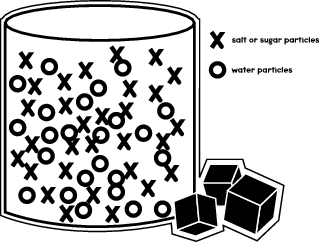
37 salt dissolving in water diagram
This animation depicts the process of dissolving salt at the molecular level. Because salt is composed of ions which have positive and negative charges, the small areas of positive and negative charge on water are attracted to the salt ions. Eventually, when enough water molecules surround ... Salt dissolves when it is stirred into water. In sea water, the water is the solvent and the salt is the solute. In sea water, the water is the solvent and salt is the solute.
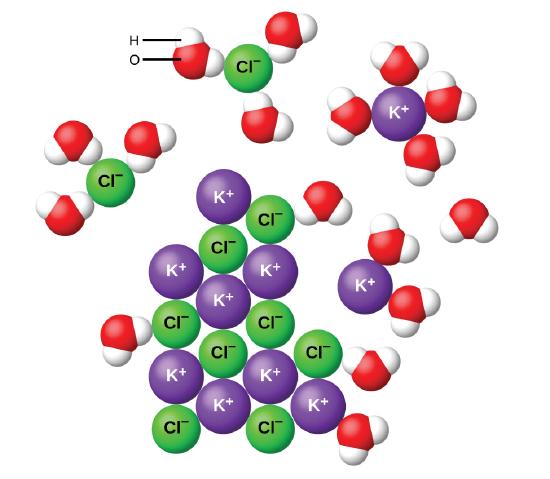
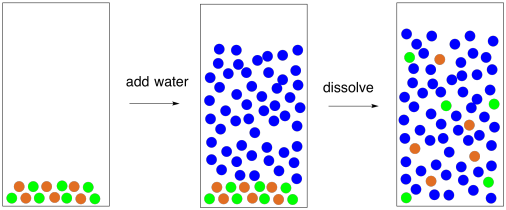
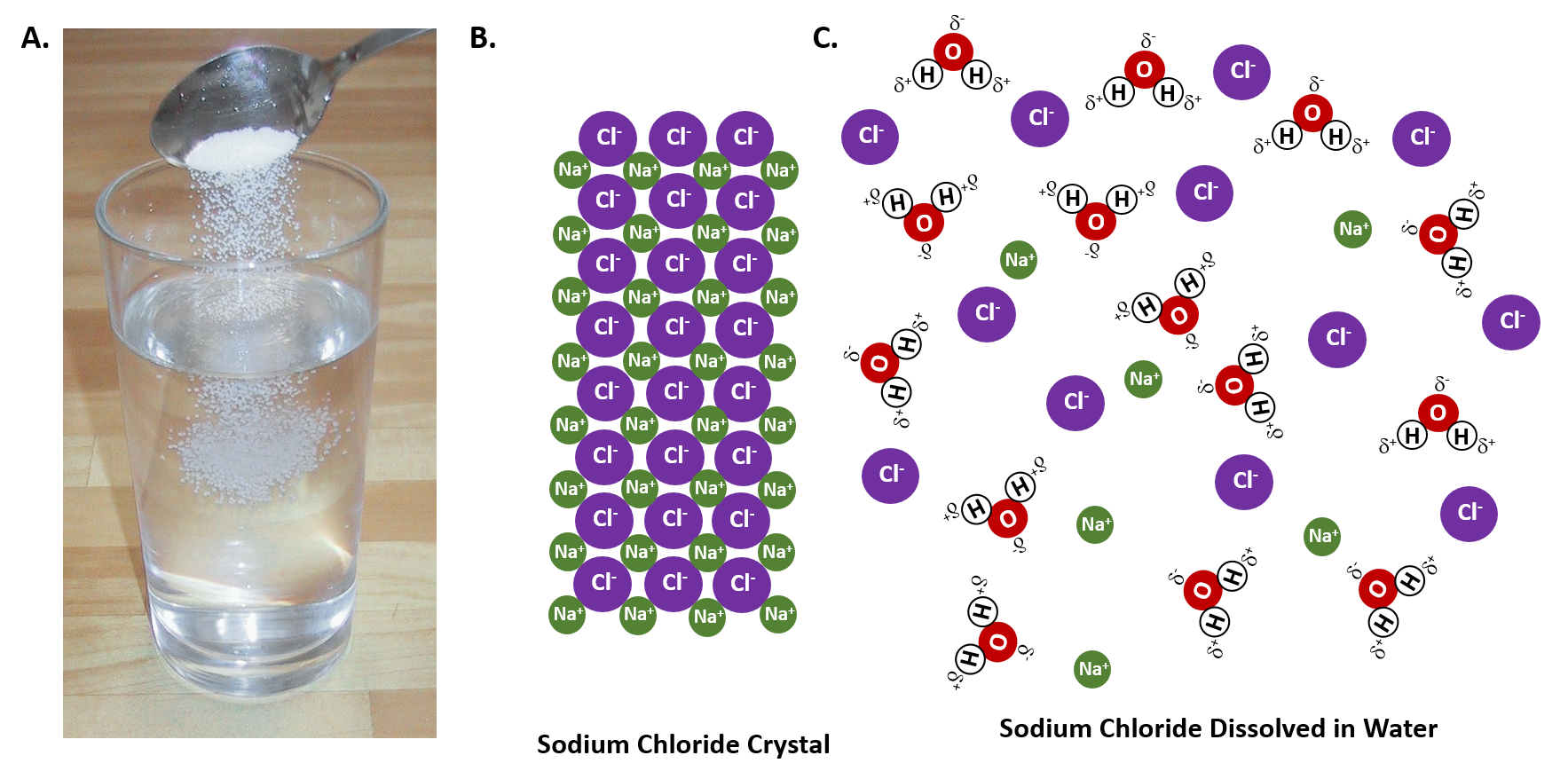
Jun 09, 2020 · After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. Why is it that the dissolved salt in the water formed into salt again? Explain that as the water evaporates, water molecules go into the air. The water molecules that evaporate become a gas called water vapor.
Salt dissolving in water diagram
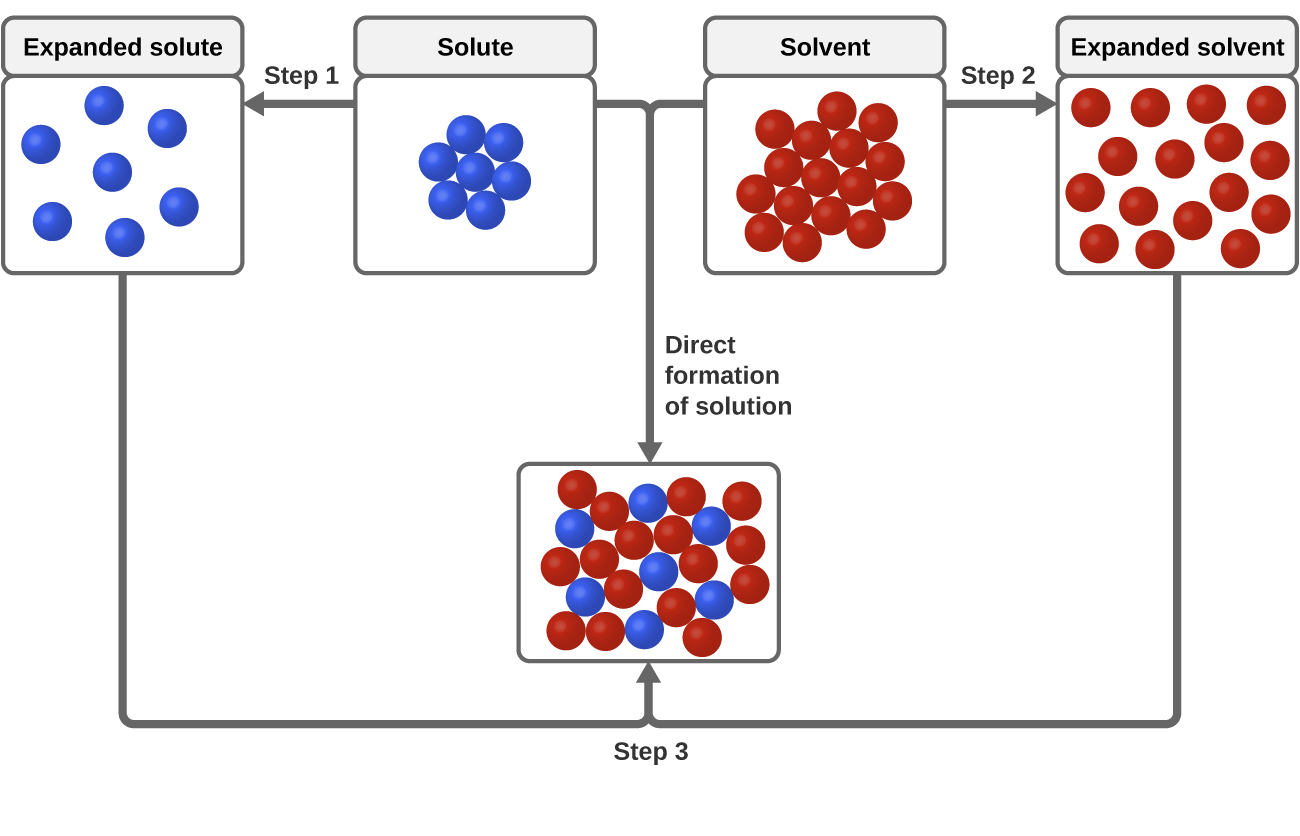
Sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal, pulling away the individual sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) ions. This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. To understand this process at the molecular level, we must apply the three steps we previously discussed. Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in ... February 20, 2018 - This study investigates how students account for a macroscopic temperature change during the dissolution of ionic salts through particulate level explanations. Semi-structured interviews were conducted with general chemistry, physical chemistry, and biophysical chemistry students.
Salt dissolving in water diagram. November 19, 2020 - "Salt dissolved in water" is a rough description of Earth's oceans. In chemistry, it results in a solution, as the ionic bond of NaCl is pulled apart by the attraction of Na to the O of H2O and the attraction of Cl to the H of H2O. Very little to no acid is produced in this solution. Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution. Students should measure about 100 ml of warm water (with beaker) and mix with 5 ml of Epsom salt (with spoon) into the water. They will pour half of the solution in another jar and place one end of the cotton string (mop string) in each of the two jars with Epsom salt solution, as shown in the diagram on the right. Let the string dip between the jars and let the jars sit for several days. In salt solution, salt is the solute. A solvent. is the substance that does the dissolving - it dissolves the solute. In salt solution, water is the solvent. During dissolving, particles of ...
water dissolves salt. After seeing an animation of water dissolving salt, students will compare how . well water and alcohol dissolve salt. They will relate their observations to the structure of salt, water, and alcohol on the molecular level. Objective. Students will be able to explain, on the molecular level, why water can dissolve salt ... Jan 23, 2022 · Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a ... The saturation level is only nominally dependent on the temperature of the water. At 20 °C one liter of water can dissolve about 357 grams of salt, a concentration of 26.3% w/w. October 24, 2017 - Answer (1 of 10): Salt will just dissolve in water and no chemical reaction occurs, because water molecule is very polar and it pull outs the sodium and chlorine ions and when its fully dissolve the water and salt solution will full of sodium and chlorine ions. Hopes this helps:) Explanation: Dissolving sodium chloride in water is a chemical change forming a solution of sodium and chloride ions. …. The sodium ions will not react violently with the water because the sodium is already oxidized (has lost an electron, forming a cation) as pointed out by anor77. NaCl (s) H2O⇌ Na+ (aq)+Cl− (aq) .
