39 concave lens ray diagram
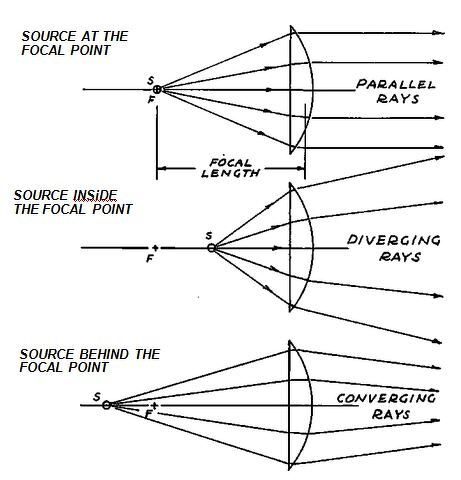
Double Concave Lens Ray Diagram. A ray diagram is a tool used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a lens. Ray diagrams for double convex lenses were drawn. Because the rays always diverged by a concave lens, the emerging rays do not The concave lens image can still more be explained by a Concave Lens Ray ... For a Concave lens,There are only 2 casesThey areObject is Placed at InfinityObject is Placed between Infinity and Optical CenterCase 1 - Object is Placed at infinityIn this Case, Object is kept far away from mirror (almost at infinite distance)So, we draw rays parallel to principal axisSince ray pa
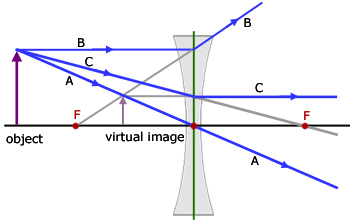
A concave lens ray diagram is a simple way of visualising the path that light rays take when passing through a concave lens. To draw a ray diagram you only need to draw two ray lines. This is sometimes referred to as “the two rules of refraction for diverging lenses”.
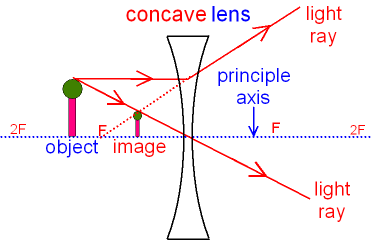
Concave lens ray diagram
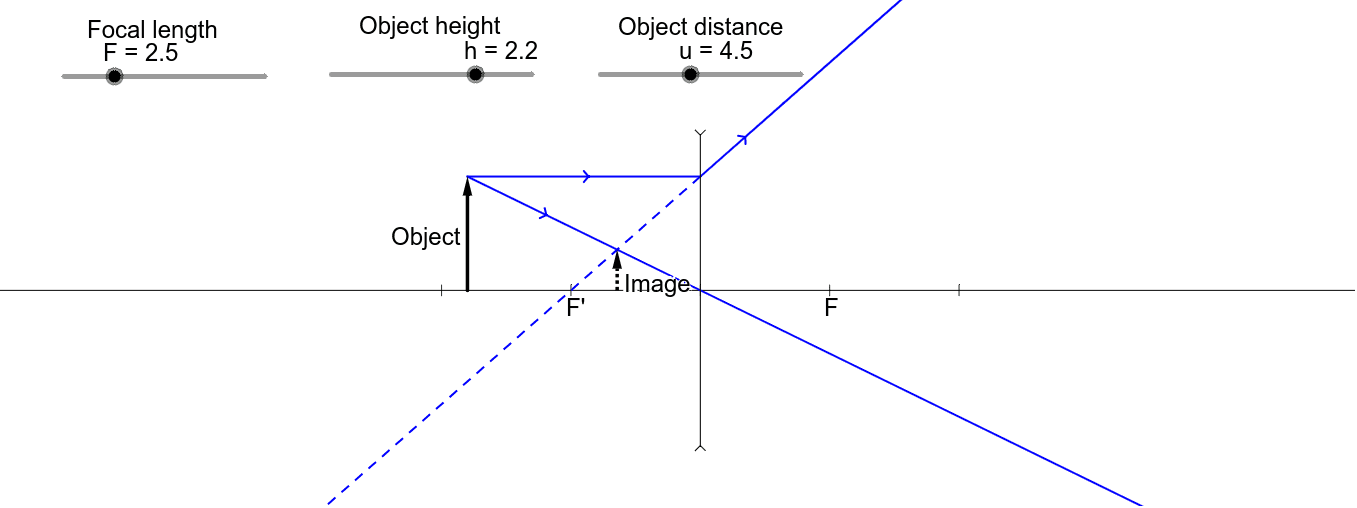
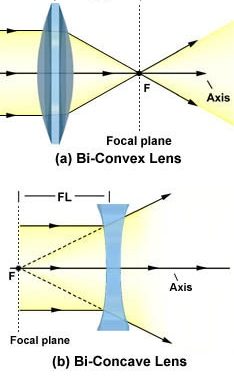
Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding... Section 3: Concave Lenses 12 3. Concave Lenses Concave lenses always produce upright, virtual images. For aconcave lens, the lens equation is the same but the value of fis nownegative. Ray diagrams for such lenses are drawn using: a ray from the top of the object through the middle of the lens; a ray from the top of the object parallel to the ... In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. The distance from the lens to the ...
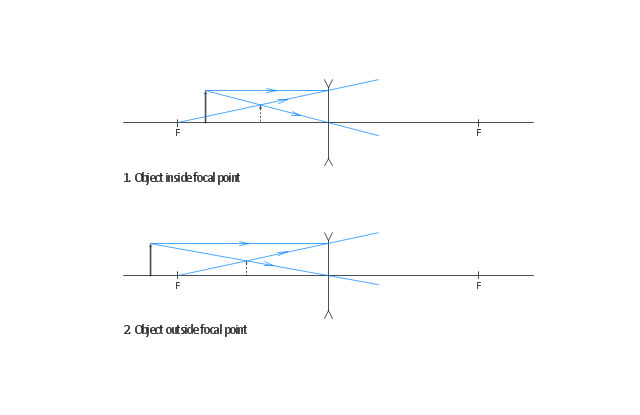
