35 schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram
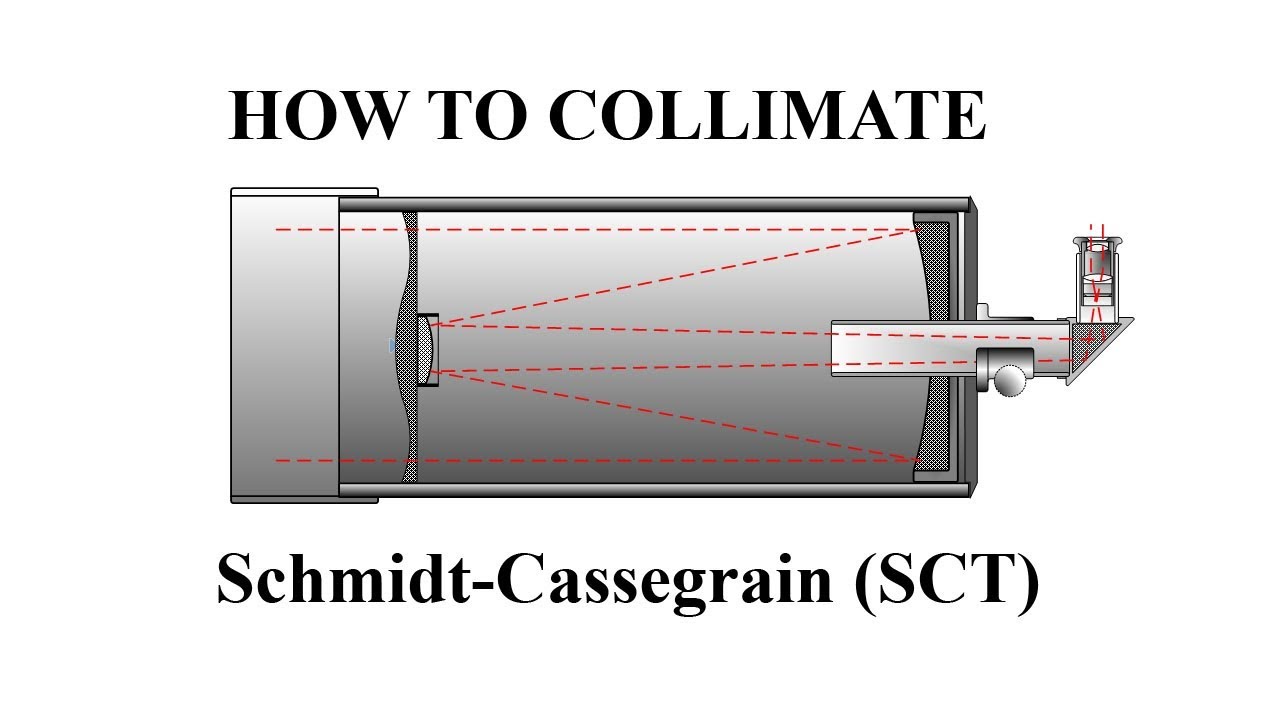
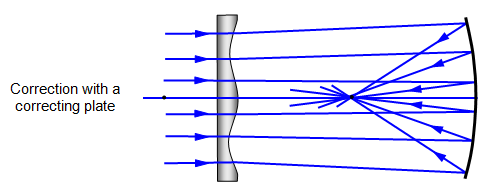
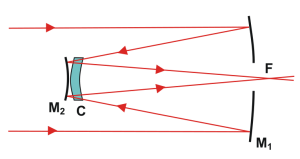
Collimating a Schmidt-Cassegrain. Collimation is critical to obtaining the best performance from your telescope. Aligning the optics of a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope (SCT) is much easier than collimating a Newtonian telescope and can easily be learned by any user. However, there are some tricks to doing it right, and some things to avoid. As the name implies, Schmidt-Cassegrains use a Schmidt corrector lens, while a Maksutov-Cassegrain uses a Maksutov corrector lens. Schmidt corrector lenses have an aspherical shape. The curve on the lens is very slight, and the glass looks perfectly flat to the eye. The curve is drawn greatly exaggerated in the diagram at the top of the page.
