40 Draw A Ray Diagram For The Following Situation Involving A Diverging Lens
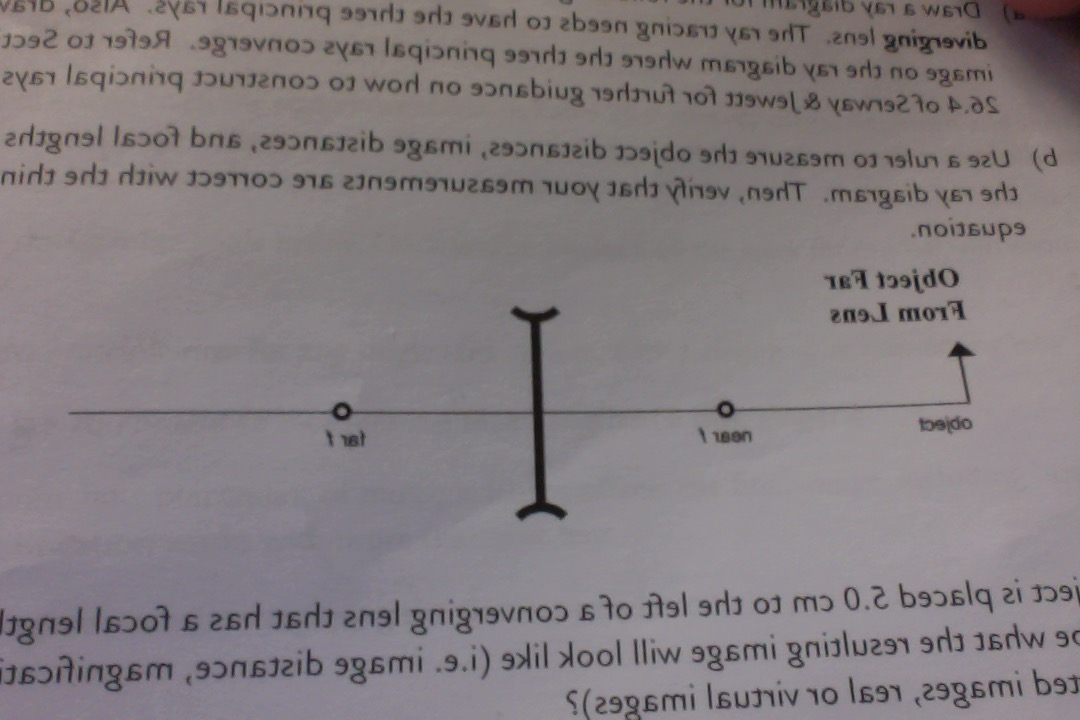
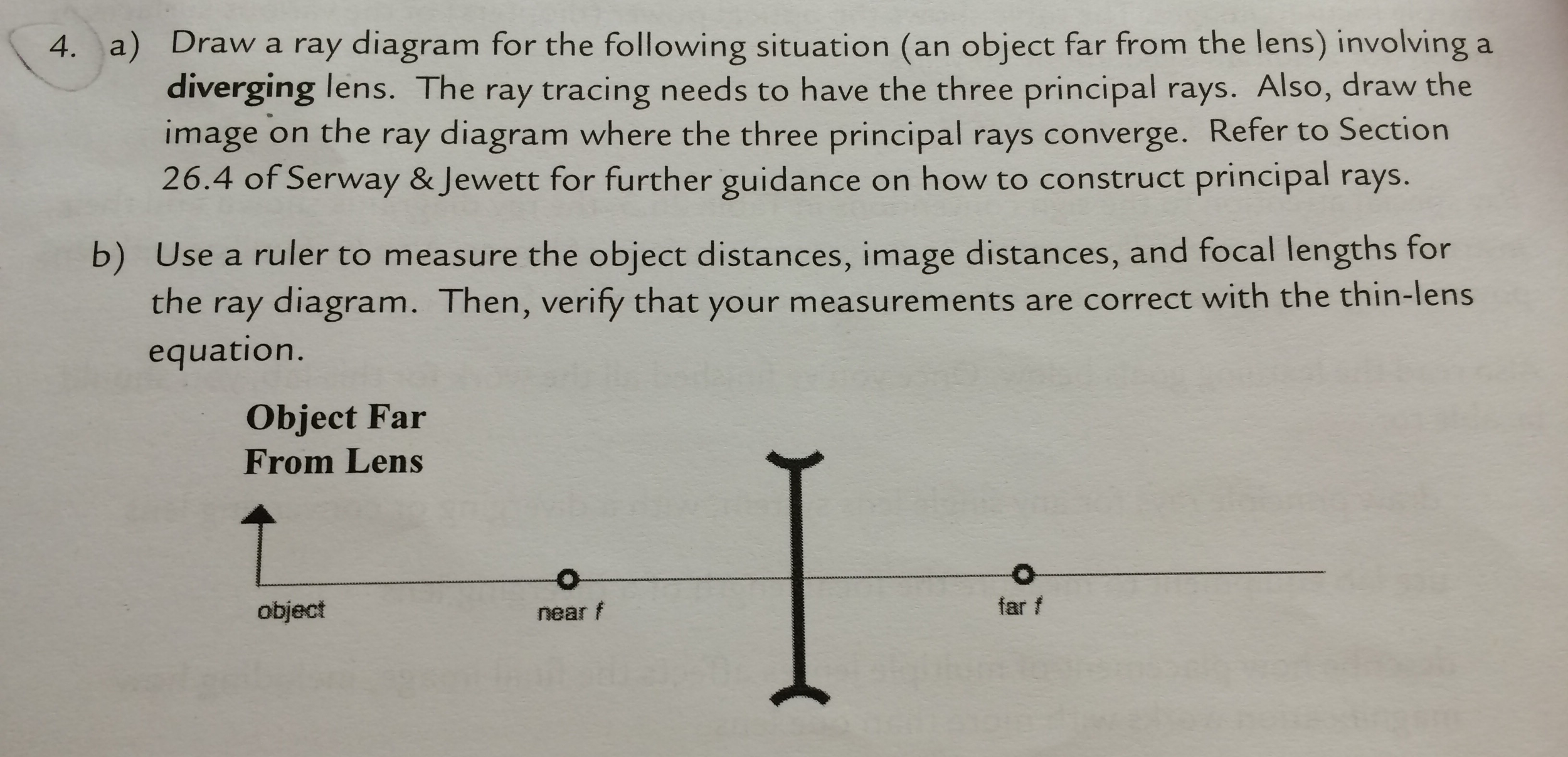
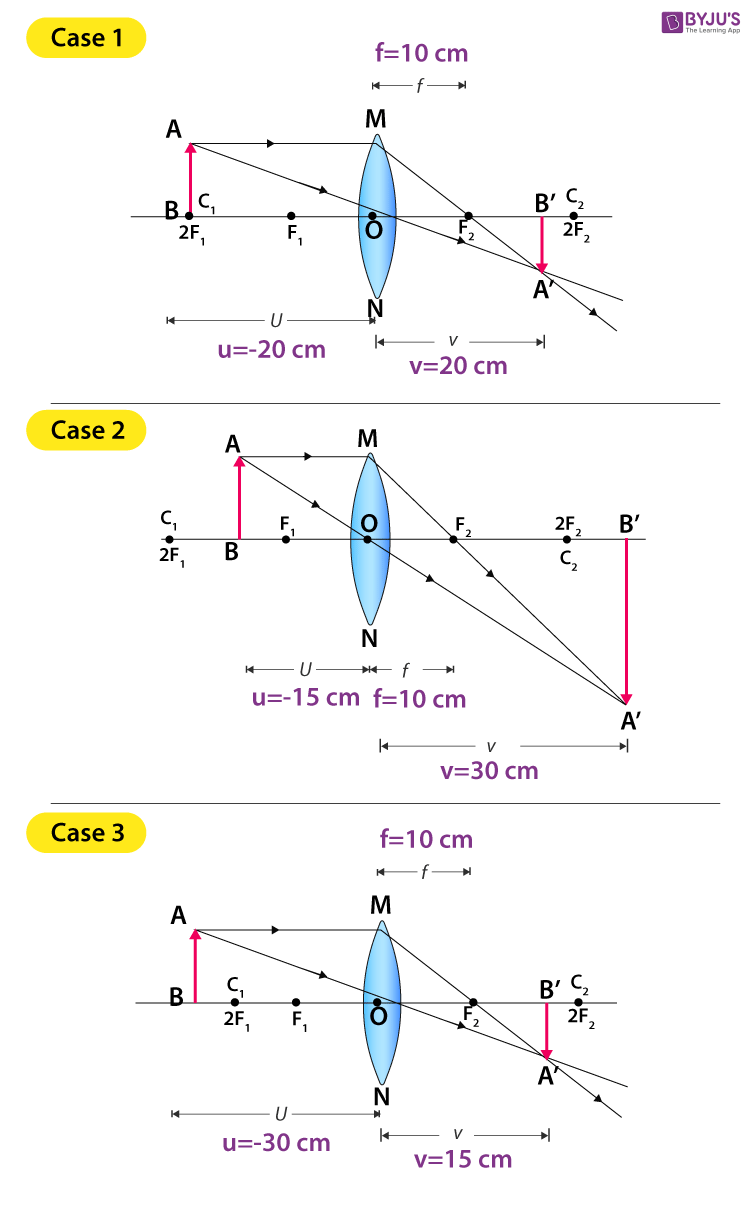
Solved A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ... a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays. Ray Diagrams - Physics Classroom The description