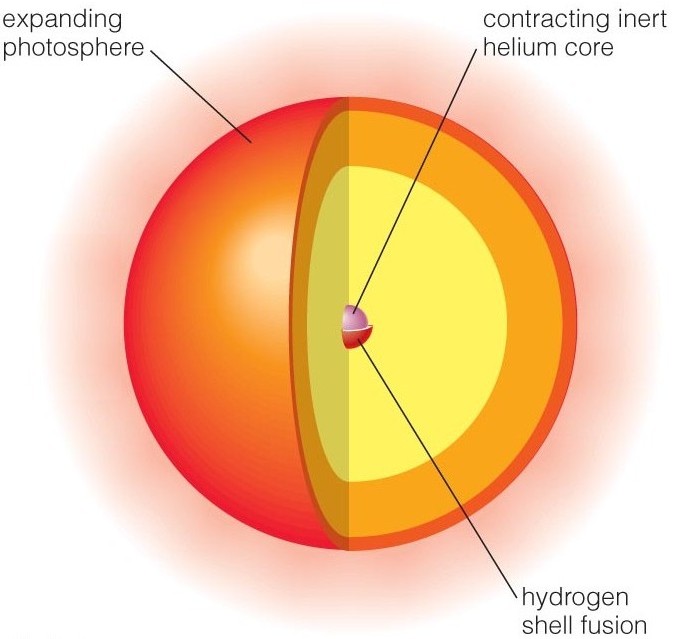
36 diagram of a star
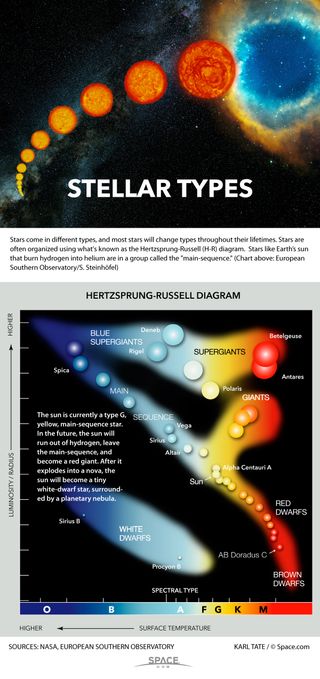
The H-R Diagram changes also - so the H-R diagram can also be thought . of as a graphical plot of stellar evolution. From the location of a star on the diagram, its luminosity, spectral type, color, temperature, mass, age, chemical composition and evolutionary history are known. Most stars are classified by surface temperature (spectral Star Diagram. A star diagram is used for organizing the characteristics of a single topic. A central space is used for displaying the topic, with each "point" of the star listing some fact, attribute, or trait about the topic. As an example, a central character in a story can be the topic, and each point around the topic can describe some ...
Finish your star by drawing a diagonal line downward and to the left to meet the starting point of the upside-down "V." If you don't want the middle lines to be visible, you can erase them and leave just a star outline. To learn more, like how to draw a 6- or 7-pointed star, keep reading the article!
