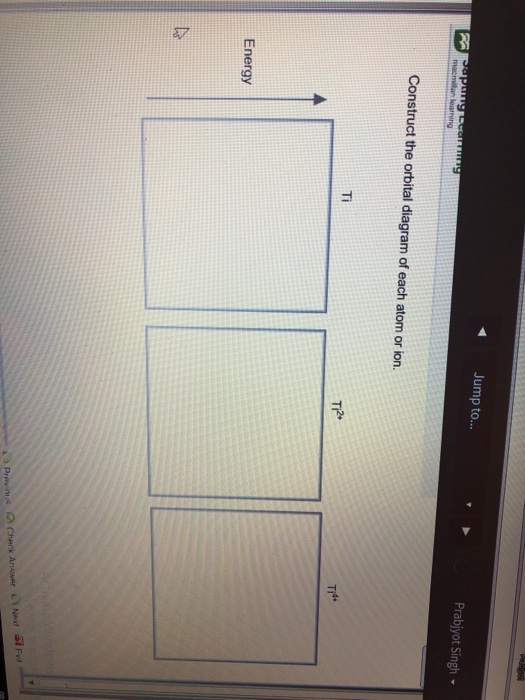
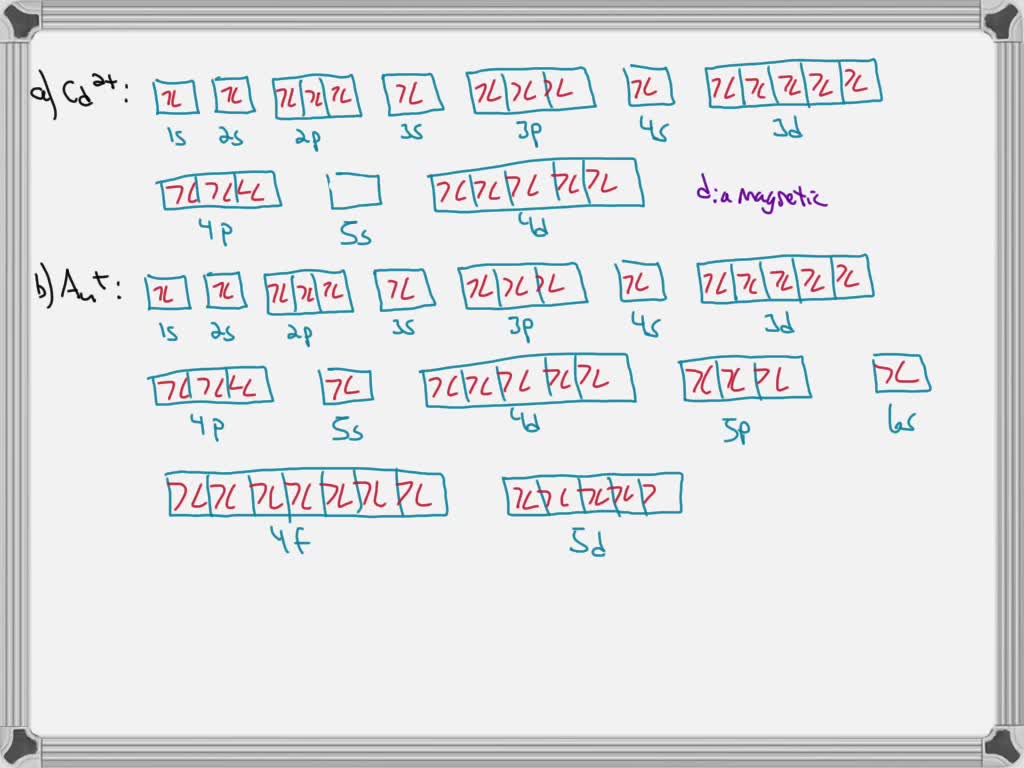
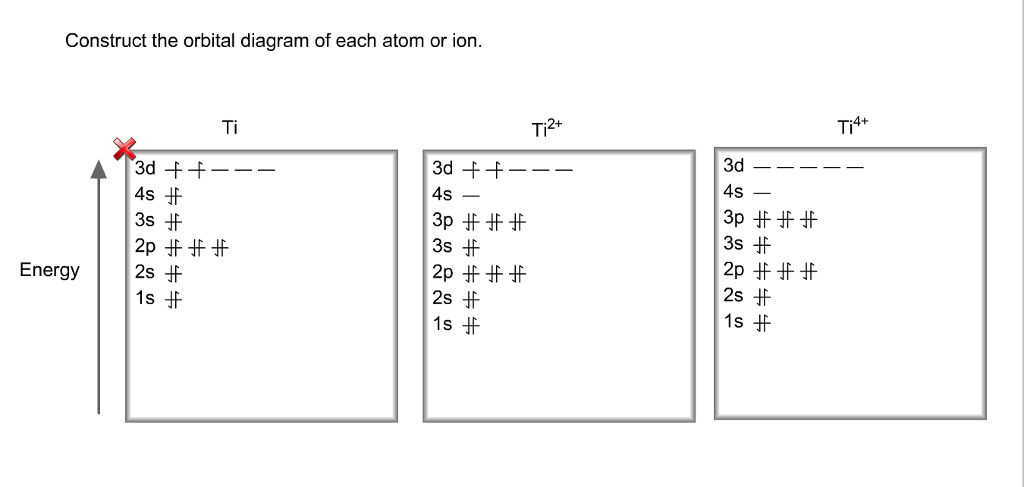
40 construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.
