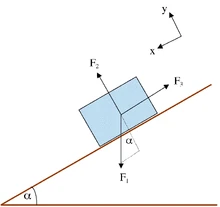
34 free body diagram block on ramp
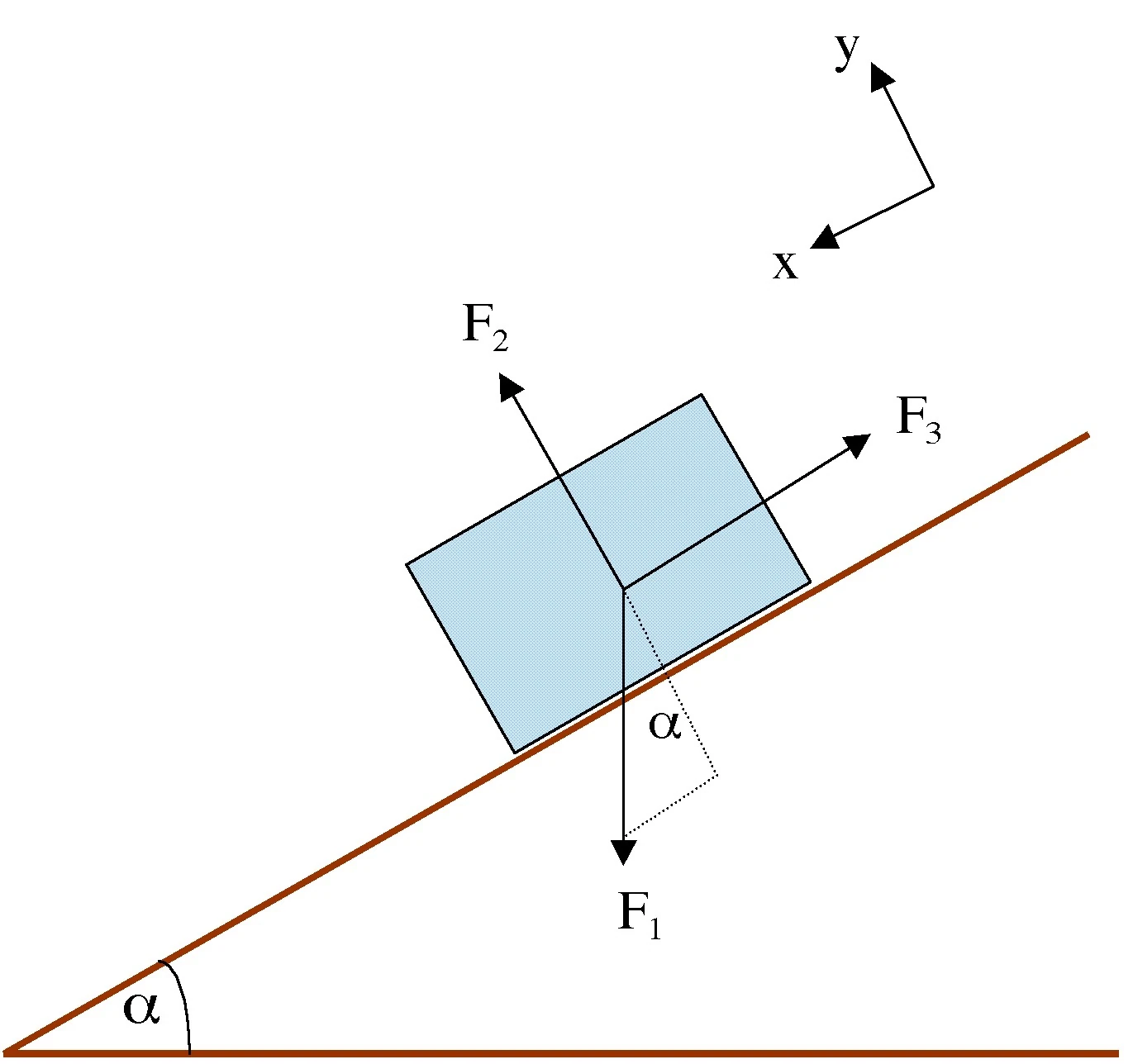
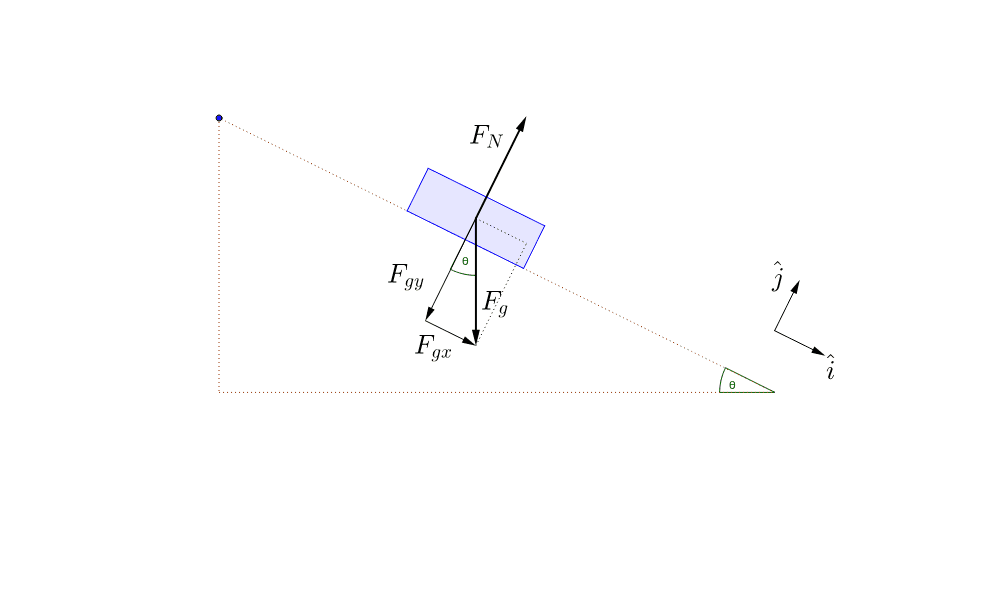
Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x– and y-components of a given force (this is often helpful when solving a problem using Newton’s first or second law). In this case, place a squiggly line through the original vector to show that it is no longer in play—it has been replaced by its x – and y -components.
A free body diagram is defined as an illustration that depicts all the forces acting on a body, along with vectors that are applied by it on the immediate environs. Apart from the acting forces and subsequent work done, the moment magnitudes are also considered to be a part of such diagrammatic representations.
Let's apply the problem-solving strategy in drawing a free-body diagram for a sled. In (Figure) (a), a sled is pulled by force P at an angle of 30° 30 °. In part (b), we show a free-body diagram for this situation, as described by steps 1 and 2 of the problem-solving strategy. In part (c), we show all forces in terms of their x - and y ...
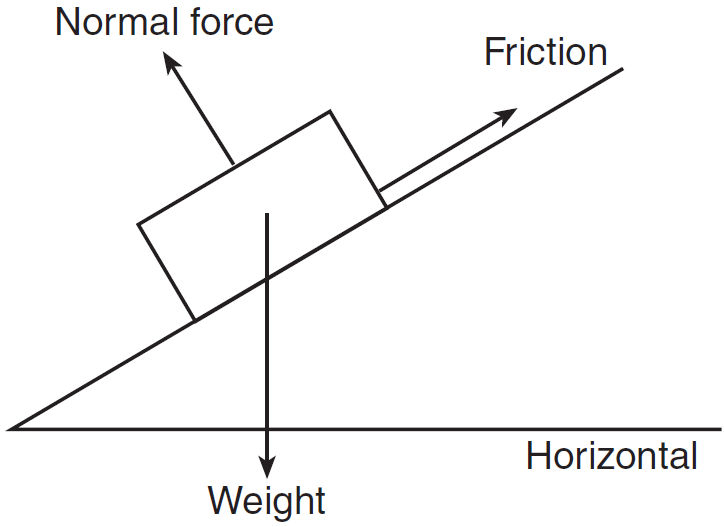
Free body diagram block on ramp
Free Body Diagrams (very important!) 2. Force due to gravity 3. Force due to strings 4. Force due to springs (just a little bit) ... Example 5.3 (Block on Ramp) Mechanics Lecture 5, Slide 20 A 1kg block slides down a frictionless ramp. The ramp has dimensions of 1m horizontally and
Figure 5.32 (a) The free-body diagram for isolated object A. (b) The free-body diagram for isolated object B. Comparing the two drawings, we see that friction acts in the opposite direction in the two figures. Because object A experiences a force that tends to pull it to the right, friction must act to the left. Because object B experiences a component of its weight that pulls it to the left ...