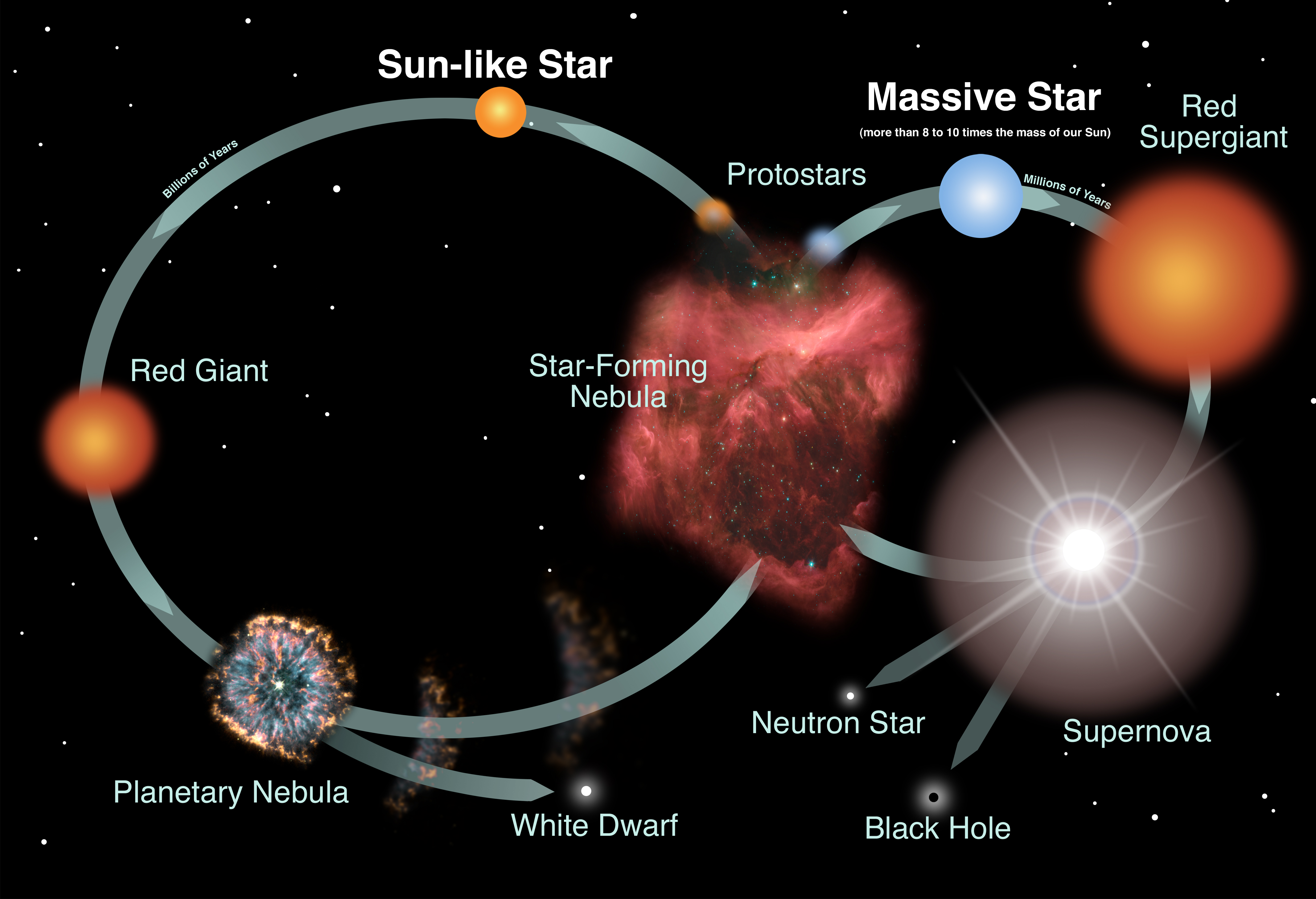
Diagram of a star
By definition a star of magnitude 1 is 100 × brighter than one of magnitude 6. Our Sun has an absolute magnitude of + 4.8. Possible axes for a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Note how the temperature scale is reversed on the horizontal axis. Also take care if using magnitude to work upwards to negative values. H-R Diagram for Stars. A Most Important Diagram Classifying stars according to their spectrum is a very powerful way to begin to understand how they work. As we said last time, the spectral sequence O, B, A, F, G, K, M is a temperature sequence, with the hottest stars being of type O (surface temperatures 30,000-40,000 K), and the coolest stars ... Discuss the physical properties of most stars found at different locations on the H–R diagram, such as radius, and for main sequence stars, mass. In this ...
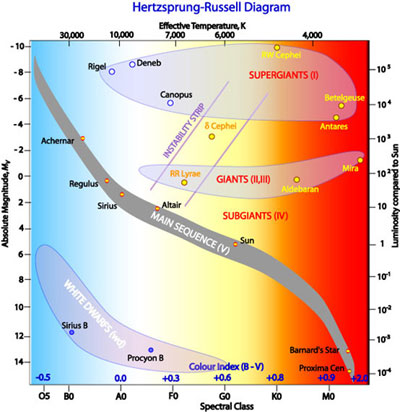
Diagram of a star. Astronomers use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram to trace the evolutionary stage of a star. The Hertzsprung diagram where the evolution of sun-like stars is ... A star in the upper right corner of the diagram would be cool and bright. The Sun rests approximately in the middle of the diagram, and it is the star which we use for comparison. A star in the lower left corner of the diagram would be hot and dim. diagram can also be thought of as a graphical plot of stellar evolution. From the location of a star on the diagram, its luminosity, spectral type, color, temperature, mass, chemical composition, age, and evolutionary history are known. Most stars are classified by temperature (spectral type) from hottest to coolest as follows: O B A F G The brightest stars therefore appear at the top of the H-R diagram with the vertical axis having the most negative value of M at the top. In some circumstances, such as when plotting stars in a specific open or globular cluster, apparent magnitude, m, or V, rather than absolute magnitude may be used.