is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the 2F point of a double convex lens. 1. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens.
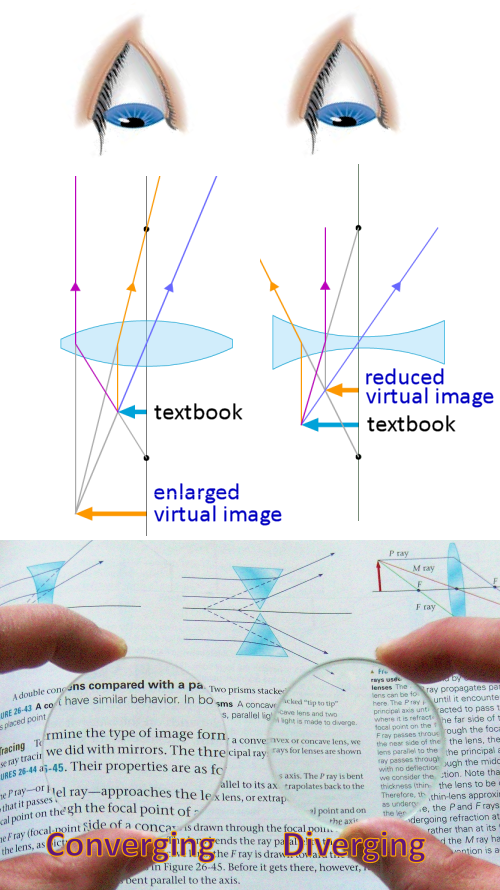
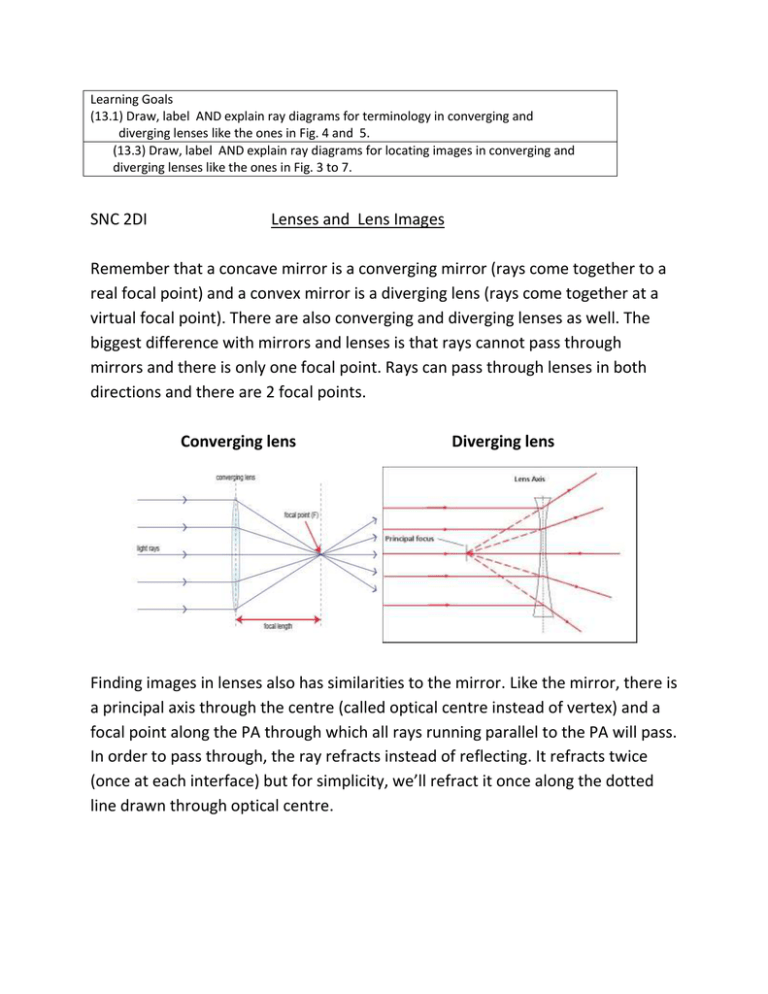
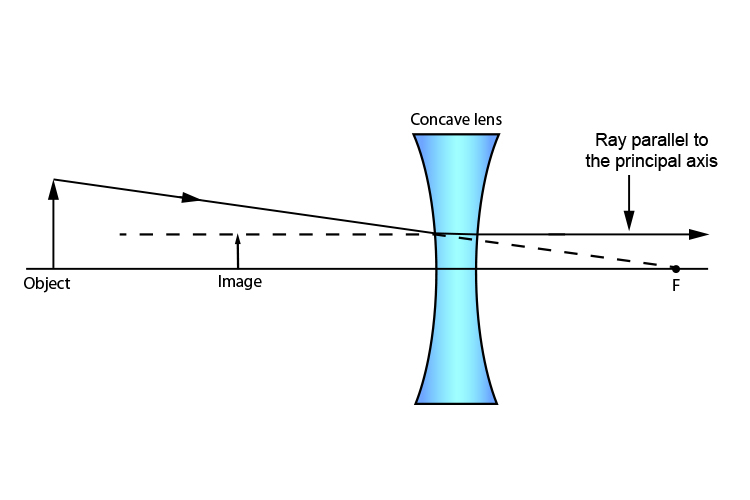
4.3: Lenses - Physics LibreTexts A ray that enters a diverging lens by heading toward the focal point on the opposite side exits parallel to the axis. (The reverse of rays 1 and 3 in ). Diverging Lens: Rays of light entering a diverging lens parallel to its axis are diverged, and all appear to originate at its focal point F. The dashed lines are not rays—they indicate the ...

Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays. PDF Mirrors and Lenses - City University of New York (b). In this case, the index of refraction of the lens material is less than that of the surrounding medium. Under these conditions, a biconvex lens will be divergent. 5. Although a ray diagram only uses 2 or 3 rays (those whose direction is easily determined using A) Draw a ray diagram for the following si... | Clutch Prep A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation.