The first element comprises a relatively thin transmissive shell concave toward the front. The second element comprises a mirror concave toward the front. The front surface of the shell may be spherical, and the rear surface aspheric, or vice versa. The central portion of the first element on either the front or back surface is mirrored to form the secondary of the system.
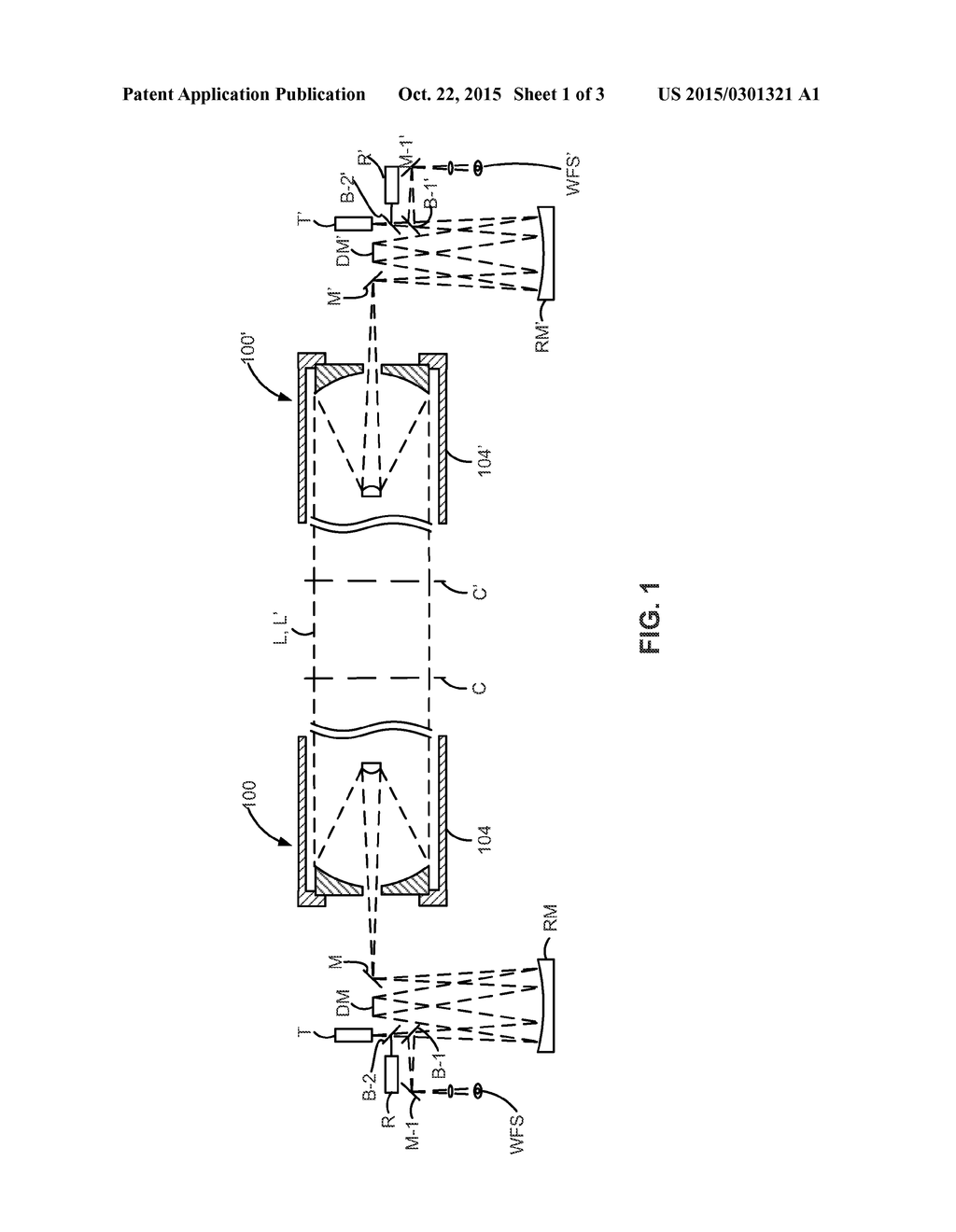
Schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram
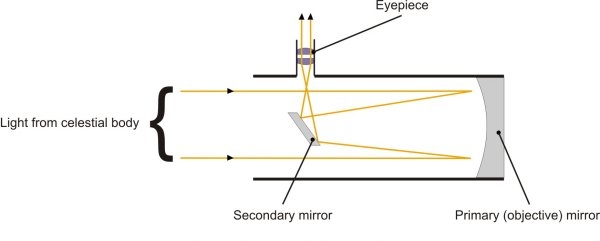
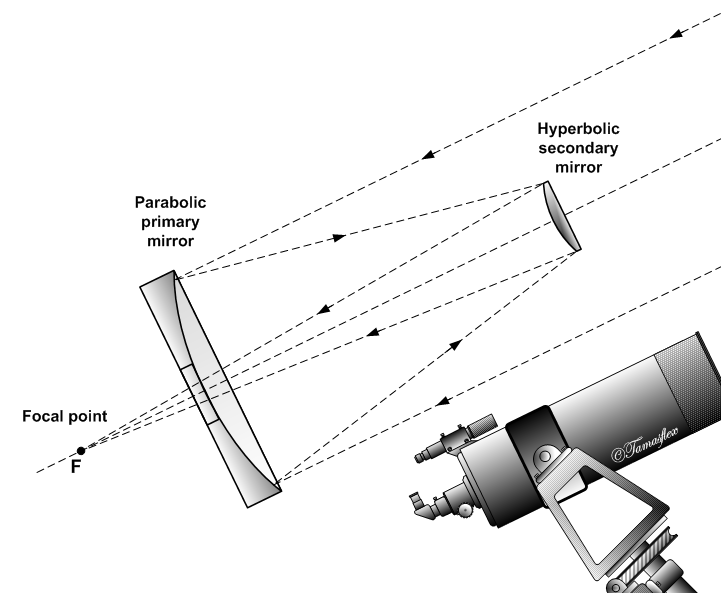
Schematic Diagram Of The Adapted Receiving Meade Schmidt Cassegrain Scientific. A Cassegrain Telescope Uses Two Mirrors As Shown In Figure Below Such Is Built With The 20 Mm Apart If Radius Of Curvature Large Mirror. Difference Between Newtonian And Cassegrain Telescope Off 65 Medpharmres Com. Schematic Drawing Of The Adapted Meade Schmidt ... In 1970, Celestron introduced the C8, an 8" f/10 Schmidt-Cassegrain. It sold for $795. The scope was an immediate success, offering high quality optics in a compact package that was reasonably affordable. This was during a time when almost all telescopes were handmade Newtonian reflectors. Figure 1-1. This cross-section diagram shows the light path of the Schmidt-Cassegrain optical system. Note that the light rays travel the length of the telescope tube three times, making this a compact design. Note that the curve of the corrector plate is greatly exaggerated.
Schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram. Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes. The Schmidt-Cassegrain is not a telescope you will find in major research observatories, but it is arguably the most widespread design used in the amateur telescope market. As its name implies, it is a hybrid of the Schmidt and Cassegrain designs. The light passes through a corrector lens and reflects off a concave spherical primary, just like in a Schmidt telescope. 102mm Wide View Manual. 11-inch Dovetail Bar Diagram. 14-inch Dovetail Bar Diagram. 2013 Sport Optics Guide. 21036-WM Instruction Manual Addendum. 28 pc. Microscope Kit Manual. 4 Color LCD Weather Station Manual (English, French, German, Italian, Spanish) 44310 LCD Handheld Microscope Manual (English, French, German, Italian, Spanish) View the secondary mirror holder from the corrector plate end of the Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope. The collimation screw nearest the ground is labeled “A”. Screws “B” and “C” are as shown in the center of the diagram above. The eyepiece should be oriented upward opposite to the position of screw “A” as shown by “EP” in the ... A Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope is a CASSEGRAIN TELESCOPE because the secondary is a convex mirror is on the main optical axis of the telescope and creates the ...
