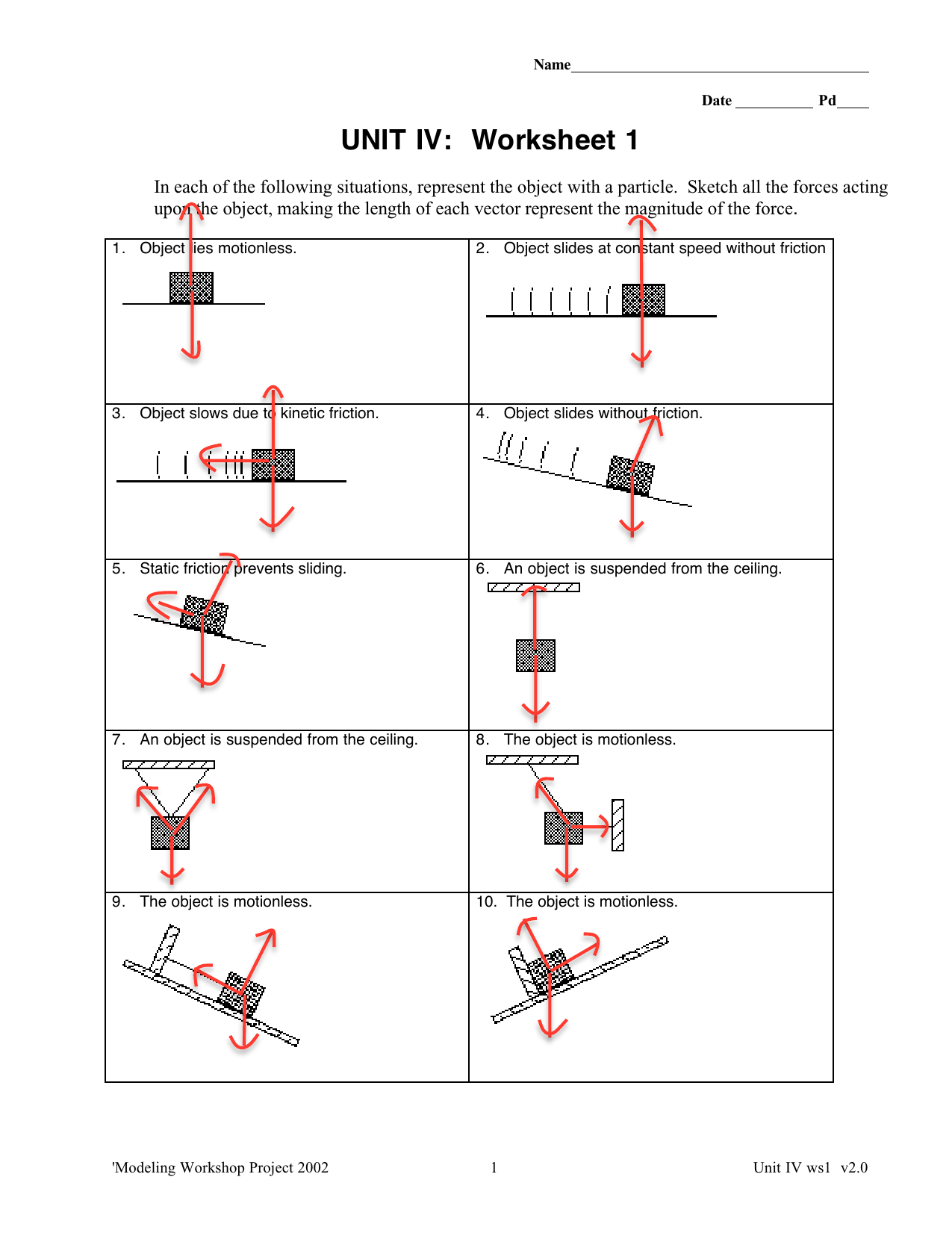
40 free body diagram static friction
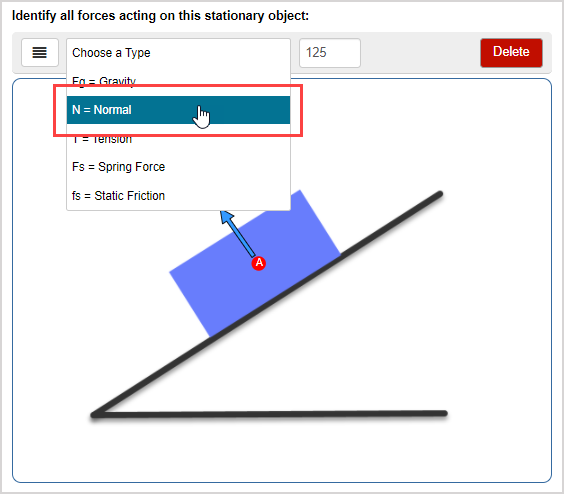
Draw a free-body diagram. (Neglect air friction) The force of gravity is the only force described. (no air resistance). Problem 8 A car runs out of gas and is coasting ... Static Friction coefficient of static friction f F s s N s u P P F N f s F F g The Force of Static Friction keeps a stationary object at C2.1 Free-Body Diagram (FBD) and Supports Free-Body Diagram (FBD) In your much dreaded class test, the first question requires you to identify all forces acting on a person who is standing. Whew, pretty easy - it must be just the person's weight (gravitational force).