13. A 15kg block on a horizontal surface has a 100N force acting on it as shown. What is the normal force? 14. An 18kg cart is connected to a 12kg hanging block as shown (ignore friction). a) Draw and label a free body diagram for the 18kg cart. b) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the cart?
Free body diagram block on ramp.
Access the answers to hundreds of Free body diagram questions that are explained in a way that's easy for you to understand. ... A 0.500 kg block is on a ramp attached to a mass hanging over a low ...
A free-body diagram for a box on a ramp, in the special case of it being the maximum angle before the box starts to slide. The video includes an introduction...
Summary. English: Block on a ramp (top) and corresponding free body diagram of just the block (bottom). The source code of this SVG is valid. This vector image was created with a text editor. This SVG file uses embedded text that can be easily translated using a text editor.
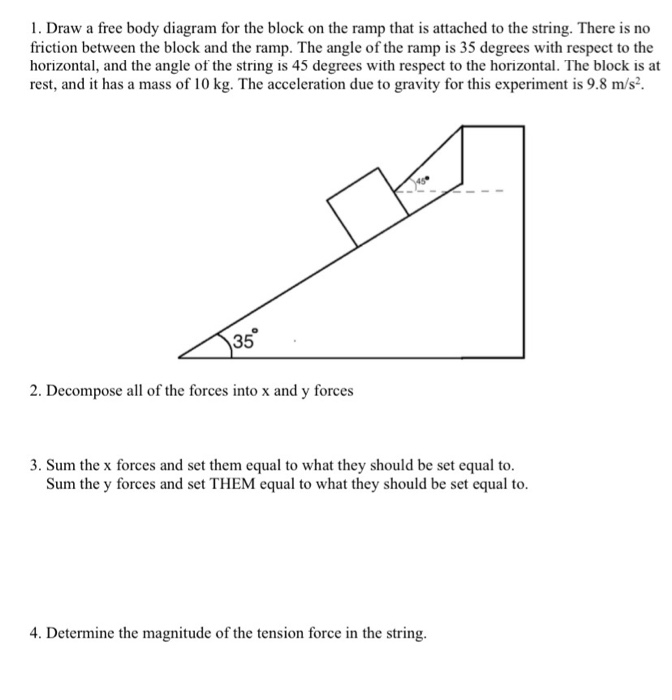
Draw a free-body diagram of the block in the space below. Label each force that you have included in your free body diagram to indicate (1) the type of force, (2) the object on which the force is exerted, and (3) the object exerting the force. Question: 1). A block is at rest on a ramp. Draw a free-body diagram of the block in the space below.
Free Body Diagram Slope. Here are a number of highest rated Free Body Diagram Slope pictures on internet. We identified it from honorable source. Its submitted by management in the best field. We assume this kind of Free Body Diagram Slope graphic could possibly be the most trending topic afterward we allowance it in google lead or facebook.
14+ Free Body Diagram Examples.As an example free body diagram on a ramp is given below in the figure. ¢¢ before we get to the analysis of problems, we need to review the rules for generating free body ¢¢ for example, if we had a beam with a roller at the left end and a pin at the right end.
