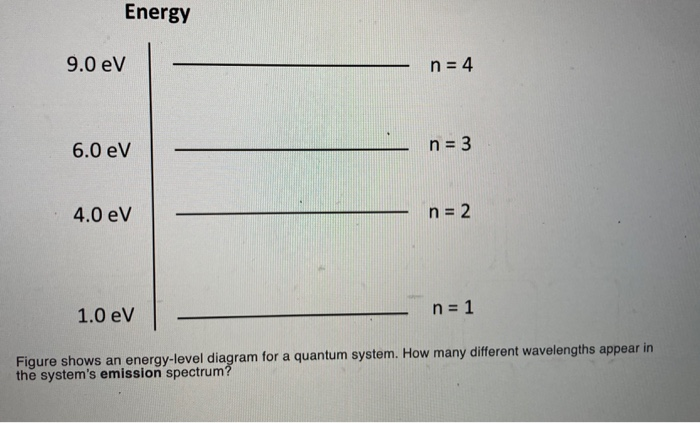
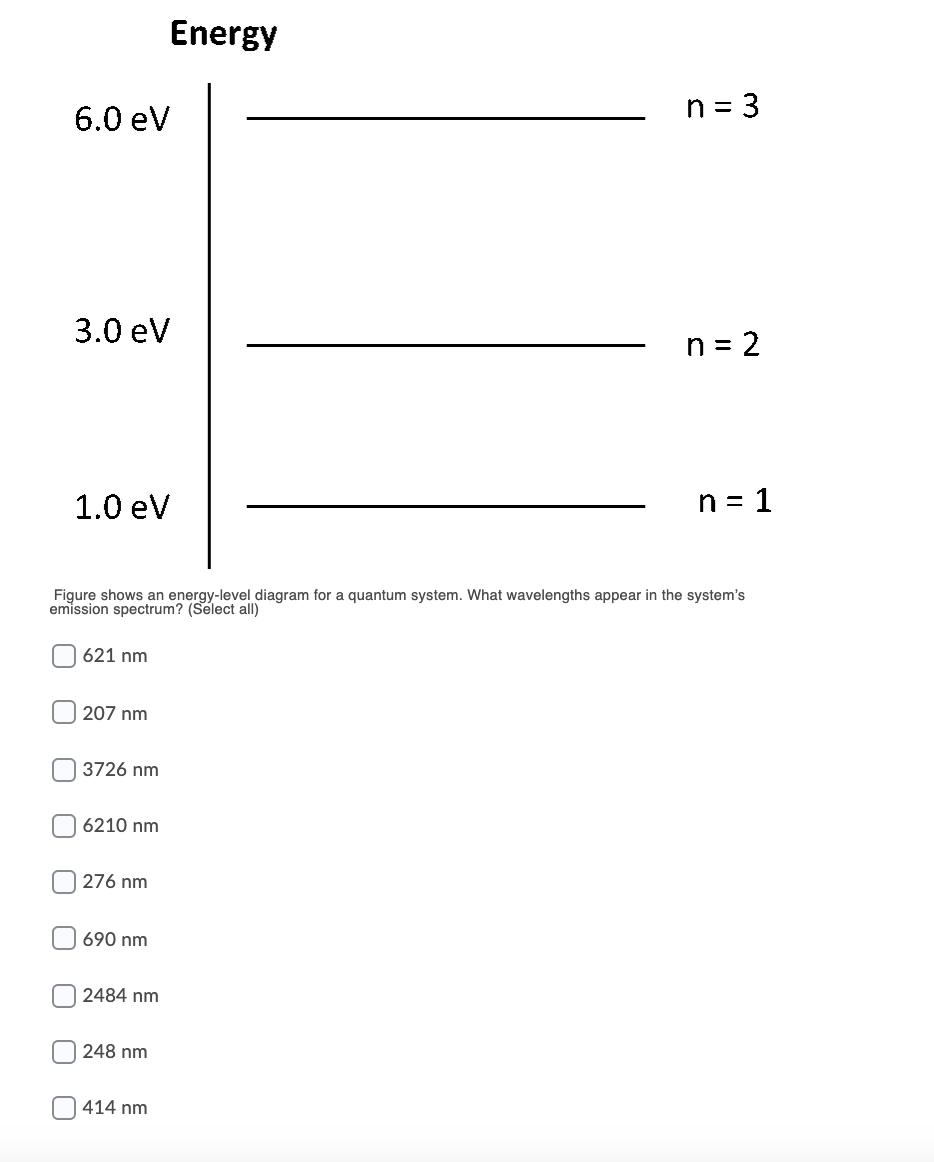
36 the figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system.(figure 1)
Imgur. The energy of the electron of a monoelectronic atom depends only on which shell the electron orbits in. The energy level of the electron of a hydrogen atom is given by the following formula, where. n. n n denotes the principal quantum number: E n = − 1312 n 2 kJ/mol. E_n=-\frac {1312} {n^2}\text { kJ/mol}. E n. A mass of 0.250 kg oscillates on a spring with the force constant 110 N/m. Calculate the ground energy level and the separation between the adjacent energy levels. Express the results in joules and in electron-volts. Are quantum effects important?