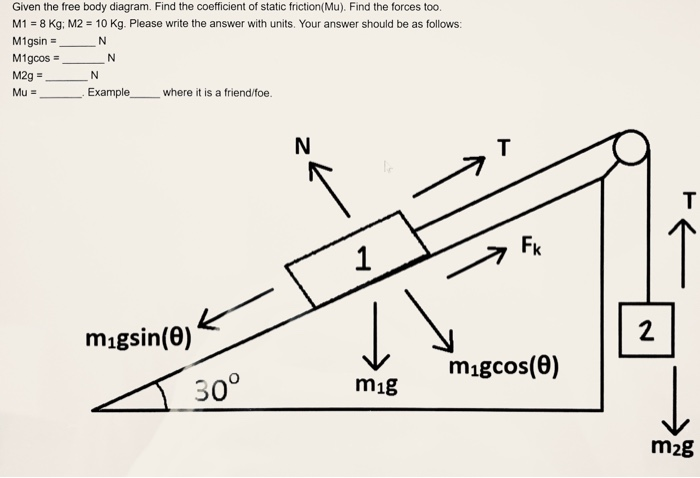
Calculate the coefficient of static friction at the floor. Homework Equations The Attempt at a Solution I've been stuck at this question for 3 days and I am still unable to find the coefficient of static friction at the floor. I have drawn the free body diagram and tried to solve it, getting a static friction of 0.3.
Free body diagram static friction
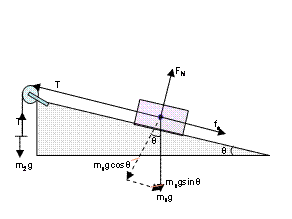
Provided by the Academic Center for Excellence 6 Free-Body Diagrams April 2017 In this system of equations, the first one establishes the relationship between the normal force and the frictional force.Because the box will not begin to move until the tension force overcomes the frictional force, the max frictional force is needed. The max frictional force is equal to the A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep the car from sliding toward the center of the turn. This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into kinetic friction and static friction. It contains plenty of examples and physics problems tha...
