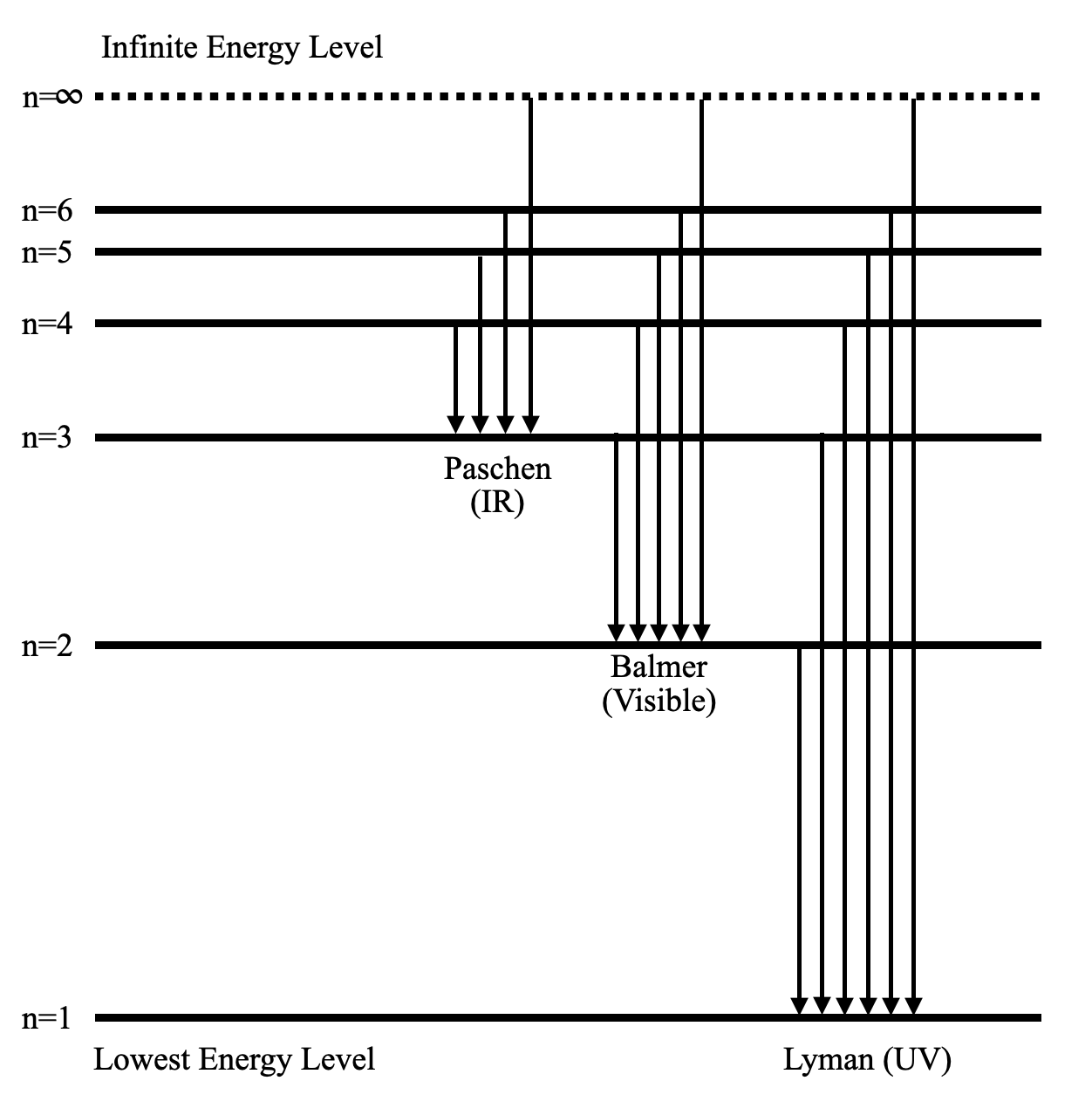
36 partial energy level diagram for hydrogen
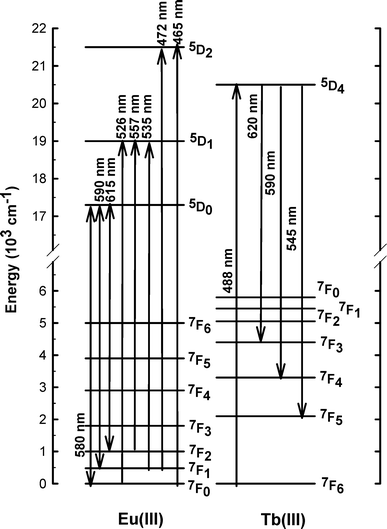
Lithium energy-level diagram Energy level diagrams for the easily excited atomic lines of lithium, sodium, potassium and rubidium. Wavelengths are given in nanometres for the spectral lines produced by transitions between the different levels. The ionization potential is indicated by the dashed line above the respective diagrams. The Selection Rule for L - The energy-level diagram for lithium ... P. Bernardo, J.C. Jansen, in Compendium of Hydrogen Energy, 2015. 14.8 Future trends. The future of hydrogen separation by membranes depends first on available sources of hydrogen. Industrial-scale CO 2 /H 2 separation for green hydrogen production by membranes should be carried out at relatively mild conditions in which CO 2 permeation might ...
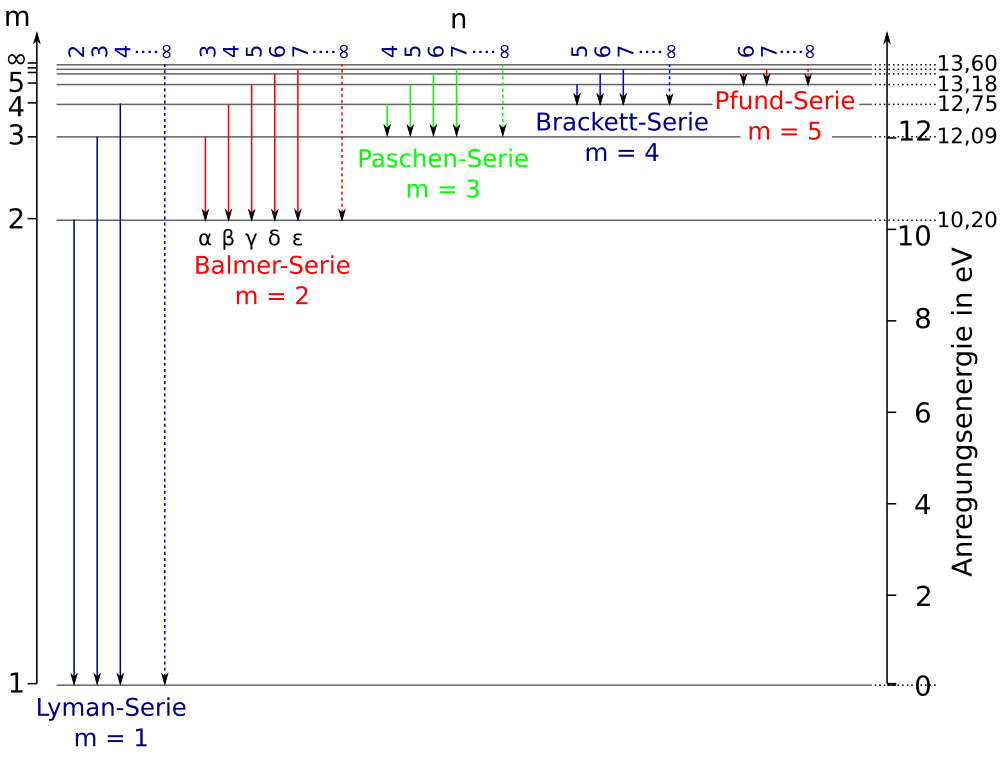
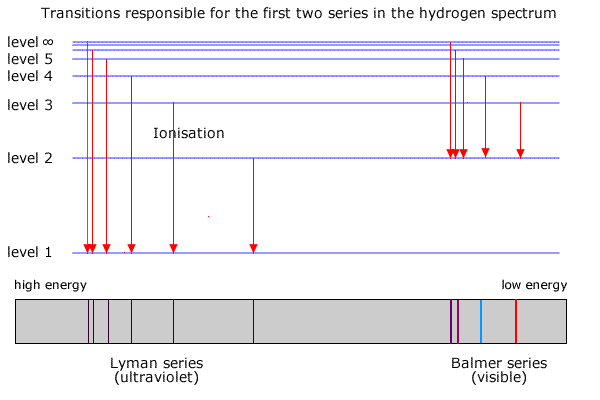
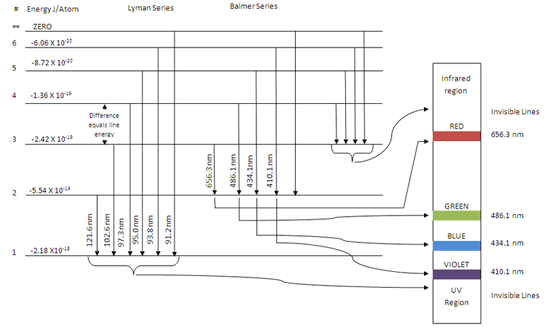