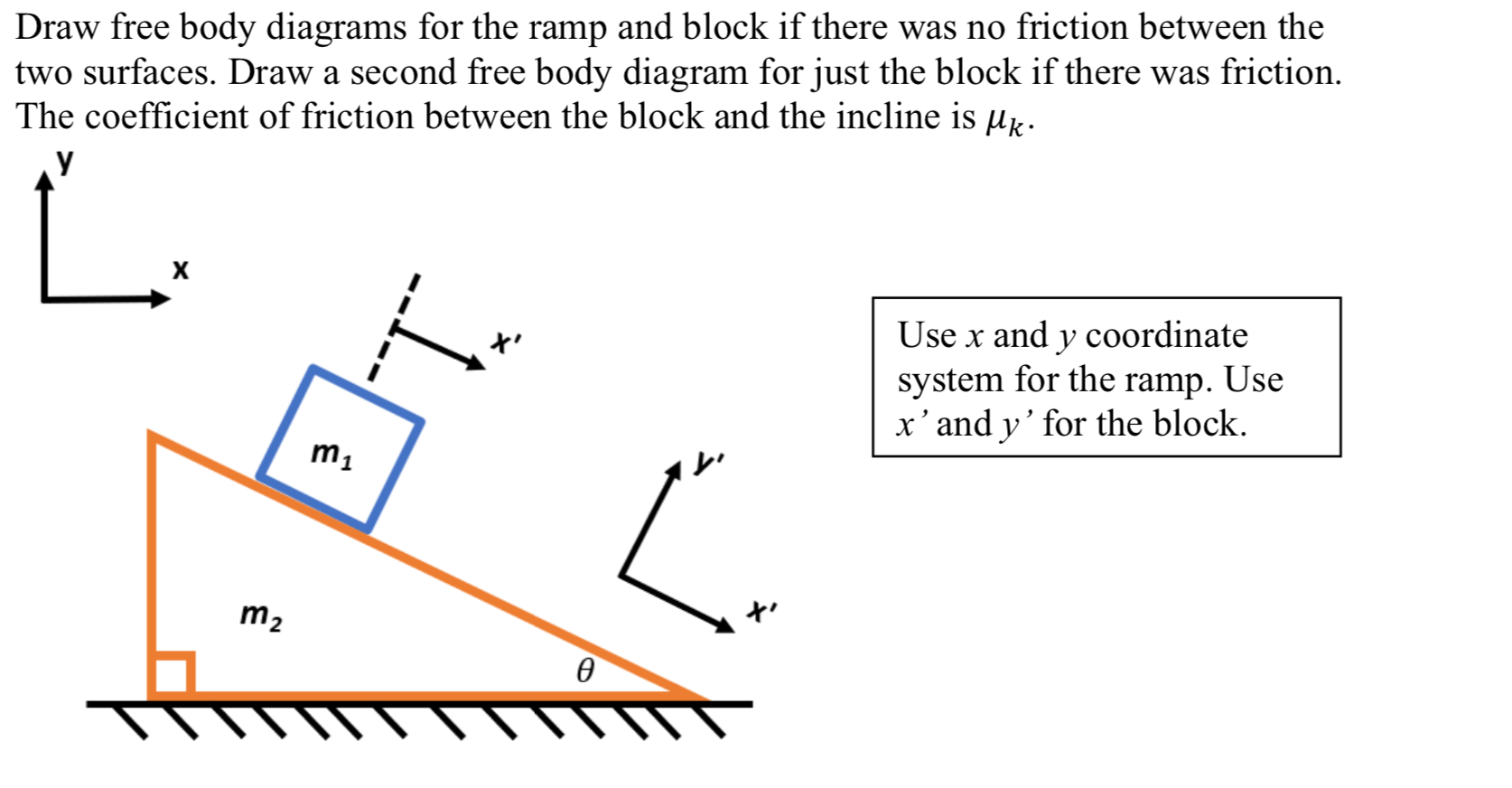
Say a block of mass m is accelerating down a ramp with mass M with inclination θ, where the coefficient of kinetic friction is between the block and the ramp is μ k. Assume the surface the ramp rests on is frictionless. I can easily determine the free body diagram of the forces acting on the block: F g x = m g sin. . ( θ)
In this case we have a block moving up a ramp, so for our convenience, we will use tilted coordinate axes, with the x axis in the direction of motion (uphill). After drawing the coordinate axes on the free-body diagram of the block, we proceed to find the components of the individual forces acting on the block:
Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x– and y-components of a given force (this is often helpful when solving a problem using Newton’s first or second law). In this case, place a squiggly line through the original vector to show that it is no longer in play—it has been replaced by its x – and y -components.
In this video I explain how to identify the forces acting on a mass that is moving down a ramp. I also explain how to draw these forces on a free body diagra...
The free-body diagram shows the forces acting upon a 100-kg crate that is sliding down an inclined plane. The plane is inclined at an angle of 30 degrees. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the incline is 0.3. Determine the net force and acceleration of the crate.
