35 diagram of sound waves
A sensory characteristic of sound produced by the amplitude (intensity) of the sound wave Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging) a system that uses reflected sound waves to detect and locate objects underwater The diagram below depicts one of the natural patterns of vibrations for a guitar string. In the pattern, you will note that there are certain positions along the string (the medium) that appear to be standing still. These positions are referred to as nodes and are labeled on the diagram.
Sound waves can bounce off smooth, hard objects in the same way as a rubber ball bounces off the ground. Although the direction of the sound changes, the echo sounds the same as the original sound. Echoes can be heard in small spaces with hard walls, like wells, or where there are lots of hard surfaces all around.
Diagram of sound waves
Sound waves. Anything that vibrates is producing sound; sound is simply a longitudinal wave passing through a medium via the vibration of particles in the medium. Consider a sound wave traveling in air. This sound wave is generated by a speaker broadcasting a single frequency, so the speaker cone is oscillating back and forth in simple harmonic ... These two waves have the same frequency but different amplitudes. These two waves have the same amplitude but different frequencies . Image courtesy of Sounds in the Sea 2001, NOAA/OER. These sound waves are reflected back by the seabed and the time taken from transmission to reception of the reflected sound waves is measured. Since the speed of sound in water is about 1500 m/sec, the depth of the sea bed is calculated which will be half the distance travelled by the sound waves. ... In the below diagram, when we select the ...
Diagram of sound waves. The sound waves arrive at the pinna (auricle), the only visible part of the ear. 2. Once the sound waves have passed the pinna, they move into the auditory canal (external acoustic meatus) before hitting the tympanic membrane (eardrum). 3. Once the sound waves reach the tympanic membrane, it begins to vibrate and they enter A sound wave is an example of a longitudinal wave and is produced by the vibrating motion of the particles that travel through a conductive medium. An example of sound waves in a longitudinal direction is the tuning fork. In Sound waves, the amplitude of the wave is the difference between the maximum pressure caused by the wave and the pressure ... The diagram below depicts a sound wave created by a tuning fork and propagated through the air in an open tube. The compressions and rarefactions are ... Diagrams 1 and 2 show two sounds with the same wavelength and frequency, so they will have the same pitch. The sound in diagram 2 has a greater amplitude than the one in diagram 1, so it will be...
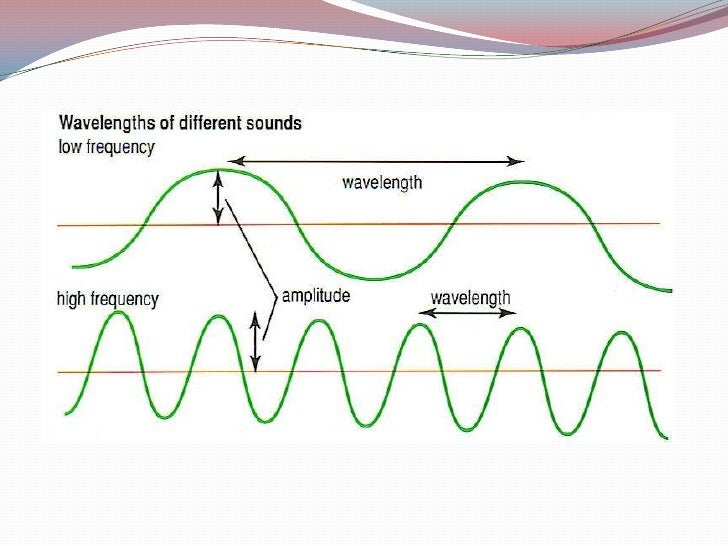
The matter that transports the sound is called the medium. Speed of Sound The speed of sound is how fast the wave or vibrations pass through the medium or matter. The type of matter has a large impact on the speed at which the sound will travel. For example, sound travels faster in water than air. Sound travels even faster in steel. A Wiggers diagram of ventricular systole graphically depicts the sequence of contractions by the myocardium of the two ventricles.Ventricular systole induces self-contraction such that pressure in both left and right ventricles rises to a level above that in the two atrial chambers, thereby closing the tricuspid and mitral valves—which are prevented from inverting by the chordae tendineae ... draw a diagram depicting low pitched sound and high pitched sound and write main difference between the two - Physics - TopperLearning.com | nmoay04xx The waveform representation converts the pressure variations of sound waves into a pictorial graph which is easier to understand. A sound wave is made of areas of high pressure alternated by an area of low pressure. The high-pressure areas are represented as the peaks of the graph. The low-pressure areas are represented as troughs of the graph.
Sound waves consist of areas of high and low pressure called compressions and rarefactions, respectively. Shown in the diagram below is a traveling wave. The shaded bar above it represents the varying pressure of the wave. Lighter areas are low pressure (rarefactions) and darker areas are high pressure (compressions). Diagram D shows beats – when two sound waves are nearly the same frequency but slightly different. The resulting wave has points of constructive interference and destructive interference. A sound wave with the beat pattern in diagram D will have a volume that varies at a regular rate – you can hear a pulse or flutter in the sound. Wave Diagram sheet Types of Waves Quad Clusters Anatomy of a Wave worksheet | Anatomy of a Wave worksheet Key Create a Wave Grid Diagrams for Labeling Waves Waves Review Sheet from Glencoe Directed Reading for Content ... Effect of Sound Waves Animation by McGraw-Hill - In the above diagram the white line represents the position of the medium when no wave is present. This medium could be imagined as a rope fixed at one end a few feet above the ground and held by you at the other end. The yellow line represents the position of the medium as a wave travels through it. We simply say that the yellow line is the wave.