The kind of telescope illustrated in the diagram (of course, not to scale!) is a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope on a fork mount. The telescope is rotated to point in different directions relative to a surface which is tilted to be at the same angle as the ground at the North Pole. A pole is actually shown in the diagram, to make the Earth's axis ... Superior Optical Design. This 12-inch Schmidt Cassegrain telescope offers a superior optical design that ensures completely coma-free images of the object you are observing. It is the perfect choice for everyone who wants to enjoy observatory-class optics that provide the most beautiful Astro images. Built-In GPS. Schmidt telescope, also called Schmidt camera, telescope in which a spherical primary mirror receives light that has passed through a thin aspherical lens, called a correcting plate, that compensates for the image distortions—namely, spherical aberrations—produced by the mirror. The Schmidt telescope is thus a catadioptric telescope; i.e., its optics involve both the reflection and ... The telescope features a 6″ Schmidt Cassegrain Optical Tube Assembly and an Aluminum Optical Tube. It has StarBright XLT coatings, which are the premium choice in this industry. This innovative coating is made up of three different layers that greatly increase contrast and light transmission.
What Is A Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope? SCT telescopes are the more commonly used compound based telescopes whilst also being more expensive. As to why, it's mostly due to these systems being lighter when fully formed and much better for other telescopic activities such as astrophotography. ... (the SCT diagram exaggerates the curve but it is ... 4 Mar 2020 — The Schmidt-Cassegrain (SCT) optical system uses a combination of mirrors and lenses and is referred to as a compound or catadioptric telescope. The Schmidt-Cassegrain was developed from the wide-field Schmidt camera, although the Cassegrain configuration gives it a much narrower field of view.The first optical element is a Schmidt corrector plate.The plate is figured by placing a vacuum on one side, and grinding the exact correction required to correct the spherical aberration caused by the spherical primary mirror. A SCHMIDT-CASSEGRAIN TELESCOPE by ANUPAM S. GARGE KWANG JAE LEE ME 555-07-09 Winter 2007 Final Report ABSTRACT The goal of the project is to find an optimal design of a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope which is popular for amateur astronomers. The telescope model includes two disciplines viz. Optics and Thermal design.