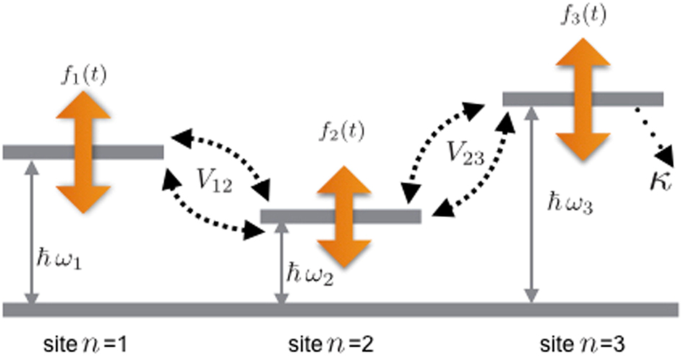
Figure 8. Schematic diagram for the possible system to implement single-photon nonreciprocal transmission based on the circuit QED system: an LC circuit is coupled to a transmon qubit via the capacity C J and they are simultaneously coupled to a superconducting transmission line, which supports many bosonic modes with a linear dispersion relation.
The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system.(figure 1)
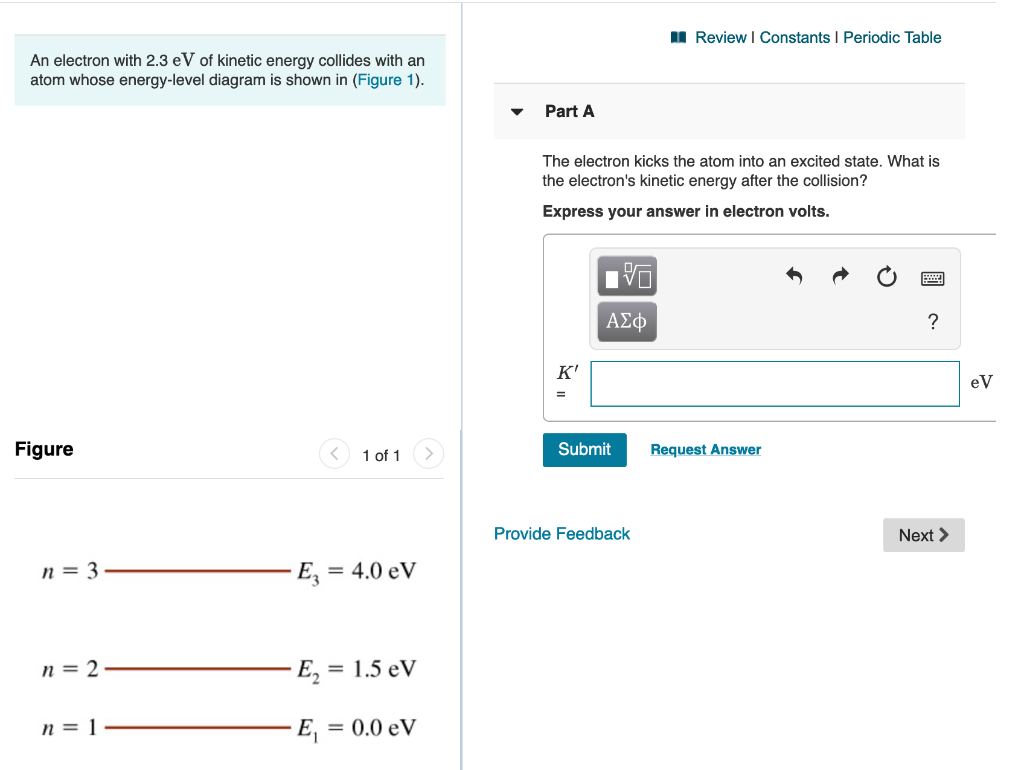
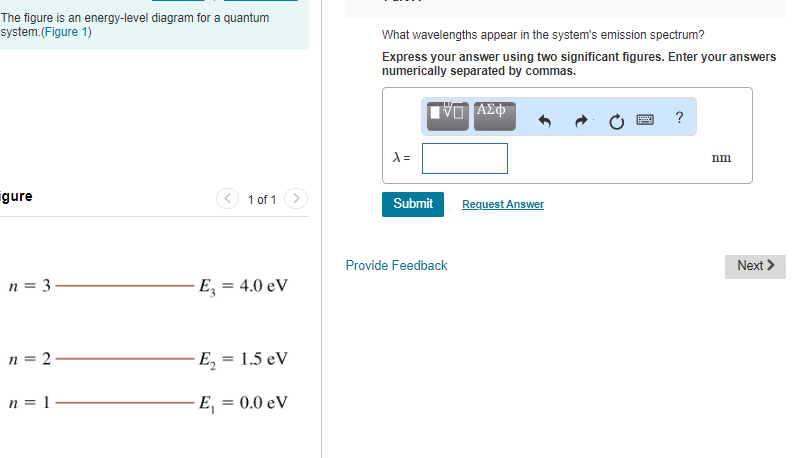
3. Angular Momentum States. p.2.July 27, 1999 electron be symbolized by S.According to classical mechanics the values of L and S are given by equations 1 and 2, respectively. L = mvr(1) S = Iv (2) According to classical mechanics, both the orbital and spin angular The spacing between energy levels is drawn to scale. (Figure 1) P<Q<R. Light with a wavelength of 435 nm illuminates a metal cathode. The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is 0.96 eV . ... (Figure 1) is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system. What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum? 829, 497, 311 nm. Transcribed image text: Problem 28.39 The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system.(Figure 1) n = 3 ----- E3 = 4.0 eV n = 2 ----- E2 = 1.5 eV n= 1 ----- E1 = 0.0 eV Part A What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum? Express your answer using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Lambda =