Physics 1120: Standing Waves and Sound Level Solutions Sound Level 1. A wire of length 4.35 m and mass 137 g is under a tension of 125 N. A standing wave has formed which has seven nodes including the endpoints. What is the frequency of this wave? Which harmonic is it? What is the fundamental
Find Sound wave diagram stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection.
The crest of a wave is the point on the medium that exhibits the maximum amount of positive or upward displacement from the rest position. Points C and J on the diagram represent the troughs of this wave. The trough of a wave is the point on the medium that exhibits the maximum amount of negative or downward displacement from the rest position.
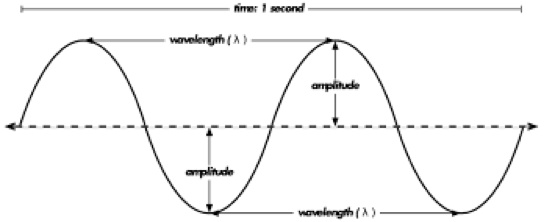
The diagram below depicts a sound wave created by a tuning fork and propagated through the air in an open tube. The compressions and rarefactions are labeled. The wavelength of a wave is merely the distance that a disturbance travels along the medium in one complete wave cycle.
The diagram shows a cartoon of a sound wave produced while a student is speaking. What happens to the sound wave when the student speaks louder? answer choices . The amplitude increases. the wavelength will double. the speed will increase. the amplitude will decrease . Tags: Question 13 .
When we talk concerning Sound Waves Worksheet Labeling, below we will see particular variation of images to inform you more. label ear diagram worksheet, sound wave worksheet answer and labeling waves worksheet answer key are three of main things we will show you based on the gallery title.
energy that travels through matter (medium) causing it to vibrate; examples include sound waves, ocean waves, and earthquake waves. longitudinal wave. type of wave in which the medium and energy travel parallel to each other or back and forth in the same direction. Wave speed. Frequency X Wavelength.
This Physics Tutorial discusses the nature of sound, its characteristic behaviors, and its association with the operation of musical instruments. Attention is given to both the purely conceptual aspect of sound waves and to the mathematical treatment of the same topic.
The diagram shows a cartoon of a sound wave produced while a student is speaking. What happens to the sound wave when the student speaks louder? answer choices . The amplitude increases. the wavelength will double. the speed will increase. the amplitude will decrease . Tags: Question 4 . SURVEY .
Physics (Grade 8): High School LearningSound | Characteristics Of Sound | Examples & Diagrams | Lecture 10- Amplitude of Sound- Characteristics of Sound- Amp...
The The Sound of Waves quotes below are all either spoken by Chiyoko or refer to Chiyoko. For each quote, you can also see the other characters and themes related to it (each theme is indicated by its own dot and icon, like this one: ).
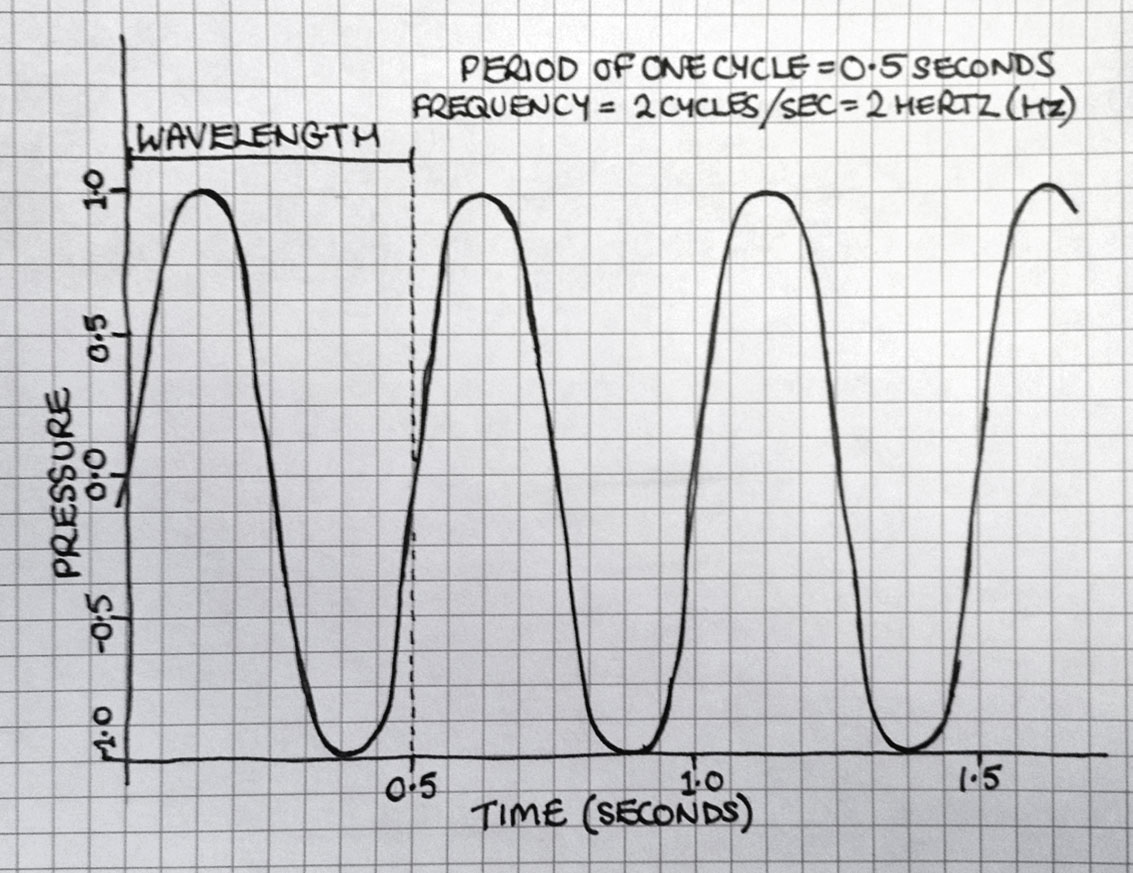
Sound wave diagram. A wave cycle occurs between two troughs. Units of Sound. When we measure sound, there are four different measurement units available to us. The first unit is called the decibel (dB). The decibel is a logarithmic ratio of the sound pressure compared to a reference pressure. The next most frequently used unit is the hertz (Hz).
Sound waves can also be shown in a standard x vs y graph, as shown here. This allows us to visualise and work with waves from a mathematical point of view. The resulting curves are known as the "waveform" (i.e. the form of the wave.) The wave shown here represents a constant tone at a set frequency.
