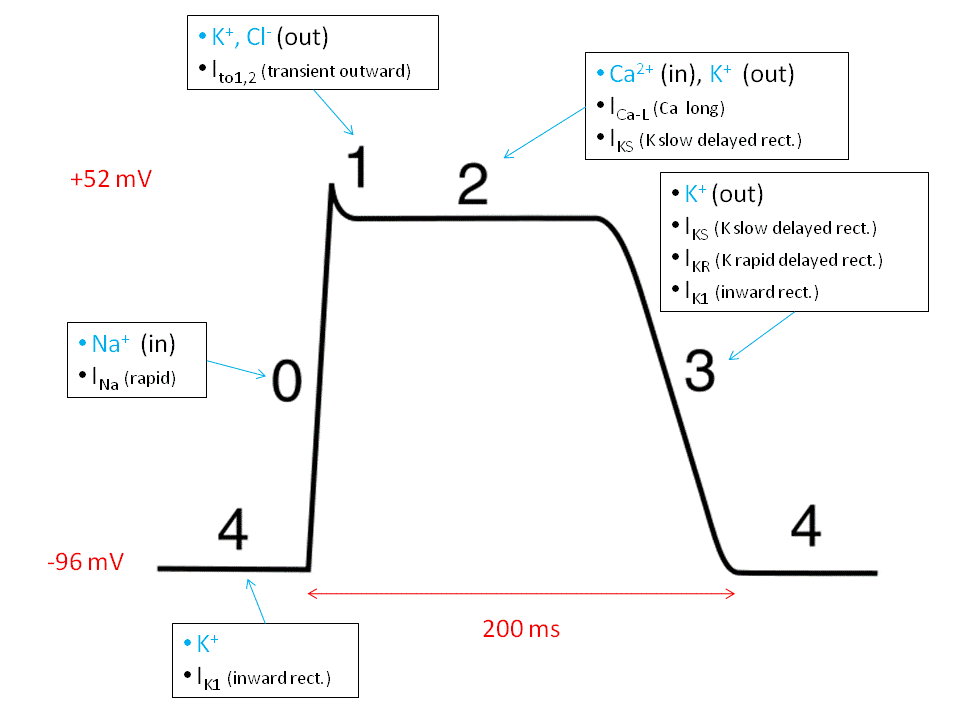
37 action potential steps diagram
Action Potential Diagram. Falling Phase of Action Potential. - after reaches peak now action potential falls, membrane Mechanism of ion selectivity and transport in resting K+ channels. (a) Schematic diagram of K+ and. When ionic current or external energy excites the portion of a cell membrane, permeability changes. Stimulus starts the rapid change in voltage or action potential. · Depolarization is caused by a rapid rise in membrane potential opening of sodium channels in ...
Neuron action potentials: The creation of a brain signal. Google Classroom Facebook Twitter. Email. Neuron membrane potentials.

Action potential steps diagram
Action Potential Steps. Let's look back at the example of reading. When you read, light enters your eyes through the pupil. The light strikes sensory cells in your retina. The three latter steps would be the falling, the undershoot, and the recovery phases. Some sources, whether physiologists or textbooks, sometimes include an initial resting phase before the rising phase when enumerating the stages of action potential, probably to illustrate the status quo of the neuron before action potential begins. Core. The Action Potential. The action potential describes the phenomenon by which excitable cells create an electrical signal via the movement of ions across the membrane.The key features of an action potential are: It relies on ionic gradients – Pre-existing ionic gradients are required for the movement of ions across the membrane. Changing the membrane’s permeability to different ions ...