Convert the free-body diagram into a more detailed diagram showing the x- and y-components of a given force (this is often helpful when solving a problem using Newton’s first or second law). In this case, place a squiggly line through the original vector to show that it is no longer in play—it has been replaced by its x - and y -components.
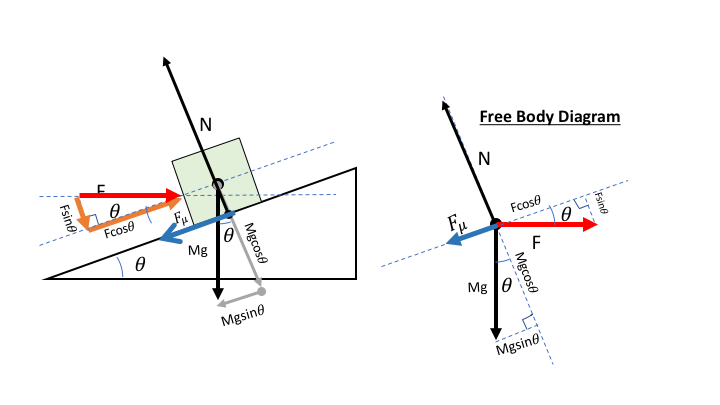
Free-body diagrams for objects on an incline must (at the minimum) depict: Gravity's downward force and the corresponding translated downhill force parallel to the surface. ... physics block on ramp free body diagram, physics block on ramp problem solver, resolving force due to gravity into components for an inclined plane, ...
A free-body diagram is a representation of an object with all the forces that act on it. The external environment (other objects, the floor on which the object sits, etc.), as well as the forces that the object exerts on other objects, are omitted in a free-body diagram. Below you can see an example of a free-body diagram:
36 free body diagram of block on incline Written By Robert T. Arbuckle Friday, December 3, 2021 Add Comment Edit 2. The normal force: The block is sitting on the incline.So the block exerts a force on the surface of the incline.So from Newt on 's Third Law (acti on-reacti on), the incline exerts a force back on the block.This force, called the 'Normal force', acts on the block so it must be ...
Multiple Objects qA block of mass m1 on a rough, horizontal surface is connected to a ball of mass m2 by a lightweight cord over a lightweight, frictionless pulley as shown in figure. A force of magnitude F at an angle θwith the horizontal is applied to the block as shown and the block slides to the right.
Statistics and Probability questions and answers. 8. What force P is needed to push the block up the ramp? Coefficinet of static friction = 0.25 Show the Free Body Diagram. Show Normal force N and Friction Force Fe (15) P-? 20N ° ) 30. Question: 8.
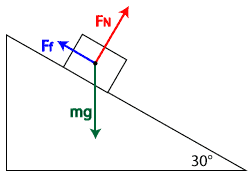
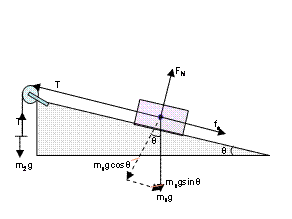
Block on ramp: Free-Body Diagram. Author: Nathaniel Cunningham. Free body diagram of a block on a ramp, without friction. Drag the point at the top of the ramp to change the ramp angle. Note how the green angles always track one another.
the distance that the block will travel up the ramp. The block starts with kinetic energy at the bottom of the ramp and has gravitational potential energy when it momentarily comes to rest at the top; however, it loses some energy to the work done by friction. A free body diagram can help you determine the force of friction on the block by ...
I'm having trouble figuring out how this free body diagram would look. The question involves a block at rest on a ramp, which is in turn at rest on a table. All objects are made of the same material, with the same coefficients of friction. Below is what I've got so far, but it doesn't seem correct.
Free Body Diagrams on friction less surface. 1. A frictionless surface is inclined at an angle of 34.4° to the horizontal. A 270-g block on the ramp is attached to a 75.0-g block using a pulley, as shown in the figure below. (a) Draw two free-body diagrams, one for the 270-g block and the other for the 75.0-g block.