Modified Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope For Use In A Free Space Optical Communications System Diagram Schematic And Image 02
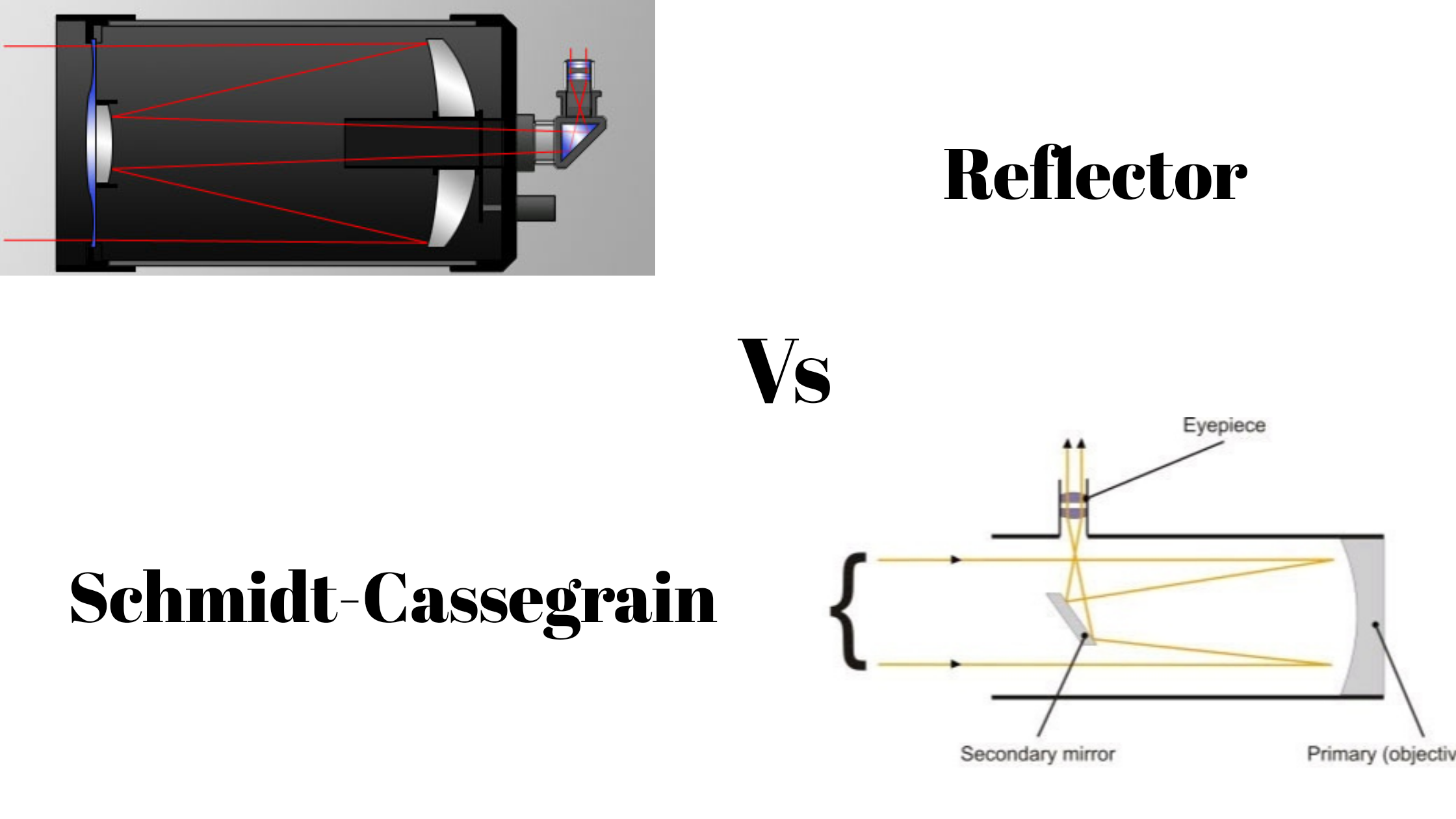
The Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope (SCT) The Schmidt Cassegrain, or SCT, is a bit stubbier (shorter) for a given aperture, as illustrated above. It uses a somewhat complex curve on a nearly flat corrector plate to compensate for the spherical primary. The aspheric curvature of the corrector plate is exaggerated in this diagram.
Schmidt-Cassegrain telescopes are some of the most popular pieces of equipment on the market, favored for their large aperture in a relatively small, lightweight package. Perhaps the best way to describe a Schmidt-Cassegrain would be to label it as "the jack of all trades" among telescope designs.
Answer (1 of 6): Here's a diagram of a Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope (SCT). The label at the bottom refers to a general class of telescopes which use a combination of mirrors and lenses. As you can see, incoming light is reflected from the primary mirror, bounced of a secondary mirror, and back th...
The SCT combines a simple spherical mirror with a specially-figured lens at the front of the tube to correct for spherical aberration, with a piece of film ...
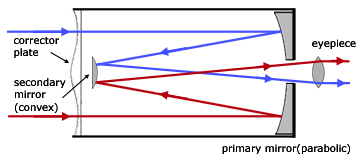
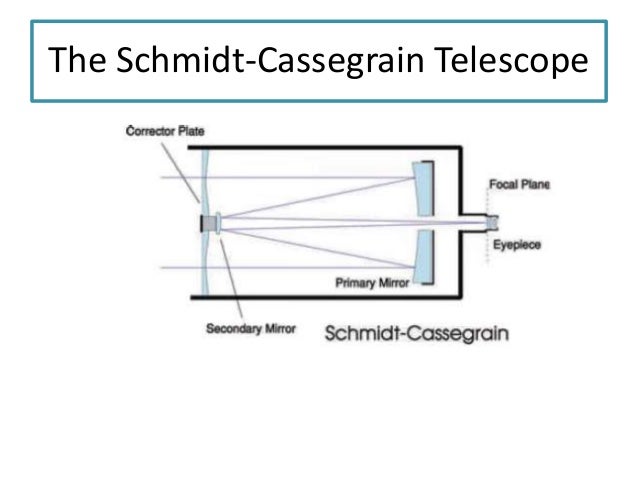
The Meade Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical System 8.25" 7" Primary Baffle Tube Secondary Baffle Field Stops Primary Mirror (f/2.5) Focal Plane The Meade 7" (178mm) Maksutov-Cassegrain Optical System Meniscus Lens The Meade 7" Maksutov-Cassegrain design optimizes imaging performance by utilizing a combination of a two-sided
A Schmidt-Cassegrain has a Schmidt correcting lens that collects an object's light. From that aspherical, or non-round, lens, the light goes to a round mirror, which reflects it back toward the telescope's front to another mirror and then to the eyepiece, which is at the telescope's back.
