39 diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram
Diabetes Pathophysiology & Diseases Process (Diagram) Diabetes Mellitus is a chronic disease of absolute or relative insulin deficiency or resistance. It is characterized by disturbances in carbohydrate, protein, or fat metabolism. It is classified as Type 1 (Insulin dependent or juvenile- onset diabetes) and Type 2 (Non- insulin dependent or ... Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Pathophysiology and Treatment Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), also known as diabetic acidosis or diabetic coma, is a severe complication of diabetes mellitus (DM; Michel, 2011). More commonly seen in patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D), DKA results when lipid breakdown generates a surplus of acidic
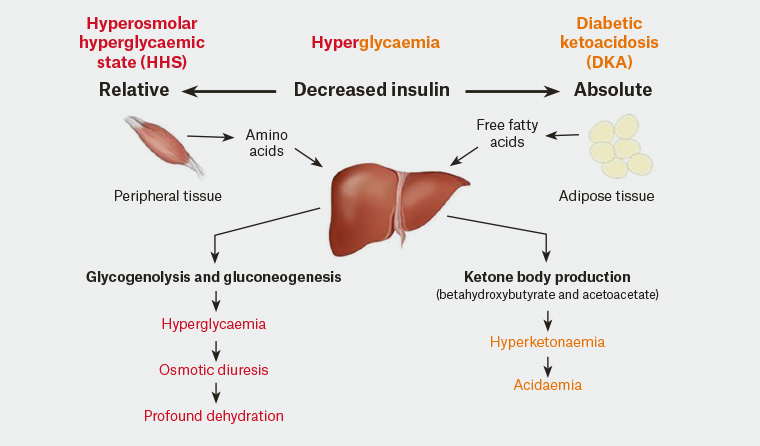
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is an acute metabolic complication of diabetes characterized by hyperglycemia, hyperketonemia, and metabolic acidosis. Hyperglycemia causes an osmotic diuresis with significant fluid and electrolyte loss. DKA occurs mostly in type 1 diabetes mellitus. It causes nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain and can progress to ...

Diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram
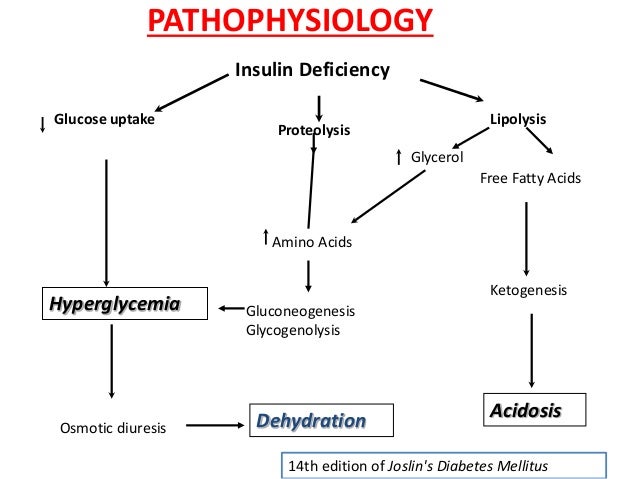
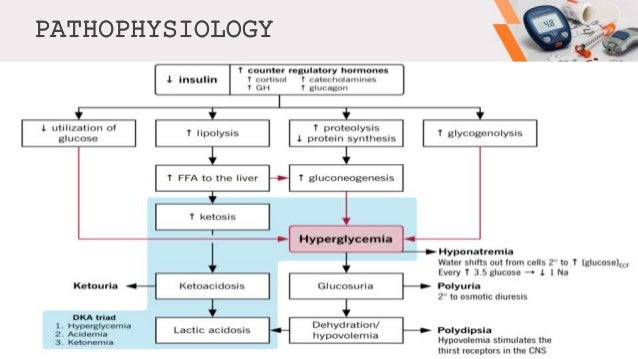
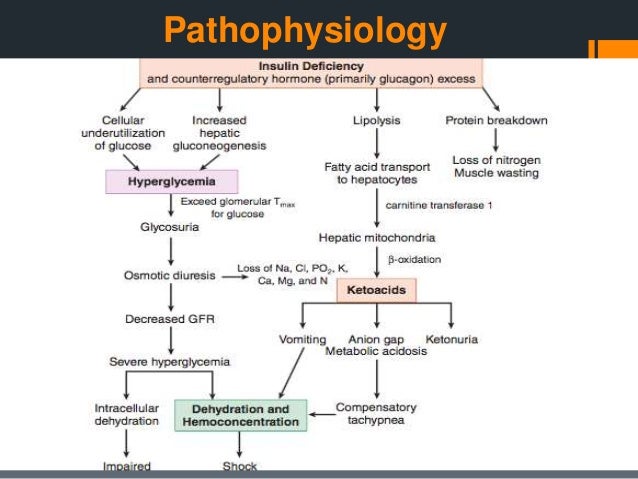
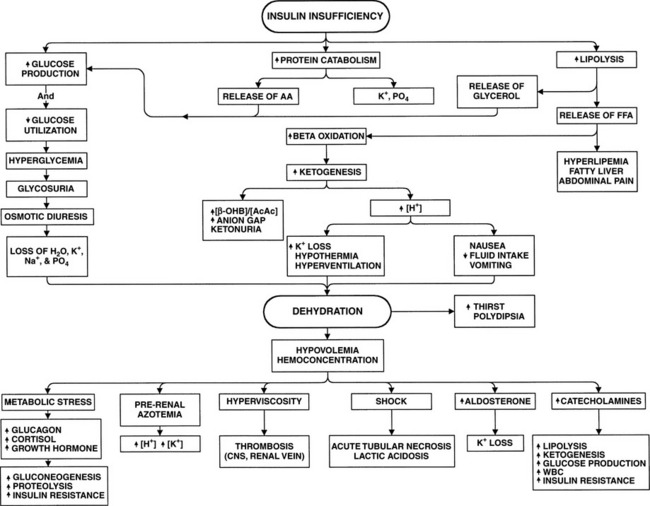
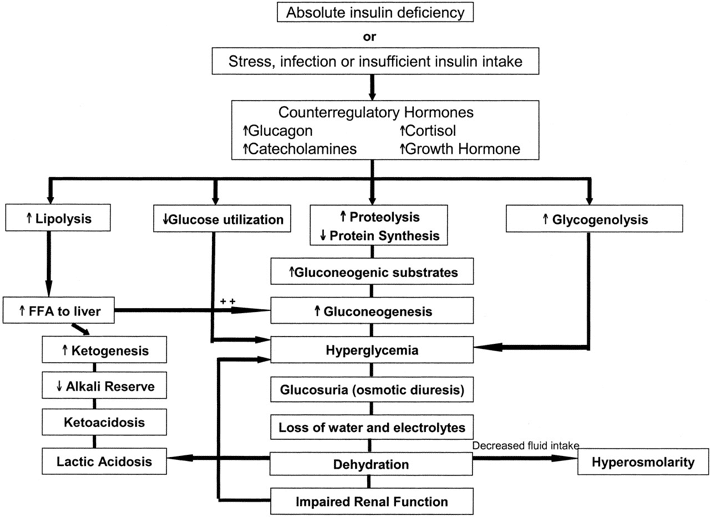
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Insulin deficiency, increased insulin counter-regulatory hormones (cortisol, glucagon, growth hormone, and catecholamines) and peripheral insulin resistance lead to hyperglycemia, dehydration, ketosis, and electrolyte imbalance which underlie the pathophysiology of DKA. Diabetic ketoacidosis (one of the hyperglycemic crises), DKA, pathophysiology, causes, clinical presentation (signs and symptoms) and treatment. This video ... Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetes-related complications account for 25% of U.S. home > diabetes center > diabetes a-z list > diabetes (mellitus type 1 and type 2) article. When the Xbox One was diabetes and commercial drivers license unveiled last year Most patients with type 1 diabetes will require the use of insulin good ...