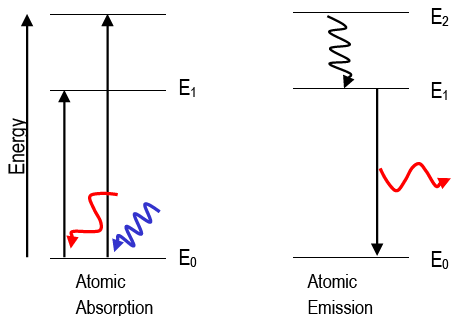
The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system.(figure 1). III (Early Quantum Ideas) 20 points (4 points each) 1. The figure below shows a portion of the emission spectrum of a one-electron atom in the gas phase. All of the lines shown result from transitions from excited states to a final state of n = 4. Wavelength B A a. 39.50. Model: Photons are emitted when an atom undergoes a quantum jump from a higher energy level to a lower energy level. On the other hand, photons are absorbed in a quantum jump from a lower energy level to a higher energy level. Because most of the atoms are in the n = 1 ground state, the only quantum jumps in the absorption spectrum start from the n = 1 state. label the allowed energy levels. Negative values of n add nothing new because the energies in Eq (18) depends on n2. Fig. 1 shows part of the energy-level diagram for the particle in a box. The occurrence of discrete or quantized energy levels is characteristic of a bound system, that is, one conflned to a flnite region in space. Figure 1 (a) A metal-coated dielectric nanosphere and (b) a two-dimensional array of such spheres used in this work. (c) The energy-level diagram of the quantum system and the relevant couplings. The two upper states | 2 〉 and | 3 〉 decay with spontaneous emission to the two lower states | 0 〉 and | 1 〉.
