39 inner ear crystals diagram
The Vestibular System: Definition, Anatomy ... - Study.com In the vestibular half of the inner ear, ... the cupula of the saccule and utricle has little crystals of calcium carbonate, called otoconia, ... Anatomy & Diagrams 10:37 ... earring piercings chart Contents show. Ear Piercing Chart.Types of Ear Piercings.Unique Ear Piercings.Why blend in when you were born to stand out? Combine your favorite colors, styles, and earring types that are unique to you.. Ear Piercing Chart and Guide.Perhaps, every second person around you has ear piercings.Earlobe piercing is the most common and easy option.. Nevertheless, it gives you comparatively more ...
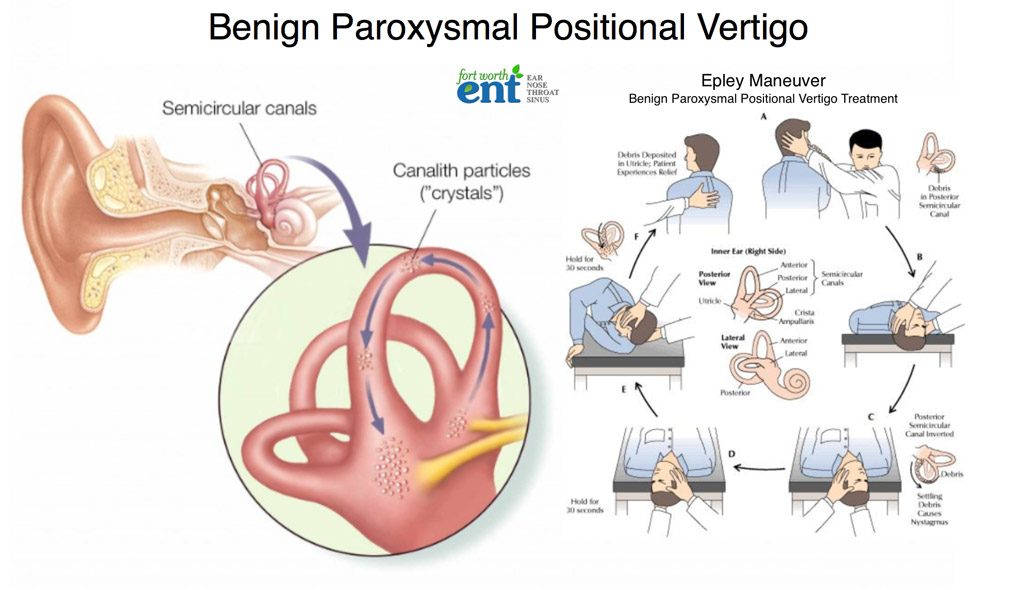
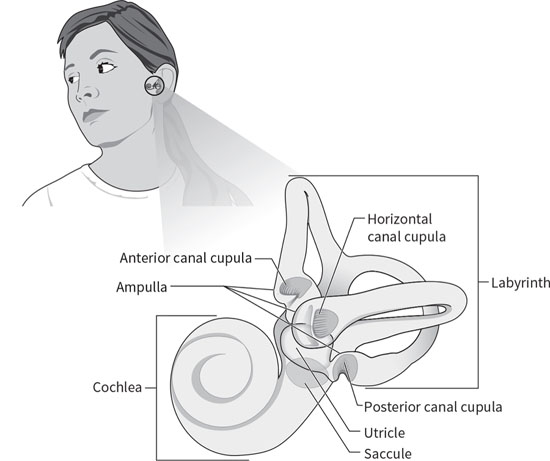
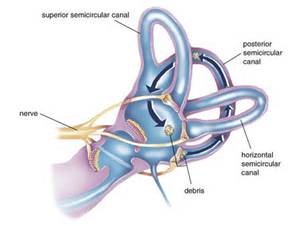
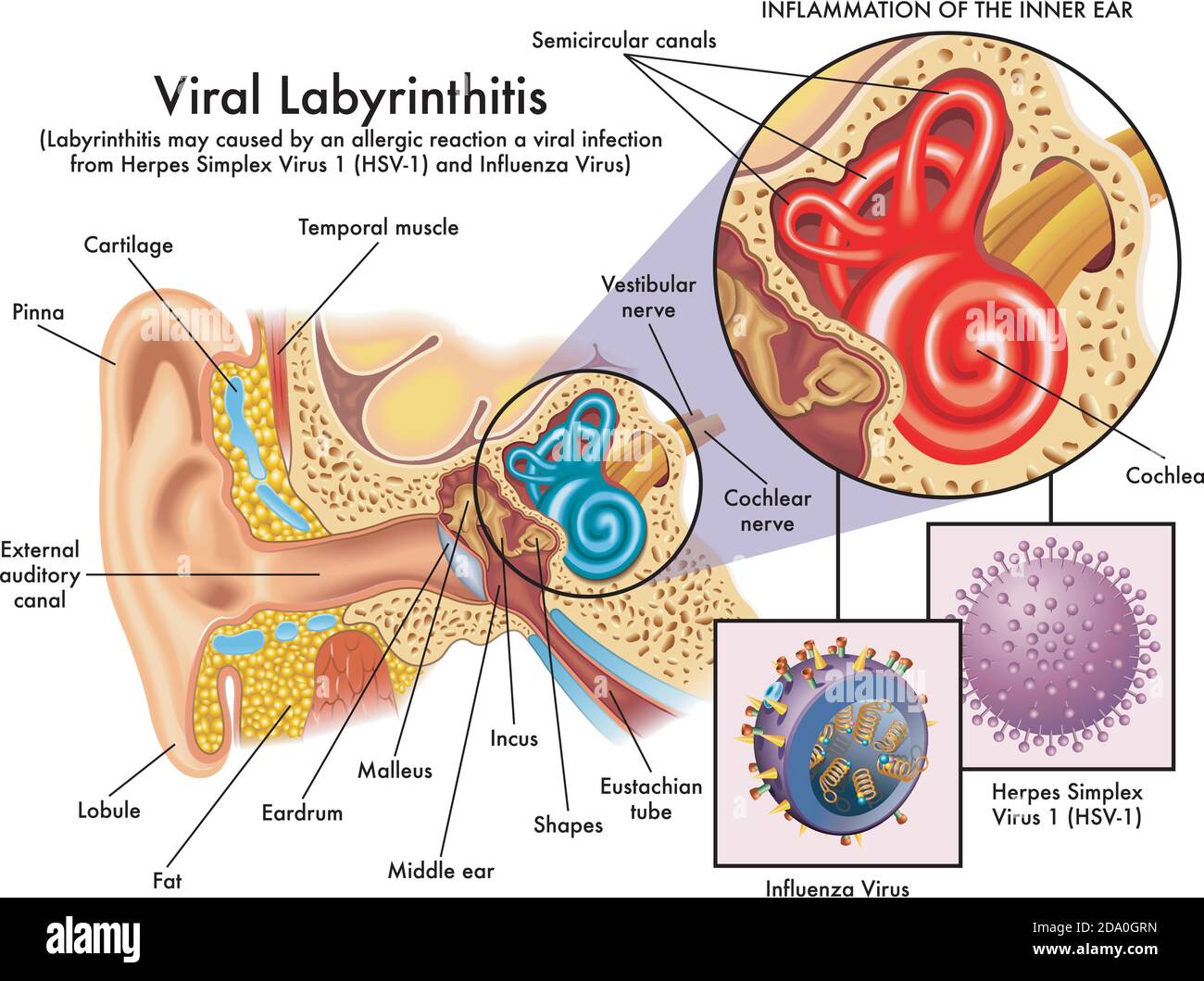
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo | Health - Patient Inner ear diagram There are three semicircular canals (anterior, lateral and posterior). These are roughly at right angles to each other and sense movement in different directions - left-right, forward-back and up-down head movements.