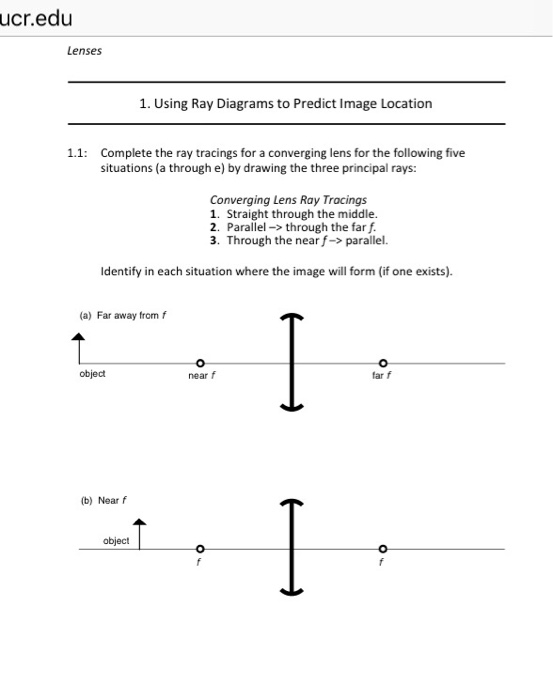
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a diverging lens. Ray Diagrams for Lenses - Georgia State University Ray Diagrams for Lenses. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. The "three principal rays" which are used for visualizing the image location and size are: Physics Tutorial: Refraction and the Ray Model of Light Earlier in Lesson 5, we learned how light is refracted by double concave lens in a manner that a virtual image is formed.We also learned about three simple rules of refraction for double concave lenses: . Any incident ray traveling parallel to the principal axis of a diverging lens will refract through the lens and travel in line with the focal point (i.e., in a direction such that its ... PDF Duffy EP 2010 ch24 - WebAssign converging lens. First, re-draw the diagram, preferably on a piece of graph paper. For parts (a) - (c), start the ray from the tip of the object and show how the ray is refracted by the lens. (a) On your diagram, draw a ray that travels parallel to the principal axis toward the lens. (b) Draw a ray that travels directly toward the center of ... How To Draw Ray Diagrams For Convex Mirrors You must be able to draw ray diagrams for plane mirrors, and be able to calculate image and object heights, Spherical Mirrors: concave and convex mirrors. For situations involving multiple lenses or mirrors, the image formed from one of these components can act as the object for another one.
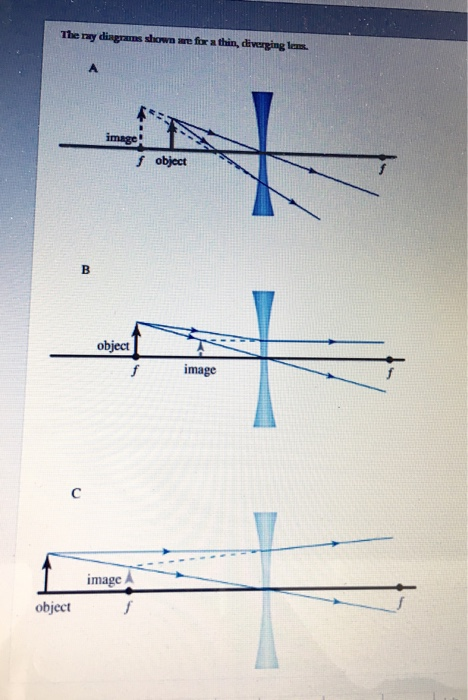
Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object ... Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays. A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an ... a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. b) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Solved a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ... a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation involving a converging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. b) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. 2.5: Thin Lenses - Physics LibreTexts A ray entering a diverging lens parallel to the optical axis exits along the line that passes through the focal point on the same side of the lens (ray 1 in part (b) of the figure). A ray passing through the center of either a converging or a diverging lens is not deviated (ray 2 in parts (a) and (b)).