When a substance dissolves in water, and each water molecule is like a tiny magnet. For a substance to dissolve in water, it must also be a polar molecule, or it must be capable of breaking into polar molecules. For example, when you add some salt in water it can be dissolved into water and become salt water. No, dissolve differently. Choose a salt. There are many different salts available, and they all have different properties.The amount of Epsom salt (MgSO 4) that you can dissolve into a given amount of water at a given temperature will differ from the amount of table salt (NaCl) that you can dissolve into the same water.. If you are trying to understand the dissolution process in general, you should stick with using ... When you dissolve salt in water, the sodium chloride dissociates in Na + ions and Cl - ions, which may be written as a chemical equation : NaCl (s) → Na + (aq) + Cl - (aq) Therefore, dissolving salt in water is a chemical change. The reactant (sodium chloride, or NaCl) is different from the products (sodium cation and chlorine anion). Dissolving an ionic salt in water Computer Simulation and Computer Animation A short computer animation illustration how positive and negative ions in a solid ionic compound dissolve in water might be used to accompany dissolving salts in water demonstration.
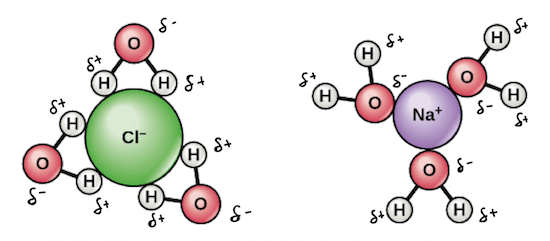
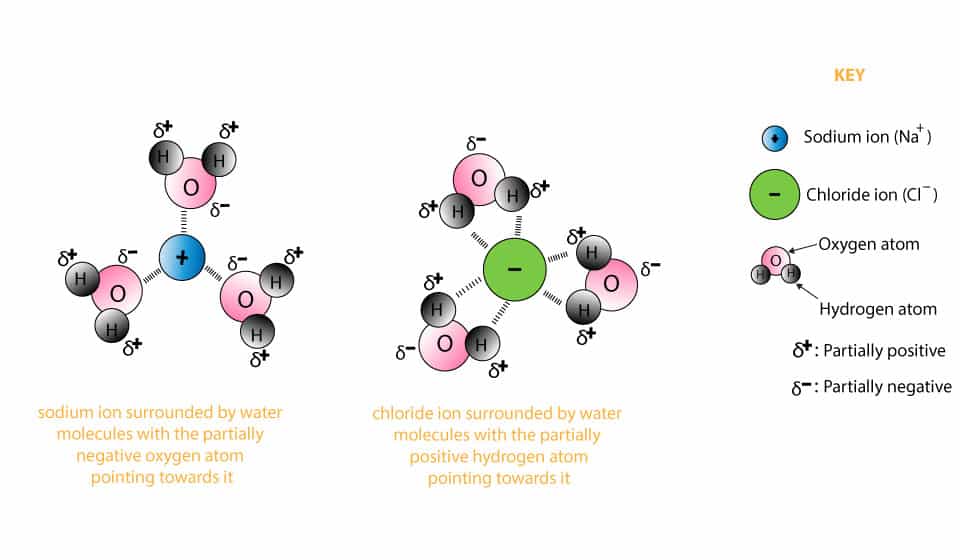
June 4, 2021 - As the crystals of NaCl molecules dissolve in water (H2O), hydrogen (H) ions of water molecules surround (-) charged chlorine (Cl) ions of salt. Likewise, (-) charged oxygen (O) ions, (-) surround (+) charged sodium (Na) ions. Electrostatic attraction is the force that causes this event.
Find step-by-step Biology solutions and your answer to the following textbook question: Draw a diagram of table salt (NaCl) dissolved in water..