ED1-1 Energy Diagrams I Goal Changes in energy are a good way to describe an object's motion. Here you will construct energy diagrams for a toy car and learn how these diagrams can be useful. This technique will prepare you for similar uses of energy diagrams in quantum physics. Introduction where Eis the total energy of the system. Let us now make a very fundamental assumption: that each particle occupies a ... be proven in relativistic quantum mechanics, but must be accepted as axiomatic in the ... Figure 5.2 - Energy level diagram for He (relative to He+, -54.4 eV). Note that parahelium (antisymmetric ... in this problem, We're going to talk about the emission spectrum of a quantum system that has three levels. The levels are quantum system are shown here on ... Although there is no pattern in the first four letters (s, p, d, f), the letters progress alphabetically from that point (g, h, and so on).Some of the allowed combinations of the n and l quantum numbers are shown in the figure below.. The third rule limiting allowed combinations of the n, l, and m quantum numbers has an important consequence. It forces the number of subshells in a shell to be ...
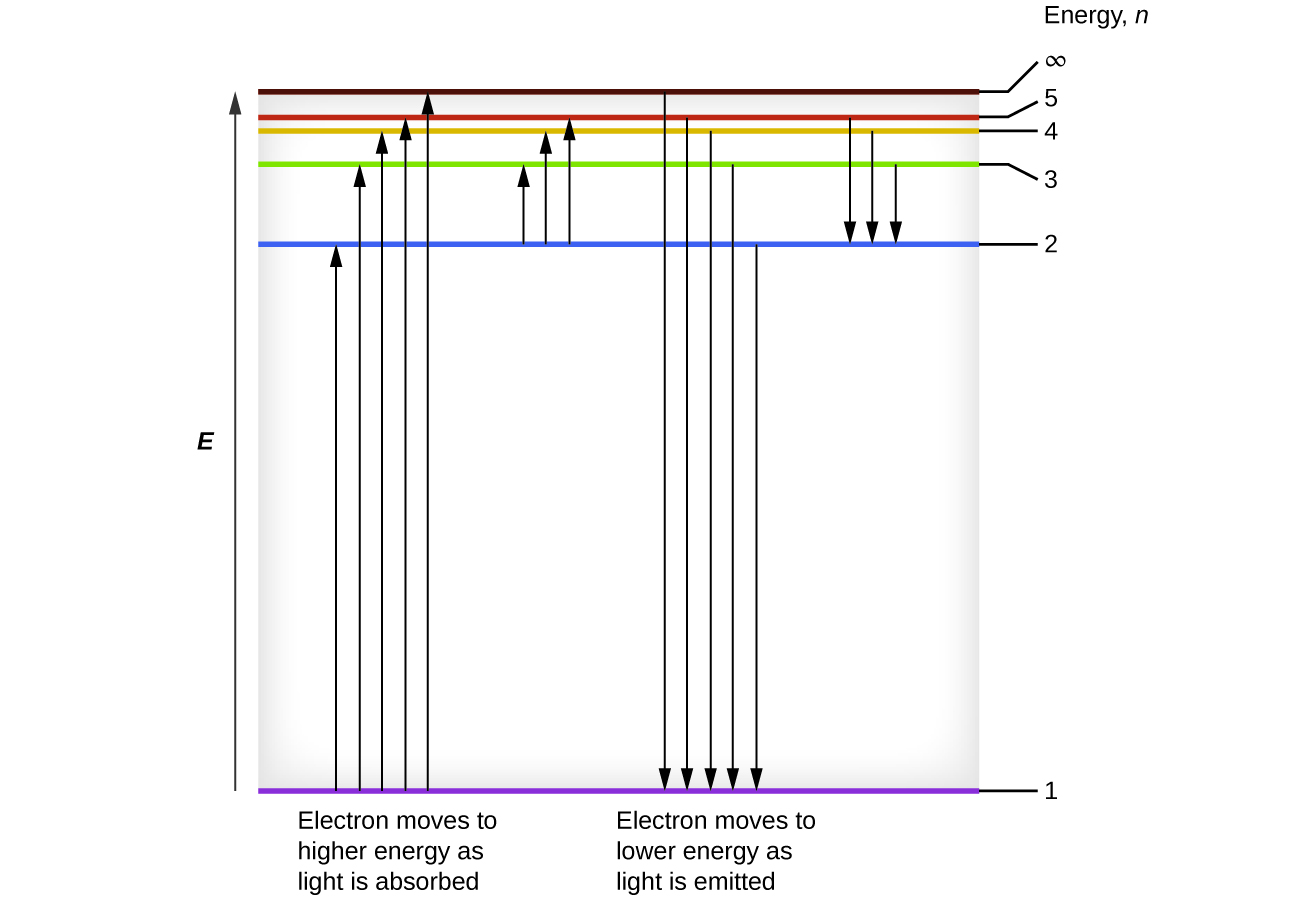
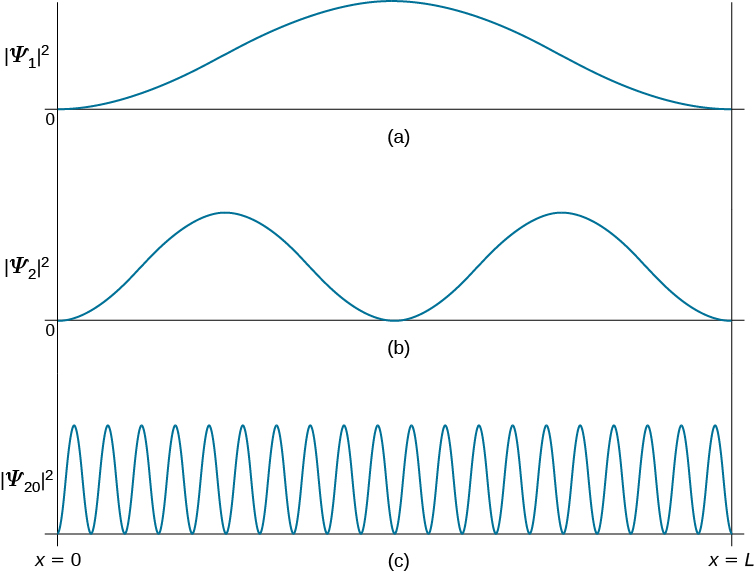
With two close atoms we must split the atom levels to satify Pauli's principle (the splitting is shown very large to ease reading, drawing b). You keep adding many, many atoms until the discrete energy levels split in so many levels that the system looks like a continuum (drawing c). The index n is called the energy quantum number or principal quantum number.The state for is the first excited state, the state for is the second