34 pacemaker cell action potential diagram
They quantitatively reproduce action potential shapes and some cellular behavior but do not include several important physiological properties such as interactions due to electrotonic coupling. Parametric computational model of the action potential of pacemaker cells. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng.
". "Action Potentials in Pacemaker Cells" by Rishi Desai and Khan Academy Medicine is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 US. The diagram relates action potential stages to refractory periods and compares skeletal muscle action potentials to cardiac muscle action potentials.
(C) Cartoon diagram of the desmosome complex. (D) Genome browser tracks for Dsp and Pkp2 loci with corresponding ATAC-seq tracks derived from Why has a potential role for Hand2 in pacemaker specication remained obscure? Because Hand2 knockout mice are embry-onically lethal (Srivastava...

Pacemaker cell action potential diagram
SAN cells generate spontaneous action potentials (APs), i.e., normal automaticity. Enzymatically isolated single sinoatrial node (SAN) cells have been extensively utilized as a model in studies of the cellular mechanisms of cardiac pacemaker rate regulation [1]. These studies have advanced our...
Oct 01, 2020 · For an easy explanation of pacemaker cell action potentials, make sure to check out the EZmed blog that makes cardiac action potentials easy! Once an action potential is generated by the SA node, it will travel though the right atrium via the internodal pathway, as well as to the left atrium via Bachmann’s bundle.
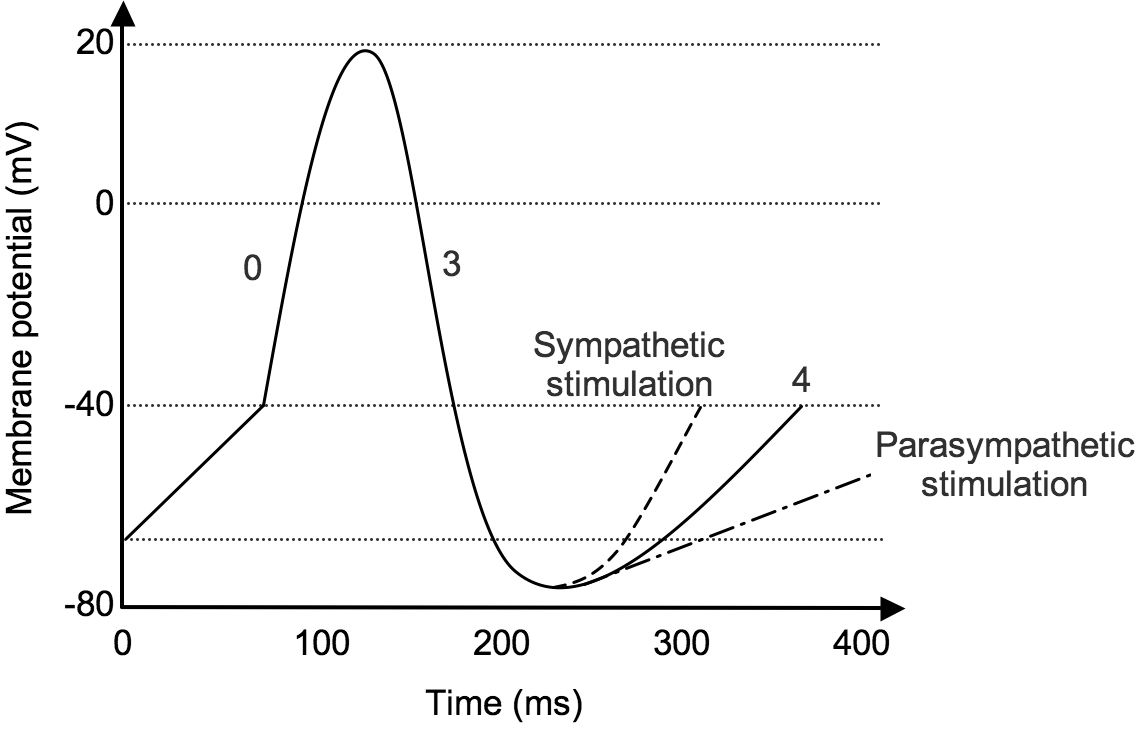
The pacemaker potential occurs at the end of one action potential and just before the start of the next. It is the slow depolarisation of the pacemaker cells e.g. cells of the sinoatrial node, towards the membrane potential threshold. This is sometimes referred to as the 'funny' current, or If.