R H is the Rydberg constant (1.097 × 10 7 m-1) for hydrogen, n 1 is the lower-energy level, and n 2 is the higher-energy level. Pre-activity questions. The visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum lies between the wavelengths of _____ and _____ nm. A certain photon has a wavelength of 550 nm. Calculate its energy in Joules.

Partial energy level diagram for hydrogen
Download scientific diagram | A simplified energy-level diagram of negative hydrogen and negative deuterium ͑ not to scale ͒ . The origin of the energy axis ... The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom. (transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞ ). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV. When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon. FIG. 2. Partial energy level diagram for Rb I, showing the split ground state 2S 1/2 and an excited state, 2P 3/2, for the two naturally occurring isotopes of Rb I. 3. How does the random thermal motion of the atoms in the gas cell affect the absorption spectrum? Why, without taking really drastic measures, would
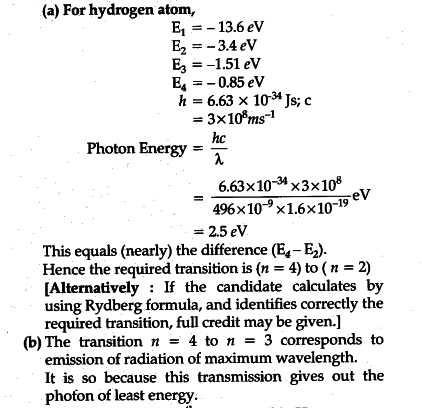
Partial energy level diagram for hydrogen. Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ The following question relates to the partial energy level diagram for the hydrogen electron: .54eV n5 .85eV n4 1.51eV n3 3.4eV n2 13.6eV n1 The question relates to electron located at E3 . What is the emission energy when the electron falls to E1 from E3 ? level diagram, or potential energy profile, as shown in Figure 13.1. The vertical axis gives the potential energy for the reaction, while the horizontal axis is a relative (i.e., time) scale that shows the progress of the reaction. The diagram indicates that there is a "hill" or energy barrier that needs to be overcome before any products ... Partial Energy Level Diagram for Hydrogen: Energy (J/atom) -1 x 10-19 -2x 10-19 -3 x 10-19 -4 x 10-19 -5 x 10-19 -6 x 10-19 Previous question Next question COMPANY Consider the following portion of the energy-level diagram for hydrogen: n = 4-0.1361 × 10-18 J n = 3-0.2420 × 10-18 J n = 2-0.5445 × 10-18 J n = 1-2.178 × 10-18 J For which of the following transitions does the light emitted have the longest wavelength?
