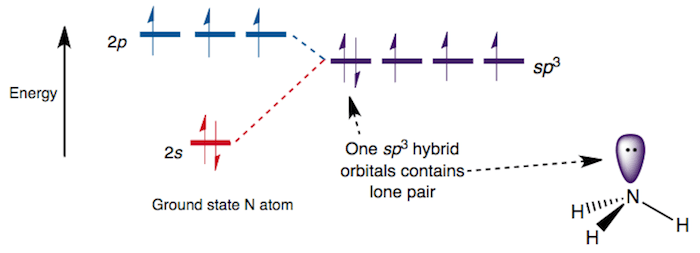
40 nh3 molecular orbital diagram
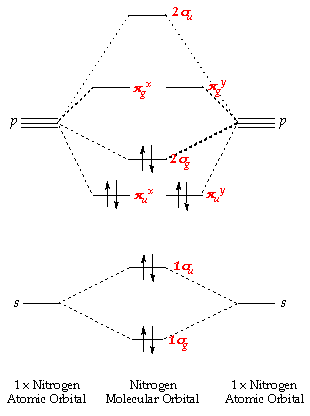
Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... Construct an orbital diagram to show the electron configuration for a neutral magnesium atom, Mg. ... The electron geometry and the molecular geometry of ammonia (NH3 ...
Nh3 Molecular orbital Diagram. molecular orbitals of ammonia molecular orbital in nh3 the homo highly occupied molecular orbital is a mostly nitrogen based orbital that corresponds to the lone pair of electrons this is why ammonia acts as a lewis base at the n atom lecture 10 part b mo diagram of nh3 che 422 inorganic chemistry molecular orbital energy level diagram of nh3 and frontier ...
Nh3 molecular orbital diagram
Molecular orbital diagram of ammonia (NH3) molecule The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of how chemical bonding is taking place within the molecules. In the case of ammonia (NH3), the molecular orbital diagram helps with understanding how sigma bonds are formed. Nh3 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule with three pendant hydrogen atoms. The MO energy diagram for NH3 is shown in Figure 3. However for the species with more than 16 electrons in Table 8 the π u antibonding molecular orbital will be occupied and the linear geometry will have a higher energy than the bend ... A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy than the original atomic orbitals.
Nh3 molecular orbital diagram. Where is the energy difference (Between which orbitals) that corresponds to o (10Dq)? Label o on the MO diagram. What type of orbitals (bonding, non-bonding, antibonding) are the "crystal field" orbitals? Explain why. Calculate the o for [Co(NH3)6]3+, then determine if it is low- or high-spin. Fill in the MO diagram accordingly. Molecular Geometry of NH3. Ammonia (NH3) has a trigonal pyramidal or distorted tetrahedral molecular shape. It is due to the presence of a single non-bonding lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom, which acts as a repulsive force on the bonding orbitals.. In NH3 molecular geometry, three hydrogen atoms are bonded to a nitrogen atom in the middle. Summary MO Theory • LCAO-MO Theory is a simple method for predicting the approximate electronic structure of molecules. • Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals. • Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. • Next we'll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in Nov 24, 2021 · For example, an ‘s’ and a ‘p’ orbital come together to form an sp hybrid orbital, one ‘s’ and two ‘p’ orbitals ( e.g. px, py ) fuse to form an sp2 hybrid orbital, and so on. Let us check what the hybridization of NH2- ion is: For finding out hybridization, we can use the following formula: H= 1/2 ( V + M – C + A) H ...
5 sigma interactions from the NH3 ligands; by reducing a reducible representation one obtains 2A1 + B1 + E . 2 pi interactions (pi donation from Cl- px and pz orbitals), which have symmetry E . And the cation atomic orbitals, which we just read off the character table. Unfortunately this results in a lot of confusing interactions in the MO diagram. NH3 Lewis Structure, Molecular Geometry, Hybridization, Bond Angle & Shape. Ammonia is a colorless compound, used in making fertilizers. It is a stable hydride formed of one nitrogen and three hydrogen atoms. The molecule has a pungent smell. It can form an NH4+ ion by accepting a proton. A 15 marker question where I go through step by step on how to create the molecular orbital diagram of NH3 using character tables.1) Look at the character ta... Answer: I think you can safely assume to start off with the molecular orbital diagram of the Nitrite anion (NO₂¯) and then remove an electron from it: What will be the molecular orbital diagram for nitrite ion? The outcome, i.e. the molecular orbital diagram for Nitrogen dioxide NO₂, should loo...