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram.
Action potential (AP) measurements of cells individualized fro. Rate profiles and pharmacological stimulation of pacemaker cell clusters (PCC). a Layout of the experimental design for PCC Mathematical models of action potentials in the periphery and center of the rabbit sinoatrial node.
Myocardial action potential (myocardium, bundle of His, Purkinje fibers) Pacemaker action potential (SA node and AV node) Phase 0 (upstroke and depolarization) Upstroke: An action potential from a pacemaker cell or adjacent cardiomyocyte causes the transmembrane potential (TMP) to rise above −90 mV.
The action potential is brought on by a rapid change in membrane permeability to certain ions, with unique properties necessary for function of the Now even temporary pacemakers are relatively sophisticated devices which can deliver a range of therapeutic options from the basic fixed rate...
Nov 22, 2021 · We identified seven spontaneously beating pacemaker cells (82.7 ± 10.8 (42–132) bpm by live-cell video recording or whole-cell patch clamp, from 3 …
Cells that use action potentials are also called excitable cells and include: neurons, muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth), cardiac The pacemaker cells are specialized cardiac myocytes that are capable of generating spontaneous action potentials and are responsible for cardiac conduction.
Find out how the pacemaker cells use the movement of sodium, calcium, and potassium to get your heart beating! Rishi is a pediatric infectious disease...
Figure 8 shows superimposed action potentials from a pacemaker cell. It can be seen that the rise time of the prepotential and the time to spike generation is greatly prolonged after drive. It also shows a reduction in amplitude of the intrinsic pacemaker potential. The spike generated in the first and third...
In the pacemaking cells of the heart (e.g., the sinoatrial node), the pacemaker potential (also called the pacemaker current) is the slow, positive increase in voltage across the cell's membrane (the membrane potential) that occurs between the end of one action potential and the beginning of the next action potential. This increase in membrane potential is what …
Action potentials are the really rapid electrical changes that occur across the membrane of certain cells, and often propagates from one cell to an adjacent cell. Cells in the heart communicate this way. That signal's gotta start somewhere, so some of these cells, called pacemaker cells...
Start studying pacemaker action potentials. Learn vocabulary, terms and more with flashcards, games and other study tools. -A cell that depolarizes spontaneously and triggers action potentials in neighboring cells -a cell that can set the heart rate by starting the contraction.
Neighbour cells with simultaneous action potentials did not influence each others cycle length. We investigated how stable synchronization @article{Bruin2004SynchronizationIC, title={Synchronization in chains of pacemaker cells by phase resetting action potential effects}, author={Gerrit de Bruin...
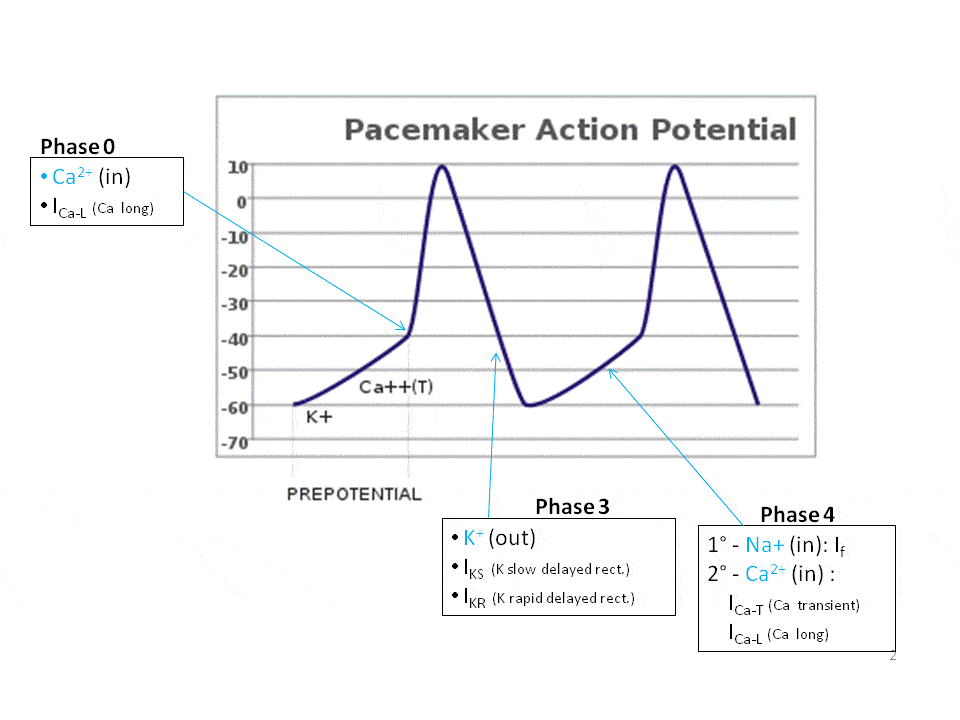
Unstable membrane potential: Pacemaker cells have an unstable membrane potential and their action potential is not usually divided into defined phases. No rapid depolarization phase: Pacemaker cells have fewer inward rectifier K+ channels than do other cardiomyocytes...