Here are a number of highest rated Rolling Ball Free Body Diagram pictures upon internet. We identified it from obedient source. Its submitted by government in the best field. We take this nice of Rolling Ball Free Body Diagram graphic could possibly be the most trending subject past we allocation it in google improvement or facebook.
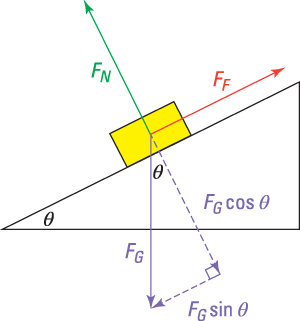
Example: A block on an inclined plane. A simple free body diagram, shown above, of a block on a ramp illustrates this. All external supports and structures have been replaced by the forces they generate. These include: mg: the product of the mass of the block and the constant of gravitation acceleration: its weight. N: the normal force of the ramp.
Sample Free Body Diagram or FBD. figure 1: FBD of a block resting on another block ( forces shown are gravity and normal reaction) figure 2: FBD of a block resting on an Inclined Plane (no friction) figure 3: A block on ramp. this time with friction. Thus we can draw a free body diagram.
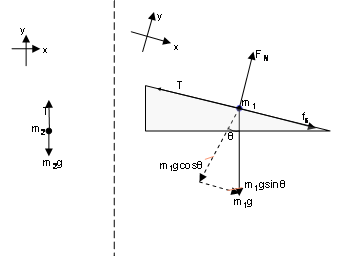
Example 8 : A system with two blocks, an inclined plane and a pulley. A) free body diagram for block m 1 (left of figure below) 1) The weight W1 exerted by the earth on the box. 2) The normal force N. 3) The force of friction Fk. 4) The tension force T exerted by the string on the block m1. B) free body diagram of block m 2 (right of figure below)
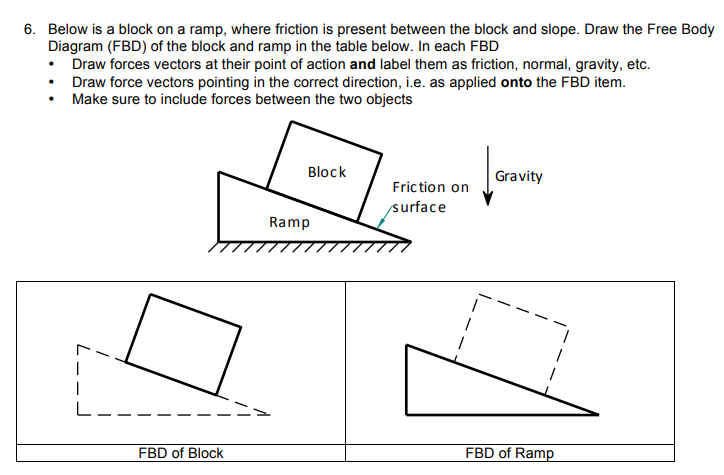
The cart would have a normal and fiction force from the ramp, a normal and friction force from the chocolate, and gravity. The chocolate would have the normal and friction force from the cart (equal and opposite to the cart's from the chocolate as per newtons third law) and gravity. This is true in general for multiple bodies, as long as they ...