Simple Molecular Orbitals - Sigma and Pi Bonds in Molecules An atomic orbital is located on a single atom. When two (or more) atomic orbitals overlap to make a bond we can change our perspective to include all of the bonded atoms and their overlapping orbitals. Since more than one atom is involved, we refer to these orbitals as molecular orbitals. Feb 11, 2020 · The lone pair of electrons from the C-H bond forms the new pi bond with the empty p orbital from the carbocation. The rate law is unimolecular (hence E1) since it depends only on the substrate. In the E2 mechanism , the C-H bond and C-LG bond break at the same time that the new C-C pi bond is formed. Nov 27, 2021 · NF3 Molecular Geometry. Molecular geometry or molecular shape is an important concept that we need to decipher while we are learning the chemical bonding of any chemical composition. While Lewis Structure gives us an idea about the internal bond types and valence electron sharing inside a given molecule, it can only explain a two-dimensional ... Nov 10, 2020 · Ammonia (NH3) which has only 1 pair of non-bonding lone pairs electrons which have comparatively lower repulsive force and bond angle is around 107 °. But in the case of NH2-, there are two pairs of non-bonding electrons presence on the nitrogen atom which exerted higher repulsion, as a result, NH2- has a bond angle 104.5 ° same as water (H2O ...
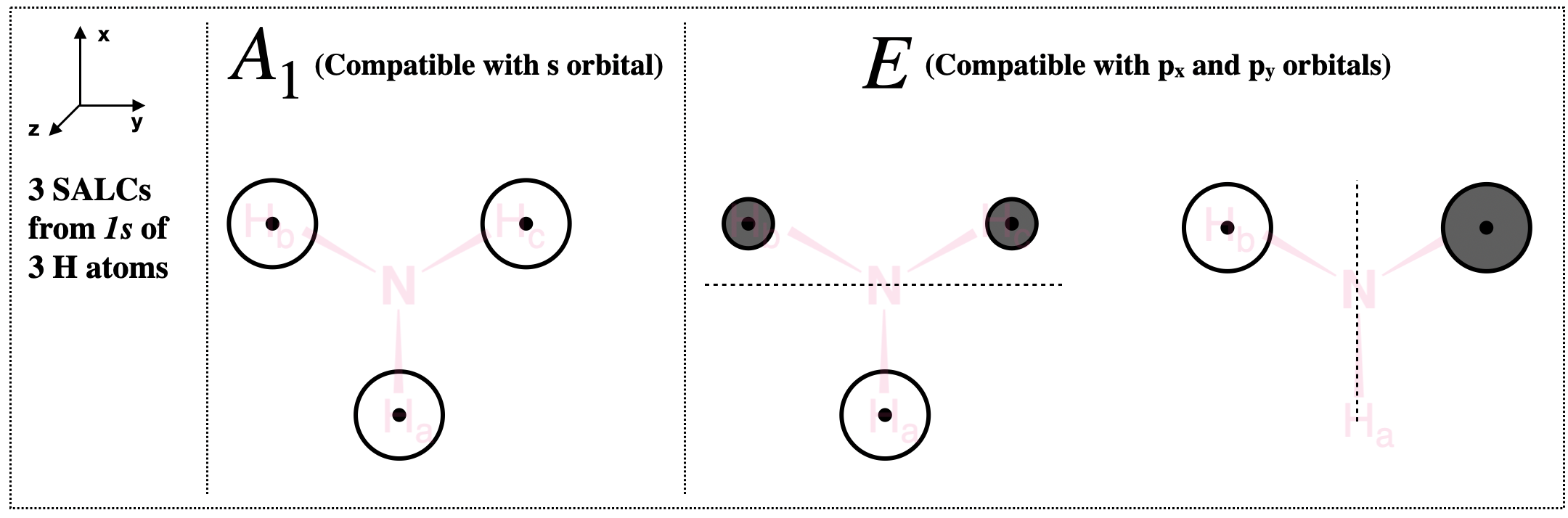
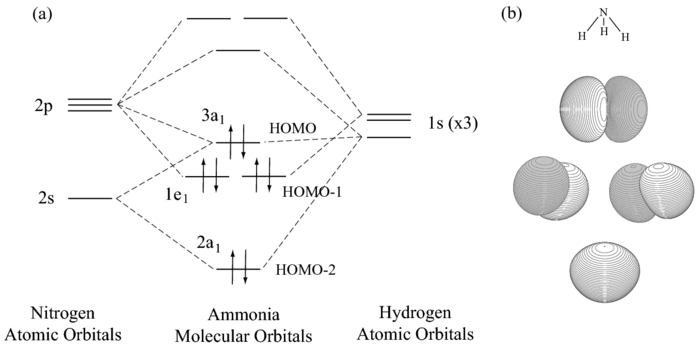
