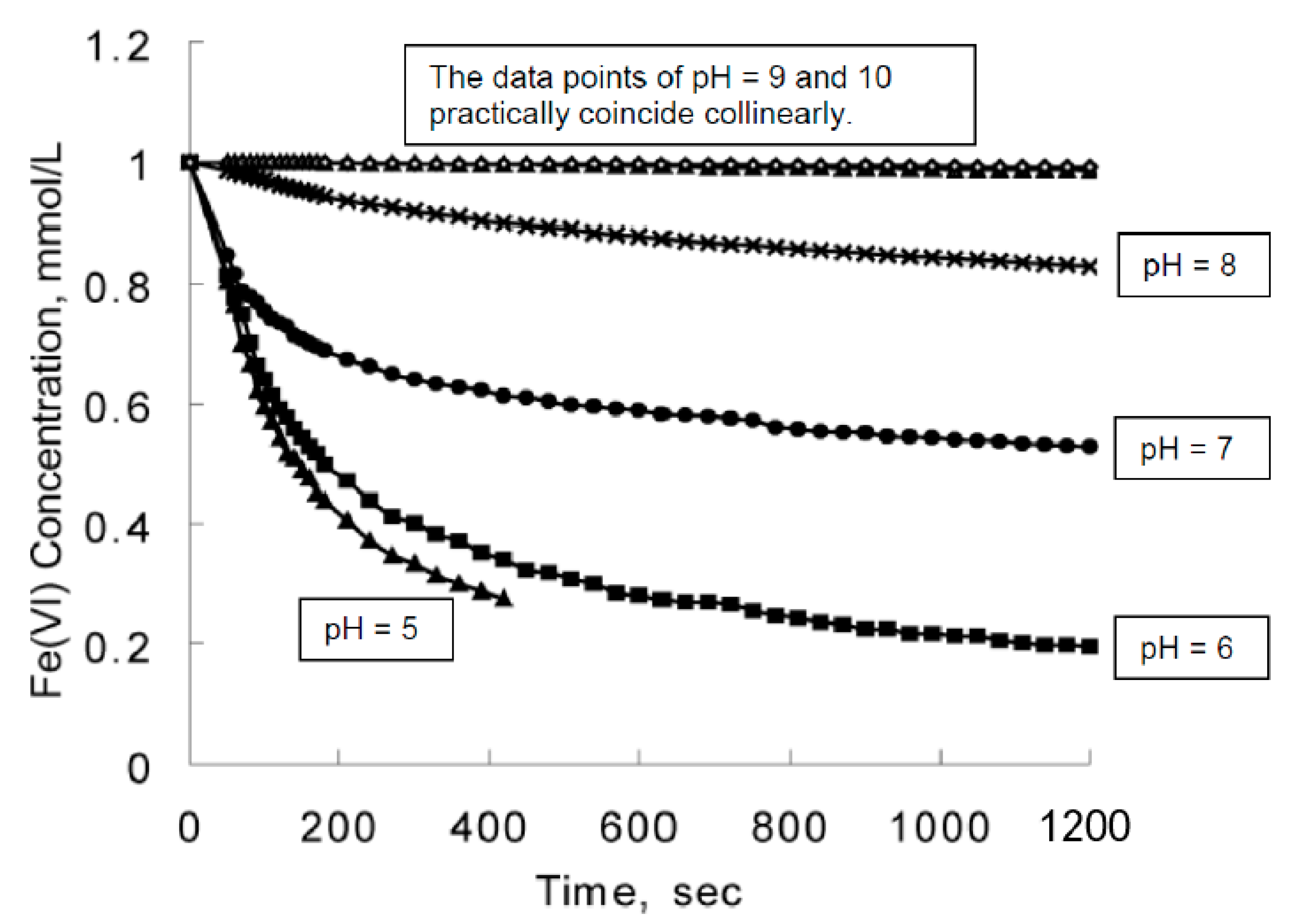
Molecules Free Full Text On The Origins Of Some Spectroscopic Properties Of Purple Iron The Tetraoxoferrate Vi Ion And Its Pourbaix Safe Space Html
Chemistry questions and answers. The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below. Write the symbol of the element from which this ion is derived: Write the formula of the oxide this ion forms: Question: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below.
Transcribed image text: The partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3-ion is shown below. What is the symbol of the element from which this ion is ...









0 Response to "35 the partial (valence-level) orbital diagram for a 3+ ion is shown below."
Post a Comment