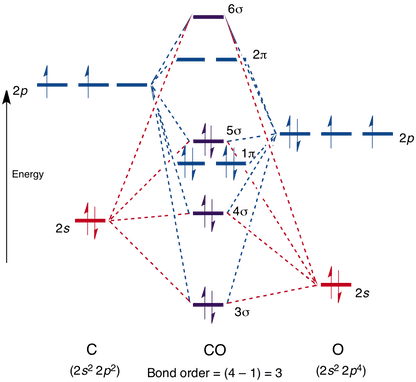
The energy level of the bonding orbitals is lower, and the energy level of the antibonding orbitals is higher. For the bond in the molecule to be stable, the covalent bonding electrons occupy the lower energy bonding orbital, which may be signified by such symbols as σ or π depending on the situation. Partial energy level diagram for hydrogen. Consider the following portion of the energy level diagram for hydrogen. Energy levels in hydrogen. E 136 ev 1n f2 1n i2 atoms can also absorb photons. If an electron from a low level is given energy it will be raised to a higher or excited level. Going to ninfinity represents the loss of the electron. All wavelengths are ending at the n2 state and ... This chemistry video tutorial focuses on the bohr model of the hydrogen atom. It explains how to calculate the amount of electron transition energy that is... 23 Mar 2005 · 5 postsor Partial (...) Diagram...? Is it a diagram with energy levels (as one which can be found in any QM book or atomic physics book),or what?
Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\) shows that the energy levels become closer and closer together as the value of n increases, as expected because of the 1/n 2 dependence of orbital energies. Figure \(\PageIndex{7}\): Orbital Energy Level Diagram for the Hydrogen Atom. Each box corresponds to one orbital. An energy-level diagram has energy plotted on the vertical axis with a horizontal line drawn to locate each energy level (Figure 1.8.4 ). Figure 1.8.4 : Energy levels predicted by the Bohr model of hydrogen (\(Z=1\)). (CC BY-NC; Ümit Kaya via LibreTexts) These turn out to be the correct energy levels, apart from small corrections that cannot ... energy-level diagram for the NO molecule. We assume that orbital order is the same as that for N2. The bond order is 2.5. Figure 9.42: The molecular orbital energy-level diagram for both the NO+ and CN-ions. Figure 9.43: A partial molecular orbital energy-level diagram for the HF molecule. Energy level diagrams for IONS Atoms with 5, 6, or 7 valence electrons gain electrons to form 3-, 2-, or 1- ions, respectively. naming non-metallic ions - the name of the atom is shortened and the suffix -ide is added. O2- is oxide Group 15 (3-) (gain 3 e) Group 16 (2-) (gain 2 e) Group 17 (1-) (gain 1 e) 1/16/2015 9 Energy level diagrams for IONS Atoms with valency of 4 generally do not form ...
The following question relates to the partial energy level diagram for the hydrogen electron:. 5 4 e V _____ n 5 . 8 5 e V _____ n 4 1. 5 1 e V _____ n 3 3. 4 e V _____ n 2 1 3. 6 e V _____ n 1 The question relates to electron located at E 3 . What is the emission energy when the electron falls to E 1 from E 3 ?
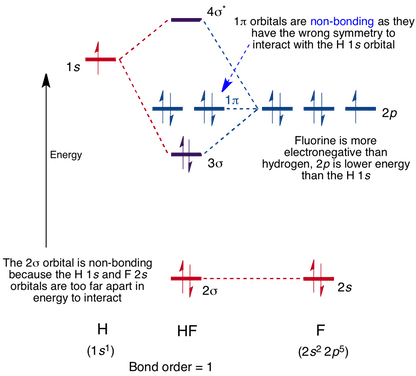
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H-F nb σ σ* Energy H -13.6 eV 1s F -18.6 eV -40.2 eV 2s 2p So H-F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine
MIT 8.04 Quantum Physics I, Spring 2016View the complete course: http://ocw.mit.edu/8-04S16Instructor: Barton ZwiebachLicense: Creative Commons BY-NC-SAMore ...
Energy level diagrams are a means of analyzing the energies electrons can accept and release as they transition from one accepted orbital to another. These energies differences correspond to the wavelengths of light in the discreet spectral lines emitted by an atom as it goes through de-excitation or by the wavelengths absorbed in an absorption spectrum. Using the Bohr Model, the energy levels ...