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
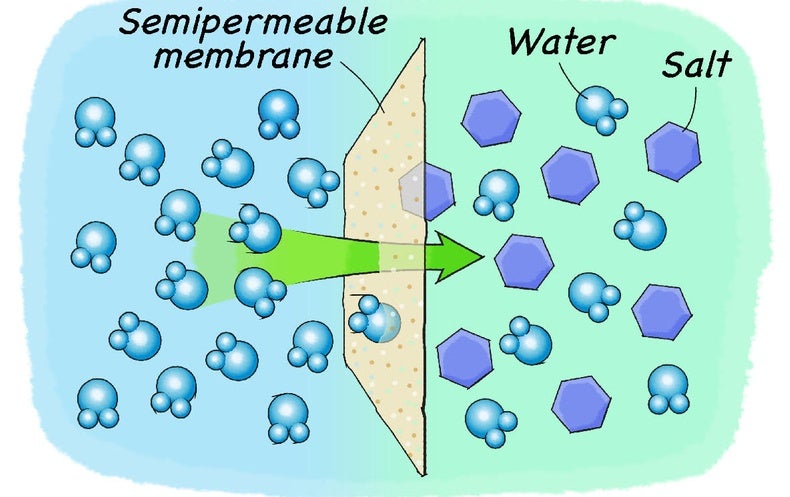
Water dissolves salt by dissociating the ions in salt from each other. Because water is a polar molecule, each of its ends holds a slight positive or negative electrical charge. These ends attract the positive and negative ions in salt and pull them apart from each other. The polarity of water comes from the differences in electronegativity in ...
Salt dissolves in water. So you would say, "Salt is _____ in water. SOLUBLE. Sand doesn't dissolve in water so you would say" Sand is _____ in water. INSOLUBLE. soluble. able to be dissolved. Insoluble. a substance that cannot be dissolved in a given solvent. Cocoa mix is an example of a _____
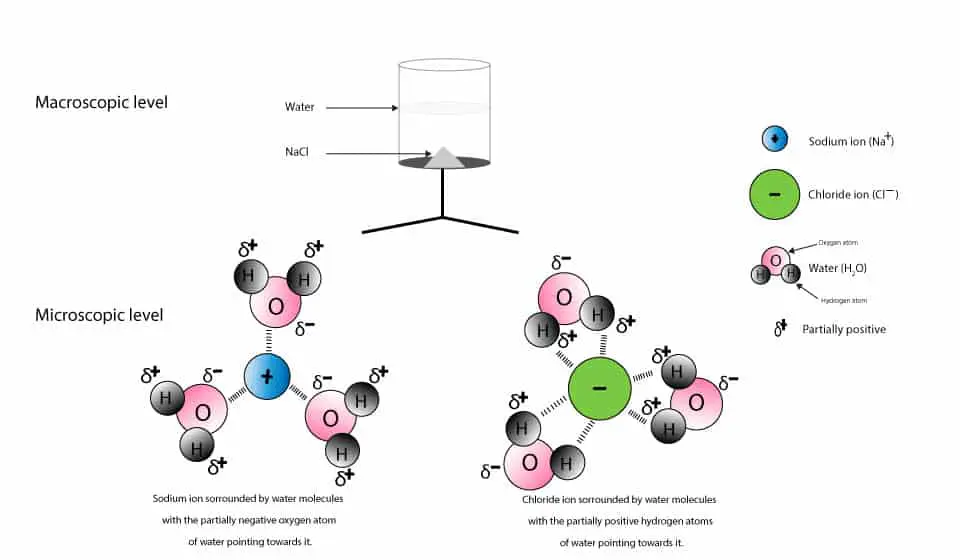
Detailed Description. This diagram shows the positive and negative parts of a water molecule. It also depicts how a charge, such as on an ion (Na or Cl, for example) can interact with a water molecule. At the molecular level, salt dissolves in water due to electrical charges and due to the fact that both water and salt compounds are polar, with positive and negative charges on opposite sides in the molecule.