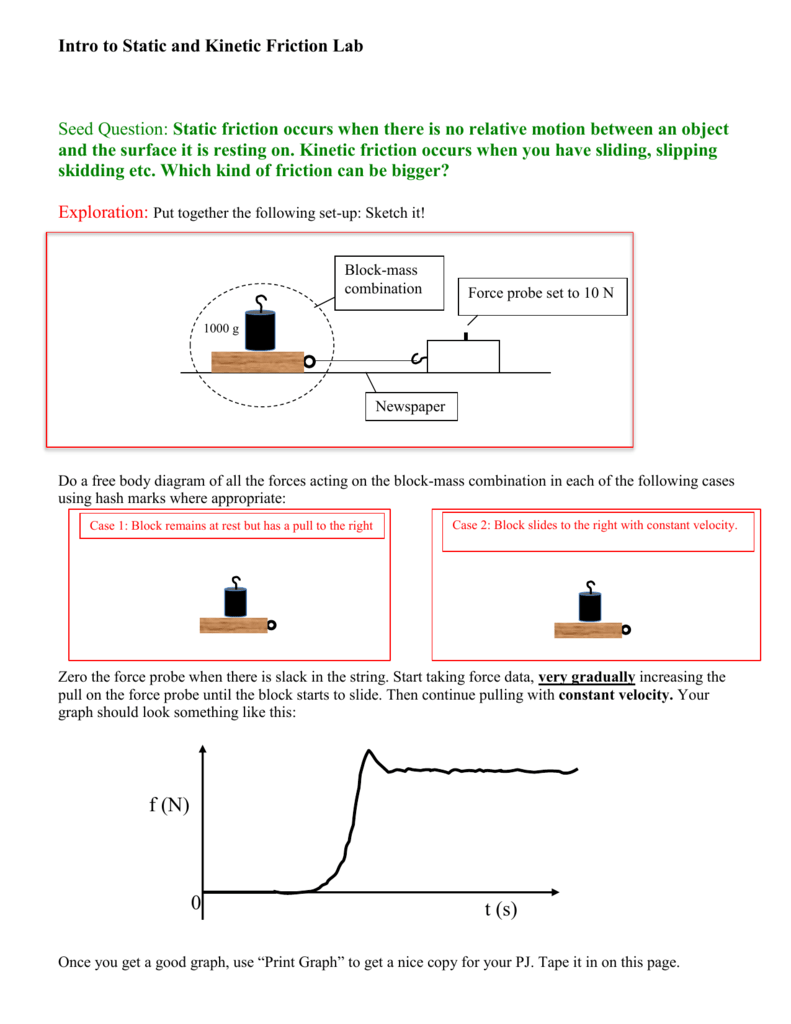
Free body diagram static friction. The free-body diagram of the crate is shown in (b). We apply Newton’s second law in the horizontal and vertical directions, including the friction force in opposition to the direction of motion of the box. ... static friction force that opposes the motion of two systems that are in contact and are not moving relative to each other. Previous ... This physics video tutorial explains how to draw free body diagrams for different situations particular those that involve constant velocity and constant acc... The free-body diagram shows the gravitational force exerted on the box by the Earth, the normal force exerted by the table, the force that you apply, and, if there is one, the static force of friction. Note that, on the free-body diagram, the force of gravity and the normal force have been shifted horizontally a little so they can be seen more easily. Static friction free body diagram. Neglect air friction the force of gravity is the only force described. Force of static friction upon sliding the baseball player will come to a complete stop due to the force of kinetic friction. Since there is no other force being applied to the object the sf is 0 and should not be part of the force diagram.
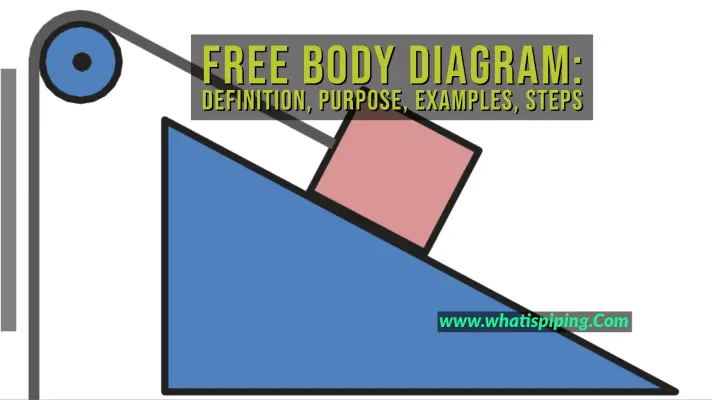
The free body diagram helps you understand and solve static and dynamic problem involving forces. It is a diagram including all forces acting on a given object without the other object in the system. You need to first understand all the forces acting on the object and then represent these force by arrows in the direction of the force to be drawn. Drawing a Free-Body Diagram In a Free-Body Diagram, the object is represented by its expression, usually a line, box, or a dot. The force vectors that act upon the object are represented by a straight arrow while moments are represented by a curved arrow around their respective axis as shown in the image below where a force is acting at B and a moment acts around A. Draw a free body diagram (“fbd”) using the skills and definitions above. Solutions to the assigned problems. Class notes: Identifying the forces we will address, the directions they point and the formulas. Class notes: Creating free body diagrams, summing up the force equations from the diagrams. Some example problems. Sep 22, 2016 · Force due to static friction is coefficient of friction * Normal reaction. As the body is resting on an inclined plane, the normal reaction is not equivalent to weight, but the component of it perpendicular to the plane on which the body rests. You need to resolve all the forces in your diagram, to arrive on your answer.