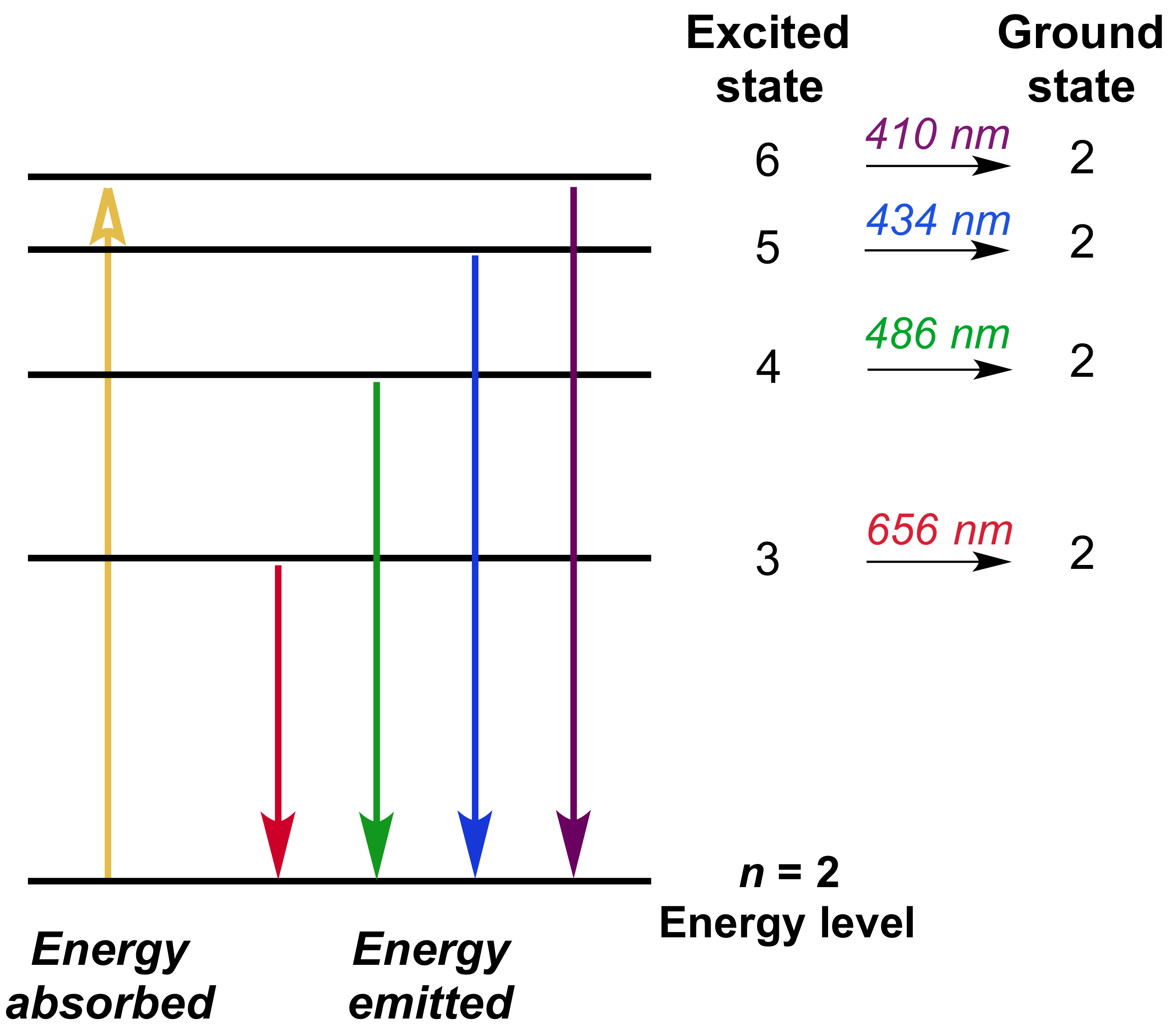
So, those are electrons falling from the higher energy levels down to the 2nd energy level. So, let's go ahead and draw them on our diagram here. So, let's say an electron fell from the 4th energy level down to the 2nd. Alright, so, that energy difference, if you do the calculations, that turns out to be the blue-green line in your line spectrum.