Inner ear crystals diagram
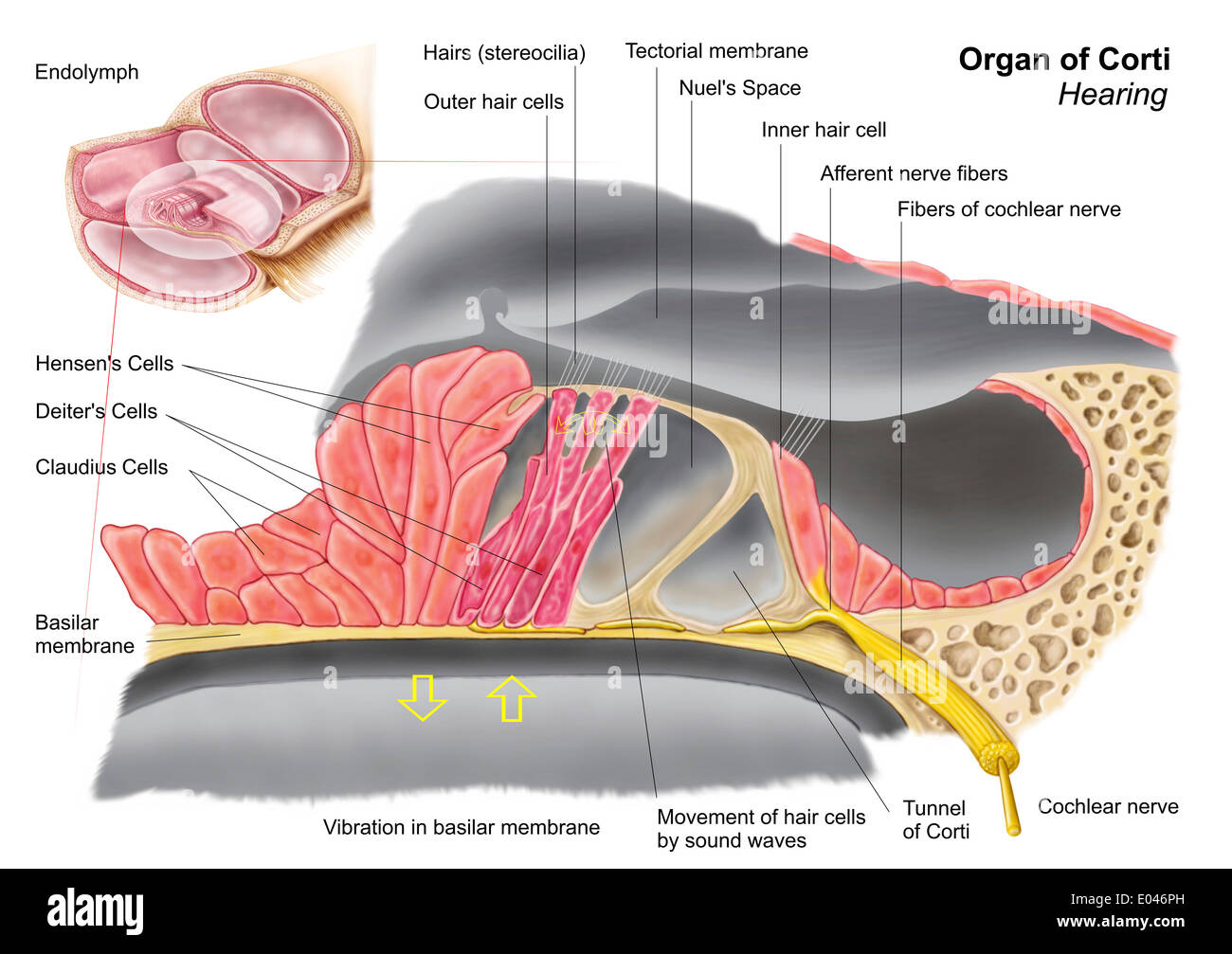
Vestibular system: Anatomy, pathway and function - Kenhub The hair cells are the motion receptors of the inner ear, embedded within the walls of the semicircular canals and otolithic organs. They are cylindrical in shape and feature many stereocilia on their apical ends. Each cell also has a single kinocilium, which sits on the lateral most end of the apical surface. Inner ear: Anatomy - Kenhub The inner ear is embedded within the petrous part of the temporal bone, anterolateral to the posterior cranial fossa, with the medial wall of the middle ear, the promontory, serving as its lateral wall. The internal ear is comprised of a bony and a membranous component. Anatomy of the Otoliths - Dizziness-and-Balance.com The utricle is one of two "otolithic organs" in the human ear, the utricle and saccule. On the diagram above, the utricle are located in the vestibule, between the semicircular canals (5), and the cochlea (9). ... Rather than having many crystals as is the case in humans, each "otolith" in fish is made of one large crystal. ... Josephson, R ...