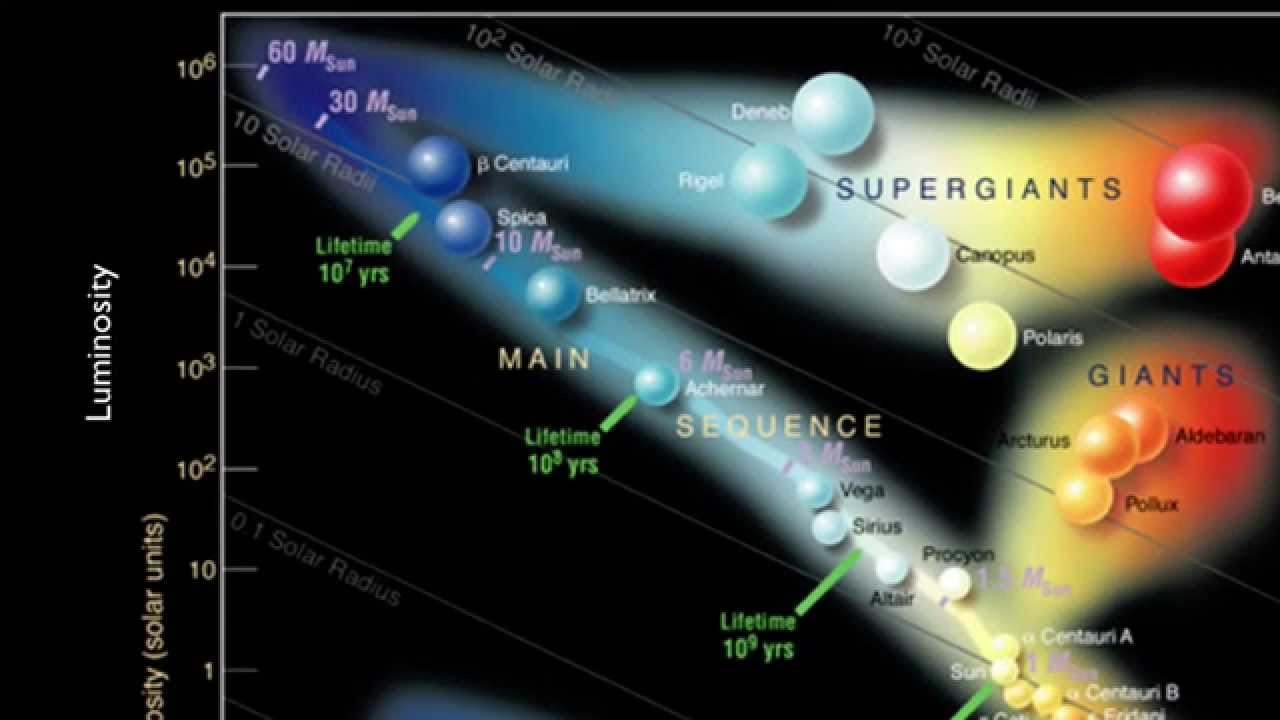
A typical HR Diagram (e.g., the one for the stars in the cluster M55, below) plots a single point per star to represent that star's color and luminosity (or brightness) as it is observed today. So, you can consider an HR Diagram of that type to represent a snapshot of a moment in the lifetimes of the stars plotted. Star Network Topology Diagram . Star networks are well known for their nodes being located in a shape of a star. There are one of the most commonly used computer network topologies - star network topologies. The way such networks look reminds of a star as there is a central node which is illustrated in the very middle of the network ... Instead of plotting the individual points, they plot a line that goes through the points of all of the stars in the HR diagram. Since this line indicates the positions of stars with a specific age, it is called an isochrone. Astronomers plot the observed colors and luminosities for the stars in a star cluster. Stars are formed in clouds of gas and dust, known as nebulae. Nuclear reactions at the centre (or core) of stars provides enough energy to make them shine brightly for many years. This stage is known as the 'main sequence'. '. The exact lifetime of a star depends very much on its size.Very large, massive stars burn their fuel much faster than smaller stars and may only last a few hundred ...