The pacemaker action potential provides the automaticity to our cardiac pacemaker cells in the SA node. It differs from the ... Cardiovascular physiology - Action potential of cardiac muscle and SA Node , medical animations Pacemaker cells (e.g., sinus ...
Figure 1. The action potential in the sinoatrial node and in contractile myocardial cells. Phase 4 of the action potential in the sinoatrial node is called ‘pacemaker potential’, because it is responsible for the spontaneous repetitive depolarization. The depolarization spreads from the sinoatrial node to the atrial and ventricular myocardium.
SAN cells generate spontaneous action potentials (APs), i.e., normal automaticity. The sympathetic nervous system increases the heart rate β-Adrenergic Stimulation Synchronizes a Broad Spectrum of Action Potential Firing Rates of Cardiac Pacemaker Cells toward a Higher Population Average.
The SA node displays intrinsic automaticity (spontaneous pacemaker activity) at a rate of 100-110 action potentials Sympathetic activation also lowers the threshold for initiating phase 0 of the action potential. Vagal activity also hyperpolarizes the pacemaker cell during Phase 4, which contributes...
Editor-In-Chief: C. Michael Gibson, M.S., M.D. The contractions of the heart are controlled by chemical impulses, which fire at a rate which controls the beat of the heart. The cells that create these rhythmical impulses are called pacemaker cells, and they directly control the heart rate.
The cardiac action potential differs from action potentials found in other types of electrically excitable cells, such as nerves. Unlike the action potential in skeletal muscle cells, the cardiac action potential is not initiated by nervous activity. Instead, it arises from a group of specialized cells, that...
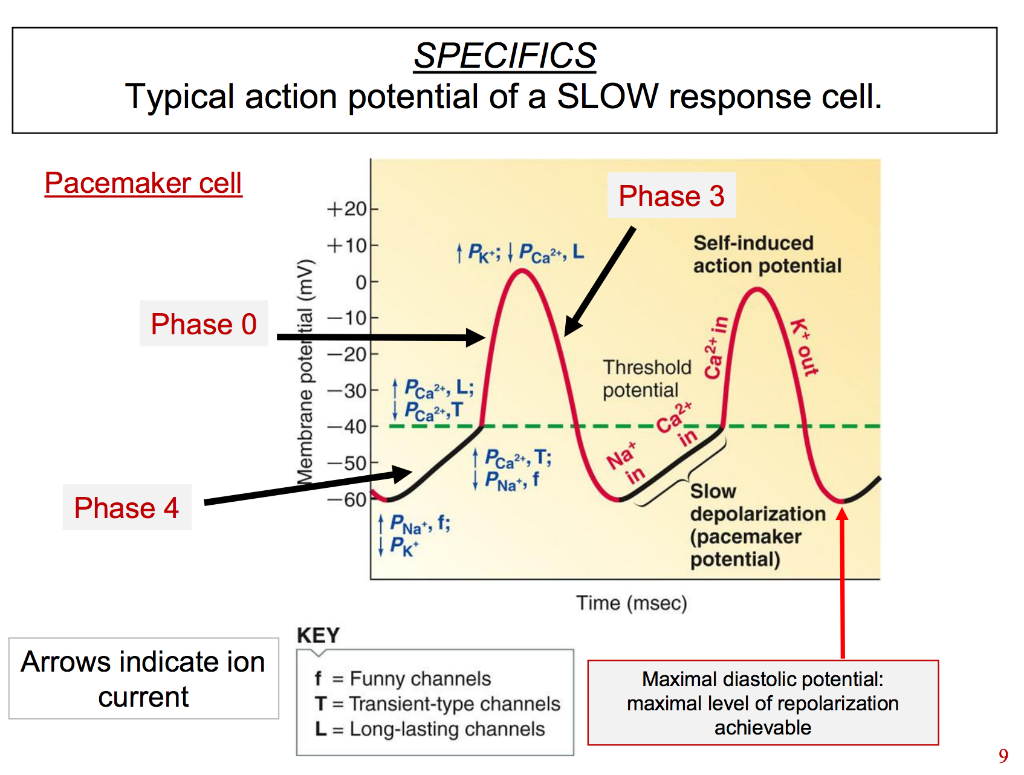
Sep 27, 2020 · Ionic basis for the resting and action potential in a ventricular heart cell. The action potential is divided into phases 0 through 4. Each phase results from a change in the balance of inward and outward ionic currents that become …
File:Pacemaker potential.svg. From Wikimedia Commons, the free media repository. Jump to navigation Jump to search. 4 derivative works. Summary[edit]. Pacemaker cell action potential diagram.