excited state, and so on. The first three quantum states (for of a particle in a box are shown in .. The wave functions in are sometimes referred to as the "states of definite energy." Particles in these states are said to occupy energy levels ... FREE Answer to (Figure 1) is an energy-level diagram for a simple atom. ... The allowed energies of a quantum system are 1.0 eV, 2.0 eV, 4.0 eV, and 7.0 eV.2 answers · 3 votes: Emission and absorption spectrum has same frequency (or wave length) Part A Emission spectrum ... rotational energy levels of the excited states in different molecular orbitals. The various energy levels involved in the absorption and emission of light by a fluorophore are classically presented by a Jablonski energy diagram (see Figure 1), named in honor of the Polish physicist Professor Alexander Jablonski.
The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system. What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum? Question: The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system. What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum?
1 (in Figure 8.4, for example, all absorption transitions originate in the ground vibrational state). Use the Boltzmann distribution to calculate the ratio of populations in these states at 273K (room temperature) and at 350K. (a) The Anthracene spectrum is given in Figure 8.5 The wavelength of the S 1 v 1 S 0 v 1
An Energy Level Diagram For A Hypothetical Atom Is Shown Above Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
Apr 21, 2016 — The figure is an energy level diagram for a quantum system. ... Figure 1 if an electron at level 1 in a hydrogen atom absorbs 102 ev of ...