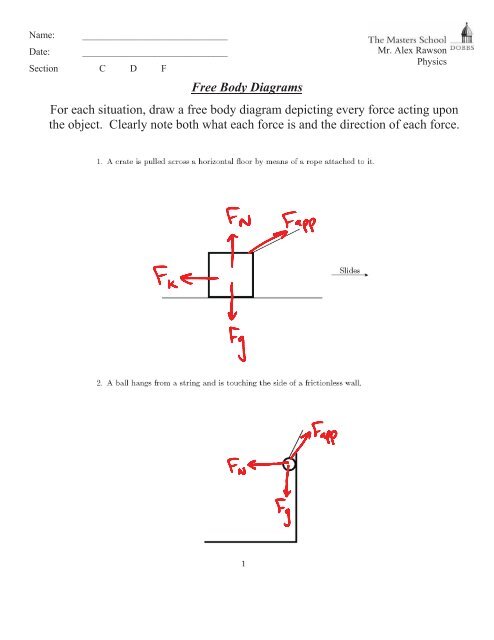
Draw a free-body diagram for the free mass. (Hint: the static friction acting on the free mass is approximately zero] (5 pts) 2. Apply Newton's 2nd Law to show that the centripetal force (Fe) is approximately equal to the tension on the free mass. (4 pts) Question: Introduction (9 pts) 1. Draw a free-body diagram for the free mass. A free-body diagram can be drawn very simply, with squares and arrows, or you can make it much more complex. The only requirement is that you or someone else looking at it should be able to understand what the diagram is telling. A free-body diagram (FBD) is a representation of a certain object showing all of the external forces that acts on it. B. the force of static friction that the floor exerts on your shoes ... Gravity, F, normal force and kinetic friction force Free Body Diagram F. qWhat is the smallest value of the force F such that the 2.0-kg block will not slide down the wall? The coefficient of static friction between A free body diagram is used to calculate static and dynamic forces acting on an object. In other words, a free body diagram is the starting point to develop a mathematical model to find and calculate various forces acting on a body. The purpose of the free body diagram is to simplify the situation for easy analysis. Figure :1.
Aug 19, 2017 · In your free body diagram, you need to show static friction since it is an external force. It will always be equal and opposite to the force which is applied horizontally to the box. If any external force is applied but still the box in at rest. If no external force is applied on the box then also it would be at rest.
free-body diagram for step 1, in which you exert no force. (c) The free-body diagram that applies to steps 2 - 4, in which the force you exert is less than or equal to the maximum possible force of static friction. (d) The free-body diagram that applies to step 5, in which your force is large enough to cause the box to move.
The free body diagram is a sketch of the forces on an object, or the causes of motion. Acceleration is the effect of those forces and therefore does not show up on the FBD. It will make an appearance in the equation. ... The force of static friction between the two cartons is.