Ionic solids (or salts) contain positive and negative ions, which are held together by the strong force of attraction between particles with opposite charges. When one of these solids dissolves in water, the ions that form the solid are released into solution, where they become associated with ...
There is an eutectic composition around 27 wt % NaCl or salt dissolved in the water. · At the eutectic point, the melting or freezing temperature is as low as it ...
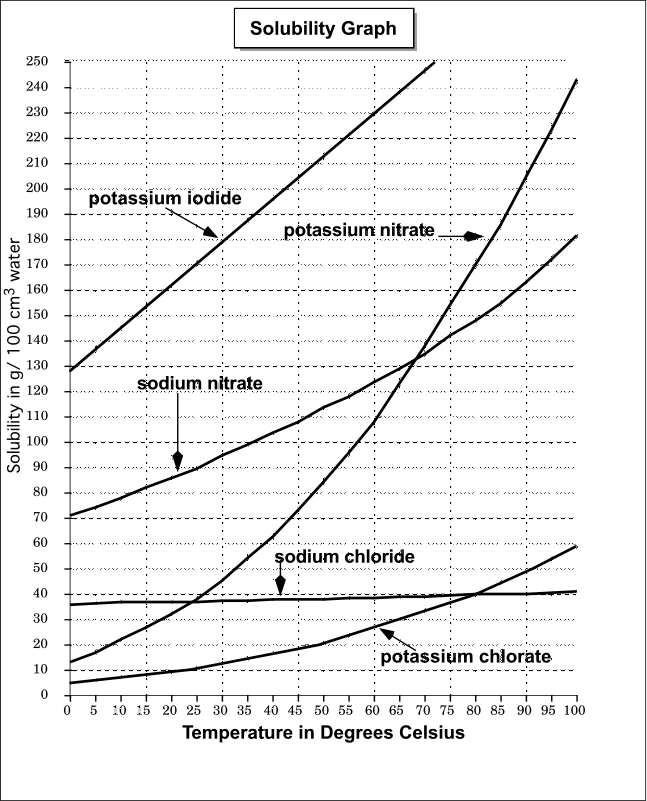
To illustrate the point the solubility diagram for a single salt, such as potassium nitrate, is shown in Fig. 1. In this diagram, the solubility of the salt in water is given by its concentration expressed in molality (mol/kg solvent, where the solvent is water) on the ordinate axis as a function of temperature on the abscissa axis. The black ...
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean.On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/l, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has approximately 35 grams (1.2 oz) of dissolved salts (predominantly sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl −) ions).Average density at the surface is 1.025 kg/l.
In separate cups, measure two samples of salt that weigh 5 g each. Place 15 mL of water and alcohol into separate cups. At the same time, add the water and alcohol to the samples of salt. Swirl both cups the same way for about 20 seconds and check for the amount of salt dissolved. Swirl for another 20 seconds and check.
If you mix two substances and the result is a homogeneous mixture, you are dealing with a solution. In the case of table salt mixed with water, Na and Cl atoms, initially bonded together in the form of a crystal, are dissolved by molecules of water. Water is a solvent. The reasons are electrostatic in nature. The cohesion of atoms and molecules derive from electrostatic links between particles ...
DIAGRAM >> A representation of the dissolving of sodium molecules in water. The negative ends of the polar water molecules are attracted to the positive sodium ions, and pull them off the crystal lattice. The positive ends of the water molecules are attracted to the negative chloride ions, and pull them off.
May 2, 2021 - Learn whether dissolving salt in water is a chemical change or a physical change. Explore arguments for both answers.
September 10, 2020 - A common misconception about dissolving is that heating and/or stirring are required for the dissolving process to occur. In this study, quantitative experimental evidence was collected and analyzed to demonstrate that neither heating nor stirring is required for dissolving.
We'll take a solution containing 100 g of potassium nitrate and 100 g of water. Now let the solution cool. At all temperatures above that marked on the graph (about 57°C), 100 g of water will dissolve more than 100 g of potassium nitrate. All the potassium nitrate will stay in solution. At 57°C, you hit the solubility curve.
