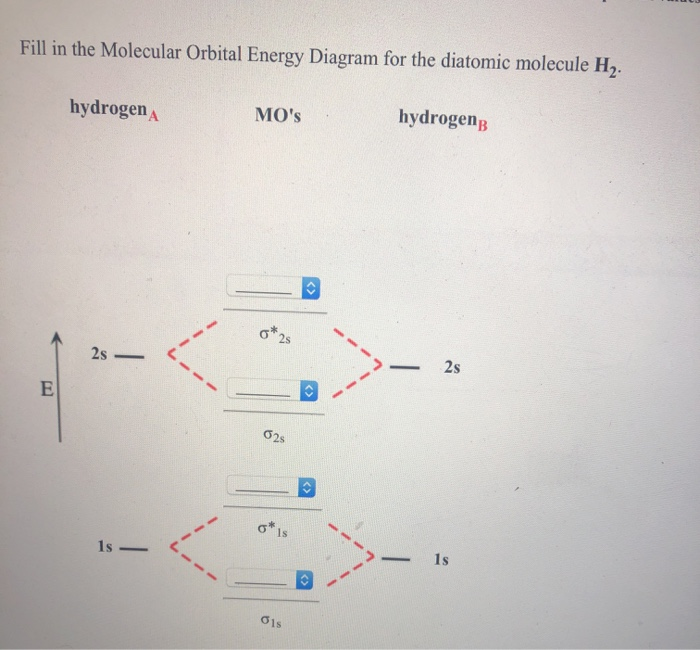
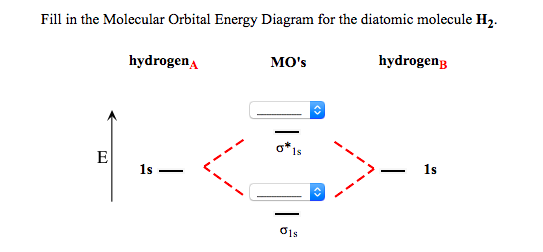
39 fill in the molecular orbital energy diagram for the diatomic molecule h2.
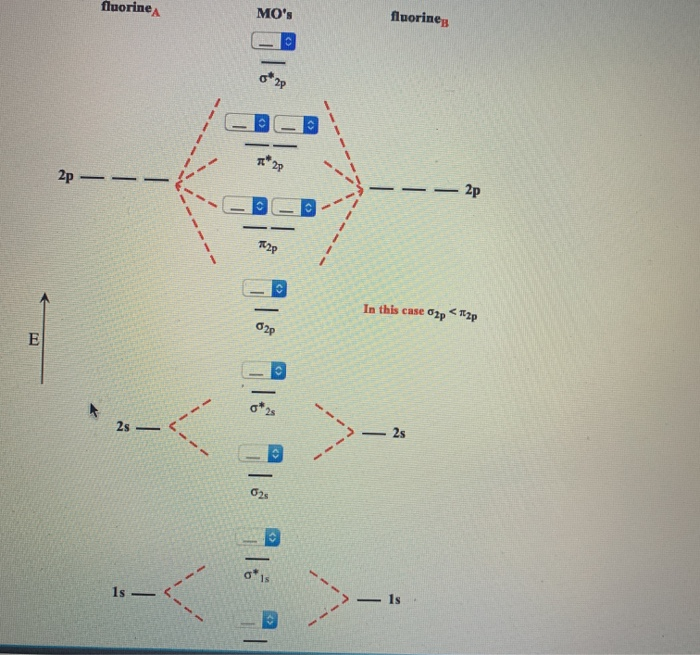
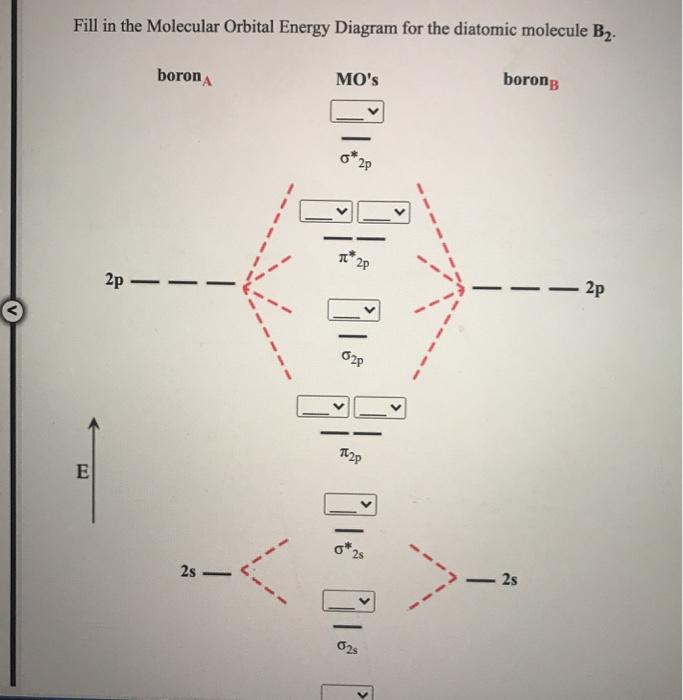
Solved Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the | Chegg.com. Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule F2 MO's fluorinep fluorineA 2p ー2p 2p In this case σ2pch2p * σ2s 1s Ơİs. The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The net contribution of the electrons to the bond strength of a molecule is identified by determining the bond order that results from the filling of the molecular orbitals by electrons.
MO Diagram for HF The AO energies suggest that the 1s orbital of hydrogen interacts mostly with a 2p orbital of fluorine. The F 2s is nonbonding. H–F nb σ σ* Energy H –13.6 eV 1s F –18.6 eV –40.2 eV 2s 2p So H–F has one σ bond and three lone electron pairs on fluorine

Fill in the molecular orbital energy diagram for the diatomic molecule h2.
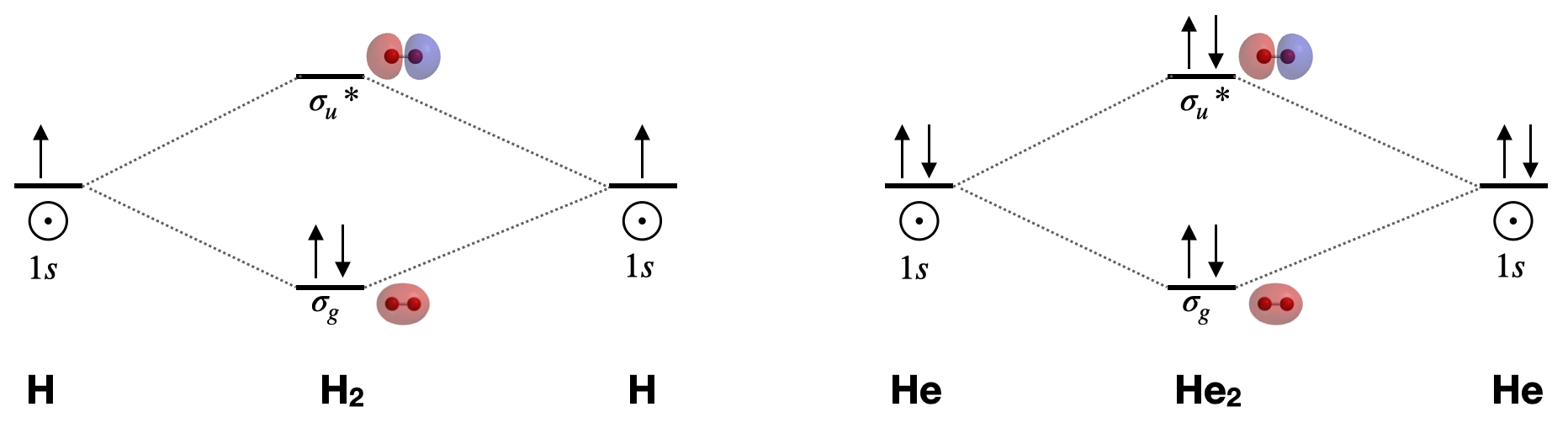
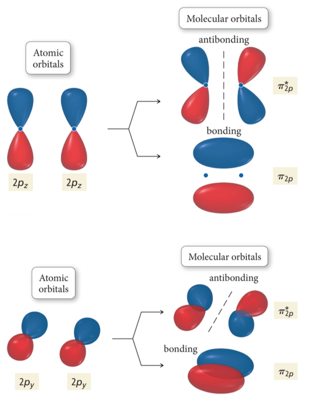