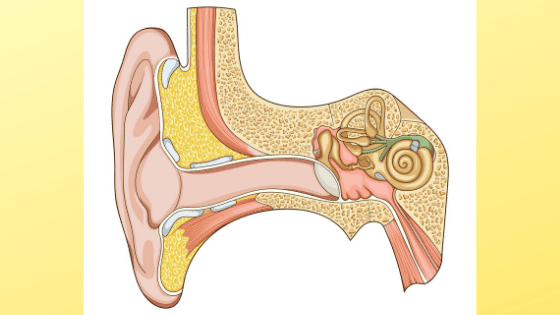
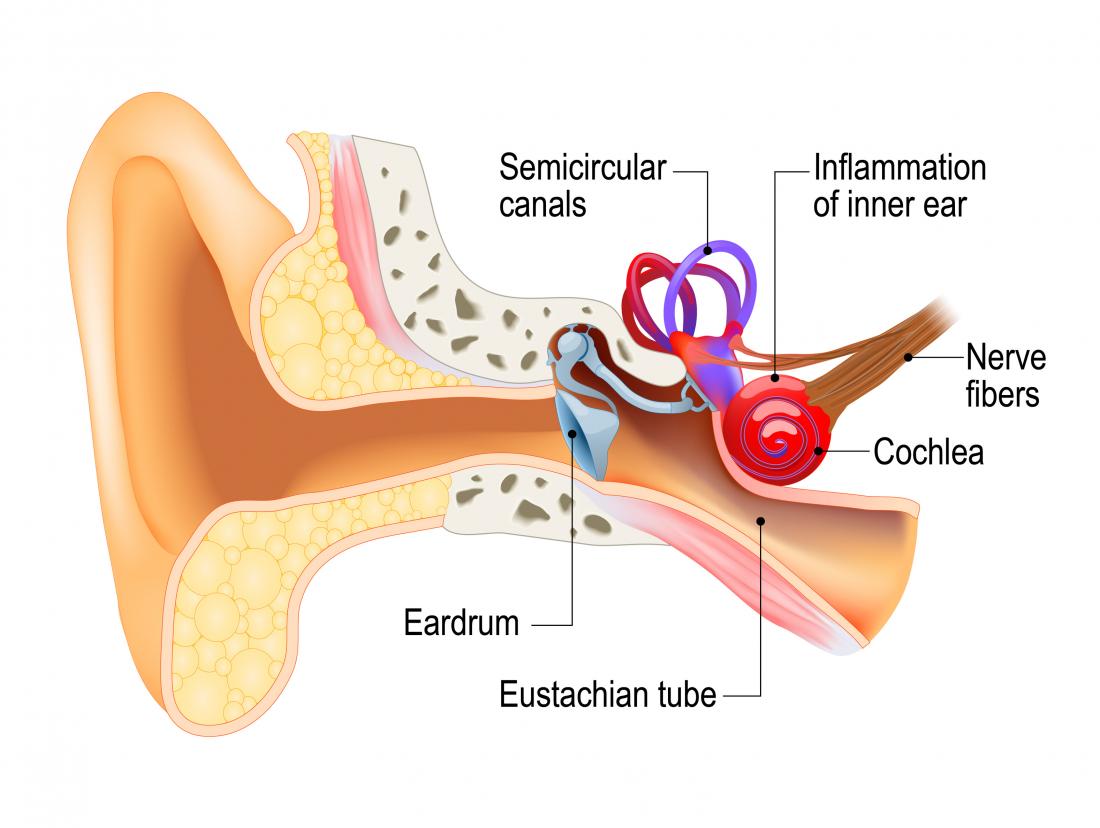
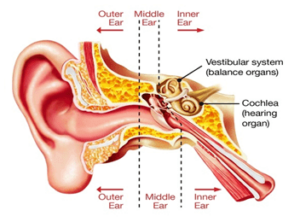
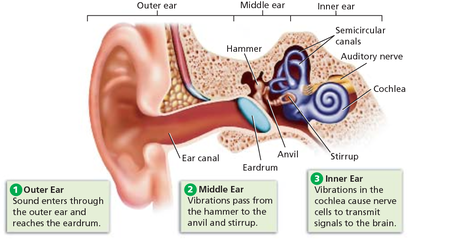
Inner ear crystals diagram. 30 Interesting Facts About Ears For Kids - MomJunction It consists of the pinna, the outer portion on either side of your head, the ear canal, and the eardrum. The pinna acts as a funnel. It gathers sound waves and directs them into your ear canal. The ear canal is a passage leading to the middle ear. The eardrum separates the outer ear from the middle ear. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) - Geeky Medics Introduction. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is an inner ear disorder characterised by recurrent brief attacks of positional vertigo. 1 BPPV is the commonest cause of vertigo. 2 The use of the word 'benign' reflects the good prognosis of BPPV, as its' cause is likely peripheral, rather than central. 5 However, studies have shown that undiagnosed and untreated cases of BPPV ... Ear Anatomy: Understanding the Outer, Middle, and Inner ... The inner ear is where the sound waves are translated into types of electrical nerve impulses. Most of the hearing and balance content is located within the bony labyrinth. After the tympanic membrane, these are the nerves that most likely contribute to hearing impairment and may require treatment or medical services [1]. Bony Labyrinth Vertigo Guide: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options The most common causes of vertigo are illnesses that affect the inner ear, including: Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo — In this condition, a change in head position causes a sudden sensation of spinning. The most likely cause is small crystals that break loose in the canals of the inner ear and touch the sensitive nerve endings inside.