14 May 2020 — The image above shows the light path of a “classical” Cassegrain telescope. Like a Newtonian, this design uses a parabolic mirror at one end of ...
Newtonian Telescope Diagram Schmidt-Cassegrain Telescope Diagram. Refractor vs. Reflector Refractors utilize specially designed lenses to focus the light into an image. The larger the lens is in a refracting telescope, the longer the optical tube must be to bring the image into focus.
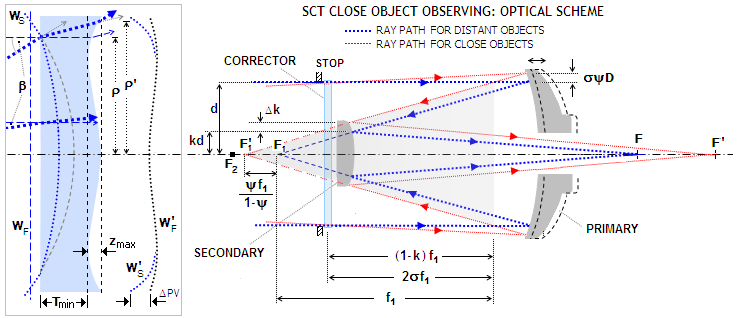
While there are many variations of the Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope design (both mirrors spherical, both mirrors aspherical, or one of each), they can be divided into two principal types: compact and non-compact.In the compact form, the corrector plate is located at or near the focus of the primary mirror.
Laurent Cassegrain, a French instrument maker, died Aug. 31, 1693, at the age of about 64. Cassegrain, whose name is well known to amateur telescope makers, is the most shadowy of historical figures; we didn't even learn his first name until 1997. In 1672, Cassegrain invented a new kind of reflecting telescope.

Pdf Design Optimization Model For A Schmidt Cassegrain Telescope Me 590 Final Report Semantic Scholar
FIGURE 174: Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope is a Cassegrain-like two-mirror system combined with a full-aperture Schmidt corrector.Various combinations of corrector separation and mirror conics are possible, with somewhat different image field properties. Prevailing commercial arrangement is a compact design with fast spherical primary and usually also spherical secondary mirror, resulting in ~ƒ ...
The Meade Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical System (Diagram not to scale) In the Schmidt-Cassegrain design of the Meade 8", 10", and 12" models, light enters from the right, passes through a thin lens with 2-sided aspheric correction ("correcting plate"), proceeds to a spherical primary mirror, and then to a convex aspheric secondary mirror.
Abstract. The basic principle of the wide-field telescope invented by the Estonian optician and astronomer Bernhard Schmidt in 1928 ([67-70], E. Schmidt [72]), is that a single concave and spherical mirror used with a pupil stop at its center of curvature has no unique axis and therefore yields equal size images at all points of its field of view.
Reflector Telescopes Joseph A. Shaw - Montana State University Dall-Kirkham • Primary mirror = ellipse • Secondary = sphere • Spherical = 0 (on axis, obj at inf) • Spherical secondary generates additional aberrations … • Field limited by coma, to about times smaller than for classical cassegrain. "poor man's cassegrain"
The Meade Schmidt-Cassegrain Optical System 8.25" 7" Primary Baffle Tube Secondary Baffle Field Stops Primary Mirror (f/2.5) Focal Plane The Meade 7" (178mm) Maksutov-Cassegrain Optical System Meniscus Lens The Meade 7" Maksutov-Cassegrain design optimizes imaging performance by utilizing a combination of a two-sided
Schmidt-Newtonian: This telescope is a cross between a Newtonian telescope and a Schmidt-Cassegrain. This telescope differs from the Schmidt-Cassegrain in that the image is formed on the side of the tube. Downsides of Catadioptric Telescopes. Obviously, catadioptric telescopes are great for their clarity and error-corrective qualities, but ...