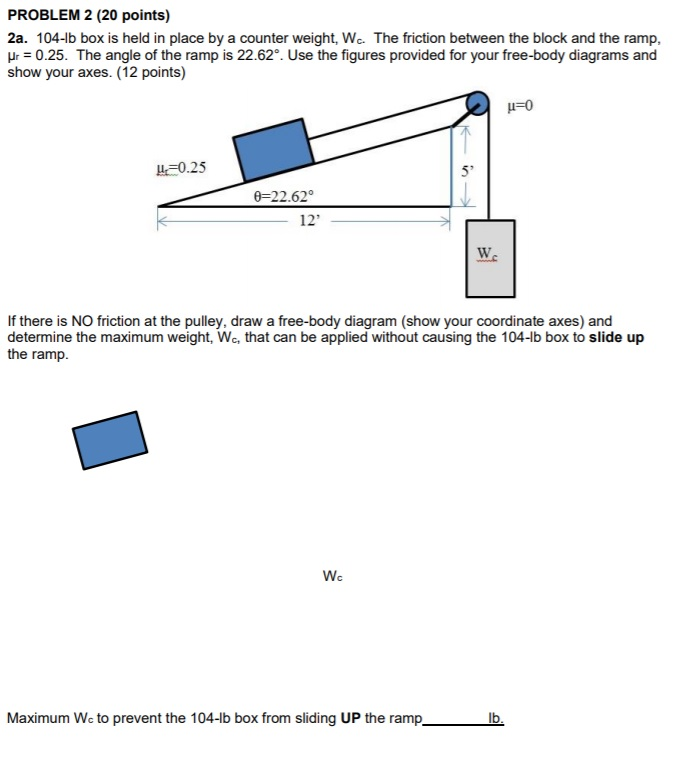


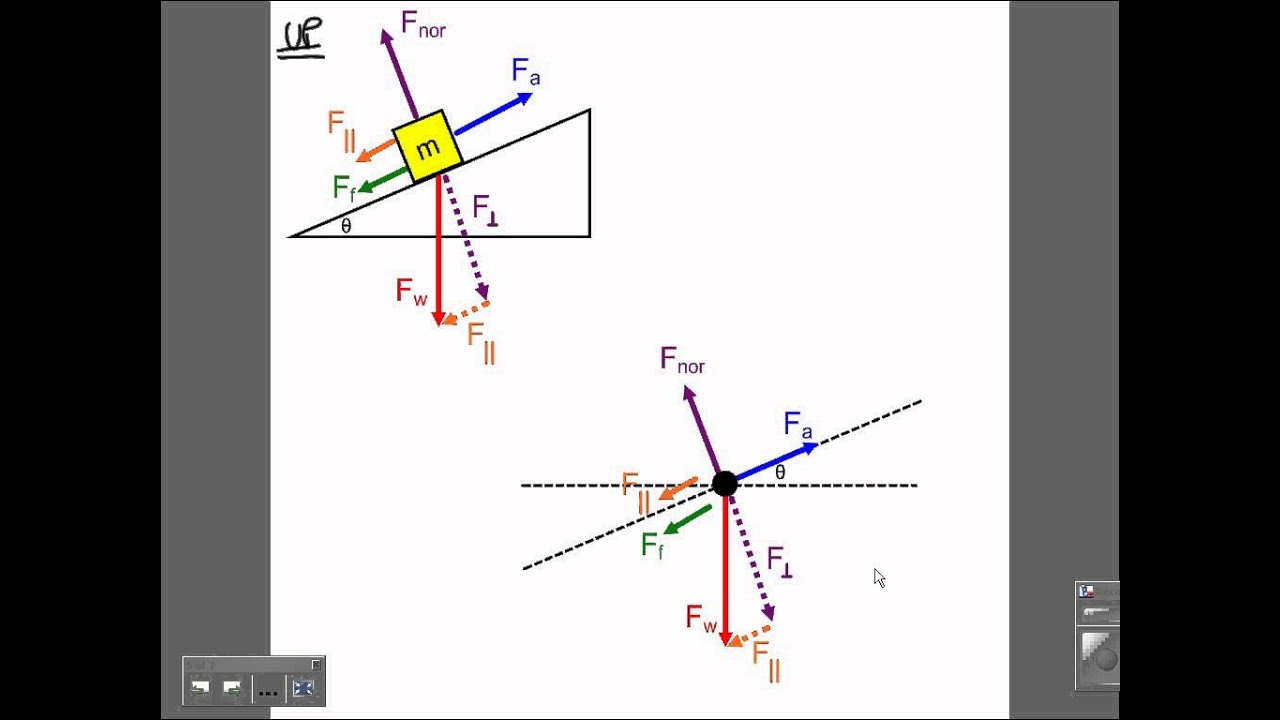









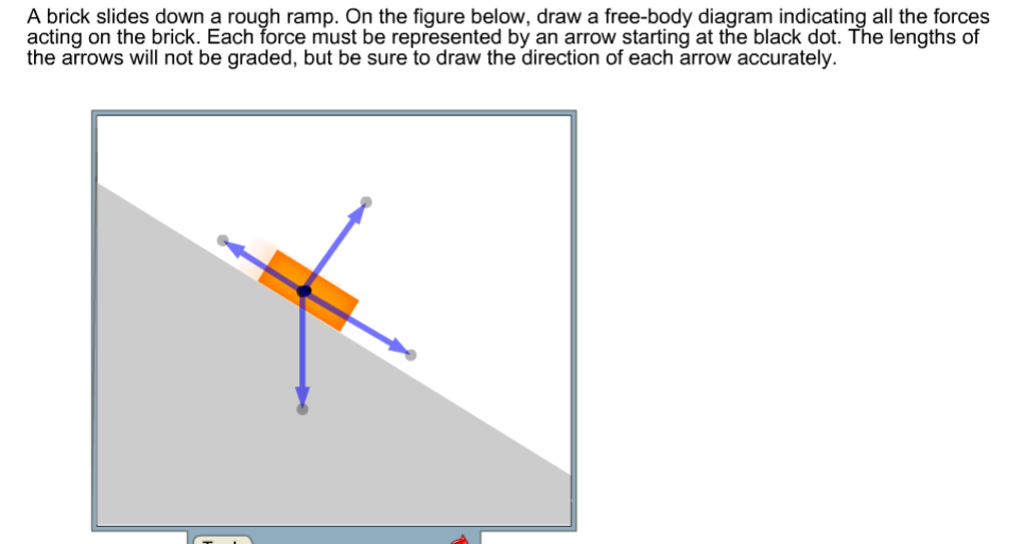