The Construction of Molecular Orbitals of NH3. Projection Operator Methode: Point Group of NH3. The symmetry elements of NH3 are E, 2C3, and 3 sigma-v. To elaborate, the molecule is of C3v symmetry with a C3 principal axis of rotation and 3 vertical planes of symmetry. The image of the ammonia molecule (NH3) is depicted in Figure \(\PageIndex{1 ...
The electronic spectra and g-factors of tetragonal [Cu(NH 3) 6] 2+, square planar [Cu(NH 3) 4] 2+, and octahedral [Ni(NH 3) 6] 2+ are fitted by using the semi-empirical (SCCC) method. Both hybridized and unhybridized ligand orbitals were tried. In the case of the copper complexes unhybridized ligand functions were necessary, while for the nickel complex both hybridized and unhybridized worked ...
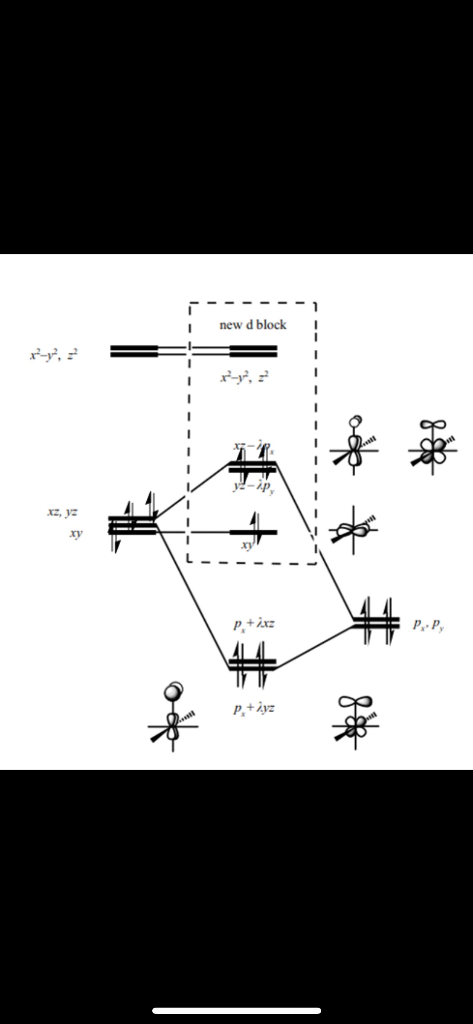
May 10, 2021 · The CFT diagram for tetrahedral complexes has d x 2 −y 2 and d z 2 orbitals equally low in energy because they are between the ligand axis and experience little repulsion. In square planar molecular geometry, a central atom is surrounded by constituent atoms, which form the corners of a square on the same plane.
Nh3 Molecular Orbital Diagram. As can be seen from the energy diagram - four of the molecular orbitals occur as Ammonia has two pairs of degenerate orbitals, one bonding and one. MO diagram of homonuclear diatomic molecules. • Filling the . 4) MO theory and molecular geometry (Walsh diagrams) . 2) Molecular Orbitals of NH3 (C3v).