Concave lens ray diagram. In figure the refracted ray parallel to the principal axis. So, the Incident ray must be appearing to meet at the principal focus of concave lens. To find the incident ray, F 2 is joined to Q and produced as shown in the figure. The ray diagram above illustrates that the image of an object in front of a double concave lens will be located at a position behind the double concave lens. A ray diagram shows the path of light from an object to mirror to an eye. Incident rays - at least two - are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection. Ray Diagrams for Concave Lenses. The ray diagrams for concave lenses inside and outside the focal point give similar results: an erect virtual image smaller than the object. The image is always formed inside the focal length of the lens.
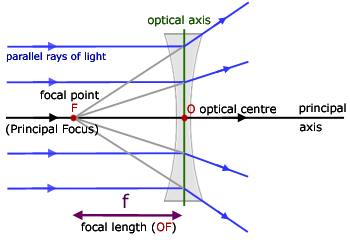
When a ray, passing through focus strikes concave or convex lenses, the reflected ray will pass parallel to the principal axis. Image Formation by Concave and Convex Lenses: Convex Lenses. When an object is placed at infinity, the real image is formed at the focus. The size of the image is much smaller than that of the object. Concave lens ray diagram class 10 The light is reflected by a mirror. The light crosses, and is refracted by, a lens. The lenses have two focal points, one on both sides of the target. A concave mirror converges light at a focal point. For lenses, light converges to a point for a convex lens. A convex mirror diverges the light, as well as a ... In a ray diagram, a convex lens is drawn as a vertical line with outward facing arrows to indicate the shape of the lens. The distance from the lens to the ... Section 3: Concave Lenses 12 3. Concave Lenses Concave lenses always produce upright, virtual images. For aconcave lens, the lens equation is the same but the value of fis nownegative. Ray diagrams for such lenses are drawn using: a ray from the top of the object through the middle of the lens; a ray from the top of the object parallel to the ...