The Schrödinger equation is a differential equation that governs the behavior of wavefunctions in quantum mechanics. The term "Schrödinger equation" actually refers to two separate equations, often called the time-dependent and time-independent Schrödinger equations. The time-dependent Schrödinger equation is a partial differential equation that describes how the wavefunction evolves …
See below. Orbital diagrams are useful to show the number of electrons, number of electron shells, number of electron pairs, and electron spin directions in a particular atom/ion. Arrows represent electrons, and their spin is represented by which way they point (up or down). Two electrons can be paired into one shell (one little box) as one orbital. Groups of boxes right next to each other ...
a) Draw a diagram of energy levels to explain the spectrum of lines of the hydrogen atom. b) Indicate, for each photon, that its region can be emitted to the electromagnetic spectrum. c) Compare, in a graph, the energies of the orbital of the hydrogen atom with the energies of the He +.
Powered by FlexBook® textbook Platform ® © CK-12 Foundation 2021; Please wait... Please wait...
Click here👆to get an answer to your question ️ The following question relates to the partial energy level diagram for the hydrogen electron: .54eV n5 .85eV n4 1.51eV n3 3.4eV n2 13.6eV n1 The question relates to a hydrogen electron located at E3 .What is the emission energy when the electron falls to E5 from E3 ?
Partial energy level diagram for hydrogen. 41126 43477 48710 65842. The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atomtransition from ground state n 0 to infinity n. Hydrogen partial energy level diagram selfhomeworkhelp submitted 7 years ago by evomax01 i did a spectroscopy lab and i need to construct a partial energy level diagram for ...
Partial oxidation cannot be used for gasifying gasoline, diesel, methanol, or ethanol, because of the decrease in energy content of the fuel. However, the hydrogen-rich gas (hence, the preference for this type of process in the petroleum industry) that is produced by …
Give the ground-state electron configuration, symbol, and group number from each partial (valence-level) orbital diagram. A zinc atom in its ground state has how many unpaired electrons? ... (energy levels) of a hydrogen atom vary as s < p < d, etc. e. the energies of subshell in the shells (energy levels) of a hydrogen atom vary as s < p < d ...
I need to make a partial energy level diagram for Hydrogen using the given values but I am not sure what that is supposed to look like. C. Atomic Spectra 5.
For the partial energy-level diagram of hydrogen, assume that all the observed transitions terminate at the n = 2 state; for example, if you observe two ...
Below is a blank energy level diagram which helps you depict electrons for any specific atom. At energy level 2, there are both s and p orbitals. The 2s has lower energy when compared to 2p. The three dashes in 2p subshells represent the same energy. 4s has lower energy when compared to 3d. Therefore, the order of energy level is as follows: s ...
1 answerThe hydrogen atom is the simplest in the universe that consists of only a proton and an electron. The electron is at the ground state, which is the nearest ...
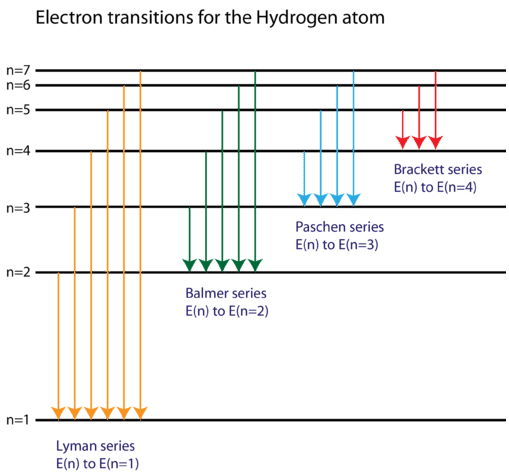
Energy level diagrams and the hydrogen atom. It's often helpful to draw a diagram showing the energy levels for the particular element you're interested in. The diagram for hydrogen is shown above. The n = 1 state is known as the ground state, while higher n states are known as excited states. If the electron in the atom makes a transition from a particular state to a lower state, it is losing ...