is a free body diagram. It seems that my mental intuition is wrong quite often while my free body diagrams always lead to the correct answer. These question seem relatively easy but just take time to set everything up and have the answer appear. Static and Kinetic frictions formulas. How they would apply to a problem with the
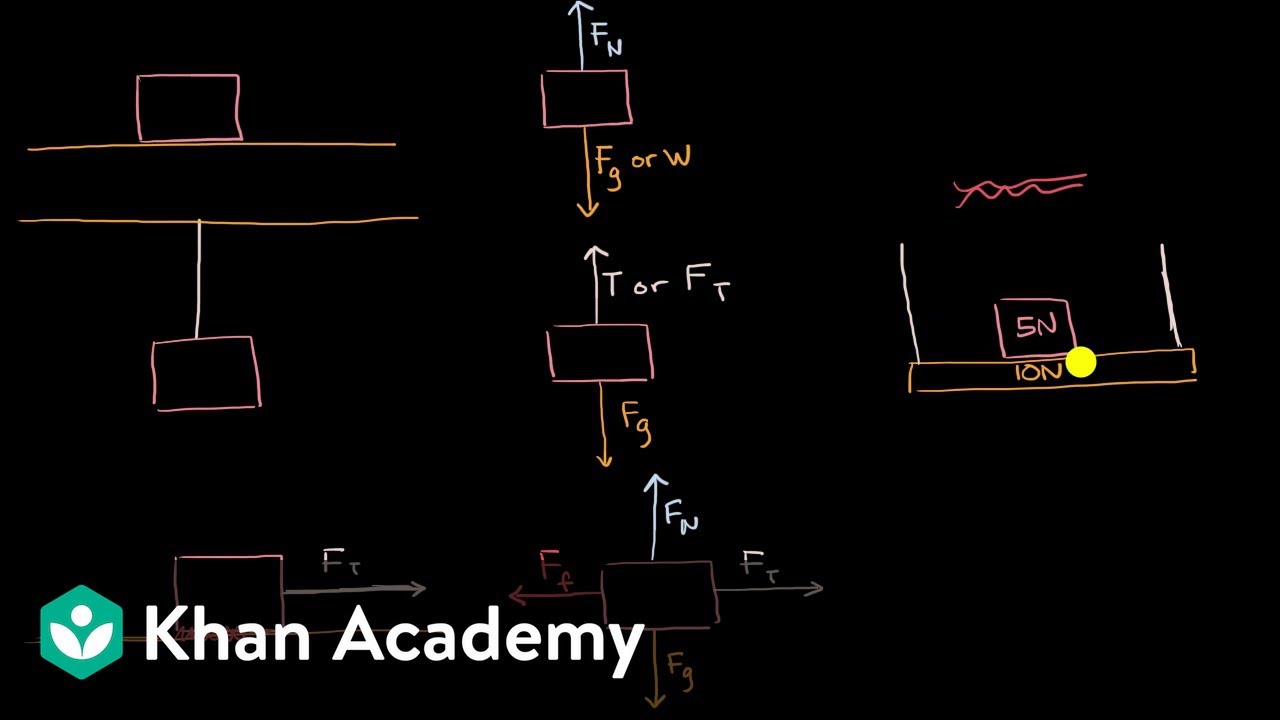
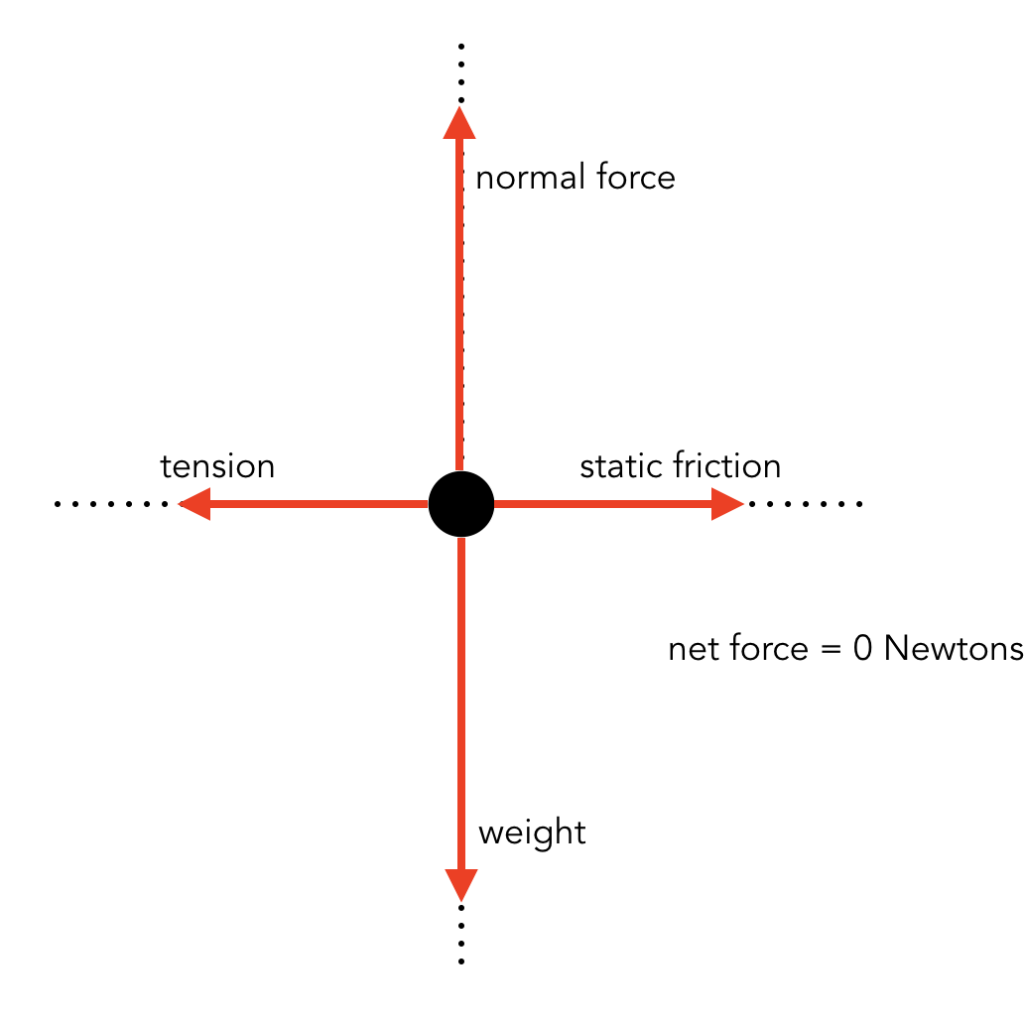
Friction Free-body diagrams. Newton's second law: F net = ma. To find the net force on an object, all the vector forces that act on the object have to be added. We use free-body diagrams to help us with this task. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting on an object in a given ...
Nov 23, 2021 · Static friction free body diagram. Free - body diagram s are diagram s used to show the rel at ive magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situ at ion. A free - body diagram is a special example of the vector diagram s th at were d is cussed in an earlier unit.
30 The Drawing Shows A Baggage Carousel At An Airport Your Suitcase Has Not Slid All The Way Down The Slope And Is Going Around At A Constant Speed On A Circle R 11 0 M As The Carousel Turns The Coefficient Of Static Friction Between The Suitcase And
Static friction free body diagram. In your free body diagram you need to show static friction since it is an external force. The static force of friction has a maximum value but when two surfaces are not moving relative to each other the static force of friction is always just enough to exactly balance any forces trying to produce relative motion.
Examples of drawing free-body diagrams. To better understand how to draw free-body diagrams using the 3 steps, let's go through several examples. Example 1. A box is pushed up an incline with friction which makes an angle of 20 ° with the horizontal. Let's draw the free-body diagram of the box. The first step is to sketch what is happening:
Answer (1 of 10): Friction. Let's just assume you are on bench seat in a carraige or something and not gripping a horse (or reindeer?) with your thighs. You are "trying" to go straight ahead, tangentially to the circular path. If the seat were frictionless, that's what you would do and would be f...
Drawing Free-Body Diagrams. Free-body diagrams are diagrams used to show the relative magnitude and direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. A free-body diagram is a special example of the vector diagrams that were discussed in an earlier unit. These diagrams will be used throughout our study of physics.