CHE 422 Inorganic Chemistry. Molecular orbital energy level diagram of NH3 and Frontier Orbitals (highest occupied molecular orbital HOMO and lowest unoccup...
Chem 302. The Molecular Orbitals of Ammonia. Determing the electronic structure of ammonia will introduce the new ideas of degenerate orbitals and degenerate axes. It is important to understand these concepts because of the large number of molecules that have point groups such as C 3v or D 3h. To determine the MO's of ammonia.
The \(e\) atomic orbitals of nitrogen will combine with the \(e\) SALCs to give a set of two degenerate bonding molecular orbitals and a set of two degenerate antibonding orbitals. Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\): The molecular orbital diagram of ammonia. Molecular orbitals surfaces calculated using Spartan software. (CC-BY-NC-SA; Kathryn Haas)
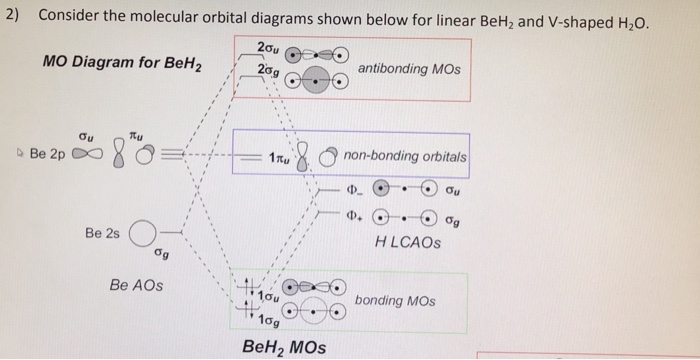
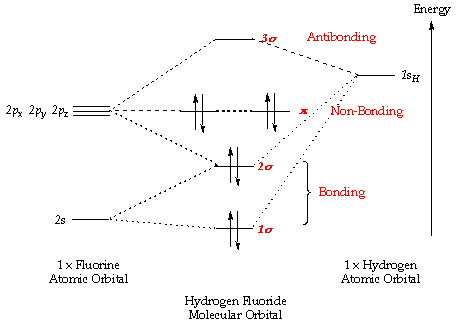
Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the molecular orbitals for a set of molecules which are related in structure. In this case, the difference is the H-X-H bond angle which decreases from 180 o to 90 o Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram Water 104.5 ° X H H H O H
The hydrogen atoms are just s orbitals overlapping those sp 3 orbitals. NH 3 Molecular Geometry And Bond Angles. If we look at the molecular geometry of ammonia it has a trigonal pyramidal or distorted tetrahedral structure. This is mainly due to the presence of a lone non-bonding pair which usually exerts greater repulsion on the bonding orbitals.
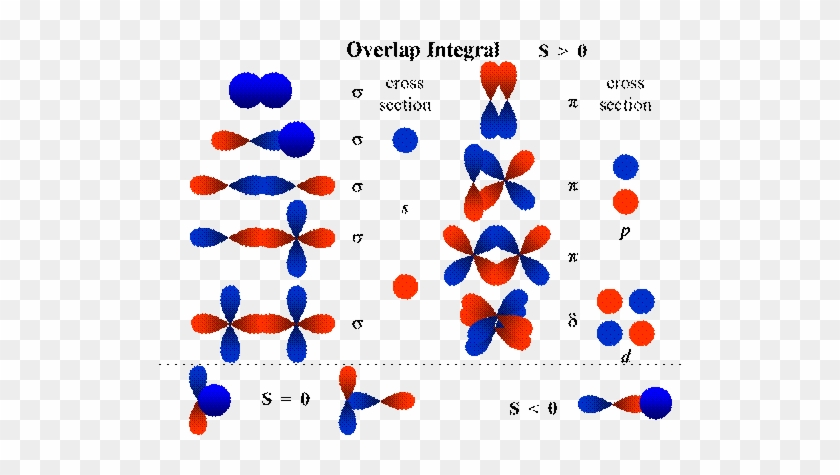
molecular orbitals. 2.The number of molecular orbitals formed is the same as that of the number of atomic orbitals combined. 3.The additive overlap results in the bonding molecular orbital while the subtractive overlap results in the antibonding overlap. 4.The energy of bonding molecular orbitals is lower than their nonbonding counterparts ...