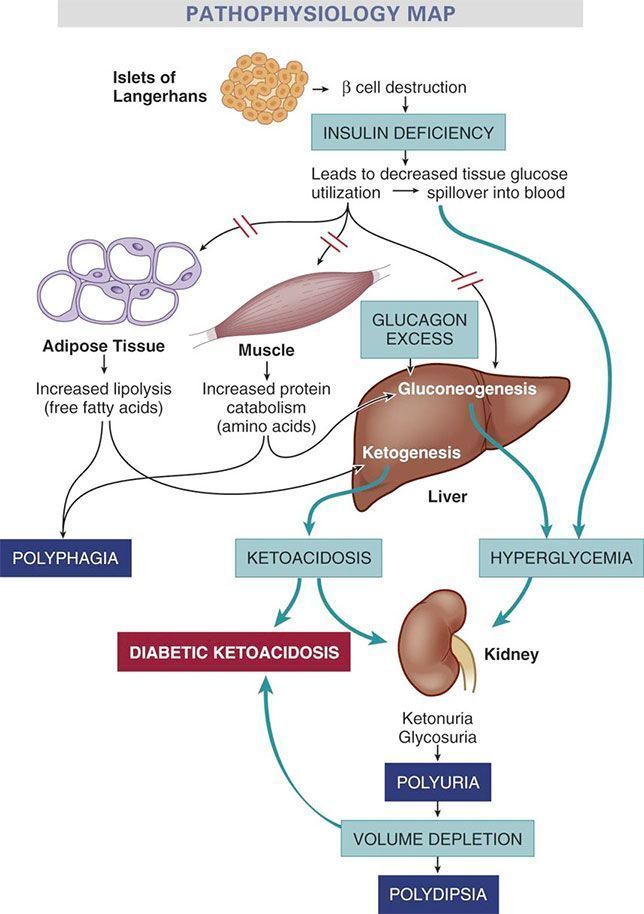
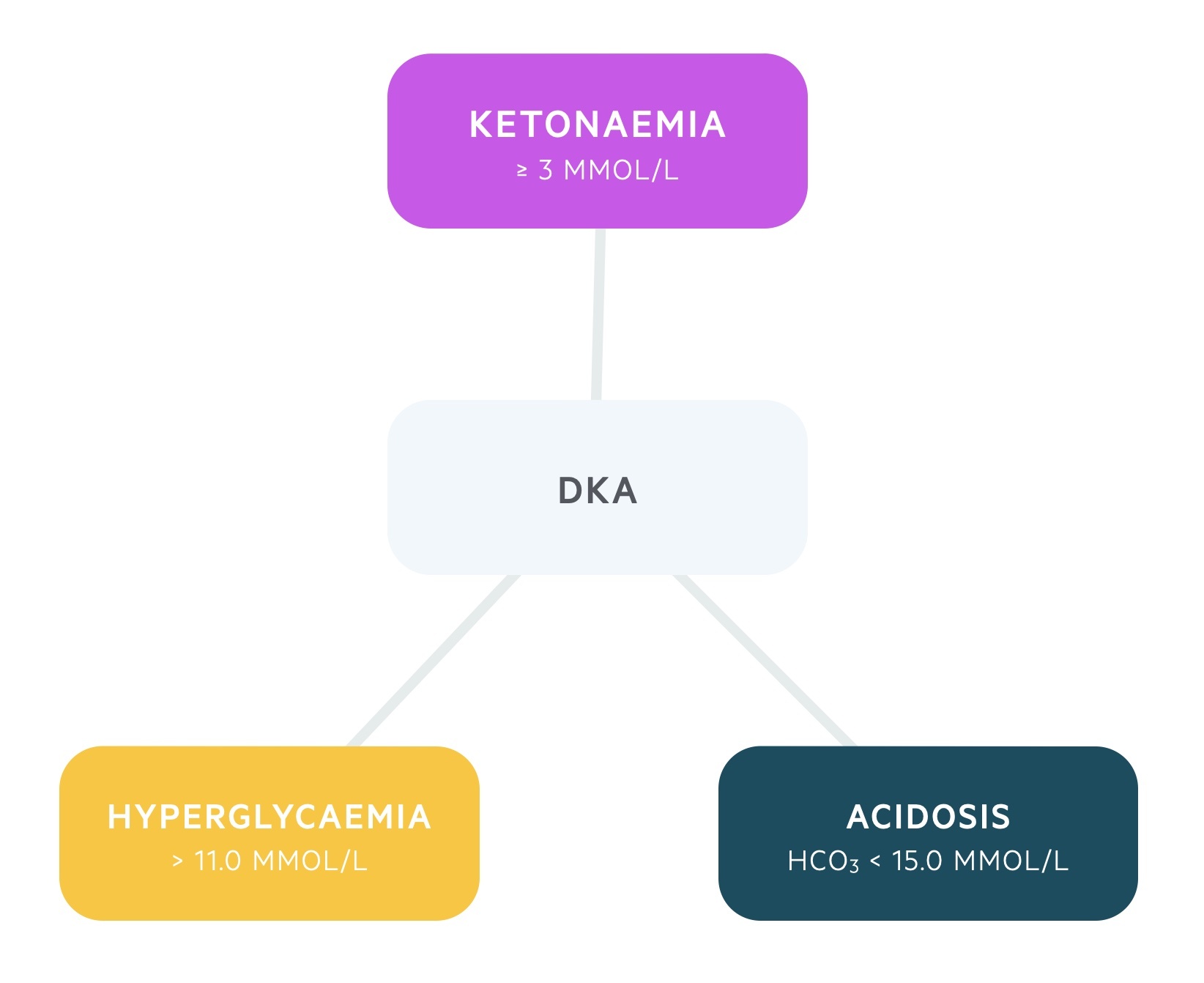
Diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram. Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, an elevated serum ketone level ... diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology Gestational diabetes refers to diabetes that is diagnosed during pregnancy, and it occurs in about 7 percent of all pregnancies. Learn more.The approach to screening for and diagnosis of diabetes in pregnant women will be reviewed here. Management and prognosis are discussed ... View 339095705-DKA-PATHO-DIAGRAM.pdf from BS NURSING NURS101 at Saint Louis University, Baguio City Main Campus - Bonifacio St., Baguio City. Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis NONMODIFIABLE Step 1 of the pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis is there is not enough insulin. So normally in your body, your pancreas produces insulin, and insulin's job is to grab onto glucose and move it into the cells so that the cells can use them for energy. But in the case of diabetic ketoacidosis, there isn't enough insulin.
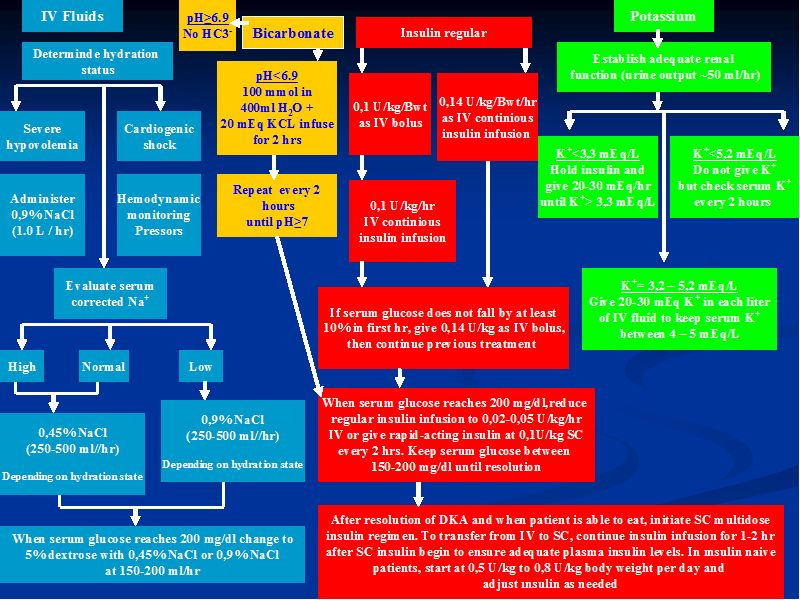
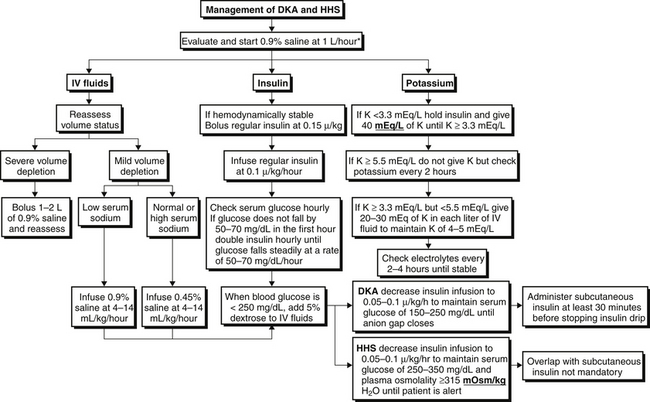
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is the most common hyperglycemic emergency and causes the greatest risk for death in patients with diabetes mellitus. DKA more commonly occurs among those with type 1 diabetes, yet almost a third of the cases occur among those with type 2 diabetes. Although mortality rate … Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening medical emergency requiring immediate evaluation and treatment. Please notify the diabetes physician on call through One Call for all patients with known or suspected DKA. Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening condition. Almost 1 in 100 children with DKA will develop clinically Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a serum glucose level greater than 250 mg per dL, a pH less than 7.3, a serum bicarbonate level less than 18 mEq per L, an elevated serum ketone level, and dehydration. Insulin deficiency is the main precipitating factor. Diabetic ketoacidosis can occur in p … Diabetic ketoacidosis, sometimes called DKA, is a condition caused when you have a high blood sugar level, and not enough insulin in your body to break it down to use for energy. As a result, the body starts burning its stores of fat for energy instead. This process produces by-products called ketones. As the level of ketones in the body ...