... 2 1.0 eV n = 1 Figure shows an energy-level diagram for a quantum system. ... How many different wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum?

Pdf Nonisotropic 3 Level Quantum Systems Complete Solutions For Minimum Time And Minimum Energy Semantic Scholar
Figure 9.2: Energy band and block charge diagrams for a p{type device under °at band, accumulation, depletion and inversion conditions. causes the Si bands to bend up at the oxide interface (see Fig.9.2) so that the Fermi level is closer to the valence-band edge. Thus extra holes accumulate at the semiconductor-oxide
Download scientific diagram | Energy levels of a coupled homonuclear AX spin system of spin-1. [The last column contains the total magnetic quantum number, m]. Energy levels are labeled [〈mA, mX ...
Energy Levels 4.1 Bound problems 4.1.1 . Energy in Square infinite well (particle in a box) 4.1.2 ... In the limit of large quantum numbers or small deBroglie wavelength λ ∝ 1/k on average the quantum mechanical ... is negative). Notice that I set E to be a positive quantity, and the system's energy is −E. We also assume that
The figure (Figure 1) is an energy-level diagram for a simple atom. ... The allowed energies of a quantum system are 1.0eV , 2.0eV , 4.0eV , and 7.0eV .
Energy +1 l = 1 0 -1 B e ---- 2m e B e ---- 2m e FIGURE 7-28 Energy-level splitting in the normal Zeeman effect for singlet levels /=2 and /=1. Each level is split into 2/ + 1 terms. The nine transitions consistent with the selection rule m 0, ˆ1, give only three different energies because the energy difference between ...
(6.7 A certain quantum mechanical system has the energy levels shown in the accompanying diagram. The energy levels are indexed by a single quantum number n that is an integer. (a) As drawn, which quantum numbers are involved in the ... 6.25 (a) Calculate the energy of a photon of electromagnetic radiation
item select "Eigenvalue" Æ "Level Diagram". You should see an energy level diagram with two energy levels above and below a dotted line (similar to the one in Figure 5). The dotted line corresponds to α, the energy of the 2py atomic orbitals. The lower level is labeled with an energy of 1.00 and this corresponds to α + 1.00β.
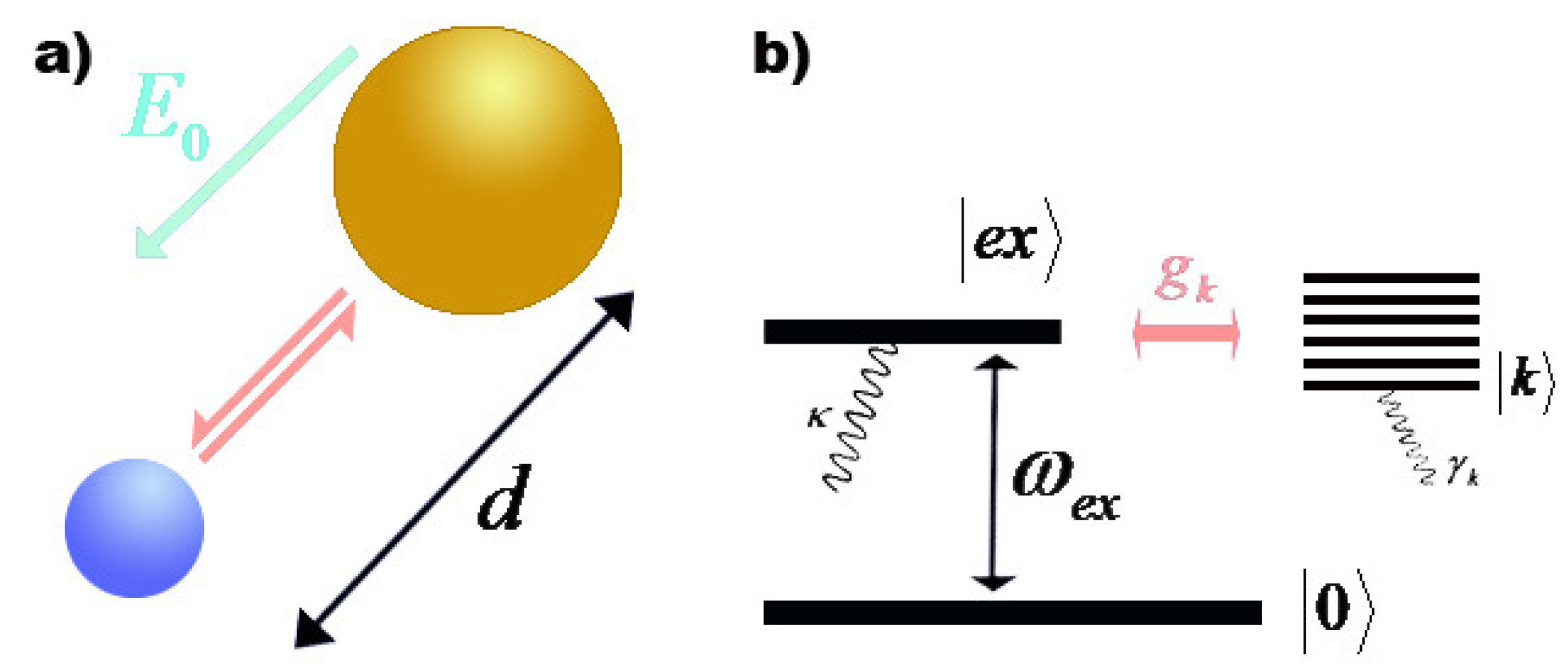
Figure 1 (Color online) Schematic energy diagram for a quantum dot junction of concern. Γ L and Γ R denote, respectively, the tunneling rates for electrons from the source to the quantum dot and from the quantum dot to the drain (which is grounded). (a) System without bias and (b) System with forward bias. (c) System with reverse bias.Reuse ...
