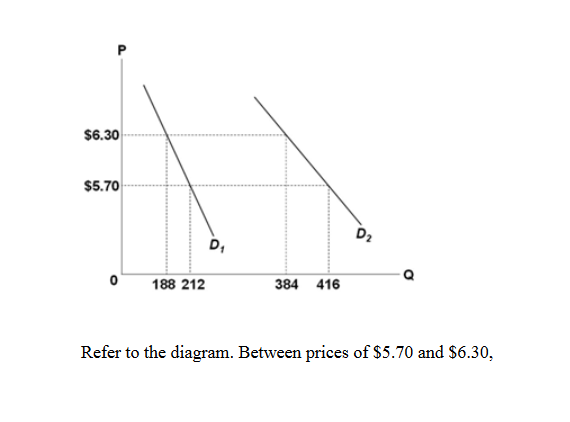
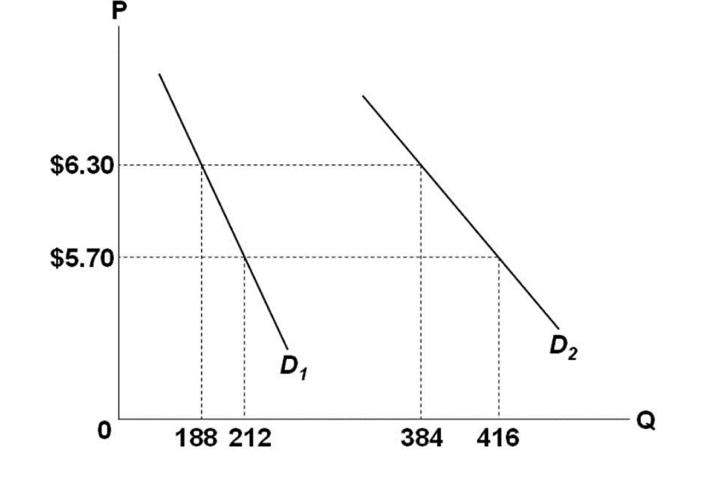
38 refer to the diagram. between prices of $5.70 and $6.30,
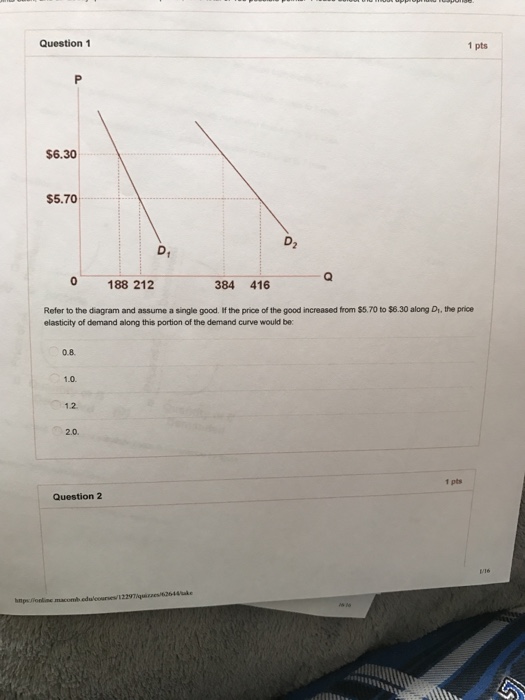
Thus, at a glance you can see the firm is making losses. At a second glance, you can see that it must be losing $1 for each unit produced (that is, average cost of $26/unit minus the price of $25/unit). With five units produced, this observation implies total losses of $5. When producing five units, marginal costs are $30/unit. Price is $25/unit. Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be: a. 0.8. b. 1.0. c. 1.2. d. 2.0. Question 5 (2 points) Marginal utility can be: a. positive, but not negative.
6. Refer to the above diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30: A. D 1 is more elastic than D 2 B. D 2 is an inferior good and D 1 is a normal good. C. D 1 and D 2 have identical elasticities. D. D 2 is more elastic than D 1 . . 7. Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good.