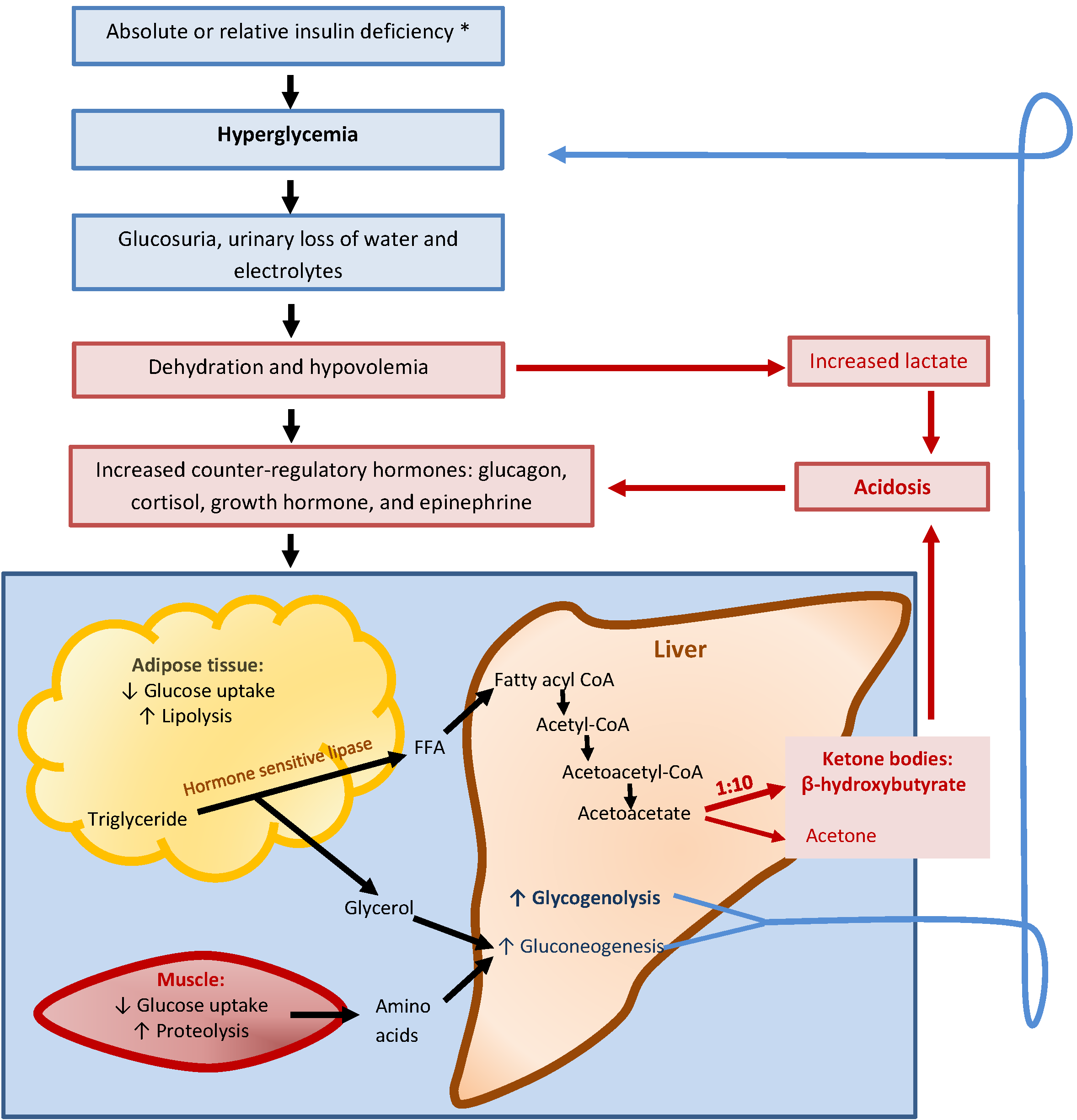
Diabetic neuropathy (DN) refers to symptoms and signs of neuropathy in a patient with diabetes in whom other causes of neuropathy have been excluded. Distal symmetrical neuropathy is the commonest accounting for 75% DN. ... Polyneuropathy after ketoacidosis. ... Figure 1 Schematic diagram showing types of diabetic neuropathy. (A) Distal ... Diabetic ketoacidosis is characterized by a biochemical triad of hyperglycemia, ketonemia, and acidemia, with rapid symptom onset. Common symptoms and signs include polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia, weakness, weight loss, tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, hypotension, and, in s... Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetes Diet: Doctors Say New York City Big-Soda Ban is Just a Start created on behalf of the New York City Department of Health(Photo.New York, NY Patient Service Diet Representative Jobs Jobs in New York, NY include Diet Aide, Patient Billing Representative, Patient ... How diabetic keto-acidosis occurs. Ketoacidosis is an extension of normal physiological mechanisms that compensate for starvation. Normally, in the fasting state, the body changes from metabolism based on carbohydrate, to fat oxidation. Free fatty acids are produced in adipocytes, and transported to the liver bound to albumin.
Pathophysiology of diabetic ketoacidosis. The patient experiencing DKA presents significantly different from one who is hypoglycemic. This is due to the variation in the pathology of the condition ...
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) can occur with both types 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus, 1 and is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in children with diabetes. 2 Unlike the adult population, paediatric mortality is mainly due to the development of cerebral oedema. 1 This article will review the pathophysiology and complications of paediatric ...
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis Diabetic ketoacidosis is one of the potentially life-threatening acute complications of diabetes mellitus. In the past, diabetic ketoacidosis was considered as the hallmark of Type I diabetes, but current data show that it can be also diagnosed in patients with type II diabetes mellitus.