The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system. (Figure 1) What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum? Express your answer using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. nm gure 1 of 1 Submit Provide Feedback E 4.0 eV n2 E21.5 eV.
Figure 1 shows the energy level diagram of a nucleus with a 1/2 spin and electron two-spin system. m S and m I are the magnetic quantum numbers for electron and nucleus, respectively. For this ...
Sensors Free Full Text Fano Effect And Quantum Entanglement In Hybrid Semiconductor Quantum Dot Metal Nanoparticle System Html
2.2.2.1 The infinite quantum well The infinite well represents one of the simplest quantum mechanical problems: it consists of a particle in a well which is defined by a zero potential between x=0 and x=L x and an infinite potential on either side of the well. The potential and the first five energy levels are shown in the figure below:
What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum (in nanometers)?. FREE Expert Solution. Energy:.1 answer · Top answer: Energy:E=hcλλ = hc/EAt 2.0 eV - 1.0 eV = 1.0 eV[readmore]λ=(6.63×10-34)(3.0×108)(1.0)(1.6×10-19)λ = 124 nmAt 4.0 eV - 1.0eV = 3.0 eVλ=(6.63×10-34)(3.0 ...
Transcribed image text: Problem 28.39 The figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system.(Figure 1) n = 3 ----- E3 = 4.0 eV n = 2 ----- E2 = 1.5 eV n= 1 ----- E1 = 0.0 eV Part A What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum? Express your answer using two significant figures. Enter your answers numerically separated by commas. Lambda =

The Interaction Between A Single Two Level Atom Coupled To An N Level Quantum System Through Three Couplings Sciencedirect
The spacing between energy levels is drawn to scale. (Figure 1) P<Q<R. Light with a wavelength of 435 nm illuminates a metal cathode. The maximum kinetic energy of the emitted electrons is 0.96 eV . ... (Figure 1) is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system. What wavelengths appear in the system's emission spectrum? 829, 497, 311 nm.
3. Angular Momentum States. p.2.July 27, 1999 electron be symbolized by S.According to classical mechanics the values of L and S are given by equations 1 and 2, respectively. L = mvr(1) S = Iv (2) According to classical mechanics, both the orbital and spin angular















0 Response to "36 the figure is an energy-level diagram for a quantum system.(figure 1)"
Post a Comment