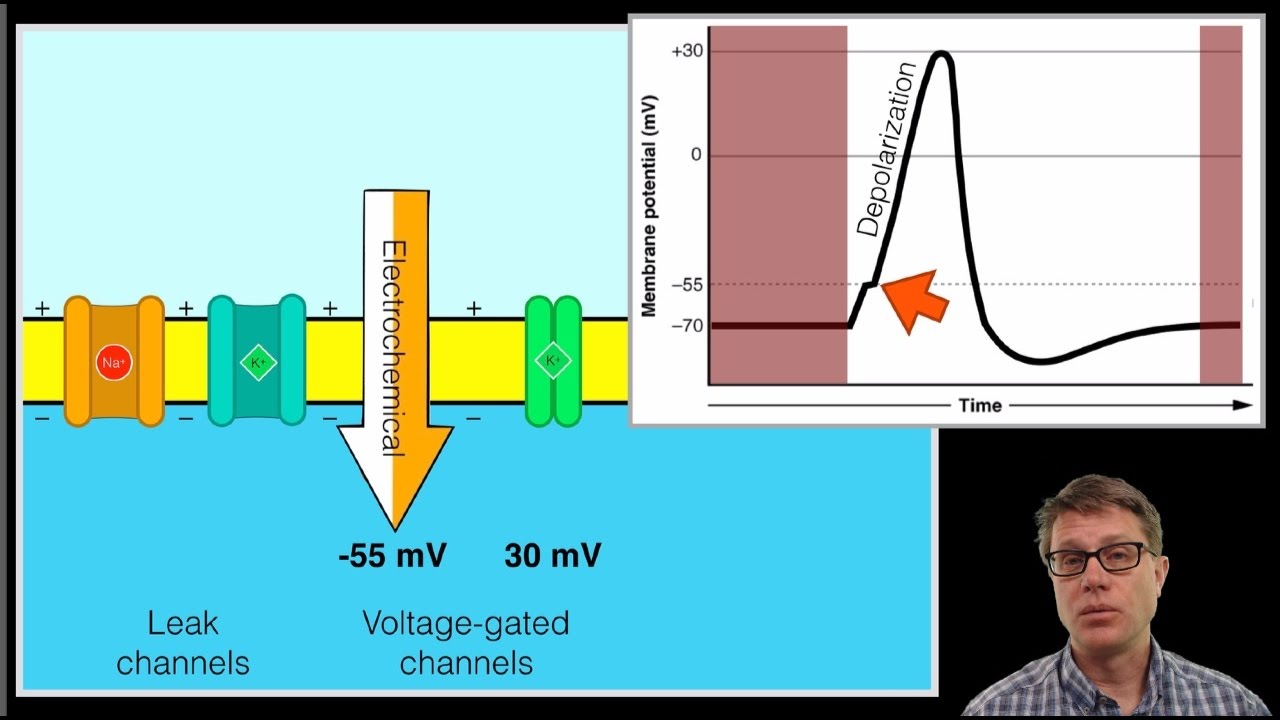
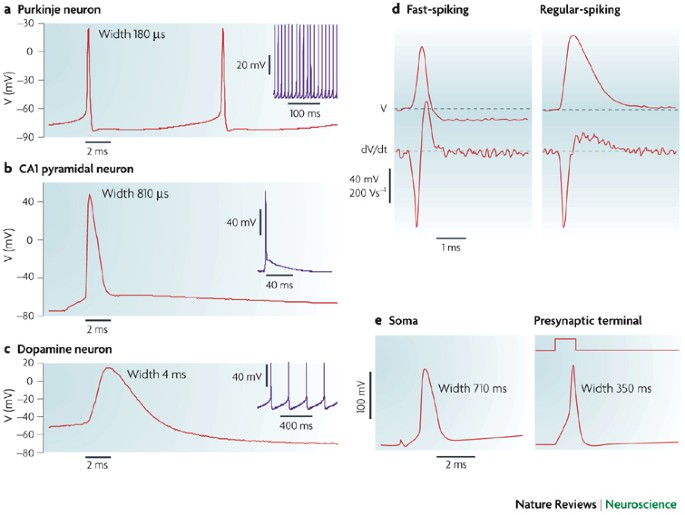
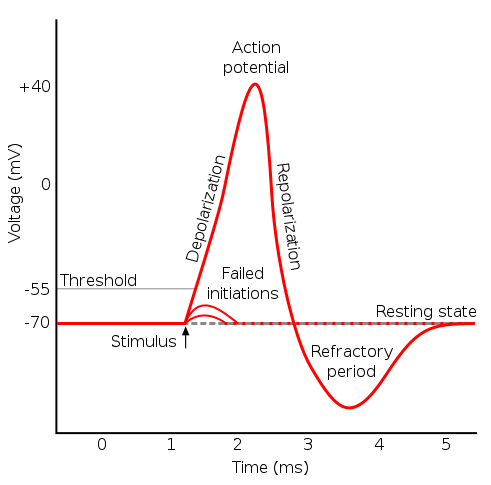
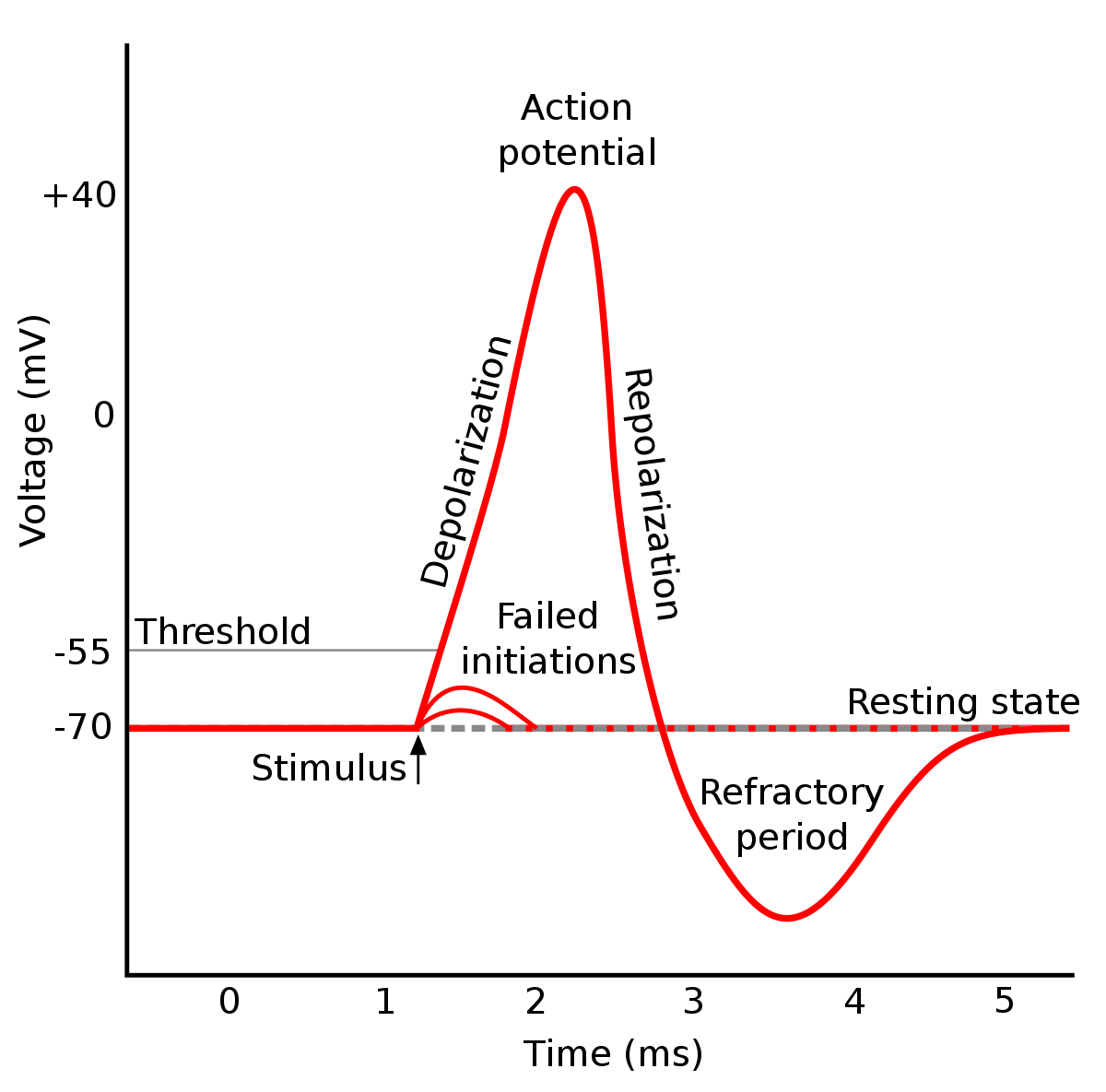
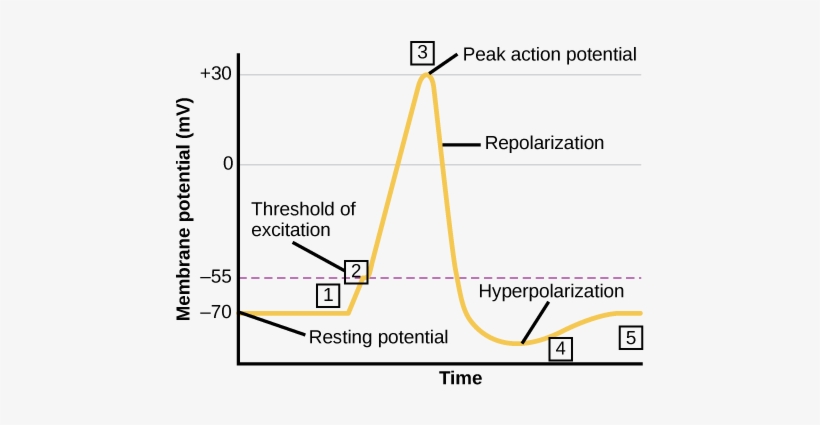
Action potential steps diagram. If depolarization reaches -55 mV, then the action potential continues and runs all the way to +30 mV, at which K + causes repolarization, including the hyperpolarizing overshoot. Also, those changes are the same for every action potential, which means that once the threshold is reached, the exact same thing happens. What has been described here is the action potential, which is presented as a graph of voltage over time in Figure 12.5.7. It is the electrical signal that nervous tissue generates for communication. The change in the membrane voltage from -70 mV at rest to +30 mV at the end of depolarization is a 100-mV change. An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the ... In this tutorial, we will review the phases of an action potential measured from a small area of a neuron's membrane. The action potential can be divided ...