Hi ! In this animation of CONCAVE Lens, you get a good confidence to draw Ray Diagrams for various Object Positions. The aim is to have a clear understanding...

Gcse Physics What Is The Ray Diagram For A Concave Lens What Is A Virtual Image What Is An Upright Image Gcse Science
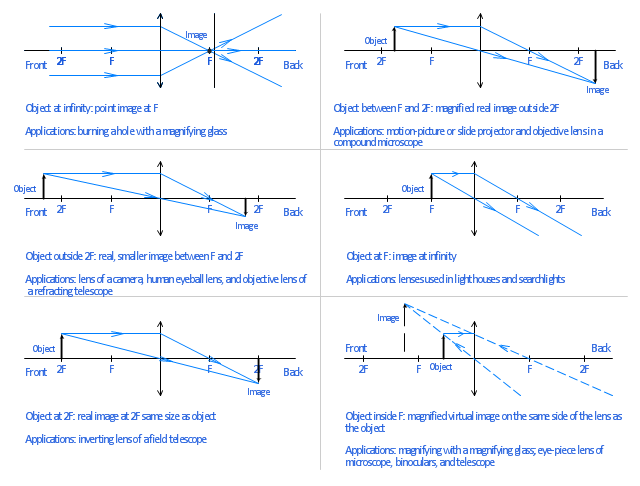
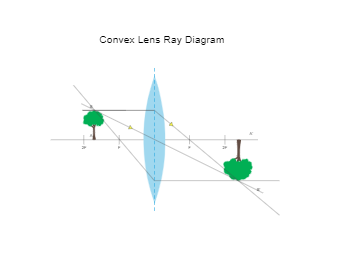
Ray Tracing Diagram For Convex Lens Physics Diagrams Optics Vector Stencils Library Ray Diagram Lenses

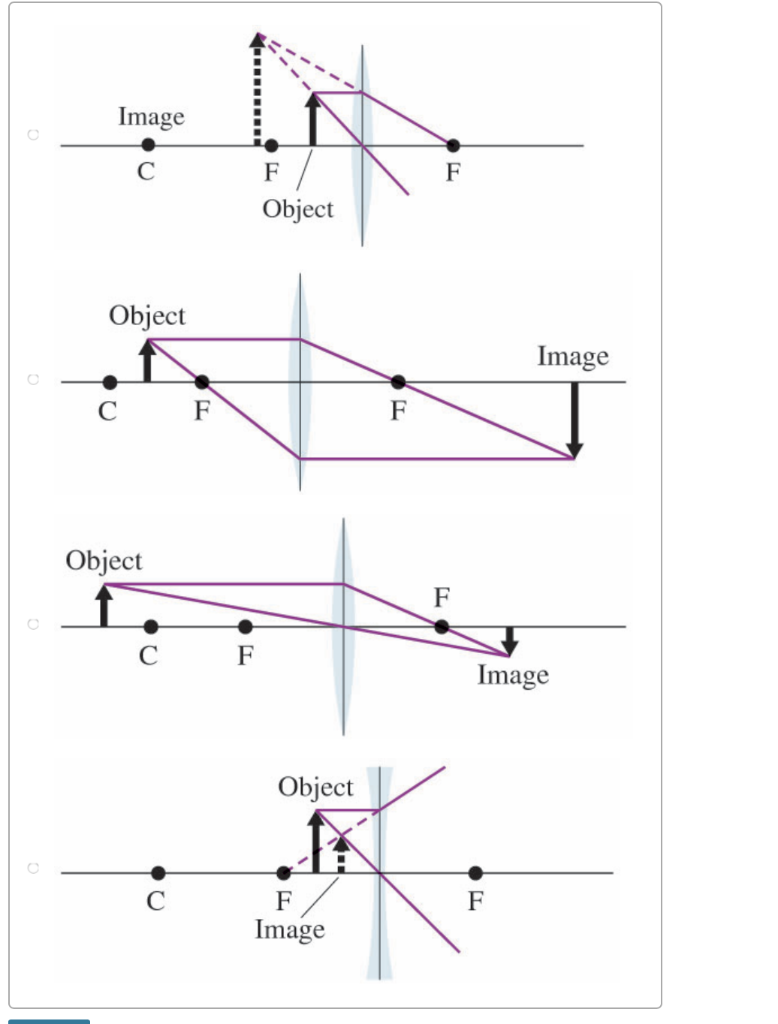