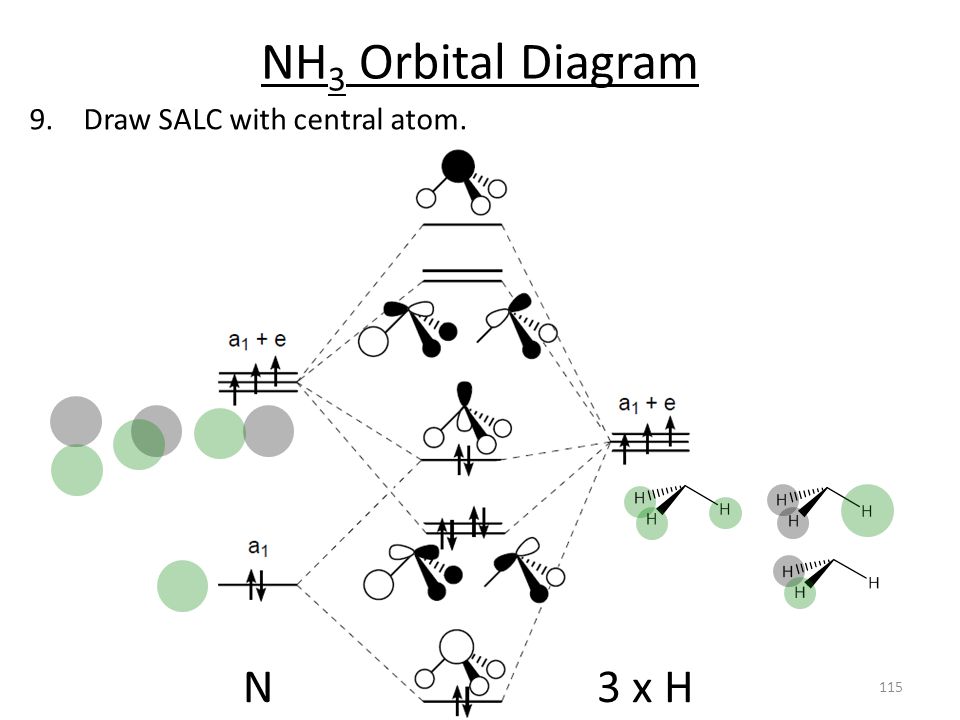
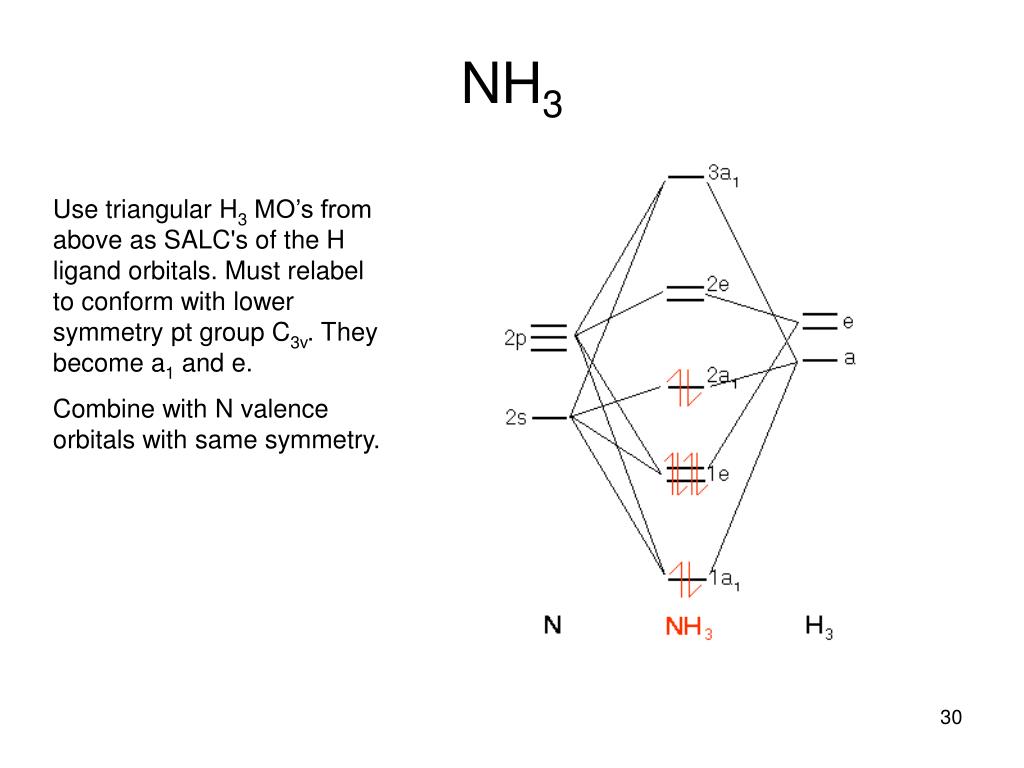
The molecular orbital diagram of NH3 is presented in Figure 5 and will be elaborated in regards to its interactions. The s orbitals for the 3 hydrogens are used to set up the sigma and anti bonding combinations of N sp 3 orbitals and the H 1s orbitals. Molecular Orbital Theory - Walsh diagram The Walsh diagram shows what happens to the ...