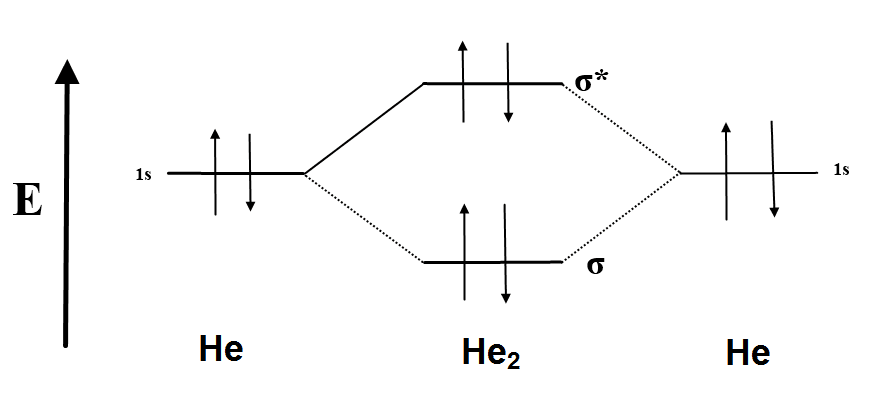
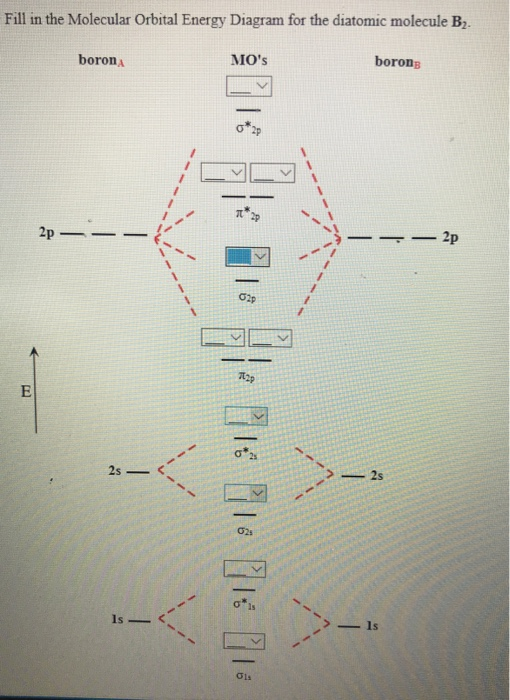
The Lewis structure for H2 is H-H, predicting a single bond between each hydrogen atom with two electrons in the bond. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the same thing--two electrons fill... The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He 2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. The Diatomic Molecules of the Second Period Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li 2 , Be 2 , B 2 , C 2 , N 2 ... The head-to-head overlap giving σ molecular orbitals results in greater overlap, making its bonding molecular orbital the most stable and lowest energy, while the σ* antibonding is least stable and has the highest energy (Figure 9.24 "Molecular orbital energy diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules made from atoms of atomic number 8-10").
Fill in the molecular orbital energy diagram for the diatomic molecule h2.. Molecular Orbital Diagram for Hydrogen Gas (H2).Fill from the bottom up, with 2 electrons total.Bonding Order is 1, and it is Diamagnetic.sigma2s(2)Check me ... Molecular Orbitals of the Second Energy Level. The 2s orbitals on one atom combine with the 2s orbitals on another to form a 2s bonding and a 2s * antibonding molecular orbital, just like the 1s and 1s * orbitals formed from the 1s atomic orbitals. If we arbitrarily define the Z axis of the coordinate system for the O 2 molecule as the axis along which the bond forms, the 2p z orbitals on the ... The filled molecular orbital diagram shows the number of electrons in both bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals. The net contribution of the electrons to the bond strength of a molecule is identified by determining the bond order that results from the filling of the molecular orbitals by electrons. Molecular Orbital Diagrams of Diatomic Molecules Introduction: In chemistry molecular orbital (MO) theory is a method for determining molecular structure in which electrons are not assigned to individual bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the nuclei in the whole molecule. The energy-level diagram for He2 is ...