The free-body diagram of box 1 is relatively complicated, with a total of 6 forces appearing. The free-body diagram for box 2 is a little easier to deal with, having 4 forces, so that's a good place to start. For box 2 - start by summing the forces in the y-direction, where there is no acceleration: This can be solved to give the normal force:
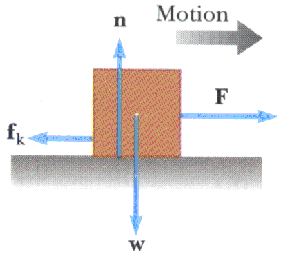
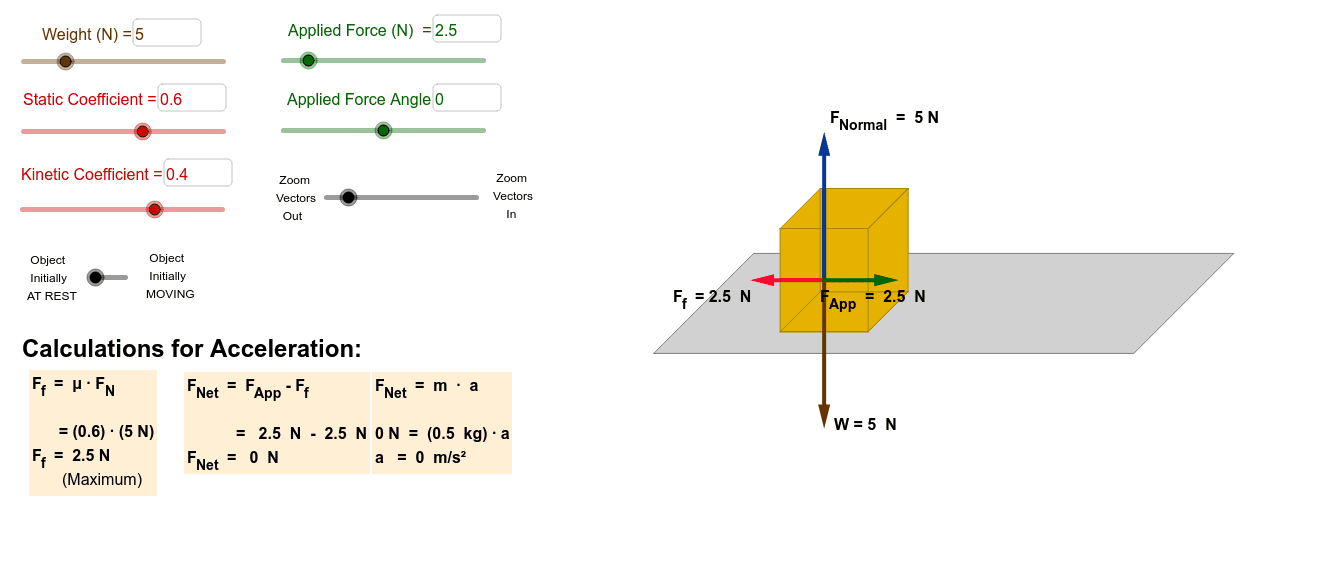
Static friction is a force that must be overcome for something to get going. The force of static friction increases with the applied force acting in the opposite direction, until it reaches a maximum value and the object just begins to move. ... [insert a free body diagram showing the applied, frictional, gravitational and normal forces on the ...
Static Friction • Static friction on an object by a surface is opposite in direction to tendancy of motion of the object relative to the surface. • The kinetic friction force on an object by can take any value between zero and a maximu value, fs,max. fs ≤ μs N • Examples: Allows us to walk, accelerates and
The role of static friction is to keep the box at rest. If we exert a horizontal force of 10 N on the box, the force of static friction acting on the box must be 10 N in the opposite direction, to keep the box from moving. The free-body diagram of this situation is shown in Figure 5.3c.
This physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into kinetic friction and static friction. It contains plenty of examples and physics problems tha...
A free-body diagram for the car is shown at left. Both the normal force, N (blue components) and the friction force, f (red components) have been resolved into horizontal and vertical components. Notice that the friction force acts up the incline, to keep the car from sliding toward the center of the turn.