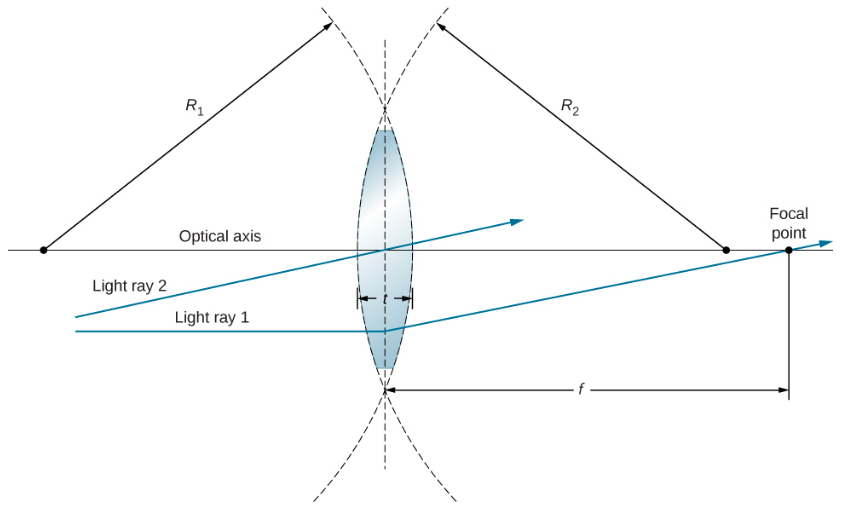
Thin Lenses - University Physics Volume 3 A ray entering a diverging lens parallel to the optical axis exits along the line that passes through the focal point on the same side of the lens (ray 1 in part (b) of the figure). A ray passing through the center of either a converging or a diverging lens is not deviated (ray 2 in parts (a) and (b)). b Diverging lens concave which is thicker at the edge than ... Diverging lens (concave) which is thicker at the edge than at the middle. Figure 2: Lens Shapes WEEK 8. 1.Vertex, V - the optical center or geometric center of the lens 2. Principal axis, P - line joining the centers of principal axis 4. Focal length, f - the distance between the focus and the optical center. refracted through the focus. PDF Experiment 6 Optics: Focal Length of A Lens (e) A lens which diverges a bundle of parallel rays is called a diverging lens, or a negative lens (its focal length is taken as negative.) The diverging lens is thicker at its edge than at its center. (f) Light rays from a point source (object) passing through a lens emerge convergent to a point or divergent from a point. PDF Duffy EP 2012 ch24 - Boston University converging lens. First, re-draw the diagram, preferably on a piece of graph paper. For parts (a) - (c), start the ray from the tip of the object and show how the ray is refracted by the lens. (a) On your diagram, draw a ray that travels parallel to the principal axis toward the lens. (b) Draw a ray that travels directly toward the center of ...
PDF The Lens Equation Convex (converging) and concave (diverging) lenses are drawn as, V W To understand image formation we use ray diagrams. Here is an example for aconvex lens: F The image of the top of the object is formed where the light rays cross. In a perfect lens all the rays from a point on the object will meet at one other point - so we only need to draw ...
Solved Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an ... Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays.
Ray Diagrams For Lenses Video & Text Solutions For College ... A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three... Solved • Jul 10, 2020
PDF 24-6 A Quantitative Approach: The Thin-Lens Equation We derived the lens equation above by using a specific case involving a convex lens. The equation can be applied to all situations involving a convex lens or a concave lens if we use the following sign conventions. The focal length is positive for a converging lens, and negative for a diverging lens.
Drawing ray diagrams for a converging lens - The Fizzics ... To explain how to draw the diagrams, there are two key things to remember. 1 A converging lens refracts the light so that any ray of light parallel to the principal axis (the thick horizontal line) is turned to pass through the focal point. Rays of light parallel to the principal axis are all refracted through the focal point.
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following si... | Clutch Prep Problem: A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) where the three principle waves converge.B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation. 1.
Physics Tutorial: Ray Diagrams - Concave Mirrors In this diagram five incident rays are drawn along with their corresponding reflected rays. Each ray intersects at the image location and then diverges to the eye of an observer. Every observer would observe the same image location and every light ray would follow the law of reflection.
A) Draw a ray diagram for the following si... | Clutch Prep A) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation ( an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. B) Use a ruler to measure the object distances, image distances, and focal lengths for the ray diagram. Then verify that your measurements are correct with the thin-lens equation.
PDF Mirrors and Lenses - City University of New York (b). In this case, the index of refraction of the lens material is less than that of the surrounding medium. Under these conditions, a biconvex lens will be divergent. 5. Although a ray diagram only uses 2 or 3 rays (those whose direction is easily determined using
a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object a) Draw a ray diagram for the following situation (an object far from the lens) involving a diverging lens. The ray tracing needs to have the three principal rays. Also, draw the image on the ray diagram where the three principal rays converge. Refer to Section 26.4 of Serway & Jewett for further guidance on how to construct principal rays.









![Expert Verified] draw the ray diagram in each case to show ...](https://hi-static.z-dn.net/files/d68/483631afd234286cd5ecd752527d1aa3.jpg)









0 Response to "40 Draw A Ray Diagram For The Following Situation Involving A Diverging Lens"
Post a Comment