› 2017/02/28 › piThe Pi Molecular Orbitals of Butadiene And How To Draw Them Feb 28, 2017 · This gives us a 2-carbon pi orbital in the centre flanked by two one-carbon orbitals on the sides. 7. The Full Molecular Orbital Diagram For The Butadienyl System (n=4) Now that we have all the pieces, all we need to do to construct the molecular orbital diagram for the butadienyl system is to arrange the orbitals in order of increasing energy. chem.libretexts.org › Bookshelves › Physical_andBohr Diagrams of Atoms and Ions - Chemistry LibreTexts Aug 15, 2020 · In all electrically-neutral atoms, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons. Each element, when electrically neutral, has a number of electrons equal to its atomic number. An early model of the atom was developed in 1913 by Danish scientist Niels Bohr (1885–1962).
phet.colorado.edu › en › simulationBuild an Atom - Atoms | Atomic Structure | Isotope Symbols ... Build an atom out of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and see how the element, charge, and mass change. Then play a game to test your ideas!
Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.
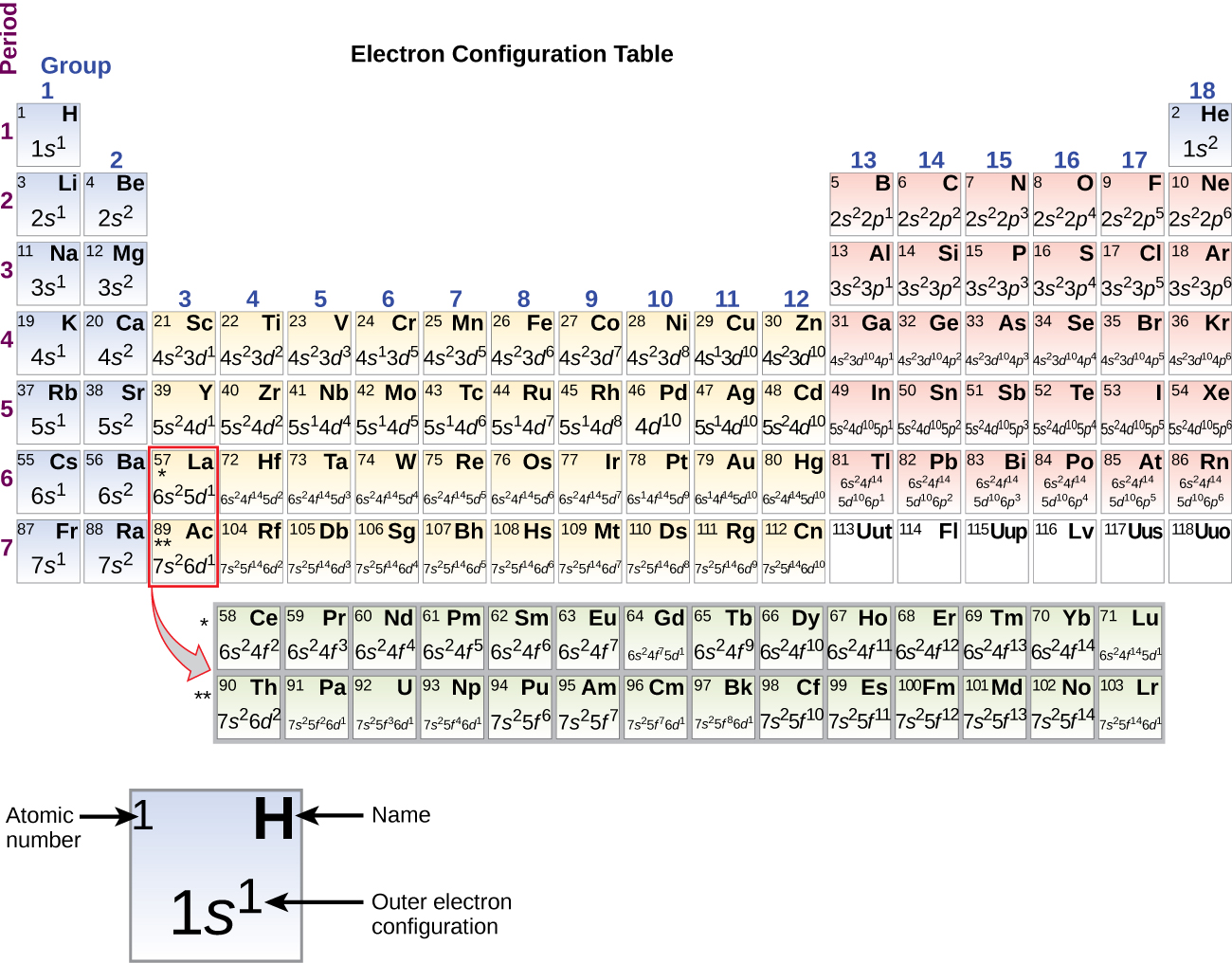
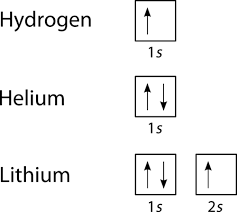
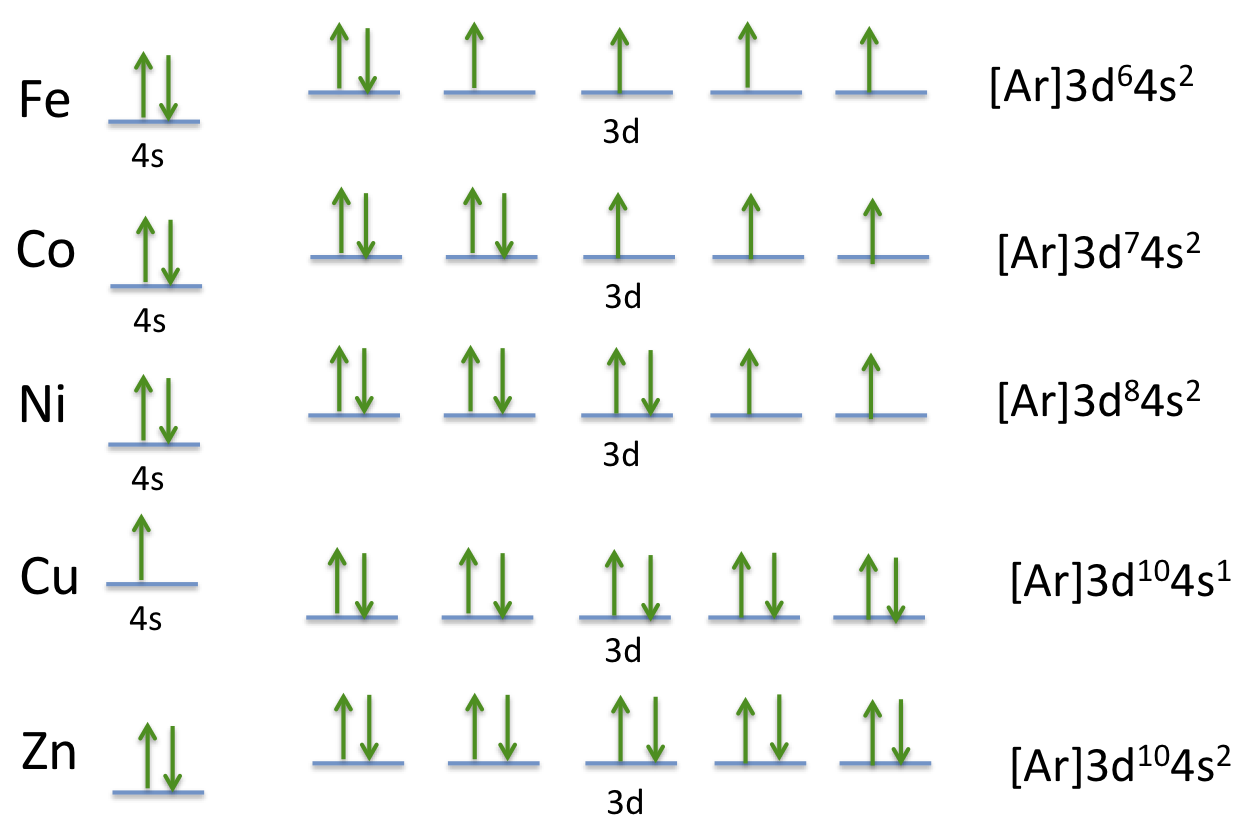
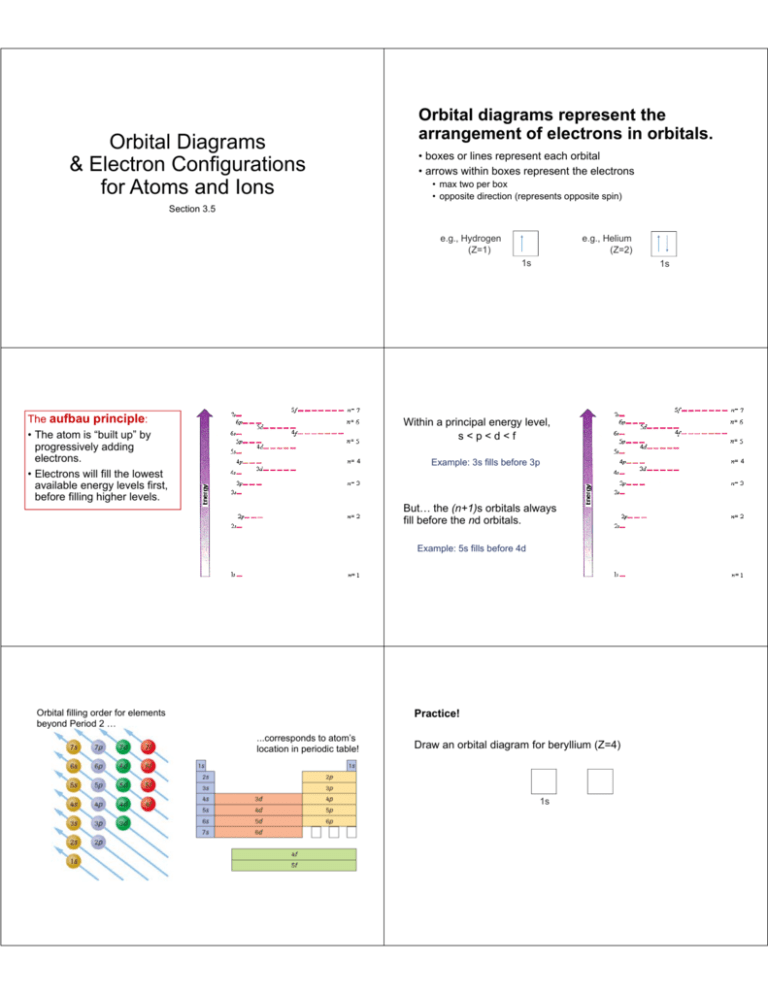
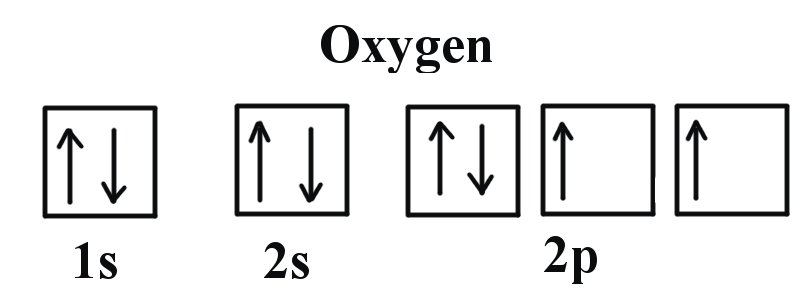
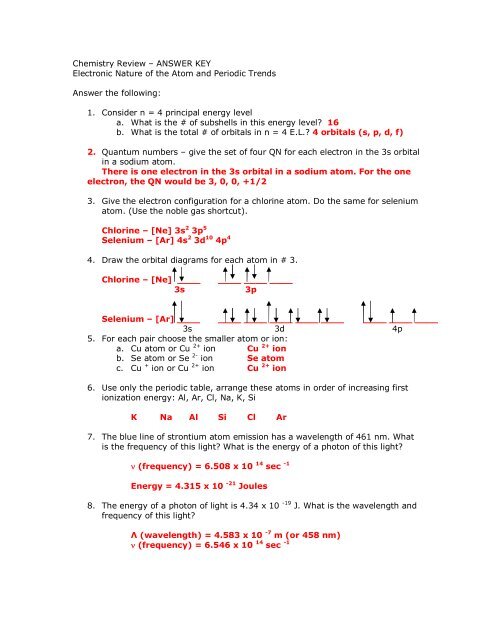
quizlet.com › 197575088 › chemistry-ch-10-flash-cardsChemistry: Ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet Construct an orbital diagram to show the electron configuration for a neutral magnesium atom, Mg. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 To form a stable ion, will magnesium gain or lose electrons? opentextbc.ca › chemistry › chapter6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations ... For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: The n = 1 shell is completely filled in a helium atom. quizlet.com › 530022269 › into-to-chem-learn-smartInto to chem Learn smart 250 concepts Flashcards - Quizlet An atom may lose or gain electrons to form an ion. Match each description of ions and their charges correctly. An ion with more electrons than its neutral atom is called a(n) An ion with fewer electrons than its neutral atom is called a(n) The charge of an ion with more electrons than its neutral atom is
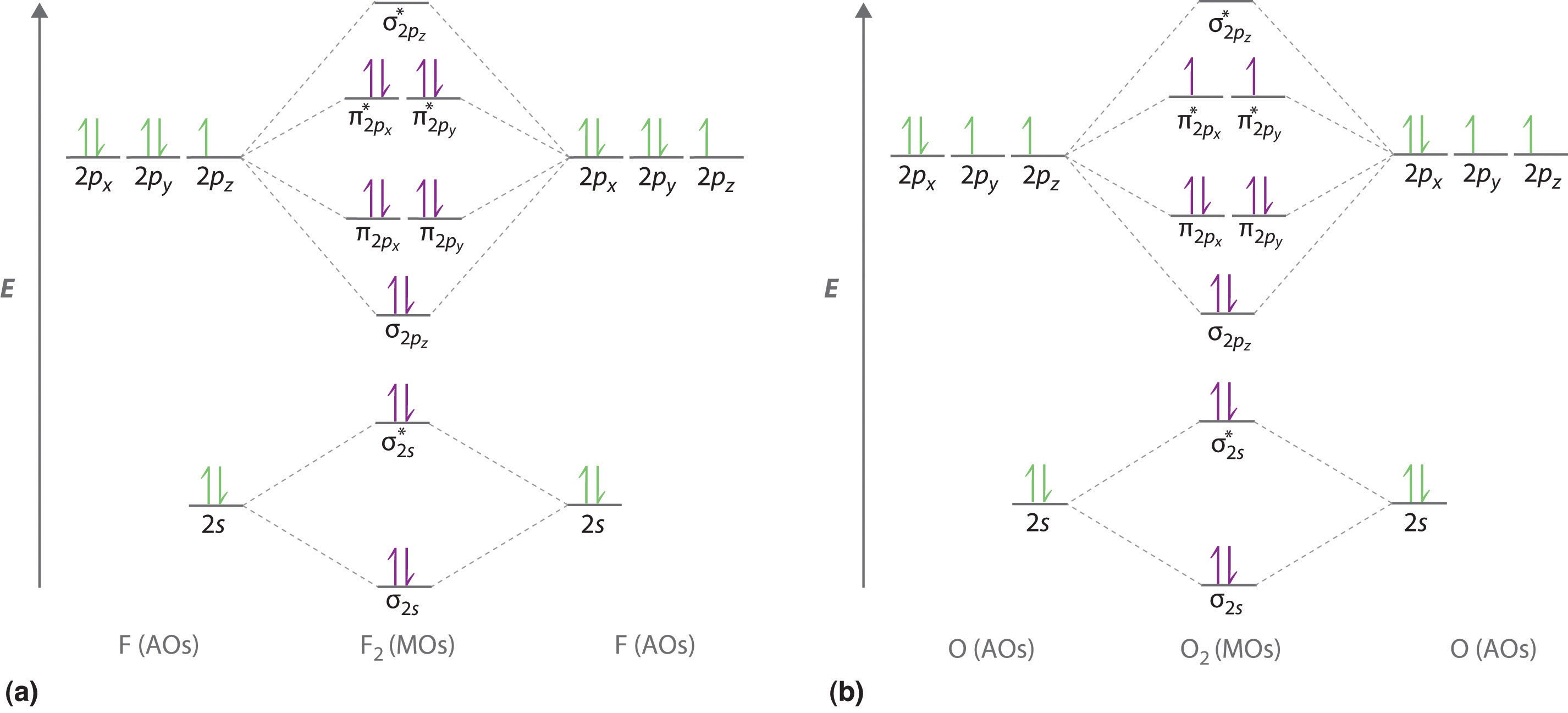
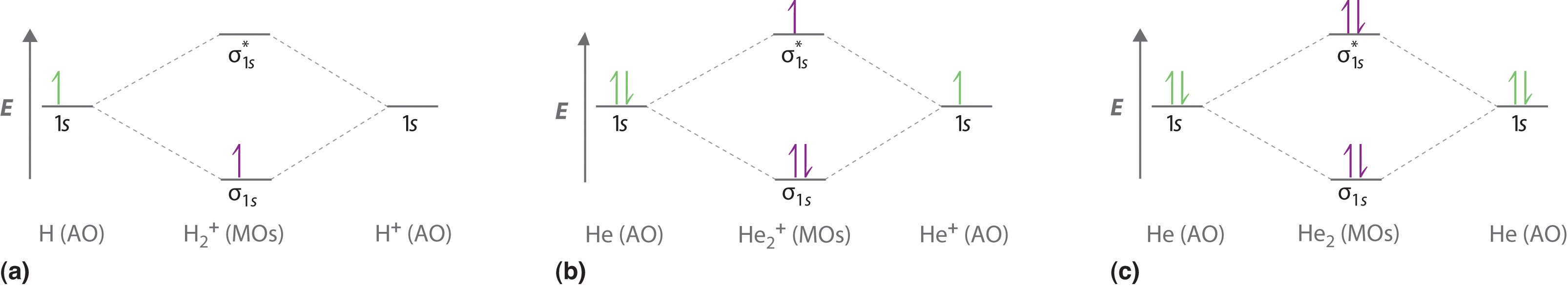
Construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion.. chem.libretexts.org › Bookshelves › General_Chemistry9.8: Molecular Orbital Theory - Chemistry LibreTexts Feb 20, 2022 · The lithium 1s orbital is the lowest-energy orbital on the diagram. Because this orbital is so small and retains its electrons so tightly, it does not contribute to bonding; we need consider only the 2 s orbital of lithium which combines with the 1 s orbital of hydrogen to form the usual pair of sigma bonding and antibonding orbitals. quizlet.com › 530022269 › into-to-chem-learn-smartInto to chem Learn smart 250 concepts Flashcards - Quizlet An atom may lose or gain electrons to form an ion. Match each description of ions and their charges correctly. An ion with more electrons than its neutral atom is called a(n) An ion with fewer electrons than its neutral atom is called a(n) The charge of an ion with more electrons than its neutral atom is opentextbc.ca › chemistry › chapter6.4 Electronic Structure of Atoms (Electron Configurations ... For orbital diagrams, this means two arrows go in each box (representing two electrons in each orbital) and the arrows must point in opposite directions (representing paired spins). The electron configuration and orbital diagram of helium are: The n = 1 shell is completely filled in a helium atom. quizlet.com › 197575088 › chemistry-ch-10-flash-cardsChemistry: Ch. 10 Flashcards | Quizlet Construct an orbital diagram to show the electron configuration for a neutral magnesium atom, Mg. 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2 To form a stable ion, will magnesium gain or lose electrons?











