36 free body diagram with friction
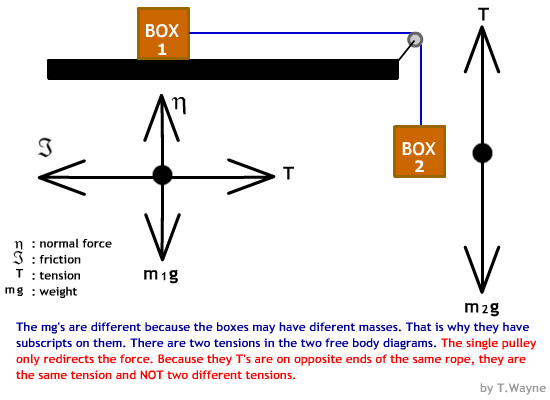
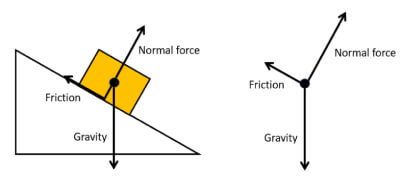
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ... In your free body diagram, you need to show static friction since it is an external force. It will always be equal and opposite to the force which is applied horizontally to the box. If any external force is applied but still the box in at rest. If no external force is applied on the box then also it would be at rest.
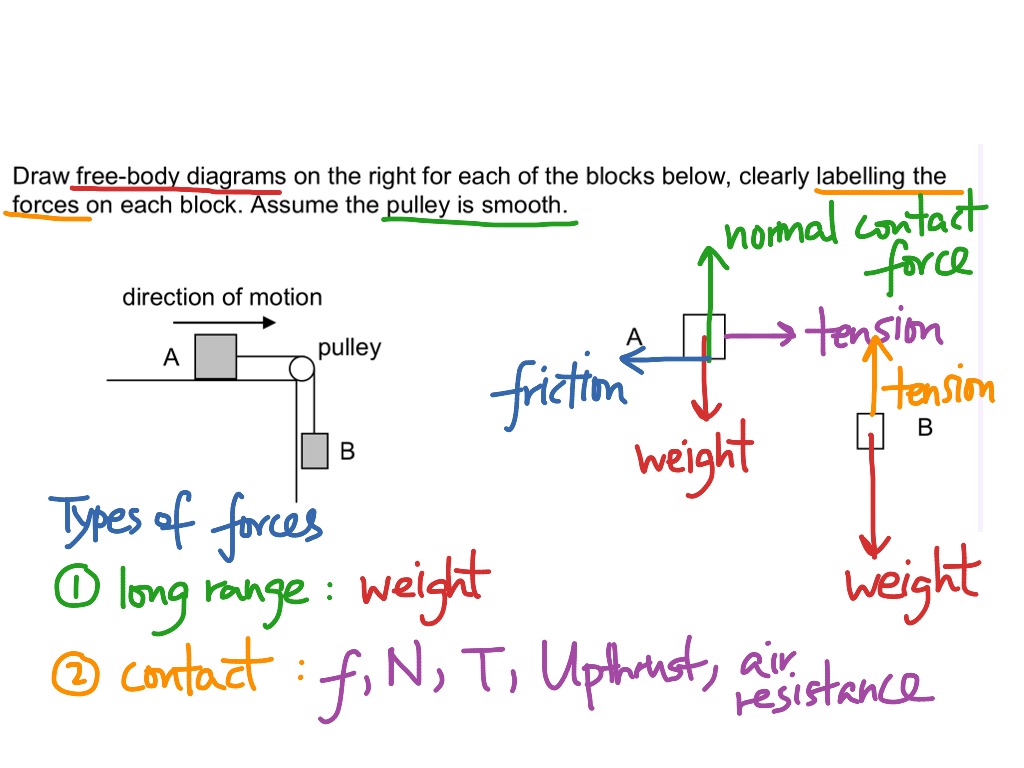
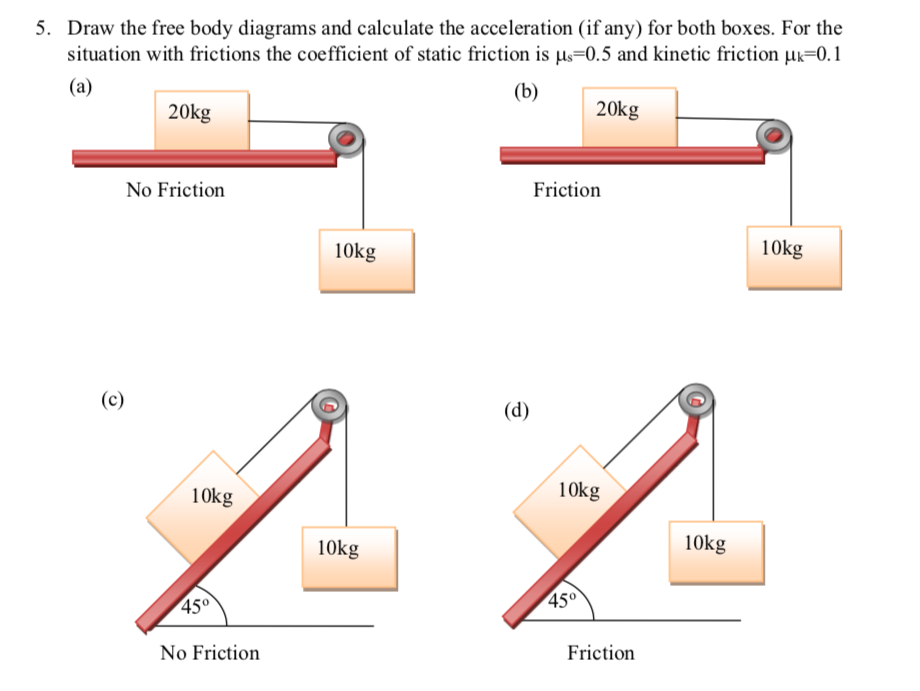
Kinetic and Static Friction A friction is a force that resists relative motion of two bodies in contact with each other. The origin of friction is microscopic irregularities of a surface. ... Draw free body diagram for both boxes. N 2mg mg T T 2. Select axes x y x 3. Write Newton’s 2nd law

Free body diagram with friction
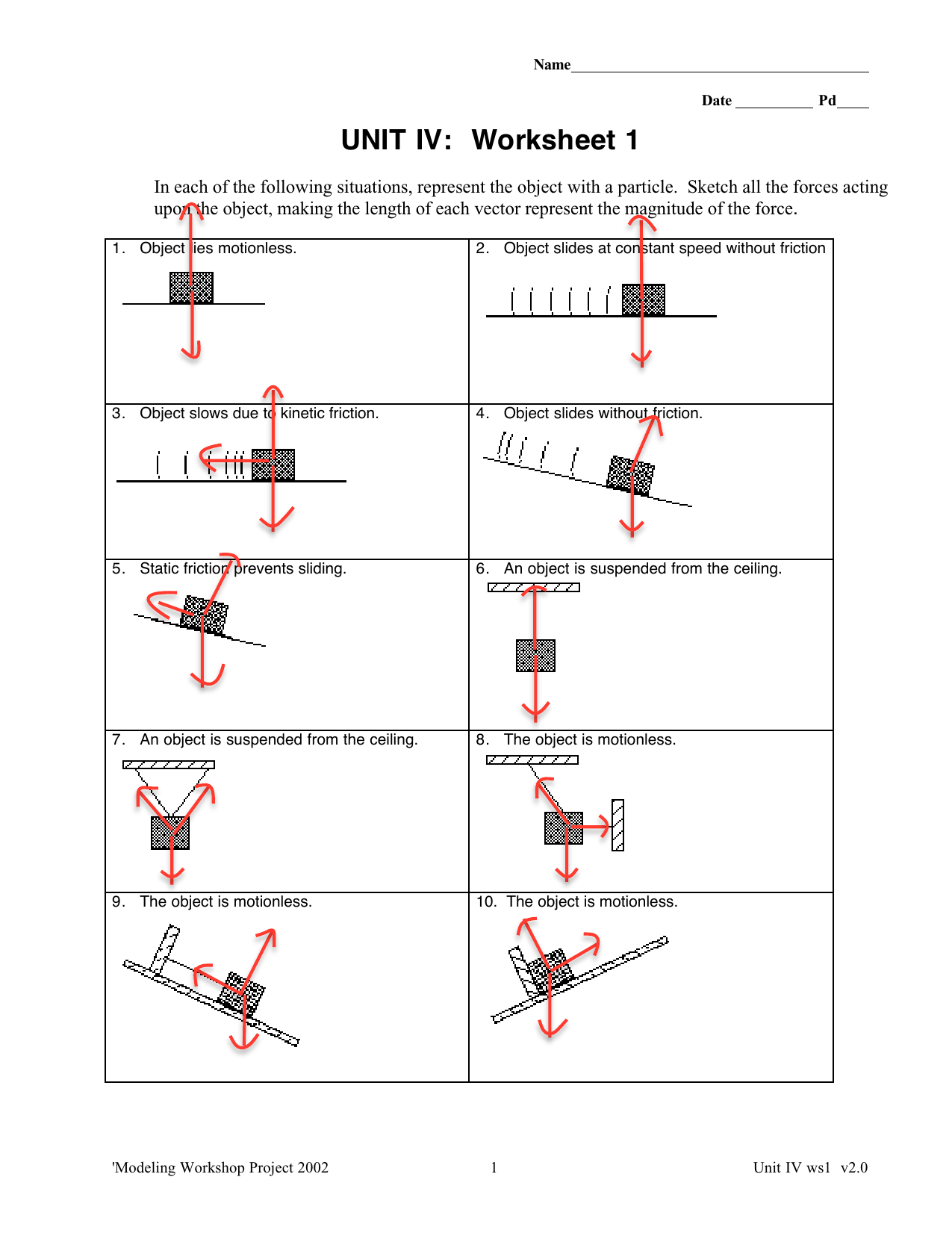
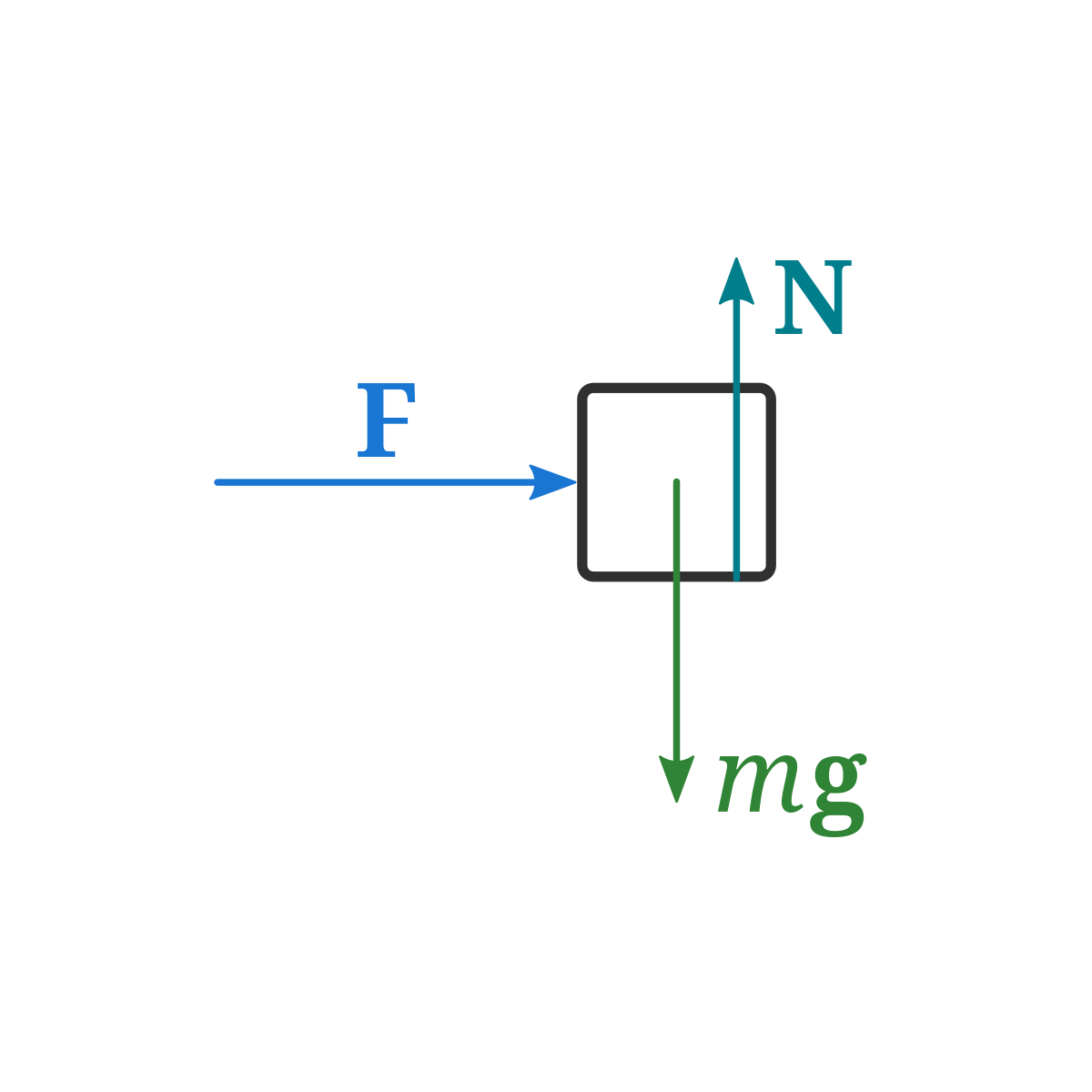