Energy levels in hydrogen. If an electron from a low level is given energy it will be raised to a higher, or excited, level. This can be done electrically, by heat, by collision with another atom, by radiation or by a free electron hitting the atom. However the electron in the atom will only be excited if the energy of the incoming quantum of energy in whatever form is exactly the same as the ...
Hydrogen (H 2 ) is currently used mainly in the chemical industry for the production of ammonia and methanol. Nevertheless, in the near future, hydrogen is expected to become a significant fuel that will largely contribute to the quality of atmospheric air. Hydrogen as a chemical element (H) is the most widespread one on the earth and as molecular dihydrogen (H<sub>2</sub>) can be obtained ...
Energy storage is the capture of energy produced at one time for use at a later time to reduce imbalances between energy demand and energy production. A device that stores energy is generally called an accumulator or battery.Energy comes in multiple forms including radiation, chemical, gravitational potential, electrical potential, electricity, elevated temperature, latent heat and kinetic.
Click here to get an answer to your question ✍️ Draw a neat labelled energy level diagram of the Hydrogen atom.19 Nov 20191 answer · Top answer: Given figure shows energy level diagram for Hydrogen atom.
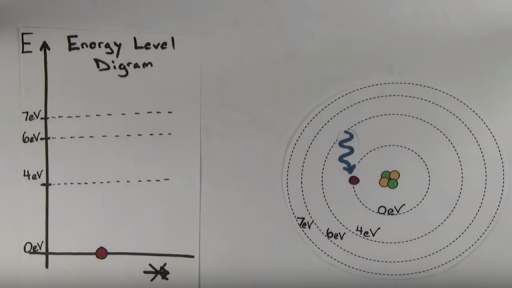
Transcribed image text: The Bohr Model Es= -3.34 X 10-19 J E-533 X 10-19 A4 E3=-6.83 X 10-19 J 3 E2=-9.00 X10-19 J 2 п Energy E1-133 X 10-18 J Electron Transitions in an atom other than hydrogen In the figure above we see a partial energy level diagram for a hypothetical atom. In our picture we are looking at 4 posssible electron transitions that could result when the atom is given sufficient ...
14+ Energy Level Diagram Of N2. • draw an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom that shows the relative separations between the energy levels. Energy level diagram of co2+ in a tetrahedral and octahedral ligand field. The bond order is three, with no unpaired electrons. This agreement with experiment was strong support for the bohr model.
13.3.2015 · Hydrogen-fueled vehicles produce no direct pollution, making them environmentally friendly. However, fossil fuels are often used in the processes for the hydrogen production and the energy content of the produced hydrogen is less than that of the fossil fuels used (Clay et al. 2004; Actual Worldwide, 2007).
View Lab Report - Partial Energy Level Diagram for Hydrogen from CHEM 2070 at Cornell University. Partial Energy Level Diagram for Hydrogen 1 = (6.626 x 10-37 KJ) (3.00 x 1017 nm/s) (6.022 x 1023
FIG. 2. Partial energy level diagram for Rb I, showing the split ground state 2S 1/2 and an excited state, 2P 3/2, for the two naturally occurring isotopes of Rb I. 3. How does the random thermal motion of the atoms in the gas cell affect the absorption spectrum? Why, without taking really drastic measures, would
The ionization energy of an atom is the energy required to remove the electron completely from the atom. (transition from ground state n = 0 to infinity n = ∞ ). For hydrogen, the ionization energy = 13.6eV. When an excited electron returns to a lower level, it loses an exact amount of energy by emitting a photon.
Download scientific diagram | A simplified energy-level diagram of negative hydrogen and negative deuterium ͑ not to scale ͒ . The origin of the energy axis ...
















0 Response to "36 partial energy level diagram for hydrogen"
Post a Comment