Refer to the diagram. between prices of $5.70 and $6.30,
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good decreases from $6.30 to $5.70, consumer expenditure would: 28. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, a leftward shift of the demand curve would: A. depreciate the dollar. B. appreciate the euro. C. reduce the equilibrium quantity of euros. D. cause a surplus of euros. Answer: C. Refer to the above diagram. The initial demand for and supply of pesos are shown by D 1 and S 1. The price elasticity of supply is the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. Elasticities can be usefully divided into five broad categories: perfectly elastic, elastic, perfectly inelastic, inelastic, and unitary. An elastic demand or elastic supply is one in which the elasticity is greater than one ...
Refer to the diagram. between prices of $5.70 and $6.30,. Refer to the diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30: D1 is more elastic than D2. Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good decreases from $6.30 to $5.70, consumer expenditure would: decrease if demand were only D2. Refer to the data. The price elasticity of demand is relatively elastic: Refer to the diagram below. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30: D1 and D2 have identical elasticities. D2 is an inferior good and D1 is a normal good. D2 is more elastic than D1 D1 is more elastic than D2. The percentage difference between two values is calculated by dividing the absolute value of the difference between two numbers by the average of those two numbers. Multiplying the result by 100 will yield the solution in percent, rather than decimal form. Refer to the equation below for clarification. year) at various prices are given as follows: Price ($) Demand (millions) Supply (millions) 60 22 14 80 20 16 100 18 18 120 16 20 a. Calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price is $80. When the price is $100. We know that the price elasticity of demand may be calculated using equation 2.1 from the text: E Q Q P P P Q Q D D D D = = D ...
Refer to the diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30: asked Aug 12, 2018 in Economics by aaden. A. D 1 is more elastic than D 2 . B. D 2 is an inferior good and D 1 is a normal good. C. D 1 and D 2 have identical elasticities. D. D 2 is more elastic than D 1 . principles-of-economics An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right, as shown in Panel (a) of Figure 3.10 "Changes in Demand and Supply". The equilibrium price rises to $7 per pound. As the price rises to the new equilibrium level, the quantity supplied increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. 6) Compared to the equilibrium price and quantity sold in a competitive market, a monopolist will charge a _____ price and sell a _____ quantity. ... 30) Refer to Scenario 10.2. Suppose that a tax of $5 for each unit produced is imposed by state government. ... Section: 10.6 117) The following diagram shows marginal value and expenditure curves ... Moe 30 Larry 15 13) Refer to Table 4-1. The table above lists the highest prices three consumers, Curly, Moe, and Larry, are willing to pay for a bottle of champagne. If the price of one of the bottles is $24 dollars, A) Curly will buy two bottles, Moe will buy one bottle and Larry will buy no bottles.
Refer to the diagram. If price is reduced from P1 to P2, total revenue will: a. increase by A - C. b. increase by C - A. c. decrease by A - C. d. decrease by C - A. b. increase by C - A. For a pure monopolist, marginal revenue is less than price because: a. the monopolist's demand curve is perfectly elastic. Refer to the diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30: asked Aug 12, 2018 in Economics by aaden. A. D 1 is more elastic than D 2. B. D 2 is an inferior good and D 1 is a normal good. C. D 1 and D 2 have identical elasticities. D. D 2 is more elastic than D 1 . principles-of-economics 3. Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good. Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be:-0.8.-1.0.-2.0.-1.2. Р $6.30 $5.70 D2 D Q 0 188 212 384 416 Refer to the diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30 Refer to the diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30 V O D1 and D2 have identical elasticities O D1 is more elastic than D2 O D2 is more elastic than Di O D2 is an inferior good and D1 is a normal good.