Equations to determine the conic constant of primary and secondary mirrors in Cassegrain telescopes. So how to figure the mirrors? Calculate K values for the mirrors in your Cassegrain. For example, in a 12.5" F/12.5 Classical Cassegrain, K p = -1 for the primary and K s = -4.00 for the secondary. The primary is a parabola, so we know how to ...
Figure 1-1. This cross-section diagram shows the light path of the Schmidt-Cassegrain optical system. Note that the light rays travel the length of the telescope tube three times, making this a compact design. Note that the curve of the corrector plate is greatly exaggerated.
In 1970, Celestron introduced the C8, an 8" f/10 Schmidt-Cassegrain. It sold for $795. The scope was an immediate success, offering high quality optics in a compact package that was reasonably affordable. This was during a time when almost all telescopes were handmade Newtonian reflectors.
Schematic Diagram Of The Adapted Receiving Meade Schmidt Cassegrain Scientific. A Cassegrain Telescope Uses Two Mirrors As Shown In Figure Below Such Is Built With The 20 Mm Apart If Radius Of Curvature Large Mirror. Difference Between Newtonian And Cassegrain Telescope Off 65 Medpharmres Com. Schematic Drawing Of The Adapted Meade Schmidt ...
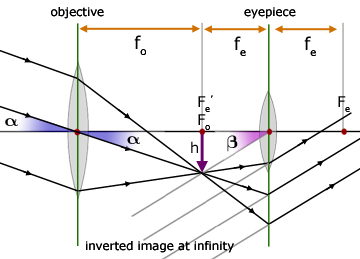
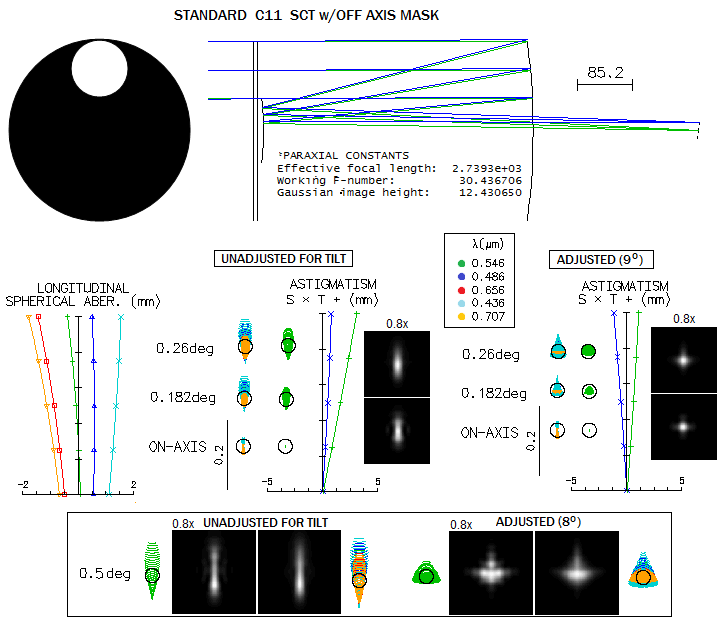

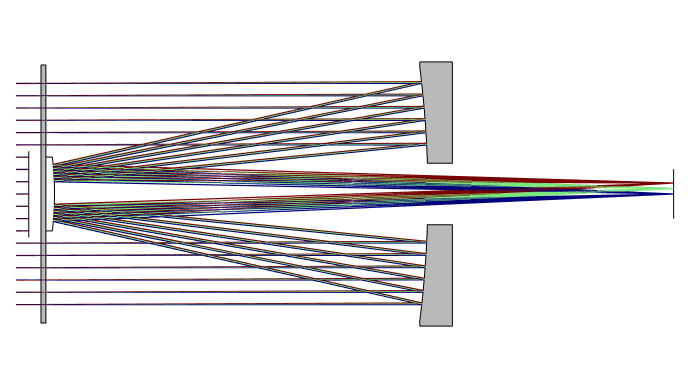








0 Response to "35 schmidt cassegrain telescope diagram"
Post a Comment