Sound waves enter the outer ear and travel through a narrow passageway called the ear canal, which leads to the eardrum. The eardrum vibrates from the incoming sound waves and sends these vibrations to three tiny bones in the middle ear. These bones are called the malleus, incus, and stapes.

Little Gull Light. Taken by the British in the War of 1812 and destroyed by the hurricane of 1815, Little Gull Island Lighthouse has had a colorful past. The tower that stands today dates from 1858.
Sound Waves are longitudinal waves while Light waves are transverse waves. Sound waves always require a medium to travel, that is, they cannot travel in vacuum, while light waves do not require any material medium since they are electromagnetic waves. The speed of light is approximately 330m/sec while the speed of light wave is 3× 10 8 m/sec.
Sound waves Sound is caused by small areas of high and low pressure progragating outward from the source. One convenient way to diagram a sound wave is to graph the pressure at each point in time, the way it might be picked up by a microphone for example: This simplest kind of pressure wave is called a sine wave. Interesting things to measure ...
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain. Only acoustic waves that have frequencies lying between about 20 Hz and 20 kHz, the audio frequency range, elicit an auditory percept in humans.
12 Sept 2019 — Diagram illustrating longitudinal and transverse waves. The high points of the transverse waves (peaks) represent more-dense areas of the ...
Unlike a pictorial diagram, a wiring diagram uses abstract or simplified shapes and lines to show components. Pictorial diagrams are often photos with labels or highly-detailed drawings of the physical components. Standard Wiring Diagram Symbols. Most symbols used on a wiring diagram look like abstract versions of the real objects they represent.
From a graph showing how a sound wave changes over time, you can extract two important features that affect what a sound sounds like to us: the amplitude and ...
Light waves diagram images. 10,810 light waves diagram stock photos, vectors, and illustrations are available royalty-free. See light waves diagram stock video clips. Image type. Orientation.
Sound waves are longitudinal waves that must pass through a medium, such as air. Echoes are reflections of sounds. The frequency of ultrasound is above 20 kHz.
Characteristics of Sound Waves Sound travels in the form of a wave. Waves are characterized by three basic quantities. They are frequency, speed, and amplitude. Two of the main characteristics of sound are pitch and loudness, which in turn are determined by the frequency and amplitude of the wave, respectively. Therefore, to understand what pitch […]
These sound waves are reflected back by the seabed and the time taken from transmission to reception of the reflected sound waves is measured. Since the speed of sound in water is about 1500 m/sec, the depth of the sea bed is calculated which will be half the distance travelled by the sound waves. ... In the below diagram, when we select the ...
These two waves have the same frequency but different amplitudes. These two waves have the same amplitude but different frequencies . Image courtesy of Sounds in the Sea 2001, NOAA/OER.
Sound waves. Anything that vibrates is producing sound; sound is simply a longitudinal wave passing through a medium via the vibration of particles in the medium. Consider a sound wave traveling in air. This sound wave is generated by a speaker broadcasting a single frequency, so the speaker cone is oscillating back and forth in simple harmonic ...























0 Response to "35 diagram of sound waves"
Post a Comment