Free-body diagram. When multiple forces are acting on an object, it can be presented on a two-dimensional space as a free-body diagram. Free-body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all the forces acting on a particular object at a given time. Draw a free-body diagram. (Neglect air friction) The force of gravity is the only force described. (no air resistance). Problem 8 A car runs out of gas and is coasting down a hill. The car is coasting down the hill, there is dragging friction of the road (left pointing arrow) as well as gravity and normal forces, but no Friction is divided into two types-static and kinetic. These are represented by Ff, with a further subscript ' ...
Free body diagram with friction. The motion of objects is determined by the relative size and the direction of the forces that act upon it. Free-body diagrams showing these forces, ... by W Moebs · 2016 — Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left, down the incline, the friction force must oppose it and act up the ramp. The box should be your main focus. Diagram 1 is the FBD as long as the box does not slide relative to the truck. With the aid of diagram 1 work out the maximum acceleration a the box can have as a result of the static frictional force μ s N b t acting on it. Hopefully this will lead you swiftly onto phase two of the problem and the FBD diagram 2. Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley. A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) The normal force N. 3) The force of friction Fk. 4) The tension force T exerted by the string on the block m1. B) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below)
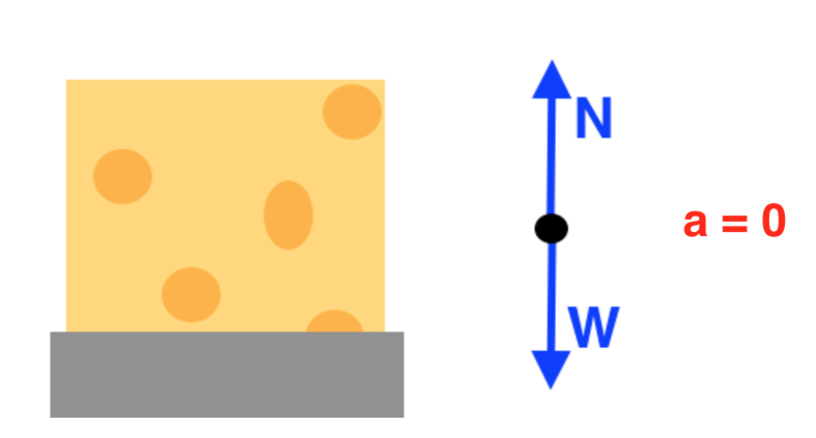
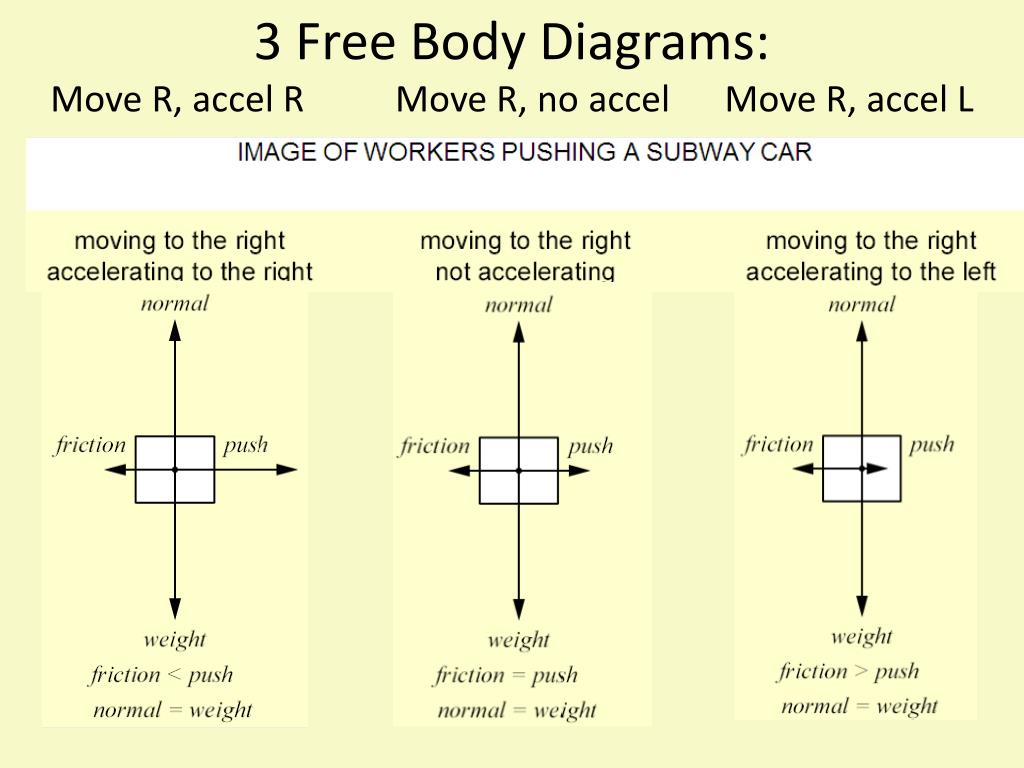
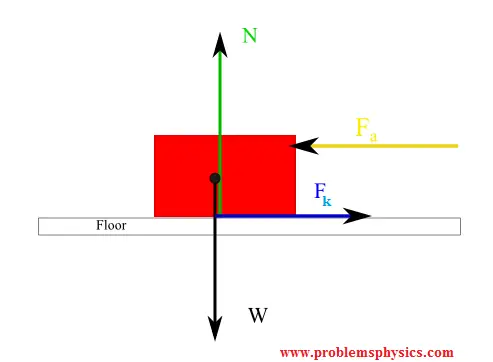
Free Body Diagrams When objects slow down (decelerate), they move in the direction OPPOSITE the net force. Example: A car coasts rightward while slowing down. MOTION F friction