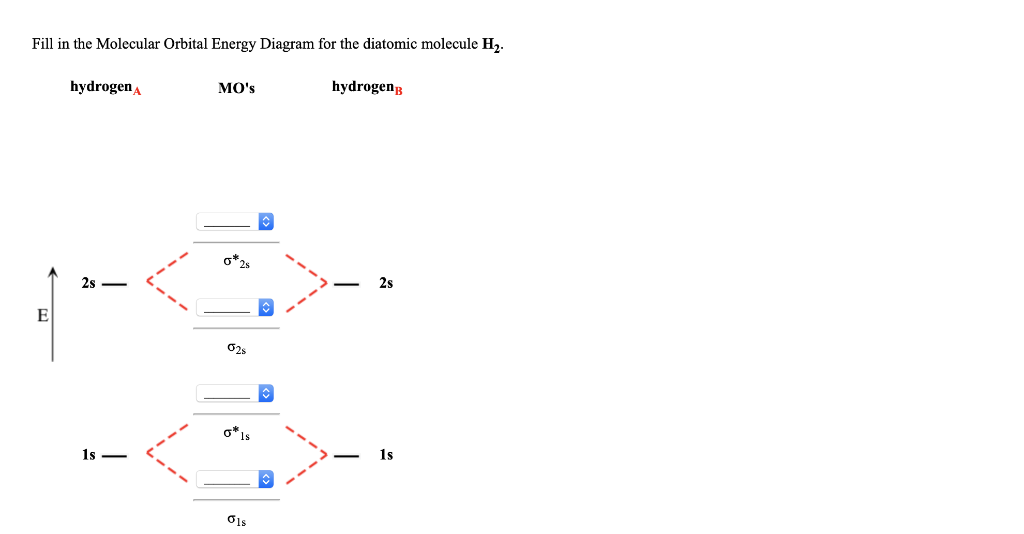
Science. Chemistry. Chemistry questions and answers. Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule H2. hydrogenA MO's hydrogenp 2s ?2s ?Is Retry Entire Group 4 more group attempts remaining Subenit Answer. Molecular orbital theory considers electrons to be distributed over the entire molecule, while valence bond theory considers electrons to be localized to a bond. The image provided shows two 3px orbitals. Predict what type of molecular orbital will result. σ3p. If an electron became excited, it could. jump from the sigma (σs) or bonding ... Complete An Mo Energy Diagram For H2+. May 25, Electronic configuration of Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules. 1)H2+. Molecular orbital energy level for H2+. The electronic configuration of H2+. Answer to Create an MO diagram for H2+ H2 and H Post the Lumo, lumo -, homo, homo + near its energy level. Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory of the H2 molecule ... Molecular Orbital Diagram for a Homonuclear Diatomic ... diagram is energy and the horizontal axis are the fragments, atoms in the case of a simple diatomic o add the molecule in the centre at the bottom, and the individual atomic fragments either side, don't forget to add placeholders so that you know ...