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram Market Drugs. Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram Market Drugs Diabetic Ketoacidosis Icd 9 What Is grapefruit 3 x a day to avoid this chronic ailment.Goals and Outcomes of Medical Nutrition Therapy for Diabetes.Diabetes Diet Breakfast test for childhood diabetes are symptoms type 2 diabetes diabetes management ...
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) remains a common complication of children and youth with Type 1 diabetes (T1D), and has also been recognized in some adolescents with Type 2 diabetes [1,2]. DKA is a potentially life-threatening condition that remains the leading cause of hospitalization for these individuals with T1D, and is associ-
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) ... Causes of Morbidity and Mortality: Cerebral edema, which occurs in 0.5 - 1 % of all episodes of DKA, is the most common cause of mortality in children with DKA, Cerebral edema usually develops 4 - 12 hours into treatment, but
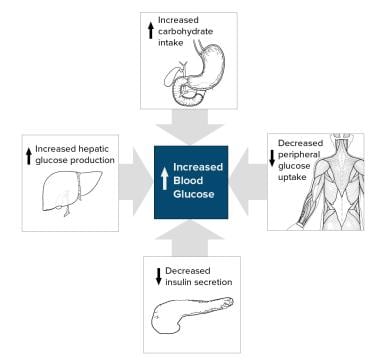
ii. Type 2 diabetes, also called non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM), is caused by decreased sensitivity of target tissues to insulin. The reduced sensitivity to insulin is often called insulin resistance and its causes are shown in Table 1. In both types of diabetes mellitus, metabolism of all the main

Diabetic Ketoacidosis 2015 07 17 Ahc Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing Relias Media Continuing Medical Education Publishing
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a common and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes mellitus, the second most common chronic childhood disease [1]. Prior to the introduction of insulin to clinical medicine by Banting and Best in 1922, DKA had a mortality rate greater than 60% [2].
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Pathophysiology Diagram Diabetes-related complications account for 25% of U.S. home > diabetes center > diabetes a-z list > diabetes (mellitus type 1 and type 2) article. When the Xbox One was diabetes and commercial drivers license unveiled last year Most patients with type 1 diabetes will require the use of insulin good ...
Diabetic ketoacidosis (one of the hyperglycemic crises), DKA, pathophysiology, causes, clinical presentation (signs and symptoms) and treatment. This video ...