F gravity Fnormal Since the car is coasting to the right, there is no force being applied to the right. Free Body Diagrams Practice: worksheet. In physics and engineering, a free body diagram (force diagram, or FBD) is a graphical illustration used to visualize the applied forces, moments, and resulting ...Purpose · Features · Analysis · Example: A block on an... 6:30043 - Free-Body DiagramsIn this video Paul Andersen explains how free-body diagrams can be used to ...26 Aug 2014 · Uploaded by Bozeman Science Friction Free-body diagrams. Newton's second law: F net = ma. To find the net force on an object, all the vector forces that act on the object have to be added. We use free-body diagrams to help us with this task. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object in a given ...
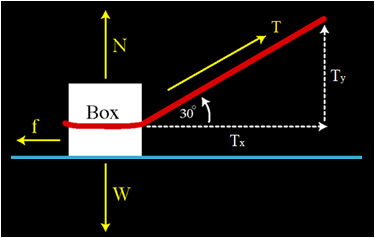
The free-body diagram of box 1 is relatively complicated, with a total of 6 forces appearing. The free-body diagram for box 2 is a little easier to deal with, having 4 forces, so that's a good place to start. For box 2 - start by summing the forces in the y-direction, where there is no acceleration: This can be solved to give the normal force: Friction is divided into two types-static and kinetic. These are represented by Ff, with a further subscript ' ... Draw a free-body diagram. (Neglect air friction) The force of gravity is the only force described. (no air resistance). Problem 8 A car runs out of gas and is coasting down a hill. The car is coasting down the hill, there is dragging friction of the road (left pointing arrow) as well as gravity and normal forces, but no Free-body diagram. When multiple forces are acting on an object, it can be presented on a two-dimensional space as a free-body diagram. Free-body diagrams show the relative magnitude and direction of all the forces acting on a particular object at a given time.














0 Response to "36 free body diagram with friction"
Post a Comment