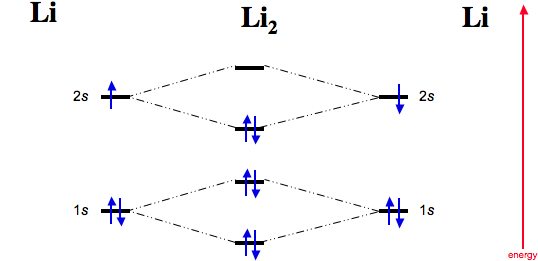
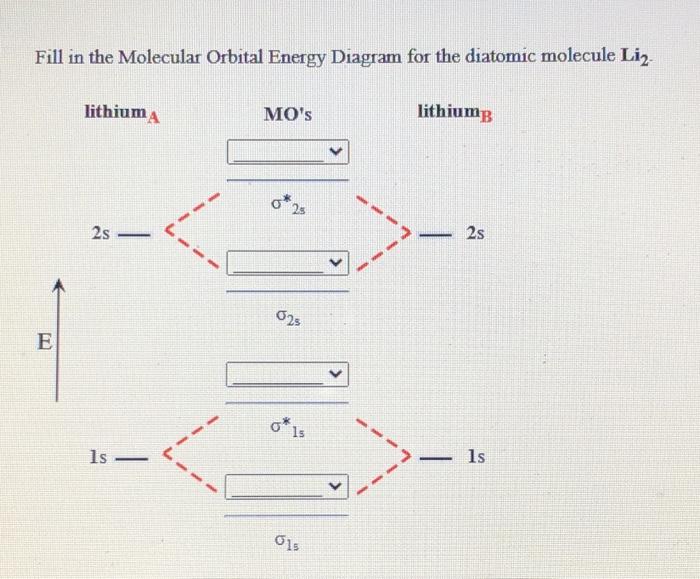
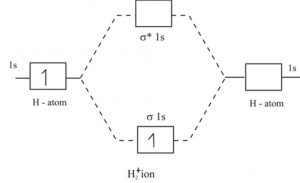
We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. Lithium has only 3 electrons, when Molecular orbital diagram is formed then two l …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule Li2. lithiuma MO's lithiums o* 2 2s - 2s 625 Ε o*ls ls ls G1s. The energy-level scheme for H2+ shown in Figure 3-5 is appropriate for diatomic molecules that have 1svalence orbitals. The hydrogen molecule-ion, H2+, has the electronic structure (σb)1; that is, it has one electron in a σ bonding orbital. Because there is one unpaired electron H2+ is paramagnetic. Chemistry questions and answers. Use the References to access important values Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule C2. carbon MO's carbong 2p - --2p T2P E 2s - 2s 625 Is - - 1s. You fill these molecular orbitals. A molecular orbital explicitly describes the spatial distribution of a single Energy Level Diagrams He2 has bond order 0 [ (2 − 2)/2 = 0], and we can make H+.The energy-level diagram for He2 is shown above, the two electrons in each of the 1s atomic orbital give total of 4 electrons in this molecule.
Who are the experts? Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high. 100% (13 ratings) Transcribed image text: Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule H2. hydrogena MO's hydrogen 2s — - 2s 1s — - 1s.
Chemistry questions and answers. Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule He2. heliump heliumA MO's * σ2s 2s * σ1s 1s Fill in the Molecular Orbital Energy Diagram for the diatomic molecule C2 carbong carbonA MO's 2p 2s σ2s * σ1s 1s 1s.
This is the molecular orbital diagram for the homonuclear diatomic Be2+, . electrons would be in a bonding orbital, we would predict the Li2 molecule to be . Learn to draw molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagrams. molecular orbital electron configuration diagram for Li2 (Figure "Molecular orbital.
The molecular orbital energy-level diagram, which is a diagram that shows the relative energies of molecular orbitals, for the H 2 molecule is shown in Figure 13. On either side of the central ladder are shown the energies of the 1 s orbitals of atoms A and B, and the central two-rung ladder shows the energies of the bonding and antibonding ...
Well, build the molecular orbital (MO) diagram. Each hydrogen atom contributes one electron, and thus, "H"_2^(-) has three electrons while "H"_2^(+) has one. Each hydrogen atom contributes one 1s atomic orbital, and thus, the orbitals overlap according to MO theory to form one sigma_(1s) and one sigma_(1s)^"*" MO by conservation of orbitals.
The head-to-head overlap giving σ molecular orbitals results in greater overlap, making its bonding molecular orbital the most stable and lowest energy, while the σ* antibonding is least stable and has the highest energy (Figure 9.24 "Molecular orbital energy diagram for homonuclear diatomic molecules made from atoms of atomic number 8-10").
The molecular orbital energy diagram predicts that He 2 will not be a stable molecule, since it has equal numbers of bonding and antibonding electrons. The Diatomic Molecules of the Second Period Eight possible homonuclear diatomic molecules might be formed by the atoms of the second period of the periodic table: Li 2 , Be 2 , B 2 , C 2 , N 2 ...
The Lewis structure for H2 is H-H, predicting a single bond between each hydrogen atom with two electrons in the bond. The orbital correlation diagram in predicts the same thing--two electrons fill...




















0 Response to "39 fill in the molecular orbital energy diagram for the diatomic molecule h2."
Post a Comment