Draw Ray Diagrams Showing The Image Formation By A Concave Lens When An Object Is Placed A Between Focus And Twice The Focal Length Of The Lens B Beyond Twice The Focal

The Photons Of Light Then Travels In All Directions Simple Convex Lens Ray Diagram Transparent Png 600x355 Free Download On Nicepng
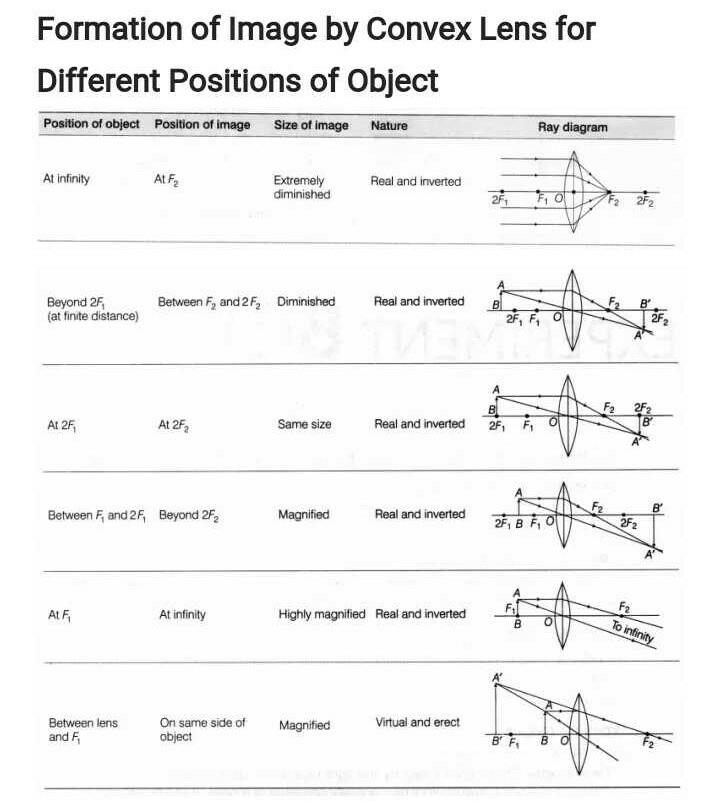
With The Help Of Ray Diagram Illustrate The Change In Position Nature And Size Of The Image Formed If The Convex Lens In Replaced By Concave Lens Of Same Focal Length
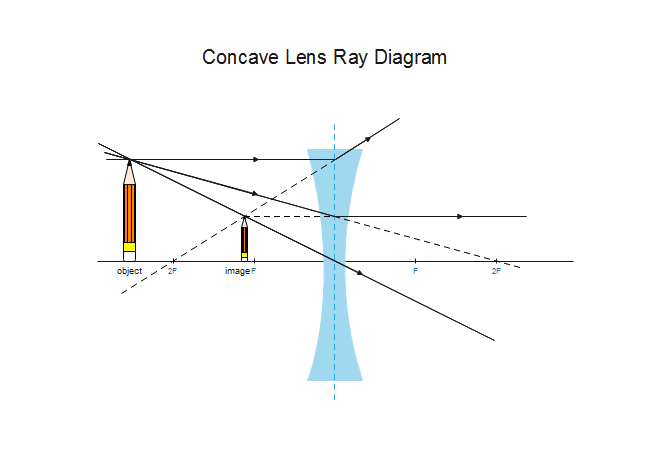















0 Response to "39 concave lens ray diagram"
Post a Comment