Lesson 1 - ScienceWiz the crystals jump. 5 4 Bang the cookie sheet with the large metal spoon. ... auditory Canal pinna The Outer Ear Click on the tympanic membrane in the diagram. tympanic membrane or eardrum Inside your ear at the end of the canal is a thin stretch of tissue called the eardrum ... located in the INNER EAR. Click on the cochlea. Human Body Quiz: Human Body Systems, Parts & Organs A layer of very fine calcium crystals is among the structures in the inner ear that help to regulate balance. Balance is a choreographed arrangement that takes sensory information from a variety of organs and integrates it to tell the body where it is in related to gravity and the earth. next question 12 Sweat is the main cause of body odor. A True Ear Discharge | Causes & Treatments for Fluid in the Ear ... Ear discharge is fluid located in the ear that can have many different characteristics. While white yellow earwax is an expected and healthy ear discharge, abnormal discharge colors can be caused by an ear infection affecting the ear canal, or a ruptured eardrum. Read below on major categories of causes and conditions you should be aware of. We also cover treatment options and signs that a ... BeadDiagrams.com To make a 7-inch bracelet (not including clasp), you will need about 23 crystals of each color (or 46 of one color). Each pair of crystals adds about 1/3-inch, if you want to make the bracelet longer (or shorter). More Photos and Demo Video Click on the photos below (or the free beading pattern) to zoom in. Video Tutorials
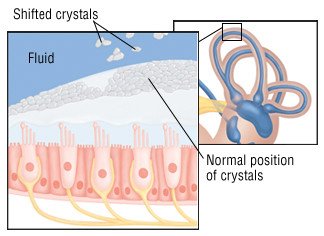
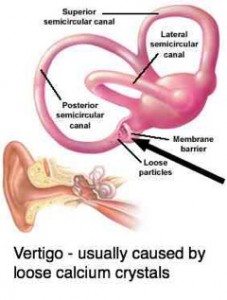
Wax Blockage Of The Ear Canal Guide: Causes, Symptoms and ... If too much wax is being produced, it can block the ear, but more commonly, the ear becomes blocked because of improper ear care and ear cleaning. If you push cotton swabs, pencils, your finger or other objects into your ear canal to try to remove wax, the force can push the wax further into the ear and compress it against the eardrum. Why Loose Ear Crystals Make You Dizzy - Cleveland Clinic At the root of the problem are tiny calcium crystals found within the chambers of the inner ear. These crystals sense gravity, "Imagine a hill with blades of grass, and on top of each blade is a crystal," explains Dr. Cherian. "Together, these crystals form an interconnected matrix. Whenever the blades of grass move, so do the crystals." Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo - StatPearls - NCBI ... Each inner ear is comprised of three SCCs situated in three perpendicular planes. Each canal has a tubular arm (crura) sprouting from a large barrel-like compartment. At the end of each of these arms, a dilated (ampullary) end is situated closer to the top or front portion. This is where the crista ampullaris with nerve receptors are present. What Are The Signs and Symptoms of an Inner Ear Infection ... Ear infections can happen anywhere in your outer, middle or inner ear. The symptoms can be very different depending on where the problem is located. If the infection is in your inner ear then it can have a particularly dramatic effect on your senses of balance and hearing. Read on to learn more about inner ear infections and how they can affect ...