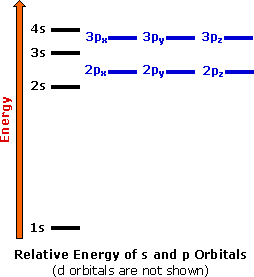
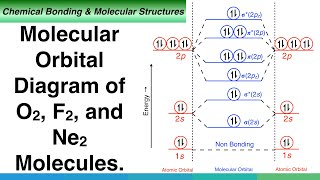




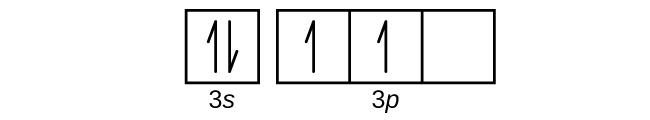
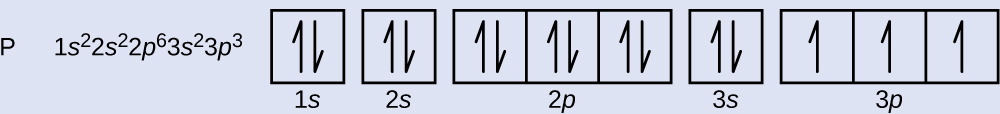





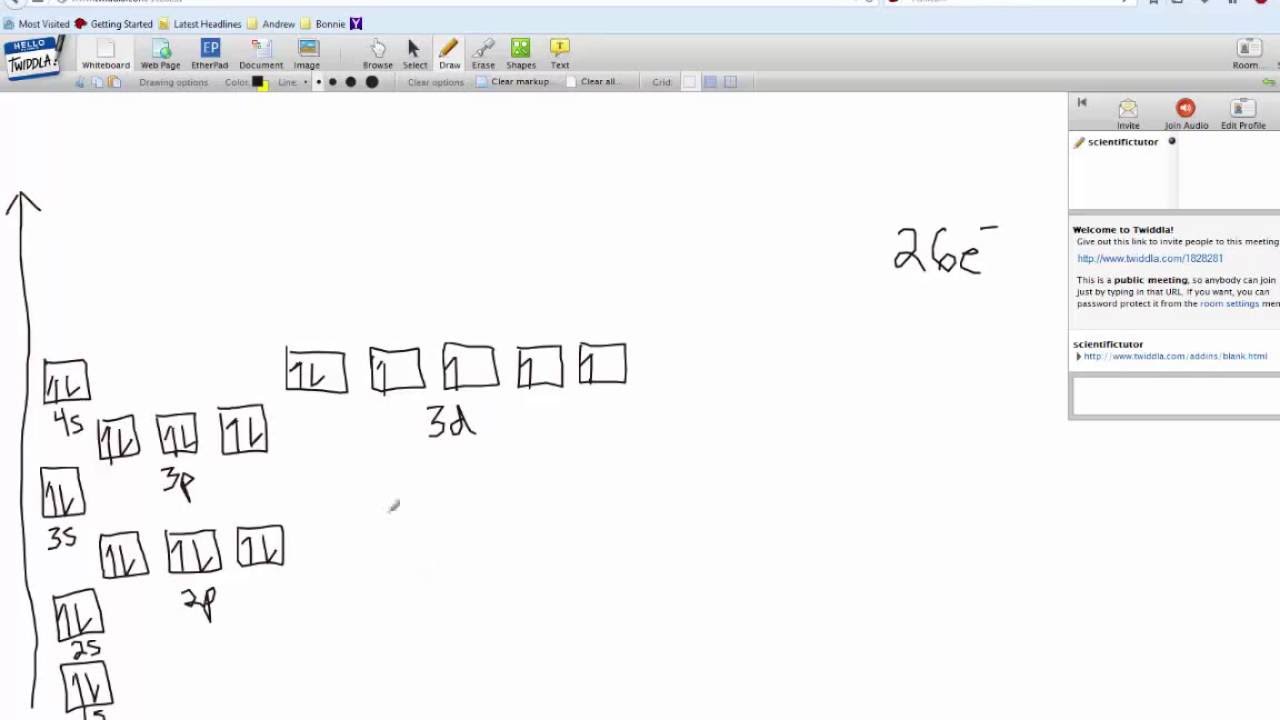
0 Response to "40 construct the orbital diagram of each atom or ion."
Post a Comment