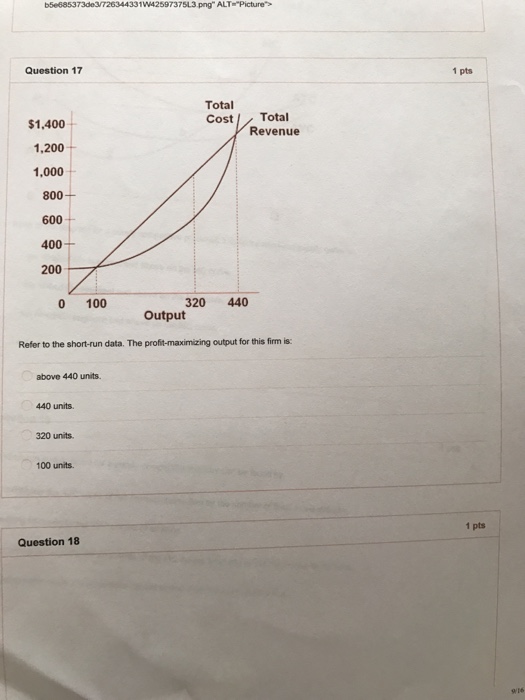
14. Assume the XYZ Corporation is producing 20 units of output. It is selling this output in a purely competitive market at $10 per unit. Its total fixed costs are $100 and its average variable cost is $3 at 20 units of output. This corporation: A. Should close down in the short run. B. Is maximizing its profits.
Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be:
The following TWO questions refer to the supply and demand curve diagram below. 3. The equilibrium price in this market is equal to: a) $6 per unit. b) $5 per unit. c) $4 per unit. d) $3 per unit. 4. At a price of $8, there is: a) Excess demand (a shortage) of 25 units. b) Excess demand (a shortage) of 15 units. c) Excess supply (a surplus) of ...
Even without graphing the curves, we are able to analyze the table and see that at a price of $30 the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. This is clearly the equilibrium point. If we graph the curves, we find that at price of 30 dollars, the quantity supplied would be 10 and the quantity demanded would be 10, that is, where the ...
Two Notes: (1) Hilti KB-TZ2 may be directly substituted for TZ in this detail. (2) In the event that SDC C applies and the enclosure (s) in question is "unimportant (i.e., Ip = 1.0 per ASCE 7)," then the enclosure (s) is seismically exempt (per ASCE 7 para. 13.1.4) and only gravity loads need be considered.
The P/Q portion of our equation corresponds to the values at the point, which are $4.5 and 4. The ΔQ/ ΔP corresponds to the inverse slope of the curve. Recall slope is calculated as rise/run. In Figure 4.1, the slope is 3−4.5 6−4 3 − 4.5 6 − 4 = 0.75, which means the inverse is 1/0.75 = 1.33.
Question: $6.30 $5.70 D D2 O 188 212 Q 384 416 Refer to the diagram. Between prices of $5.70 and $6.30, Multiple Choice D2 is an inferior good and Dy is a normal good. Di is more elastic than D2 Dy and D2 have identişal elasticities. D2 is more elastic than D1. Supply P Price 0 Q, Quantity Refer to the above graph showing the market for a product.
$6.30 $5.70 188 212 384 416 Q 15. Refer to the above diagram, Betweenprices ofS5.70 and S6.30: A) DI is more elastic than C) DI End D2 have identical elasticities. B) DI is an inferiorgcodandDl is a normal good D) Is moreelasticthanDl page 3
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be: 1.2.
If the price of the good decreases from $6.30 to $5.70, consumer expenditure would: B. decrease if demand were D2 only. Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good.
Answers is the place to go to get the answers you need and to ask the questions you want
3. Refer to the above diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good increased from $5.70 to $6.30 along D1, the price elasticity of demand along this portion of the demand curve would be: A. 0.8. B. 1.0. C. 1.2. D. 2.0. 4. The elasticity of supply of product X is unitary if the price of X rises by: A.
The price elasticity of supply is the percentage change in quantity supplied divided by the percentage change in price. Elasticities can be usefully divided into five broad categories: perfectly elastic, elastic, perfectly inelastic, inelastic, and unitary. An elastic demand or elastic supply is one in which the elasticity is greater than one ...
28. Refer to the above diagram. Other things equal, a leftward shift of the demand curve would: A. depreciate the dollar. B. appreciate the euro. C. reduce the equilibrium quantity of euros. D. cause a surplus of euros. Answer: C. Refer to the above diagram. The initial demand for and supply of pesos are shown by D 1 and S 1.
Refer to the diagram and assume a single good. If the price of the good decreases from $6.30 to $5.70, consumer expenditure would:




















0 Response to "38 refer to the diagram. between prices of $5.70 and $6.30,"
Post a Comment