Earwax Blockage Symptoms, Removal & Home Remedies for Buildup The tapered end is placed inside the ear, and an assistant lights the other end, while making sure your hair does not catch on fire. In theory, as the flame burns, a vacuum is created, which draws the wax out of the ear. Limited clinical trials, however, showed that no vacuum was created, and no wax was removed.
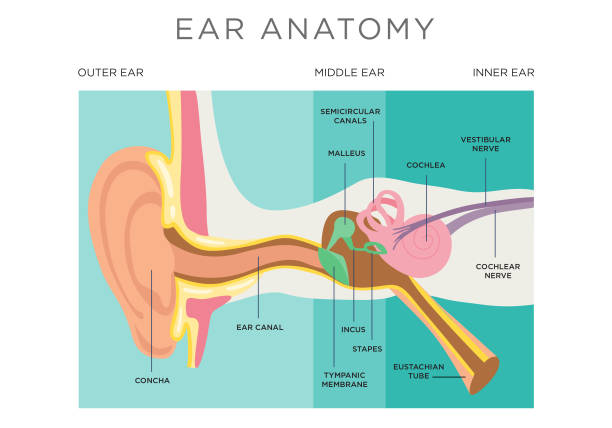
Eustachian Tube: Anatomy, Location, and Function The eustachian tube consists of bone, cartilage, and fibrous tissue. The hollow tube is lined with cilia, hair-like projections that sweep mucus away from the middle ear toward the nasopharynx. 1 Six muscles contribute to the opening and closing of the eustachian tube. They are located in the ear, head, neck, soft palate, and jaw. 1 Function
How to get rid of Vertigo fast - 11 treatment tips ... It receives input from the eyes, muscles, joints, and vestibular system of the inner ear and then produces nerve impulses for the person to have a correct perception of his environment. Our ears contain parts called saccule and utricle, two otolithic organs in the inner ear, as well as 3 semicircular canals located in the vestibular system.
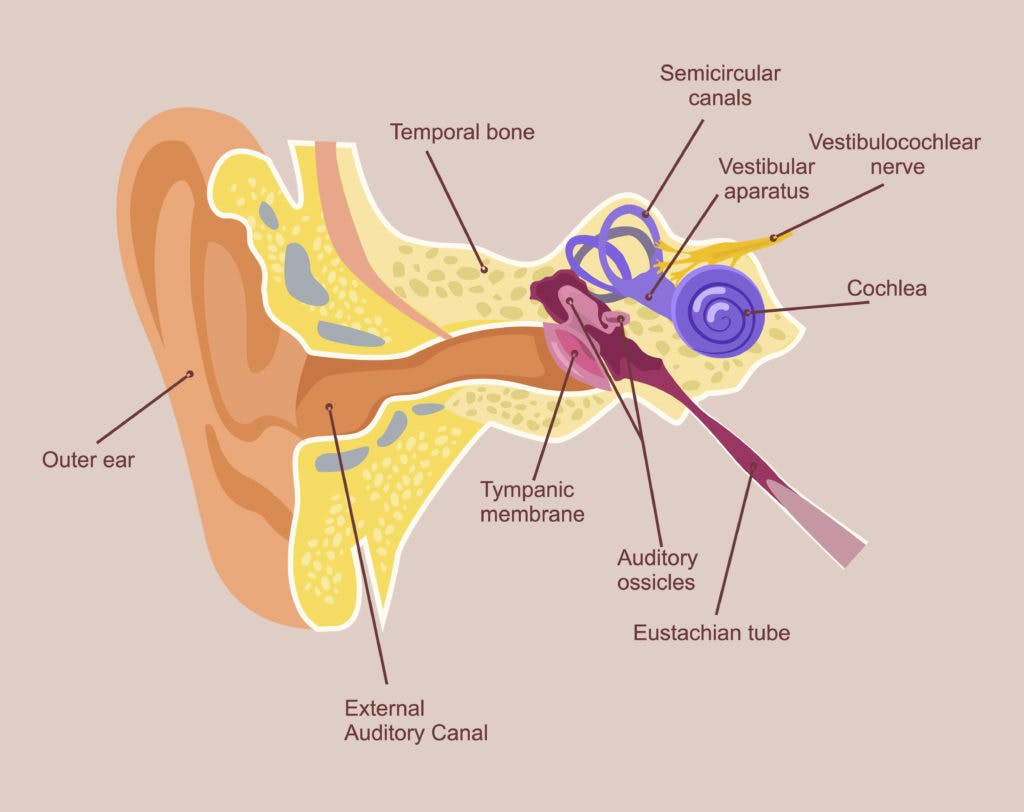
Ear: Anatomy, Human Ear Diagram, Functions, Parts - Embibe The inner ear consists of a labyrinth of fluid-filled chambers within the cavity formed by the temporal bone of the skull. The inner ear is also called labyrinth and is composed of two types of labyrinth, i.e. bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth, which in turn are composed of canals and sacs.