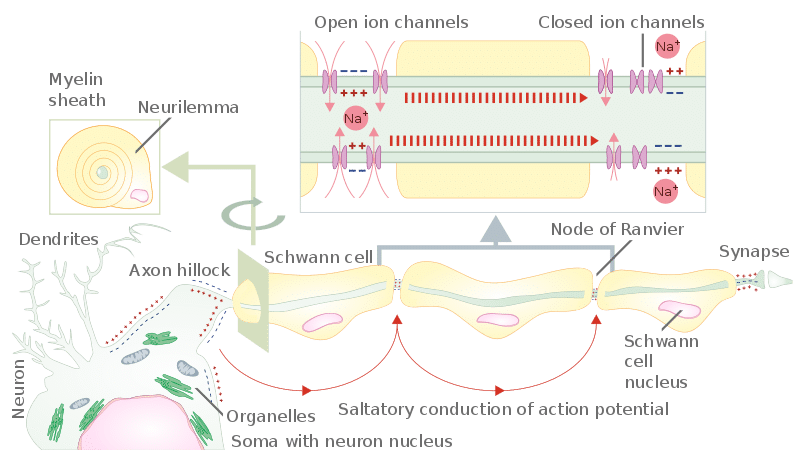
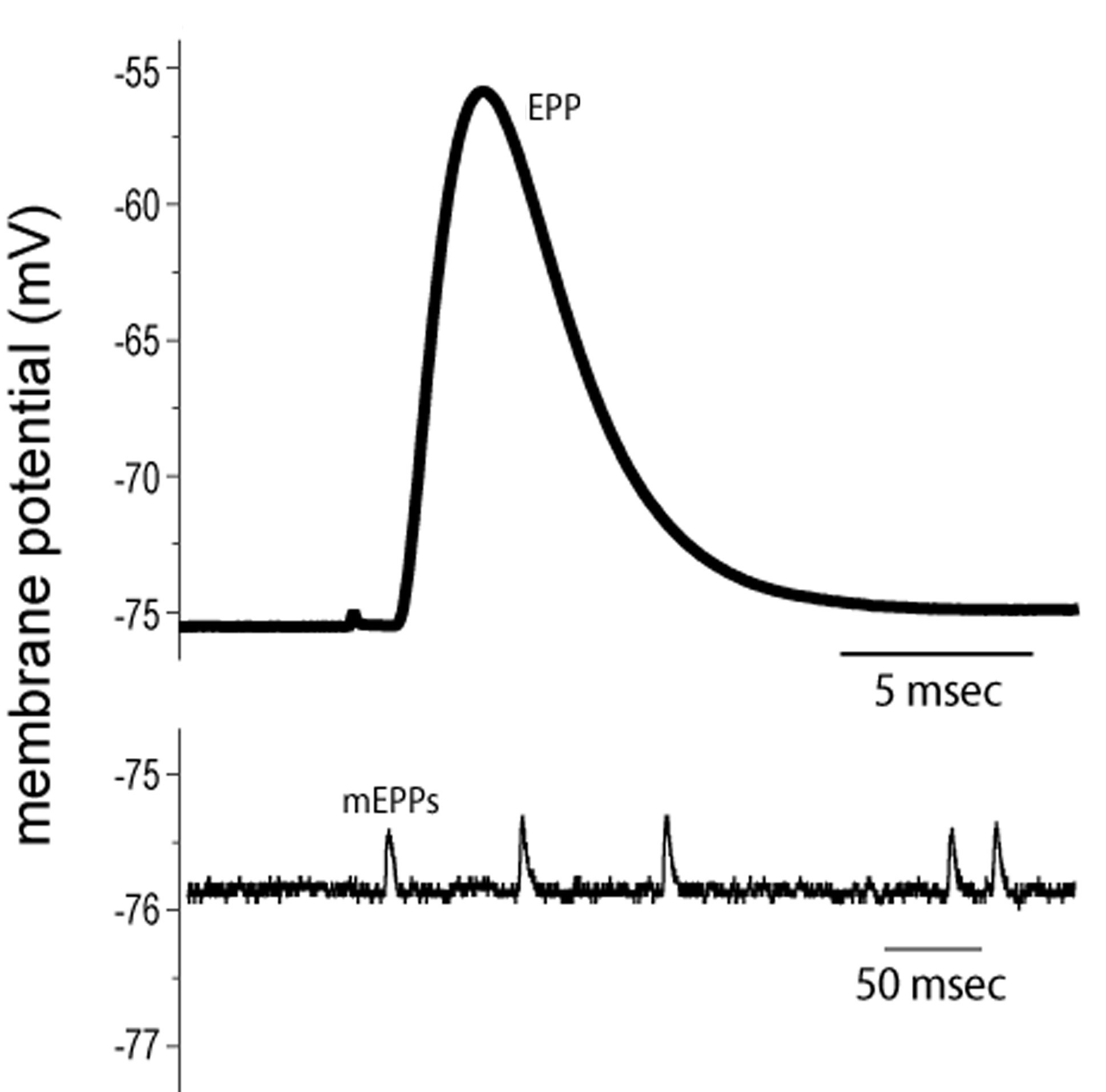
STEPS IN THE ACTION POTENTIAL 1. The presynaptic neuron sends neurotransmitters to postsynaptic neuron. (A chemical message) 2. Neurotransmitters bind to receptors. 3. The neurotransmitters produce either an EPSP or an IPSP 4. The EPSP’s and IPSP’s sum together – either spatially or temporally. 5. The soma becomes more positive. 6. An action potential has three phases: depolarization, overshoot, repolarization. There are two more states of the membrane potential related to the action ...Phases: Depolarization; Overshoot; Repolariz...Stimuli: Subthreshold; Threshold; Suprathresh...Definition: Sudden, fast, transitory and propag...Synapse: Presynaptic membrane; Synaptic cleft; ... The action potential thus moves along the axon as a wave of depolarization traveling away from the cell body. • Label where the action potential is in these two diagrams: Page 17. Conduction Velocity Depends on Diameter and Myelination of the Axon • Conduction velocity is the speed with which an action potential is propagated. Approximate plot of a typical action potential shows its various phases as the action potential passes a point on a cell membrane. The membrane potential starts ...Membrane potential · Threshold potential · Cardiac action · Saltatory conduction