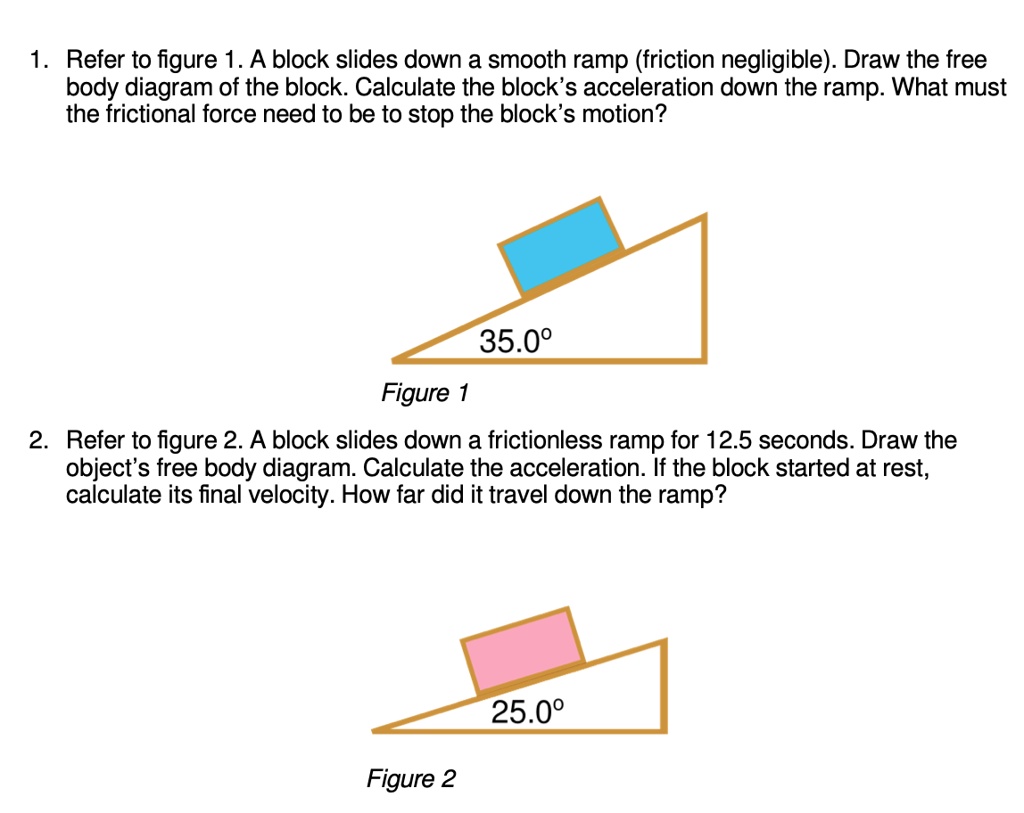
0 Response to "34 free body diagram block on ramp"
Post a Comment