An action potential is triggered by depolarization, which translates loosely to a temporary canceling out of the normal charge imbalance, or a restoration of equilibrium. Phase 4 of the cardiac muscle cell potential is called the diastolic interval, because this period corresponds to diastole, or the interval...
The above diagram is an action potential recorded in the ventricular cardiac cell of the heart. 4) Resting potentials in these cells is set by a large K+ permeability due to a combintation of the leak K+ channel and a voltage-gated K+ channel (called …
The rate and rhythm of spontaneous action potential firing of sinoatrial node cells are regulated by stochastic mechanisms that determine the level of Citation: Yaniv Y, Tsutsui K and Lakatta EG (2015) Potential effects of intrinsic heart pacemaker cell mechanisms on dysrhythmic cardiac action...
Pacemaker-induced action potentials excite the entire ventricular myocardium resulting in effective mechanical contractions. Figure 9 Diagram of the Transmembrane Potential of an Automatic Cell. Principles of Cardiac Electrophysiology. 15.
Pacemaker cell action potential diagram.
The cardiac action potential is a brief change in voltage (membrane potential) across the cell membrane of heart cells. This is caused by the movement of charged atoms (called ions) between the inside and outside of the cell, through proteins called ion channels.The cardiac action potential differs from action potentials found in other types of electrically excitable cells, such …
Here is some really important information that is from a very reputable and helpful company in the USA.  HomeInfoAbout UsFAQContact UsE-mail Electronic Harassment Advanced Electronic Security Co. performs Electronic Sweeping and Surveys, using the best possible Technical Surveillance Counter Measures (TSCM), to determine if you're being electronically harassed. We then recommend the proper course of action to eliminate the electronic harassment threat. What is Electronic Harassment? If so...
Cardiac action potential in pacemaker cells and contractile myocytes, electrophysiology of a heartbeat. This video is available for ... In this video, we take a look at the graph representing the cardiomyocyte action potential and what each region of the graph ...
The pacemaker cells are distinct from normal cardiac myocytes, in that they do not have a resting potential: instead, their membranes depolarise gradually via the "funny" current (If) A Comparison of the Ionic Events During the Cardiac Action Potentials in the Myocyte and the Pacemaker Cell.
Aug 21, 2021 · An action potential (AP) is the mode through which a neuron transports electrical signals. It is defined as a brief change in the voltage across the membrane due to the flow of certain ions into and out of the neuron. In this article we will discuss how an action potential is generated and how conduction of an action potential occurs.
The contraction of cardiac muscle (heart muscle) in all animals is initiated by electrical impulses known as action potentials. The rate at which these impulses fire controls the rate of cardiac contraction, that is, the heart rate.
... sinus rhythm is generated by pacemaker cells of the sinoatrial (SA) node. The particularity of these cells is their spontaneous depolarization during Phase 4 of the action potential. This diastolic depolarization slowly increases the membrane potential to a threshold around -40 mV and then the...























0 Response to "34 pacemaker cell action potential diagram"
Post a Comment