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, abbreviated as H–R diagram, HR diagram or HRD, is a scatter plot of stars showing the relationship between the stars' ...Historical backgroundForms of diagramInterpretation1 of 3In the nineteenth century large-scale photographic spectroscopic surveys of stars were performed at Harvard College Observatory, producing spectral classifications for tens of thousands of stars, culm...Continue on en.wikipedia.org »2 of 3There are several forms of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram, and the nomenclature is not very well defined. All forms share the same general layout: stars of greater luminosity are toward the top of th...Continue on en.wikipedia.org »3 of 3Most of the stars occupy the region in the diagram along the line called the main sequence. During the stage of their lives in which stars are found on the main sequence line, they are fusing hydrogen...Continue on en.wikipedia.org » It shows stars of different ages and in different stages, all at the same time. -A star in the upper left corner of the diagram would be hot and bright. -A star in the upper right corner of the diagram would be cool and bright. -The Sun rests approximately in the middle of the diagram, and it is the star which we use for comparison. Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, in astronomy, graph in which the absolute magnitudes (intrinsic brightness) of stars are plotted against their spectral types ... In 1905, Danish astronomer Einar Hertzsprung, and independently American astronomer Henry Norris Russell, noticed that the luminosity of stars decreased ...
A star diagram is used for organizing the characteristics of a single topic. A central space is used for displaying the topic, with each "point" of the star listing some fact, attribute, or trait about the topic. As an example, a central character in a story can be the topic, and each point around the topic can describe some part of that character's life or relationships.
The computer network diagram example "10Base-T star topology" was created using the ConceptDraw PRO diagramming and vector drawing software extended with the Computer and Networks solution from the Computer and Networks area of ConceptDraw Solution Park. Star topology. Used Solutions.
Star Delta Starter Circuit Diagram. The motor terminal connection in the case of star and delta is shown in the above figure where U1 V1 W1 is the start terminal of each winding and U2 V2 W2 is the finish of each winding. L1, L2, and L3 are the three-phase line connecting terminals.
The star schema is the simplest type of Data Warehouse schema. It is known as star schema as its structure resembles a star. Comparing Snowflake vs Star schema, a Snowflake Schema is an extension of a Star Schema, and it adds additional dimensions. It is called snowflake because its diagram resembles a Snowflake.
Figure 19.15 Luminosity Classes. Stars of the same temperature (or spectral class) can fall into different luminosity classes on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. By studying details of the spectrum for each star, astronomers can determine which luminosity class they fall in (whether they are main-sequence stars, giant stars, or supergiant stars).
The STAR Diagram offers a way of seeing and understanding the conditions that shape a generative team. Whether you use it to plan for an effective team or to intervene when things go awry, the STAR diagram offers a way to see, understand, and influence the patterns in your teamat home, at work, or in your community.
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is a graph that plots the temperature of a star against its absolute magnitude or luminosity. It was created by astronomers ...