d orbitals •l = 2, so there are 2l + 1 = 5 d-orbitals per shell, enough room for 10 electrons. •This is why there are 10 elements in each row of the d-block. σ‐MOs for Octahedral Complexes 1. Point group Oh 2. The six ligands can interact with the metal in a sigma or pi fashion.
In NH3, the HOMO (Highly Occupied Molecular Orbital) is a mostly nitrogen based orbital that corresponds to the Lone pair of electrons. This is why ammonia acts as a Lewis base at the N atom. The LUMO (Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital) is the 2e level that has more H character this shows why NH3 can also act as a Lewis acid through the H atoms.
The molecular orbital diagram of NH3 is presented in Figure 5 and will be elaborated in regards to its interactions. The s orbitals for the 3 hydrogens are used to set up the sigma and anti bonding combinations of N sp 3 orbitals and the H 1s orbitals. Polyatomic Molecular Orbital Theory Transformational properties of atomic orbitals Atomic ...
Because the electronegativity of the two atoms are unequal, the molecular orbital diagram will no longer be symmetric. Instead, the more electronegative element is drawn lower in energy and ...
Fig. 2. Simplified molecular orbital diagram for a low spia octahedral complex, such as [Co(NH3 )g, where A = energy difference a, e, and t may be antisymmetric (subscript ungerade) or centrosymmetric (subscript, gerade) symmetry orbitals.
Specific combinations of atomic orbitals are use to build molecular orbitals. As seen here the p z orbital, like the 1s and 2s orbitals, has A 1 symetry; they are totally symmetric to the operations of the C 3v point group.. The p x and p y are affected by the C 3v point group operations by equal amounts and hence are degenerate. These atomic orbitals have e symmetry as defined by the ...
The molecular orbital diagram of NH3 is presented in Figure 5 and will be elaborated in regards to its interactions. The s orbitals for the 3 hydrogens are used to set up the sigma and anti bonding combinations of N sp 3 orbitals and the H 1s orbitals. Derive the molecular orbital diagrams for linear and bent H 2 O.
A molecular orbital is a region of space in a covalent species where electrons are likely to be found. The combination of two atomic orbitals always forms two molecular orbitals; the bonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy, and the antibonding molecular orbital, which is _____ in energy than the original atomic orbitals.
Nh3 Molecular Orbital Diagram. Ammonia is a trigonal pyramidal molecule with three pendant hydrogen atoms. The MO energy diagram for NH3 is shown in Figure 3. However for the species with more than 16 electrons in Table 8 the π u antibonding molecular orbital will be occupied and the linear geometry will have a higher energy than the bend ...
Molecular orbital diagram of ammonia (NH3) molecule The molecular orbital diagram is a diagrammatic representation of how chemical bonding is taking place within the molecules. In the case of ammonia (NH3), the molecular orbital diagram helps with understanding how sigma bonds are formed.




















0 Response to "40 nh3 molecular orbital diagram"
Post a Comment