Provided by the Academic Center for Excellence 6 Free-Body Diagrams April 2017 In this system of equations, the first one establishes the relationship between the normal force and the frictional force.Because the box will not begin to move until the tension force overcomes the frictional force, the max frictional force is needed. The max frictional force is equal to the

Free Body Diagram For The Static Friction Of An Object With A Horizontal Force Applied Physics Stack Exchange

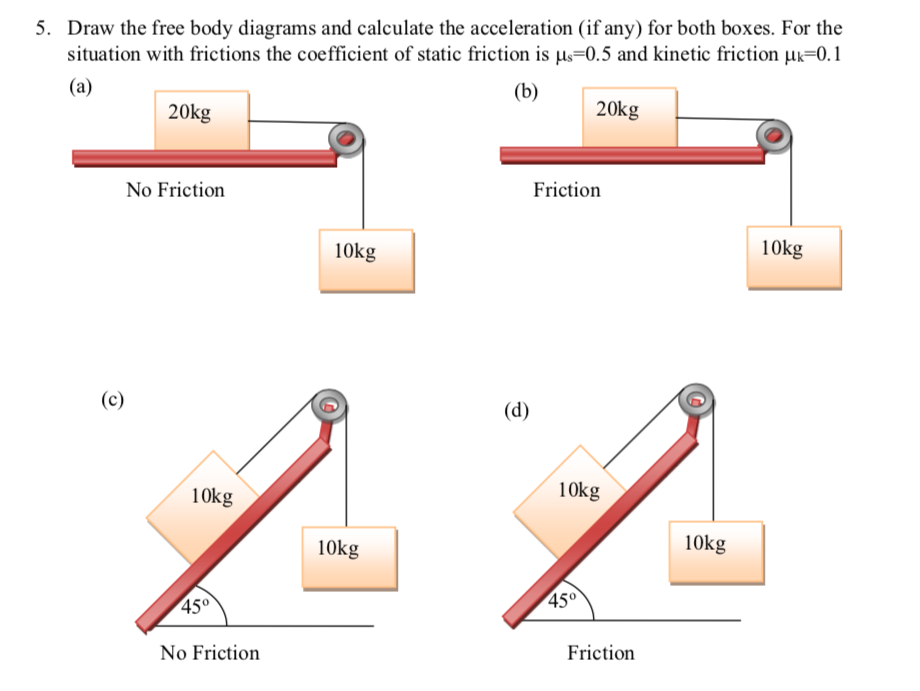
3 Friction Total 30 Marks A Draw The Free Body Diagram Of The Two Boxes A And B 10 Marks B If The Coefficient O Homeworklib














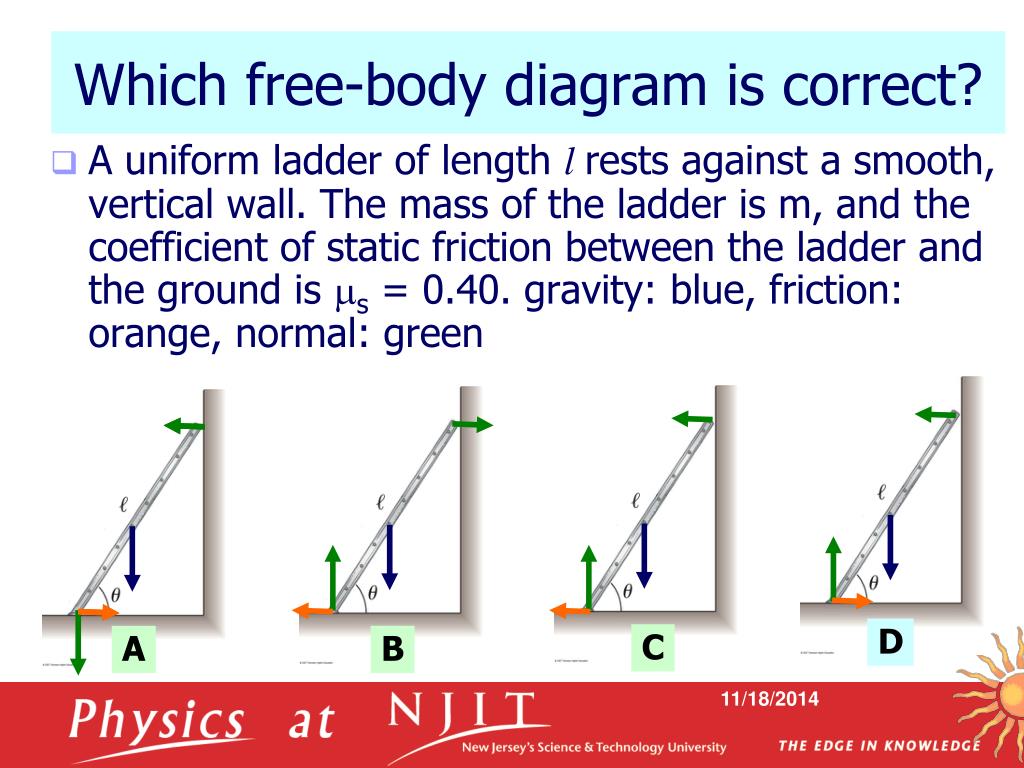

0 Response to "40 free body diagram static friction"
Post a Comment