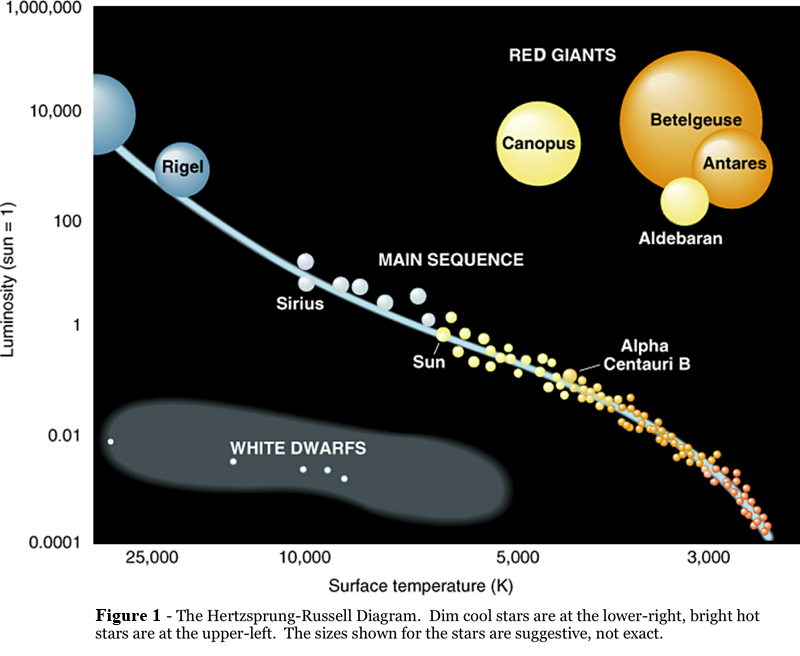
Figure 1: The HR Diagram A star's luminosity (or Absolute Magnitude) and temperature (or spectral type or B-V color index) determine its position of the HR diagram. As you can see from the diagram above, the hottest, most luminous stars lie at the upper left of the diagram, and the coolest, dimmest stars lie at the lower right.
D. Calculating the Radii of the Stars Using the HR Diagram in Figure 1, estimate the luminosity and temperature of all the stars listed in Table 1 and record their values in Table 1. Now calculate the stars' radii in units of meters and solar radii (see EQs #2 and 3). You must show your calculation explicitly for at least one
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is named after two astronomers, Danish astronomer Eijer Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell. This diagram is a result of the work carried out by both these astronomers independently. Hertzsprung had plotted the luminosity of a star against its color and effective temperature. This was done in 1911.
It helps define something called a star's spectral class, which astronomers also figure out by studying the wavelengths of light that come from the star. So, in a standard H-R diagram, spectral classes are labeled from hottest to coolest stars, with the letters O, B, A, F, G, K, M (and out to L, N, and R).
The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram is one of the most important tools in the study of stellar evolution.Developed independently in the early 1900s by Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell, it plots the temperature of stars against their luminosity (the theoretical HR diagram), or the colour of stars (or spectral type) against their absolute magnitude (the observational HR diagram, also known ...
It is one of the most important and widely used diagrams in astronomy, with applications that extend far beyond the purposes for which it was originally developed more than a century ago. Figure 18.14 H-R Diagram for a Selected Sample of Stars. In such diagrams, luminosity is plotted along the vertical axis.
Enter Outer Radius, Inner Radius, number of star Points and hit Calculate to draw a full scale printable template to mark out your stars. Hit to open new page, create and print a PDF of the image at 100% Printer Scale. Check Dimensions to display all dimensions and draw the smallest bounding circle and rectangle (that the star will fit inside).
Star, Webbing, Cluster Diagrams. Star, Webbing, Cluster diagrams are a type of graphic organizer that condense and organize data about multiple traits, fact, or attributes associated a single topic.. Star diagrams are useful for basic brainstorming about a topic or simply listing all the major traits related to a theme.
We simply compare the observed HR diagram to the theoretical diagram, paying special attention to the upper end of the main sequence. Here, for example, is the color-magnitude diagram for the Pleiades: The main-sequence turnoff occurs at a color of about (B-V) = -0.1; that's blue, and means there are some massive, hot, powerful stars.
Discuss the physical properties of most stars found at different locations on the H–R diagram, such as radius, and for main sequence stars, mass. In this ...
H-R Diagram for Stars. A Most Important Diagram Classifying stars according to their spectrum is a very powerful way to begin to understand how they work. As we said last time, the spectral sequence O, B, A, F, G, K, M is a temperature sequence, with the hottest stars being of type O (surface temperatures 30,000-40,000 K), and the coolest stars ...
By definition a star of magnitude 1 is 100 × brighter than one of magnitude 6. Our Sun has an absolute magnitude of + 4.8. Possible axes for a Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram. Note how the temperature scale is reversed on the horizontal axis. Also take care if using magnitude to work upwards to negative values.




















0 Response to "36 diagram of a star"
Post a Comment