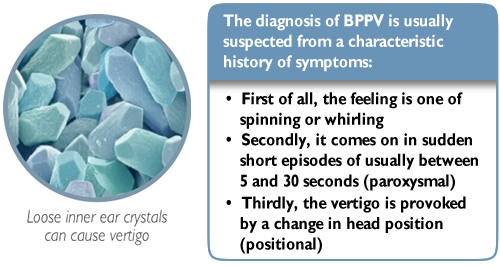
Vestibular Dysfunction - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Paroxysmal positional vertigo is a mechanical disorder of the inner ear causing short intervals of transient vertigo, often with autonomic symptoms. Benign positional peripheral vertigo accounts for up to 8% of individuals with moderate to severe dizziness/vertigo. Women and patients over age fifty are among the most affected.
A Step by Step Guide on Epley Maneuver for Vertigo | New ... Sit on the edge of your bed with your head turned 45-degree to your left. Grab a pillow and place it on the bed in a way that it comes between your shoulders as you lie down. With your face up, quickly lie down on the bed with the pillow right underneath your shoulders. Wait for 30 seconds or until your vertigo stops.
Airplane ear - Symptoms and causes - Mayo Clinic The middle ear includes three small bones — the hammer (malleus), anvil (incus) and stirrup (stapes). The middle ear is separated from your external ear by the eardrum and connected to the back of your nose and throat by a narrow passageway called the eustachian tube. The cochlea, a snail-shaped structure, is part of your inner ear.
BPPV -- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo BPPV is caused by crystals dislodged from the utricle of the inner ear. In Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) dizziness and vertigo is triggered by particular positions because of debris which has collected within a part of the inner ear. This debris can be thought of as "ear rocks", although the formal name is "otoconia".
What is Inner Ear Nerve Damage, Know its Symptoms, Causes ... The inner ear nerve is a sensory one which is also known as the auditory nerve or vestibulocochlear nerve. It has 2 branches with the first being the cochlear branch that helps to carry sound waves from the inner ear to the brain. The second branch is the vestibular branch which helps in balancing the body correctly.
Inner Ear Anatomy | Structure, Function & Components ... The space of the inner ear is defined by a bony labyrinth and a membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth is comprised of an open cavity that contains the membranous labyrinth. The membranous...
Anatomy of the Otoliths - Dizziness-and-Balance.com The utricle is one of two "otolithic organs" in the human ear, the utricle and saccule. On the diagram above, the utricle are located in the vestibule, between the semicircular canals (5), and the cochlea (9). ... Rather than having many crystals as is the case in humans, each "otolith" in fish is made of one large crystal. ... Josephson, R ...
Inner ear: Anatomy - Kenhub The inner ear is embedded within the petrous part of the temporal bone, anterolateral to the posterior cranial fossa, with the medial wall of the middle ear, the promontory, serving as its lateral wall. The internal ear is comprised of a bony and a membranous component.
Vestibular system: Anatomy, pathway and function - Kenhub The hair cells are the motion receptors of the inner ear, embedded within the walls of the semicircular canals and otolithic organs. They are cylindrical in shape and feature many stereocilia on their apical ends. Each cell also has a single kinocilium, which sits on the lateral most end of the apical surface.

















0 Response to "39 inner ear crystals diagram"
Post a Comment