13 Aug 2020 — The action potential has three main stages: depolarization, repolarization, and hyperpolarization. Depolarization is caused when positively ... The Action Potential. Resting membrane potential describes the steady state of the cell, which is a dynamic process that is balanced by ion leakage and ion pumping. Without any outside influence, it will not change. To get an electrical signal started, the membrane potential has to change. Transmission of a signal within a neuron (from dendrite to axon terminal) is carried by a brief reversal of the resting membrane potential called an action ... Core. The Action Potential. The action potential describes the phenomenon by which excitable cells create an electrical signal via the movement of ions across the membrane.The key features of an action potential are: It relies on ionic gradients – Pre-existing ionic gradients are required for the movement of ions across the membrane. Changing the membrane’s permeability to different ions ...
The three latter steps would be the falling, the undershoot, and the recovery phases. Some sources, whether physiologists or textbooks, sometimes include an initial resting phase before the rising phase when enumerating the stages of action potential, probably to illustrate the status quo of the neuron before action potential begins.
Action Potential Steps. Let's look back at the example of reading. When you read, light enters your eyes through the pupil. The light strikes sensory cells in your retina.














:format(jpeg)/images/article/en/action-potential/pJRivfYxfsvi7mIh8xRQg_Action_potential_curve.png)

:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/11524/Action_potential_ions.png)






0 Response to "37 action potential steps diagram"
Post a Comment