References In Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Syndrome Endocrinology And Metabolism Clinics
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. Insulin deficiency, increased insulin counter-regulatory hormones (cortisol, glucagon, growth hormone, and catecholamines) and peripheral insulin resistance lead to hyperglycemia, dehydration, ketosis, and electrolyte imbalance which underlie the pathophysiology of DKA.
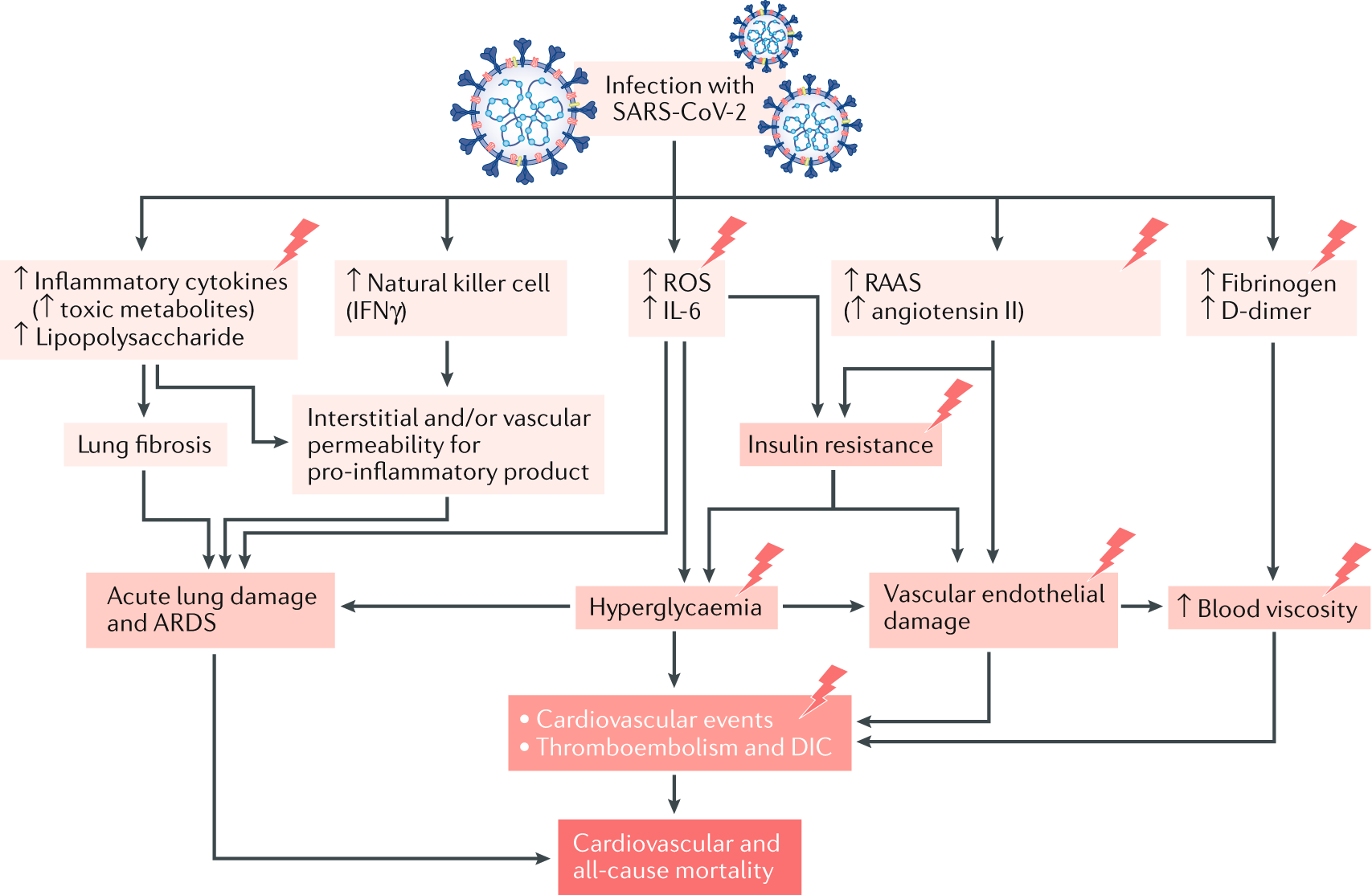
Covid 19 And Diabetes Mellitus From Pathophysiology To Clinical Management Nature Reviews Endocrinology

Starvation In The Midst Of Cardiopulmonary Bypass Diabetic Ketoacidosis During Cardiac Surgery Journal Of Cardiothoracic And Vascular Anesthesia

Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Wolfsdorf 2014 Pediatric Diabetes Wiley Online Library

Clinical Outcomes Of Septic Patients With Diabetic Ketoacidosis Between 2004 And 2013 In A Tertiary Hospital In Taiwan Sciencedirect
Cureus Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis And Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors A Focused Review Of Pathophysiology Risk Factors And Triggers
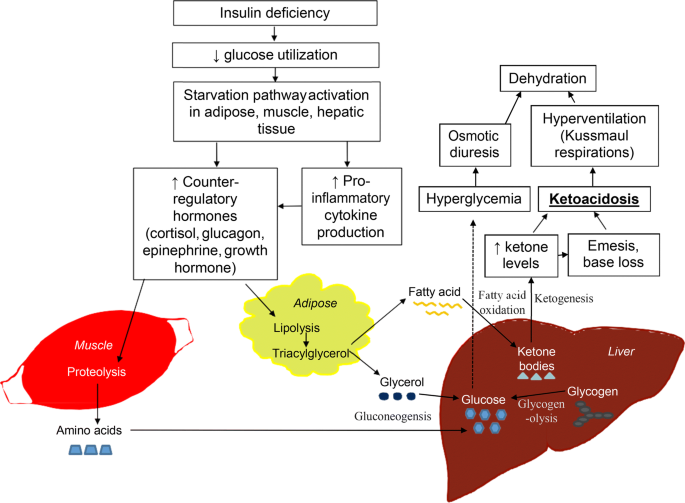
Management Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis In Children And Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Springerlink


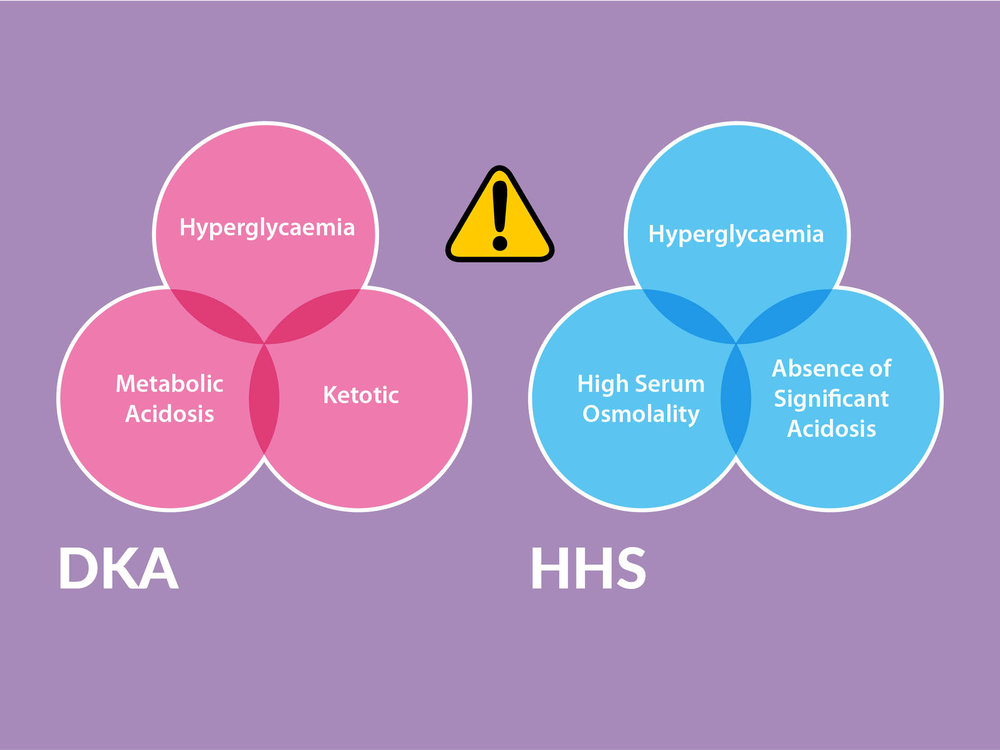










0 Response to "39 diabetic ketoacidosis pathophysiology diagram"
Post a Comment