Students continue exploring the particle nature of matter by first dissolving salt in water, then allowing the water to evaporate, and finally observing the solid salt left behind. After viewing a model of salt, students help develop models for the processes of salt dissolving, water evaporating to form a gas, and salt re-forming as a crystal.
Find dissolving salt in water stock images in HD and millions of other royalty-free stock photos, illustrations and vectors in the Shutterstock collection. Thousands of new, high-quality pictures added every day.
VIDEO ANSWER: we can easily draw a diagram of sodium chloride dissolved in water. Let's just do some quick review, though. Sodium chloride is in a C l.
Water molecules pulling apart the ions (sodium and chloride) in a salt crystal, and then dissolving the salt. ... Water molecules pulling apart the ions (sodium and chloride) in a salt crystal ...
Why water makes a good solvent, and what kinds of molecules dissolve best in it.
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in a homogeneous solution.
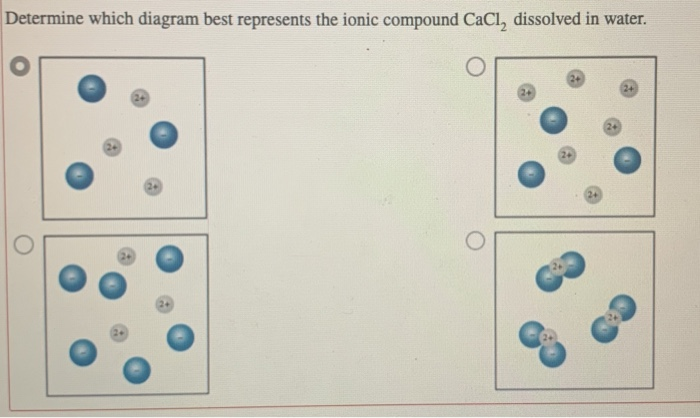
A salt is dissolved in water. A student draws a particulate diagram of the solution with accurate relative sizes and numbers of ions, but forgets to label the ions. Which of the following is most likely the salt that the student is studying, based on the diagram shown below? O NazN Mgo Mg3N2 MgF2 NaF Na20 ; Question: A salt is dissolved in ...
When table salt, sodium chloride, dissolves in water, it dissociates into its respective cations and anions, Na+ and Cl-. How does water stabilize the Na+? It uses the partially negatively charged oxygen side. One oxygen from the water cannot stabilize the Na+ alone, but several oxygens from ...
Water typically dissolves many ionic compounds and polar molecules. Nonpolar molecules such as those found in grease or oil do not dissolve in water. We will first examine the process that occurs when an ionic compound such as table salt (sodium chloride) dissolves in water.
Solubility Diagram. Show all questions. 1 / 12. At approximately what temperature does the solubility of sodium chloride, NaCl, match the solubility of potassium dichromate, K 2 Cr 2 O 7? 83 ºC. 60 ºC. 50 ºC. 30 ºC. Which salt is LEAST soluble at 0 ºC?
February 20, 2018 - This study investigates how students account for a macroscopic temperature change during the dissolution of ionic salts through particulate level explanations. Semi-structured interviews were conducted with general chemistry, physical chemistry, and biophysical chemistry students.
Water molecules pull the sodium and chloride ions apart, breaking the ionic bond that held them together. After the salt compounds are pulled apart, the sodium and chloride atoms are surrounded by water molecules, as this diagram shows. Once this happens, the salt is dissolved, resulting in ...
Sodium chloride (NaCl) dissolves when water molecules continuously attack the NaCl crystal, pulling away the individual sodium (Na +) and chloride (Cl -) ions. This nonstop attack continuous until the whole NaCl crystal disintegrates. To understand this process at the molecular level, we must apply the three steps we previously discussed.















0 Response to "37 salt dissolving in water diagram"
Post a Comment